In this article, you will learn about the AGGREGATE function in Excel. We will explore its uses, aggregate data, with multiple criteria, combine aggregate with IF function, INDEX function, and aggregate vs subtotal.
AGGREGATE Function in Excel: Syntax
- Description
The AGGREGATE function is used on different functions like AVERAGE, COUNT, MAX, MIN, SUM, PRODUCT, etc., with the option to ignore hidden rows and error values to get certain results.
- Generic Syntax
Syntax with References
=AGGREGATE(function_num, options, ref1, ref2, …)
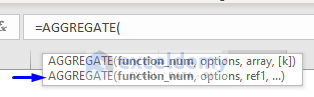
Syntax with Array Formula
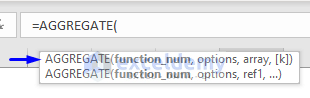
=AGGREGATE(function_num, options, array, [k])
- Arguments Description
Arguments in the Reference form,
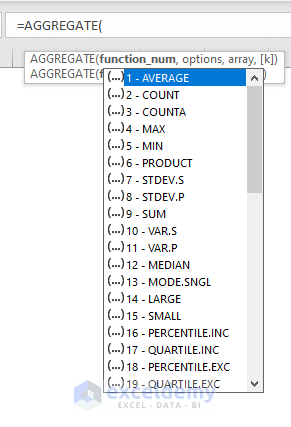 function_num = Required, operations to perform. There are 19 functions are available to perform with the AGGREGATE function. Each function is defined by individual numbers. (see the table below)
function_num = Required, operations to perform. There are 19 functions are available to perform with the AGGREGATE function. Each function is defined by individual numbers. (see the table below)
| Function Name | Function Number |
|---|---|
| AVERAGE | 1 |
| COUNT | 2 |
| COUNTA | 3 |
| MAX | 4 |
| MIN | 5 |
| PRODUCT | 6 |
| STDEV.S | 7 |
| STDEV.P | 8 |
| SUM | 9 |
| VAR.S | 10 |
| VAR.P | 11 |
| MEDIAN | 12 |
| MODE.SNGL | 13 |
| LARGE | 14 |
| SMALL | 15 |
| PERCENTILE.INC | 16 |
| QUARTILE.INC | 17 |
| PERCENTILE.EXC | 18 |
| QUARTILE.EXC | 19 |
options = Required, values to ignore. There are 7 values each representing the option to ignore while performing the operations with the functions defined.
| Option Number | Option Name |
|---|---|
| 0 or omitted | Ignore nested SUBTOTAL and AGGREGATE functions |
| 1 | Ignore hidden rows, nested SUBTOTAL and AGGREGATE functions |
| 2 | Ignore error values, nested SUBTOTAL and AGGREGATE functions |
| 3 | Ignore hidden rows, error values, nested SUBTOTAL and AGGREGATE functions |
| 4 | Ignore nothing |
| 5 | Ignore hidden rows |
| 6 | Ignore error values |
| 7 | Ignore hidden rows and error values |
ref1 = Required, the first numeric argument for functions to perform the operation. It could be one single value, array value, cell reference etc.
ref2 = Optional, it could be numeric values from 2 to 253
Arguments in the Array Formula,
function_num = (as discussed above)
options = (as discussed above)
array = Required, range of numbers or cell references based on that the functions will perform.
[k] = Optional, this argument is needed only when performing with the function number from 14 to 19 (see the function_num table).
Return Value
Return values based on the function specified.
Example 1 – Using the AGGREGATE Function in Excel to Calculate the AVERAGE
Let’s learn how to calculate the AVERAGE (statistical mean) of values with the AGGREGATE function. See the following example.
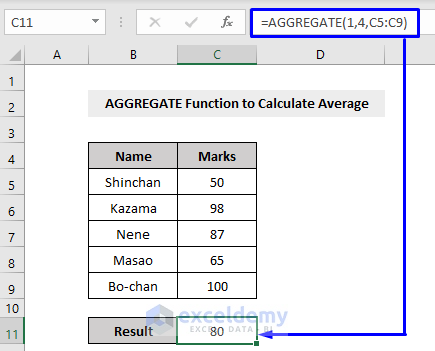
Here we got the AVERAGE result by running an AGGREGATE function. Look closely inside the parentheses of the function.
