In many real-life situations in business or games, we need to predict the result or output. The PROB function in Excel is a quite useful tool to do that. In financial analysis, the PROB function can be used to estimate business losses, profits, and risks.
The above image is an overview of the PROB function. This article will guide you in detail with some easy examples of how to use the PROB function in Excel with vivid illustrations.
What is Probability?
Probability defines the chance of occurrence of an event. There are many real-life situations in which we may need to predict the outcome of an event. We may be sure or not sure of the occurrence of an event. In that case, we may say that there is a probability of this event to occur or not occur. Probability generally has great applications in games and businesses to predict the probability of a situation. Also, probability has huge applications in this new area of artificial intelligence.
The probability can be calculated with a simple formula by dividing the favorable number of outcomes by the total number of possible outcomes. The value of the probability lies between 0 and 1 because the possible number of outcomes can never cross the total number of outcomes. Also, the favorable number of outcomes cannot be negative.
Probability = Favorable Number of Outcomes/Total Possible Outcomes = x/NIntroduction to Excel PROB Function
The PROB function is categorized under Statistical functions.
Purpose:
To numerically anticipate that a set of values in a given range are between two limits.
Syntax:
=PROB(x_range, prob_range, [lower_limit], [upper_limit])Arguments:
| Arguments | Required/Optional | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| x_range | Required | The range of numeric values which are associated with probabilities. |
| prob_range | Required | A set of probabilities that are associated with the values in x_range. |
| lower_limit | Optional | The lower bound on the x_range for which you want a probability. |
| upper_limit | Optional | The upper bound on the x_range for which you want a probability. |
Return Parameter:
The probability for a set of events associated with a given range.
Available in:
MS Excel 2007 and upper versions.
Using the PROB Function in Excel: 3 Easy Examples
We will describe three cases of the use of the Excel PROB function with three suitable examples. Please keep going through the following sections to the last.
Example 1: Find the Probability of a Single Event with the PROB Function
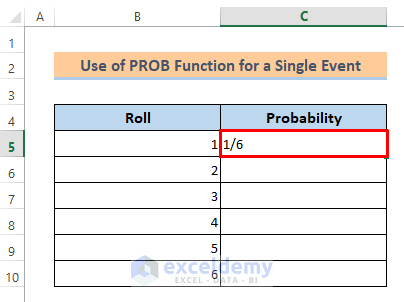
To show the first example I have made a dataset that represents the 6 rolls of a dice. By using the PROB function, we’ll be able to find the probability of any roll or for any range of roll. But before that, we’ve to find the probability of each roll manually.
Here, we have a total of 6 rolls. So, the probability of getting roll 1 will be 1/6.
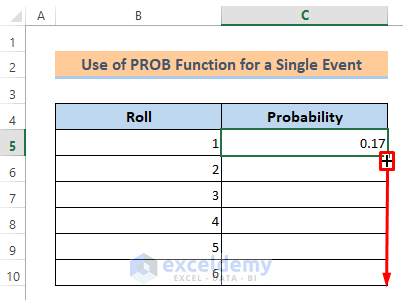
- Type it in cell C5 and press the Enter button.
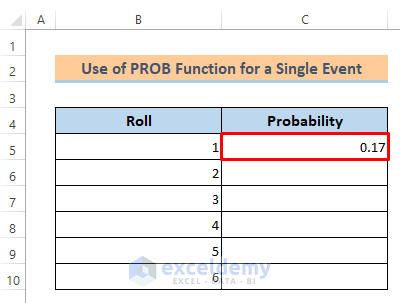
- Then, we’ll get the probability of 0.17 for roll 1.
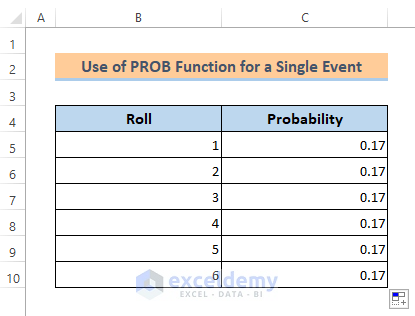
The probability of other rolls will be the same because each roll has one chance. So,
- Drag the Fill Handle icon to copy the value for the other cells.
