In Excel, a range is a group of one or more connected cells. The Range property in VBA is a way that lets you find the range address and interact with it.
In this Excel tutorial, you will learn how to
- Set a fixed and dynamic range
- Define range using a Named Range
- Set ranges with Named Range
- Select a range
- Offset a range
- Loop through a range
- Use Range properties
- Apply Range methods
- Convert array to range or vice-versa
- Referring ranges from another worksheet or workbook
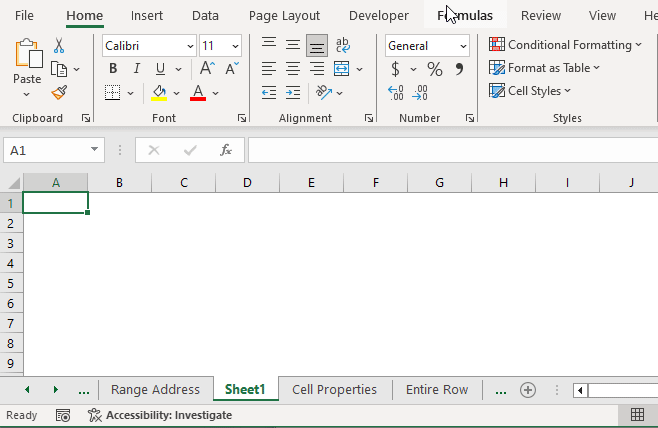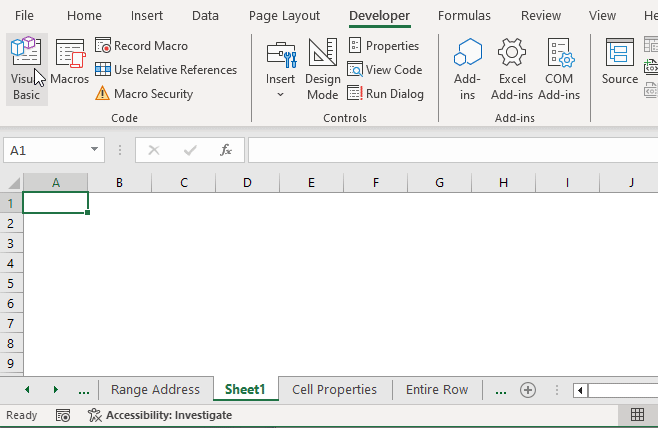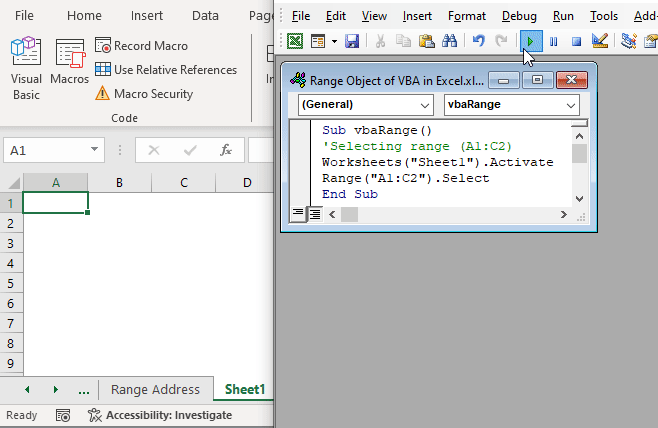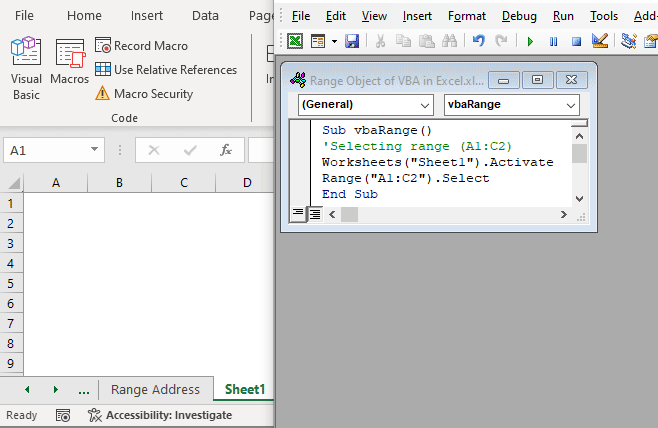
Understanding how to work with VBA Range Object makes you an expert in performing different cell and range operations, such as referring ranges, changing range values, selecting, sorting, or copying them. See the below overview image where you can select a range using the Range object in VBA.