1 = function number, means the AVERAGE function
4 = option, means we will ignore nothing
C5:C9 = cell references that have the values to calculate the AVERAGE
Example 2 – Getting the Total COUNT of Values with the AGGREGATE Function
The COUNT function counts how many values are present in a defined range.
Look at the following example. There are 5 values in the Marks column, so we got 5 as our result by performing an AGGREGATE function.
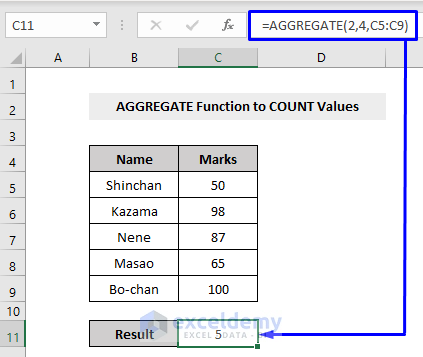
Here,
2 = function number, means the COUNT function
4 = option, means we will ignore nothing
C5:C9 = cell references that have the values to COUNT values
You can also perform the COUNTA function. See the following example where the Marks column consisted of numbers and texts.
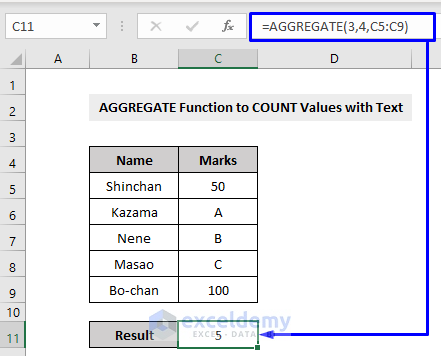
By performing the COUNTA function inside the AGGREGATE function, we extracted the result 5.
Here,
3 = function number, means the COUNTA function
4 = option, means we will ignore nothing
C5:C9 = cell references that have the values to count values with texts
Example 3 – Extracting Maximum or Minimum Values with the AGGREGATE Function in Excel
Pass the function number of the MAX function as the parameter of the AGGREGATE function. We added a #N/A error in our dataset. So, when we run the AGGREGATE function now, we will get errors.
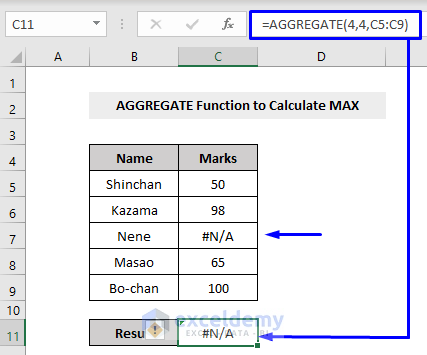
To calculate the MAX from a range with error values, we have to set the options parameter as 6, which will ignore error values
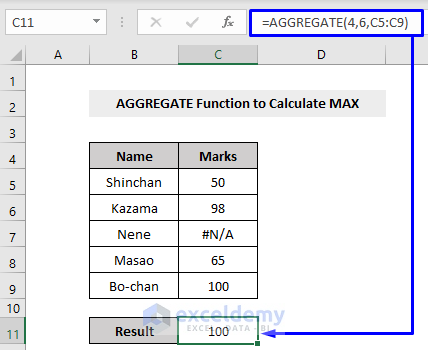
After defining the parameter to ignore error values, if we execute the MAX with the AGGREGATE function, we will still get our desired result even if we have error values lying in the dataset. (see the following picture)
To extract the minimum value from a dataset that has hidden rows, we have to set the parameter as 5 to ignore hidden rows
This will produce the result based on the MIN function ignoring the value concealed in the hidden rows.
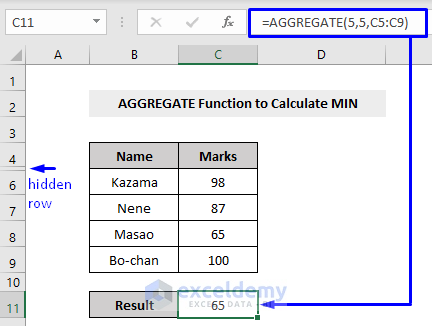
We had a minimum value 50 in the 5th row. Since the row is hidden, our AGGREGATE function returns the next minimum value, 65.
Example 4 – Calculating the SUM with the AGGREGATE Function
We have to set the options parameter to 7 this time. Consider the following example.