- Then, we got all the roll’s probability here.
The Probability of Getting the Rolls from 4 to 6:
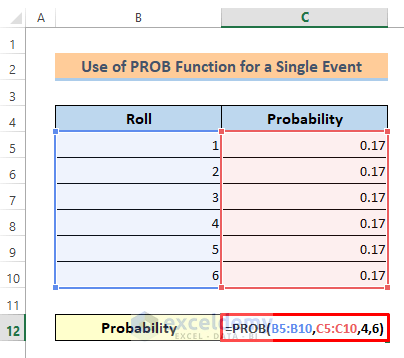
Now, let’s find the probability of getting the rolls from 4 to 6.
Steps:
⏩ Type the following formula in cell C5:
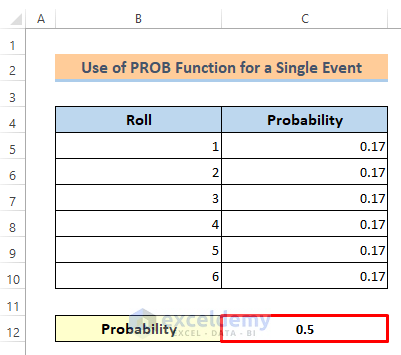
=PROB(B5:B10,C5:C10,4,6)Lastly, you will get the probability of getting the rolls from 4 to 6 is 0.5.
Example 2: Excel PROB Function to Find the Probability for Two Simultaneous Events
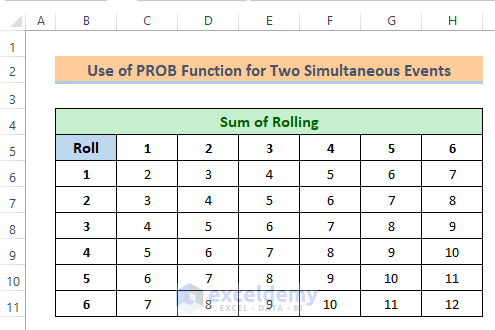
In this method, we’ll learn how to find the probability of two events occurring simultaneously. So, I have made a new dataset that represents the rolls of two dice. I placed the rolls of the first dice in Row 3 and the rolls of the second dice in Column B.
First, we’ll find the probable sum of each simultaneous roll by using a formula.
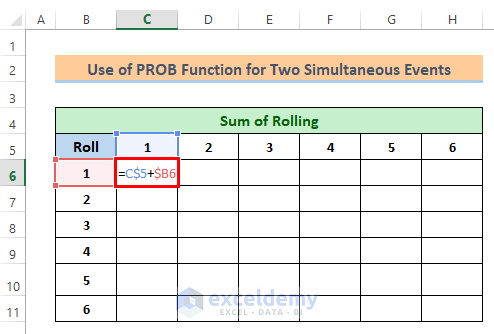
- To get the sum in cell C6, type the following formula-
=C$5+$B6- Then press the Enter button.
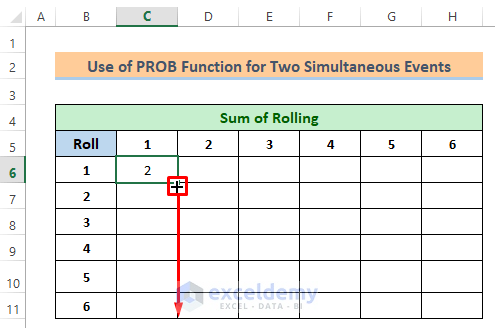
- Later, drag down the Fill Handle icon as shown in the image below-
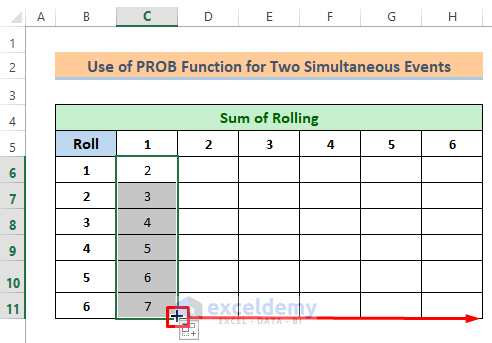
- Then drag the Fill Handle icon rightward and you will get all the sums.