Note: We have used Microsoft 365 to prepare this tutorial. However, all methods and examples demonstrated in this tutorial apply to Excel 2021, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, and Excel 2010 versions as well.
What is VBA Range Object in Excel?
The VBA Range object represents a single cell, an entire row, a complete column, a selection of cells encompassing one or more continuous blocks, a 3D range, or all the 17,179,869,184 cells in a Worksheet. In VBA, every worksheet has a Range property which you can use to access cells for task automation.
Here is the Excel object hierarchy:
Application → Workbook → Worksheet → Range
Excel VBA Range function allows you to access a specific range by indicating the sheet’s name and the cell address. If you don’t mention a sheet name, Excel automatically searches for the range in the Active Sheet. For instance, when the Range Object sheet is active, both of these lines will point to the same cell range.
Range("B6")and
Worksheets("Range Object").Range("B6")What is the Difference Between Range Object and Range Property in Excel VBA?
The Range object is a built-in object in the VBA object hierarchy that represents a collection of cells in a worksheet. The Range object has various properties and methods that can be used for modifying the cells in that range. For example, in the following VBA code, we have used the Interior.Color property under Range object to set Fill Color in cells of range A1:D5.
Sub UnderstandingRangeObject()
Range(“A1:D5”).Interior.Color = RGB(240,220,200)
End SubOn the other hand, the Range property is a property of various objects in Excel VBA, including Worksheet and Range objects. For example, in the following VBA code, we have used Range property under ActiveSheet object.
Sub UnderstandingRangeProperty
Set trgt_rng = ActiveSheet.Range(“A1:D5”)
End SubHow to Set a Range with Excel VBA
You can set a range in Excel VBA in several ways. See all the methods to apply according to your requirements.
1. Using Range Address
To represent a single cell or a range of cells, you can use the Range Object where the argument names the range. Here is the syntax to specify a range:
To specify a range that has one cell, for instance, cell B6, you can write:
Range ("B6")Referring to a range of cells for example range B6 to E16, there are two acceptable ways:
Range("B6:E16")and
Range("B6", "E16")To enclose the range address, you can see the above syntaxes use double quotations (” “). As alternatives, you can use the Square brackets without the quotations to type quickly. For example:
You may use [B6:E16] instead of Range(“B6:E16”) for referring to the range B6:E16.
2. Using Cells Property
You can use the Cells property for referring to a range in VBA. Using the Cells property is useful while looping through rows or columns. The Cells property takes two arguments:
Cells (Row, Column)For the Row arguments, you need to use numeric values only. You may use either a string or numeric value for Column arguments. In the below example, both code lines refer to A1:E5:
Range(Cells(1,1),Cells(5,5))or
Range (Cells(1,”A”),Cells(5,”E”))For referring to a single cell, you can simply use the below lines without mentioning the Range object.
Cells(6, 2) or Cells(6, “B”)
3. Referring Entire Rows as Range
For referring to an entire row, or multiple rows, use the Range object in VBA.
Here are the syntaxes for both single and multiple rows.
For single row range:
Range("6:6")For multi-row range:
Range("6:8")4. Setting Entire Columns as Range
To set an entire column or multiple columns, use the following syntaxes.
For single-column range:
Range ("B:B")For multiple column range:
Range ("B:E")5. Setting Non-Contagious Cells as Range
To set non-contagious cells as a range in VBA, use Comma (,) to separate each area. For referring to range B6:C6 and E6:E16 at once, you can use this line:
Range("B6:C16, E6:E16")6. Using Resize Property to Set Range
The Resize property in Excel VBA changes the size of a range.
Imagine, your current range is B6 and you want to resize the range to B6:E9. Therefore, the syntax of the Range object in VBA is-
Range("B6").Resize(4, 4)Read More: VBA to Set Range in Excel
How to Set a Dynamic Range in Excel VBA
In the previous examples, you specified a fixed range size when using the VBA Range object. However, when dealing with variable-sized ranges, you often don’t know the exact size of the range. In such situations, you need dynamic ranges in Excel VBA. Here are a few ways to set a dynamic range in VBA.