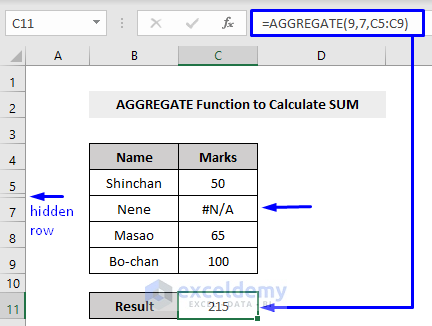
Here,
9 = function number, means the SUM function
7 = option, means we will ignore hidden rows and error values
C5:C9 = cell references that have the values to SUM the values
Example 5 – Using the AGGREGATE Function in Excel to Measure the PRODUCT of Values
The PRODUCT function returns the multiplicated result of all the values that you provide.
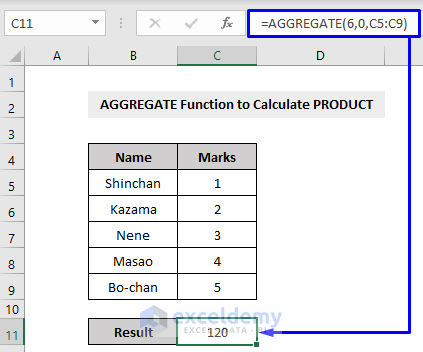
Here,
6 = function number, means the PRODUCT function
0 = option, as we are performing a generic PRODUCT function so we will ignore nested SUBTOTAL and AGGREGATE functions
C5:C9 = cell references that have the values to calculate the PRODUCT of the values
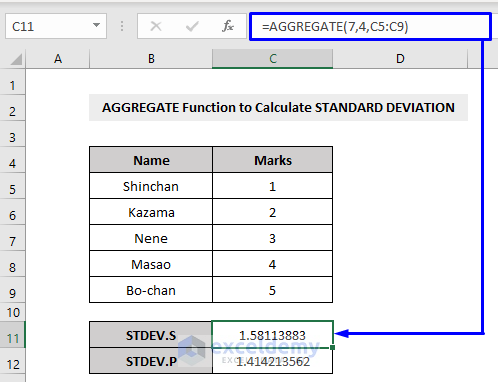
Example 6 – Excel’s AGGREGATE Function to Measure the Standard Deviation
Excel’s STDEV function is a statistical function, which refers to the Standard Deviation for a sample dataset. It uses the following equation.
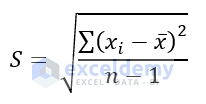
Here,
xi = takes on each value in the dataset
x¯ = average (statistical mean) of the dataset
n = number of values
With the AGGREGATE function, you can calculate the Standard Deviation for a sample dataset with the STDEV.S function (function number 7).
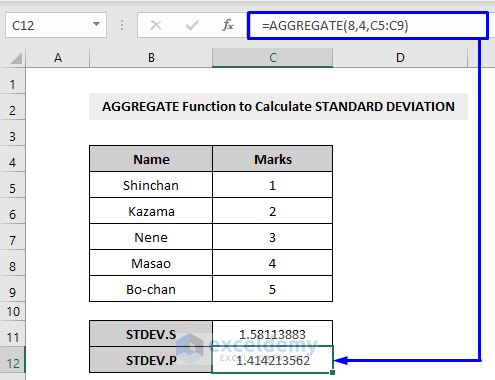
To calculate the Standard Deviation for a whole population you can use the STDEV.P function (function number 8).
Read More: Combining AGGREGATE with IF Function in Excel
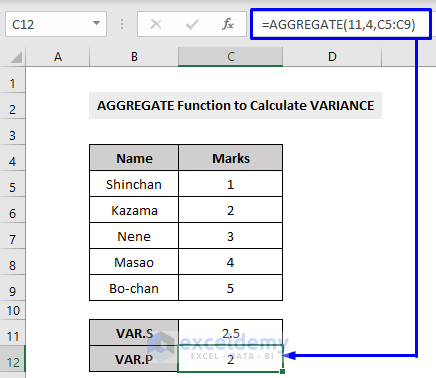
Example 7 – Applying the AGGREGATE Function in Excel to Calculate the VARIANCE
VAR function is another statistical function in Excel, which estimates the variance of a sample dataset. It uses the following equation.
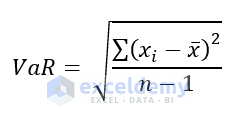
Here,
xi = takes on each value in the dataset
x¯ = average (statistical mean) of the dataset
n = number of values
To calculate the VARIANCE of a sample dataset with the AGGREGATE function, use the VAR.S function, which is function number 10.