Now we have got all the sums. Notice that the lowest sum is 2 and the highest sum is 12.
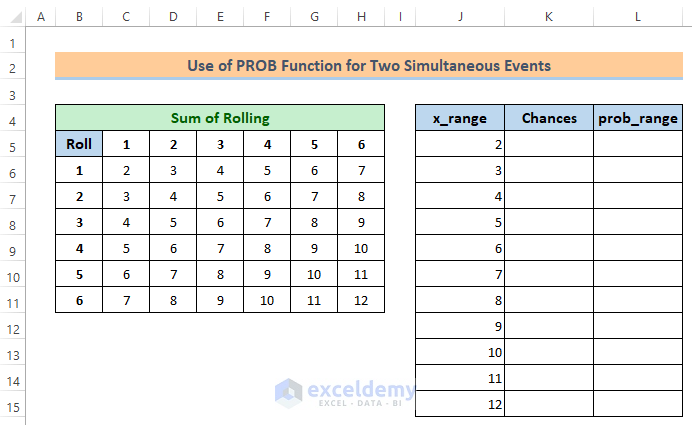
- Then, I placed the sum values in a new table as x_range for the PROB function.
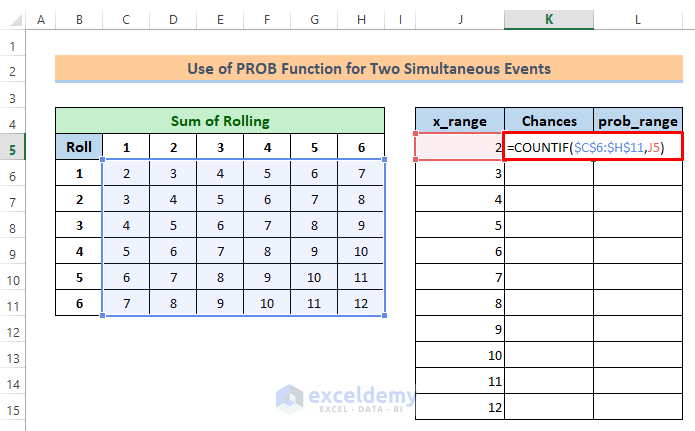
Now, we’ll find the chances of each sum using the COUNTIF function.
Steps:
⏩ In cell K5 write the following formula:
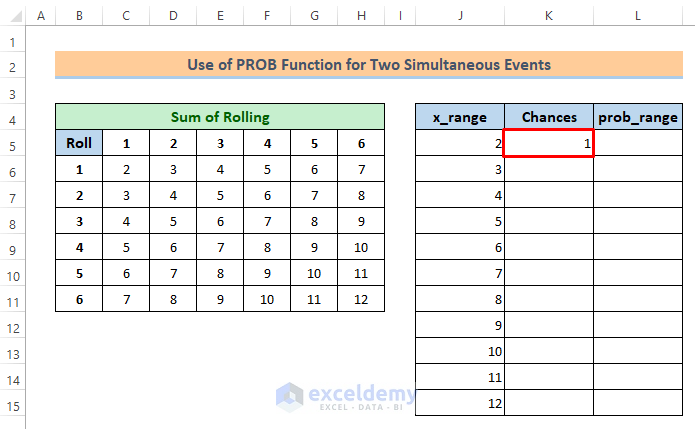
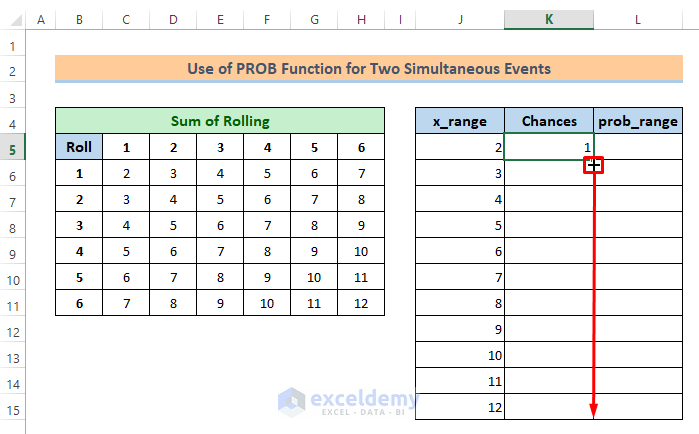
=COUNTIF($C$6:$H$11,J5)You will get output 1. We can check on the sum table that there is only one sum value, 2.