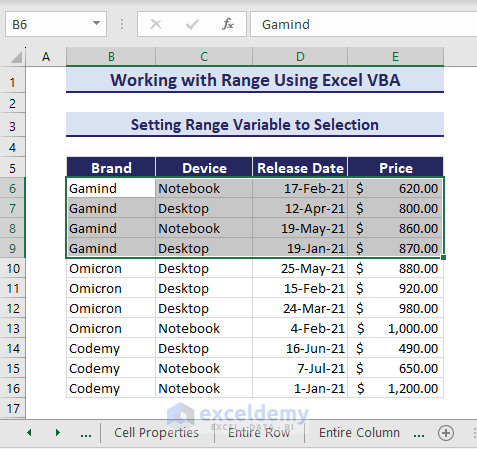
1. Setting Range Variable to Selection
You can set range variables to selection in Excel VBA and then use the variables to access properties and methods. Consider the below dataset where the range B6:E9 is selected:
Using the following code to change the cell color of the selected region as range variables:
Sub SettingRangeVariabletoSelection()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Selection
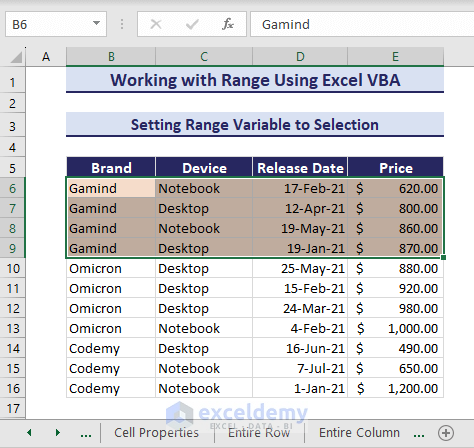
rng.Interior.Color = RGB(245, 220, 202)
End SubThus, the interior color of the selected range changes.
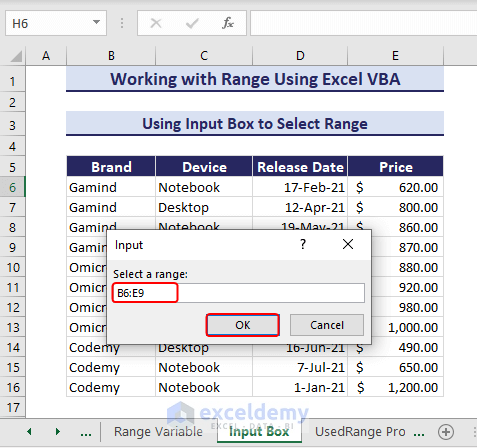
2. Using Input Box to Select Range
In this method, you will use an input box to select a range and change its color. Consider the previous dataset and run the below VBA code:
Sub UsingInputBoxtoSelectRange()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Set rng = Application.InputBox("Select a range:", Type:=8)
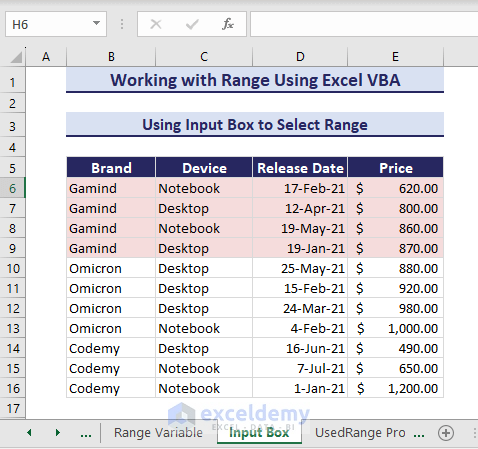
rng.Interior.Color = RGB(245, 220, 220)
End Sub- Enter the desired range in the message box and select OK. Here, we input range B6:E9.
As a result, the interior color of the desired range changes.