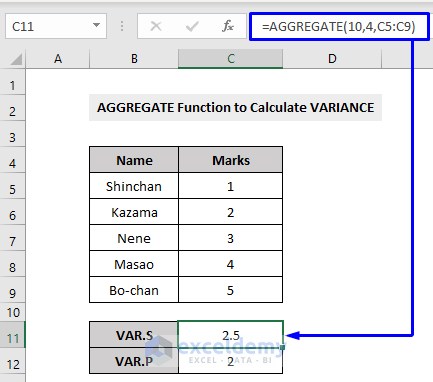
To calculate the VARIANCE of an entire population, you have to use the VAR.P function, which is function number 11 in Excel.
Example 8 – Calculating the MEDIAN Value with Excel AGGREGATE Function
The MEDIAN function in Excel returns the middle number of the set of data.
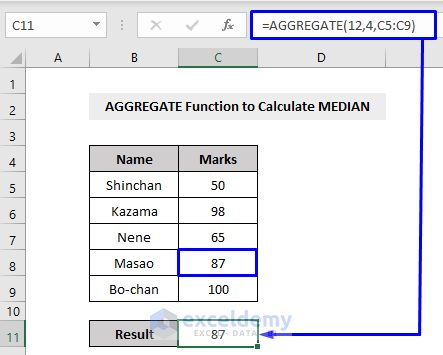
In the above example, there are 5 numbers, 50, 65, 87, 98, 100 – among which 87 is the middle number. After performing the MEDIAN function with the help of AGGREGATE, we got the desired output, 87, in our result cell.
Example 9 – Applying the AGGREGATE Function to Measure the MODE in Excel
Excel’s MODE.SNGL function returns the most frequently occurred value within a range. This is also a statistical function in Excel.
Consider the following example where 98 occurs 2 times while the rest of the numbers occur only once.
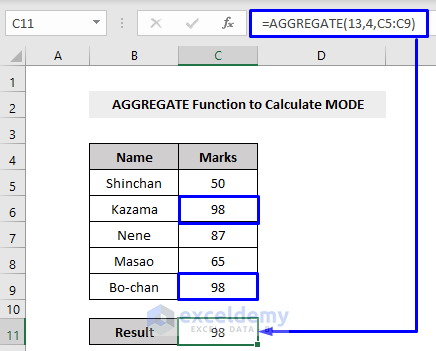
By running the MODE function inside AGGREGATE, it puts the number 98 in our result cell.
Example 10 – Calculating the LARGE Value with Excel’s AGGREGATE Function
The LARGE function returns the largest number among a given dataset. It’s function number is 14, and we also need to insert the [k] as the fourth parameter.
Here’s an overview of the function:
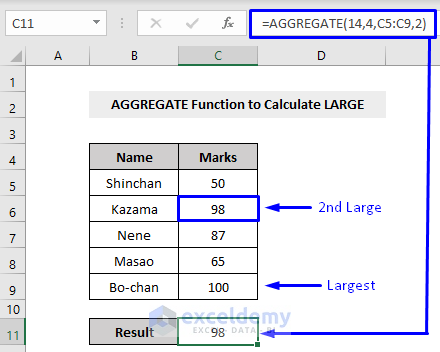
Here,
14 = function number, means the LARGE function
4 = option, means we will ignore nothing
C5:C9 = cell references that have the values to extract the result
2 = 2nd largest value (if you want to get the largest value within a dataset then write 1, if you want to get the 3rd largest value then write 3 and so on)
The largest value in our dataset is 100. But as we put 2 in the k-th argument, that means we wanted to have the 2nd largest value among our dataset. 98 is the 2nd largest so we got 98 as our output.
Example 11 – Measuring the SMALL Value with the AGGREGATE Function
Excel’s SMALL function returns the smallest number among a given dataset. Its function number is 15, and we need to insert the [k] as the fourth parameter. Here’s an overview.