⏩ Then to get the other chances just drag the Fill Handle icon over the cells as shown in the image below.
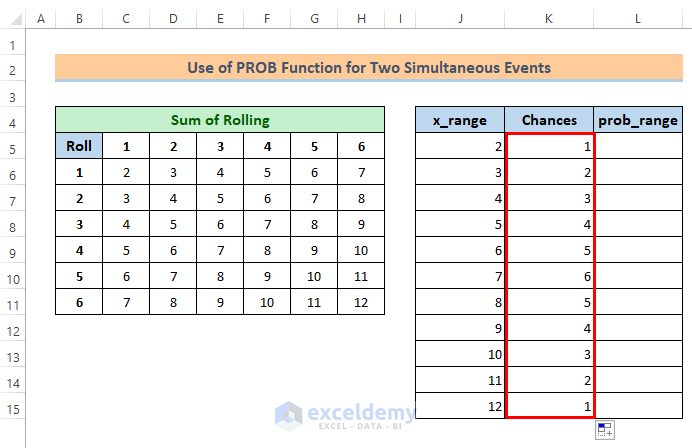
Now we got all the chances.
At this moment, we’ll find the probability of chances and will place it in column L as prob_range for the PROB function. You will notice in the sum table that there is a total of 36 possible sums.
Now, we can calculate the probability of each sum by using the basic probability equation:
Probability = Favorable Number of Outcomes/Total Possible Outcomes
Calculate the Probability for Each Sum:
Please follow the steps below for that.
Steps:
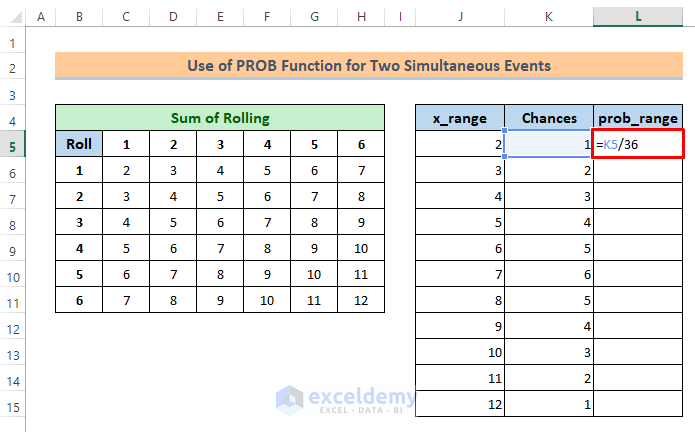