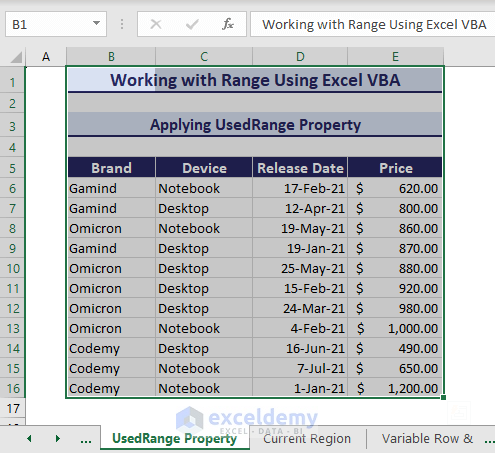
3. Applying UsedRange Property
Consider a dataset where you are constantly entering values and do not know how big it could get, you can use the UsedRange property. The following VBA code will select the used region:
Sub ApplyingUsedRangeProperties()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Select
End SubRunning the VBA code selects the whole used region.
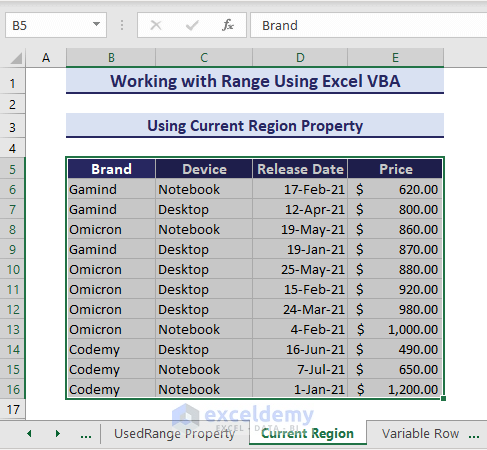
4. Using CurrentRegion Property
This CurrentRegion property can cover all the contagious cells of the active cell region. Here is the VBA code to select the contagious cells of B6:
Sub UsingCurrentRegionProperties()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("B6").CurrentRegion.Select
End SubAs you can see, the current region of cell B6 gets selected.
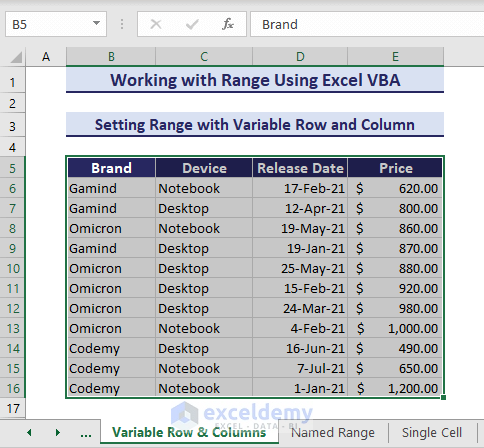
5. Setting Range with Variable Row and Column
Let’s say, you want to set a range with variable row and column numbers. To do this, you can specify the first row and column with variables and use the End property to get the last row and column. The End property for the Range object refers to the last cell within the range. Consider the following VBA code:
Sub SettingVariableRowColumn()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
first_row = 5
first_col = 2 ' or "B"
last_row = Cells(Rows.Count, first_col).End(xlUp).Row
last_col = Cells(first_row, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Range(Cells(first_row, first_col), Cells(last_row, last_col)).Select
End SubHere, we have assigned the first row and first column as 5 and 2 which indicates cell B5. Then, we can assign the last rows and columns using the End property. After that, we selected the region by setting the range with variable row and column numbers.
Read More: VBA to Use Range Based on Column Number in Excel
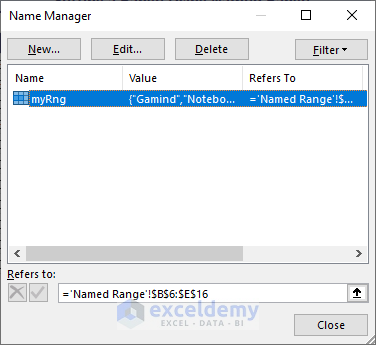
How to Set a Range Using Named Range in Excel VBA
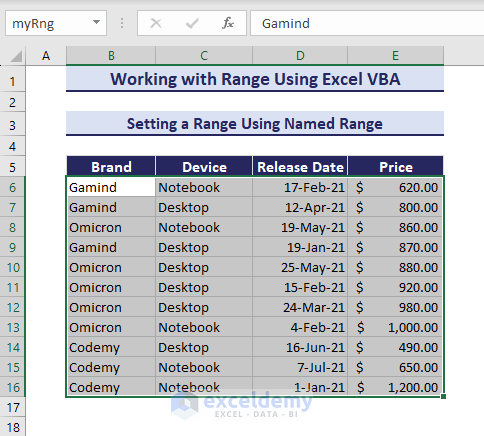
You can set a range using Named Range in Excel VBA by enclosing the range name with double-quotations in the Range object argument. Let’s assume, you have a Named Range named myRng that represents range B6:E16.