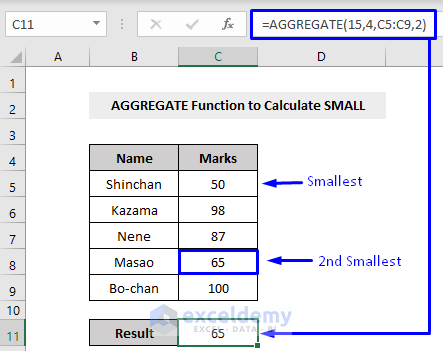
Here,
15 = function number, means the SMALL function
4 = option, means we will ignore nothing
C5:C9 = cell references that have the values to extract the result
2 = 2nd smallest value (if you want to get the smallest value within a dataset then write 1, if you want to get the 3rd smallest value then write 3 and so on)
The smallest value in our dataset is 50. But as we put 2 in the k-th argument, that means we wanted to have the 2nd smallest value among our dataset. As 65 is the 2nd smallest so we got 65 as our output.
Example 12 – Using the AGGREGATE Function to Measure the PERCENTILE in Excel
The value of k can be a decimal or a percentage. For the 10th percentile, the value should be entered as 0.1 or 10%.
For instance, a percentile calculated with 0.2 as k means 20% of values are less than or equal to the calculated result, a percentile of k = 0.5 means 50% of the values are less than or equal to the calculated result.
The AGGREGATE function uses PERCENTILE.INC (function number 16) and PERCENTILE.EXC (function number 18) to calculate the percentile value of a given dataset.
The PERCENTILE.INC returns the inclusive k-th percentile between 0 and 1.
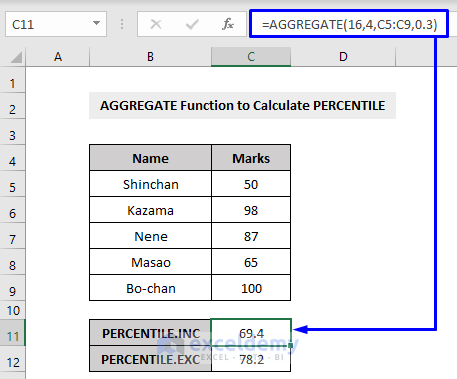
The PERCENTILE.EXC returns the exclusive k-th percentile between 0 and 1.
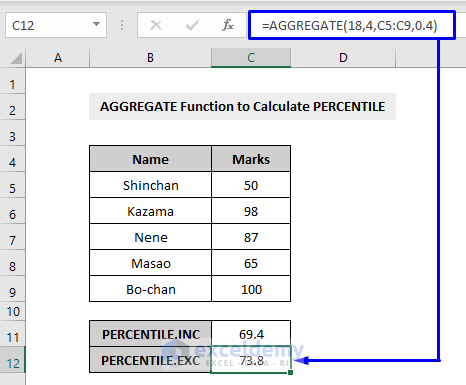
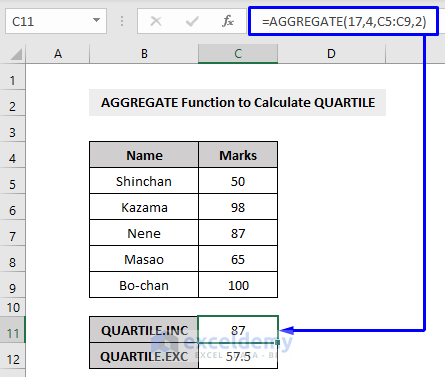
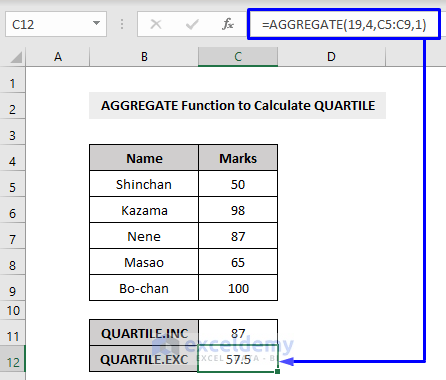
Example 13 – Calculating the QUARTILE with the AGGREGATE Function in Excel
Excel’s QUARTILE function returns the quarter part (each of four equal groups) of a whole set of data.
The QUARTILE function accepts five values,
0 = Minimum value
1 = First quartile, 25th percentile
2 = Second quartile, 50th percentile
3 = Third quartile, 75th percentile
4 = Maximum value
The AGGREGATE function works with QUARTILE.INC (function number 17) and QUARTILE.EXC (function number 19) functions to produce the quartile results.
The QUARTILE.INC function calculates based on a percentile range of 0 to 1 inclusive.
The QUARTILE.EXC function calculates based on a percentile range of 0 to 1 exclusive.
Download the Practice Workbook
Excel AGGREGATE Function: Knowledge Hub
<< Go Back to Excel Functions | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