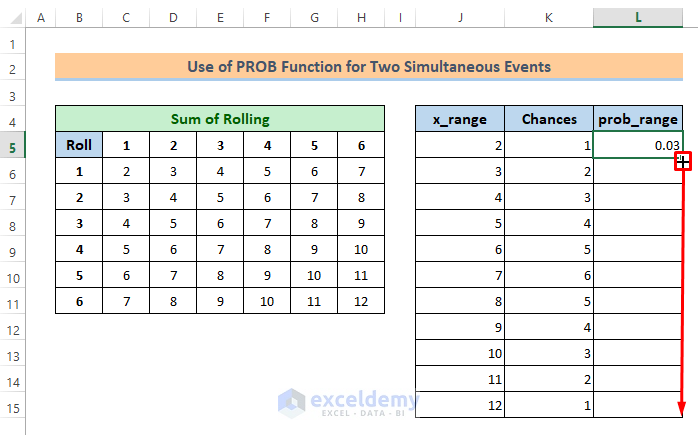
⏩ Write the following formula in cell L5:
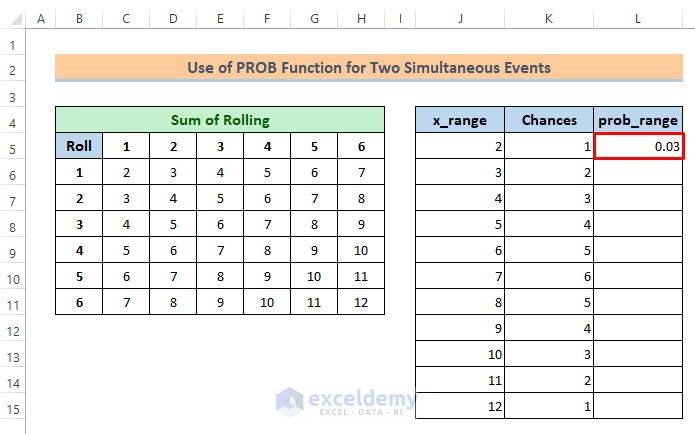
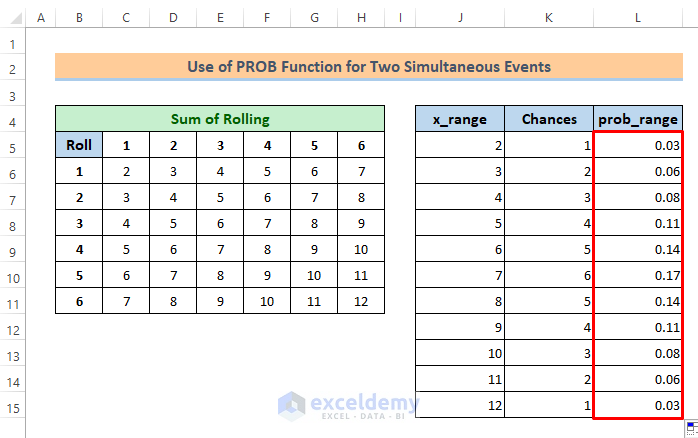
=K5/36Soon after you will get the probability for sum 2 is 0.03.
⏩ Next, just drag the Fill Handle icon to get the other probabilities.
We have got all the probabilities now which is the prob_range for the PROB function.
1. Probability of Getting a Sum Less Than 9
Now, let’s go for the final outcome. At first, I’ll show the probability of getting a sum less than 9.
Steps:
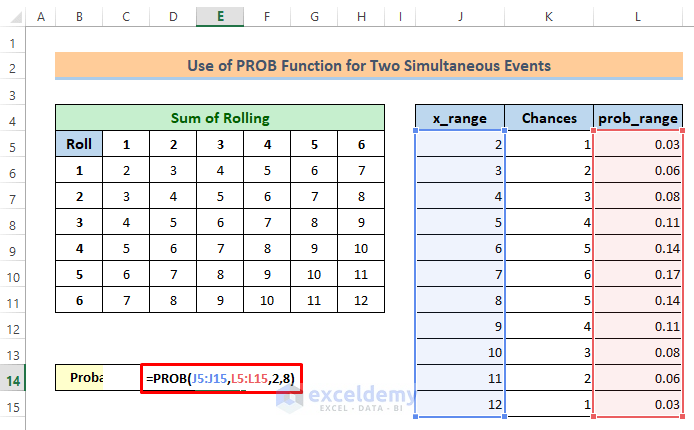
⏩ Activate cell E14.
⏩ Then write the following formula in it and press the Enter button.
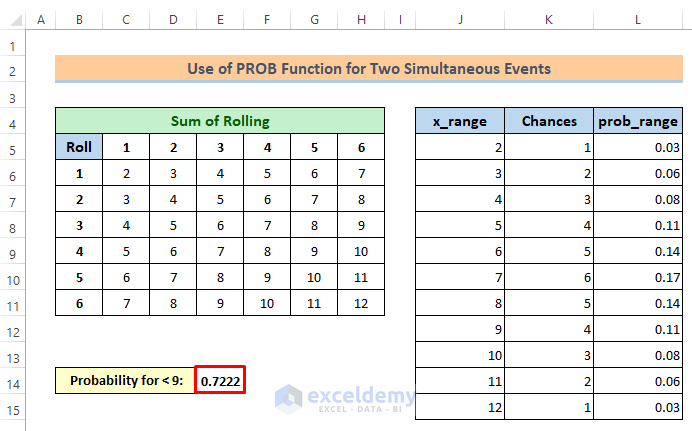
=PROB(J5:J15,L5:L15,2,8)Then, you will get the probability of getting a sum less than 9 is 0.7222.
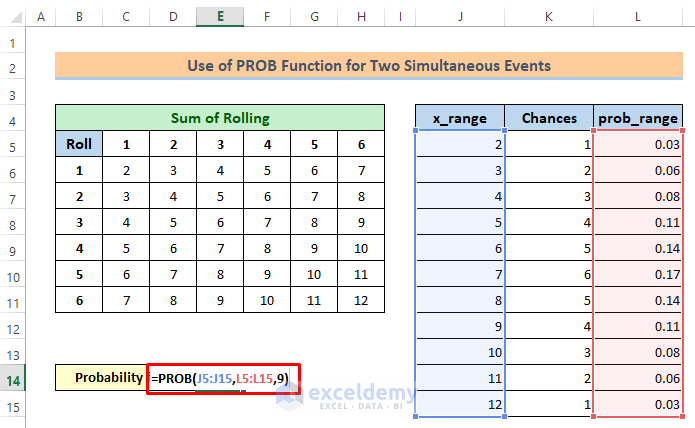
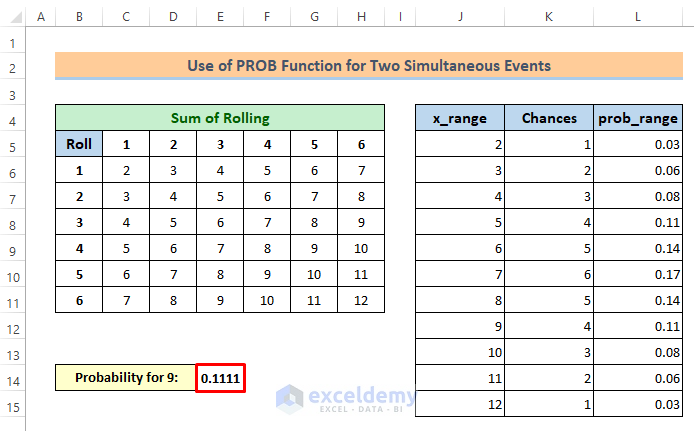
2. Probability of Getting a Sum Equal to 9
If you want to calculate the probability of the sum equal to 9, then follow the steps below:
Steps:
⏩ Type the following formula-
=PROB(J5:J15,L5:L15,9)⏩ Click the Enter button.
You will get the probability for 9 is 0.1111.
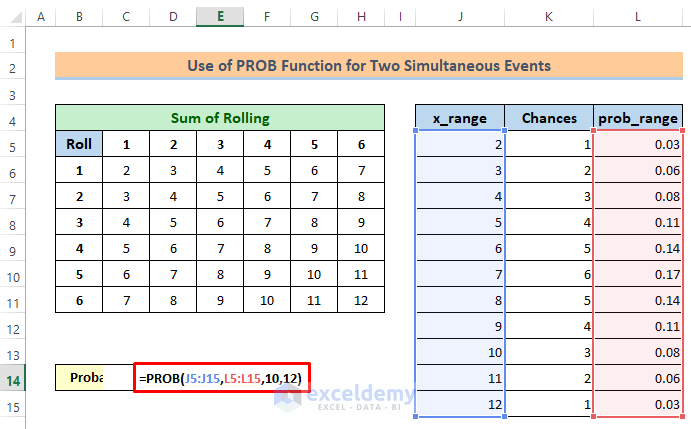
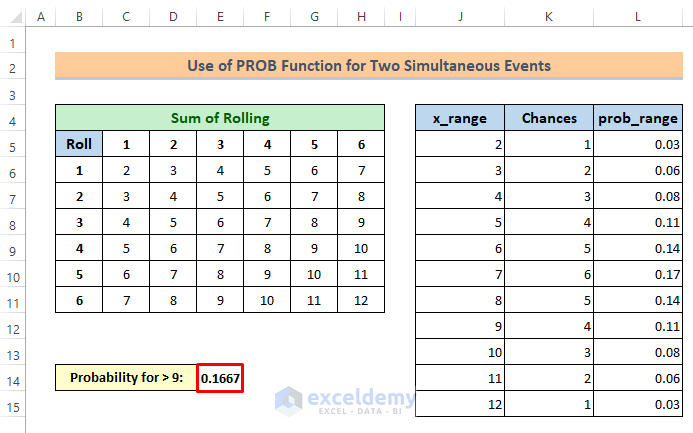
3. Probability of Getting a Sum Greater Than 9
To find the probability for the sum of rolling greater than 9,
Steps:
⏩ Write the following formula-
=PROB(J5:J15,L5:L15,10,12)Then you will get the output like this:
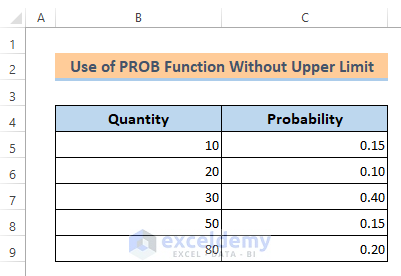
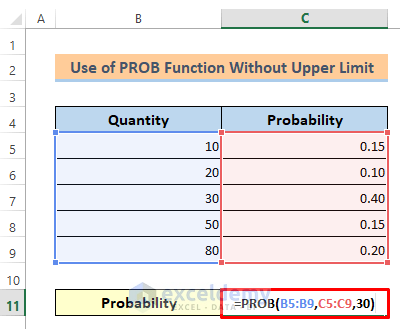
Example 3: Use of PROB Function without the Upper Limit
In this last method, we’ll learn to find the probability of a range if the upper limit is not given. Actually, if the upper limit is not given then the PROB function finds the probability according to the lower limit. To show that I have made a new dataset that represents a product’s selling probability for different quantities.
Steps:
⏩ Write the following formula in cell C11:
=PROB(B5:B9,C5:C9,30)⏩ Finally, just hit the Enter button.
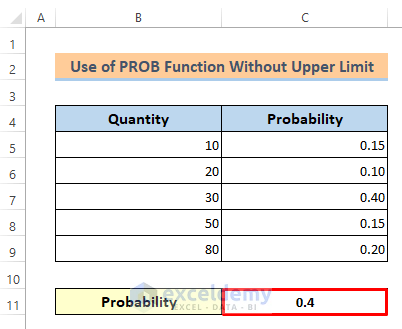
Then you will see that the result is just according to the lower limit which is 0.4.
Things to Remember
- The PROB function will return the #NUM! Error If any value in prob_range ≤ 0 or if any value in prob_range > 1.
- The PROB function will return #NUM! Error if the sum of the values in prob_range is not equal to 1.
- The PROB function will return the probability for lower_limit if upper_limit is omitted,
- The PROB function will return the #N/A Error If x_range and prob_range contain a different number of data points.
Download Practice Workbook
You can download the free Excel template from here and practice on your own.
Conclusion
I hope all of the methods described above will be good enough to use the PROB function in Excel. Feel free to ask any question in the comment section and please give me feedback.
<< Go Back to Excel Functions | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!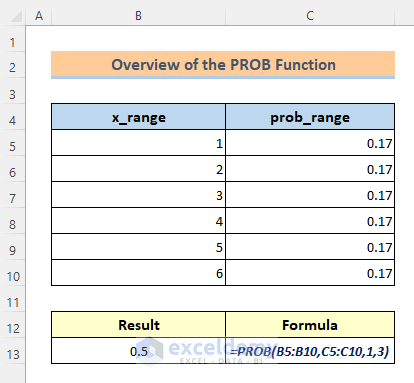




Thank you so much for your fundamental information regarding Excel.