In the following VBA code, set the range using the named range:
Sub SettingRangeUsingNamedRange()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("myRng").Select
End SubAs a result, the Named Range gets selected.
How to Select Range with VBA in Excel
You can select a range using the Select method of the Range object in VBA. In the previous sections, you have learned how to specify a range. Here, you will see some practical examples of selecting ranges with VBA.
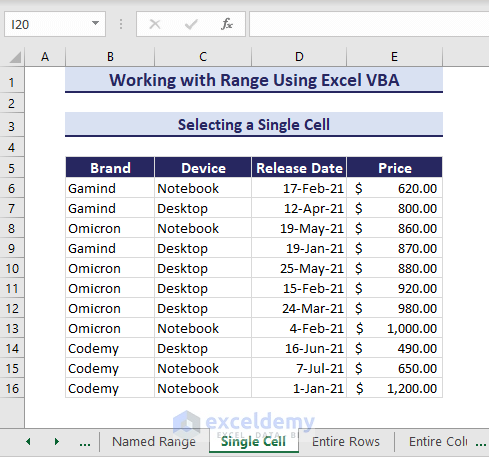
1. Selecting a Single Cell
Let’s consider the dataset that represents the sales data of some brands.
To select a single cell B6, run the below VBA code:
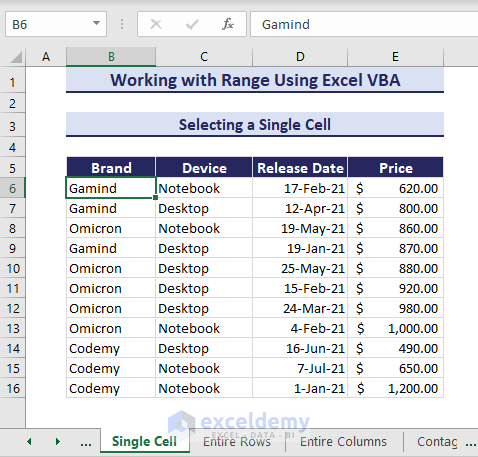
Sub SelectingaSingleCell()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("B6").Select
End SubRunning the code selects the cell B6.
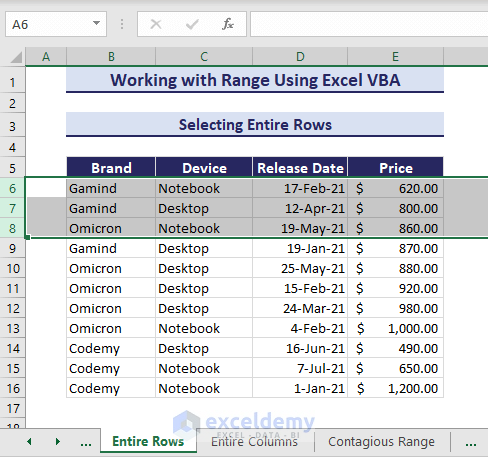
2. Selecting Entire Rows
To select the entire rows 6 to 8, use the following VBA code:
Sub SelectingEntireRows()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("6:8").Select
End Sub3. Selecting Entire Columns
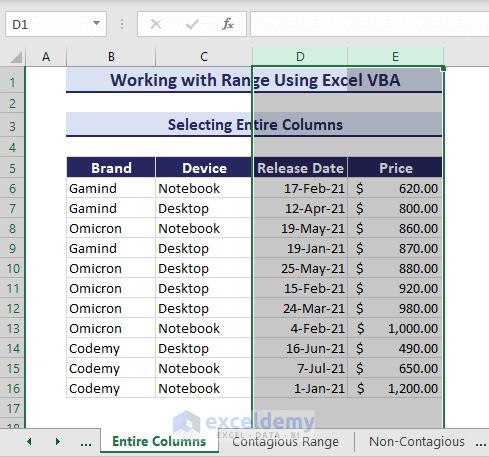
Similarly, select the entire columns D & E using the following VBA code:
Sub SelectingEntireColumn()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("D:E").Select
End Sub4. Selecting Contagious Range
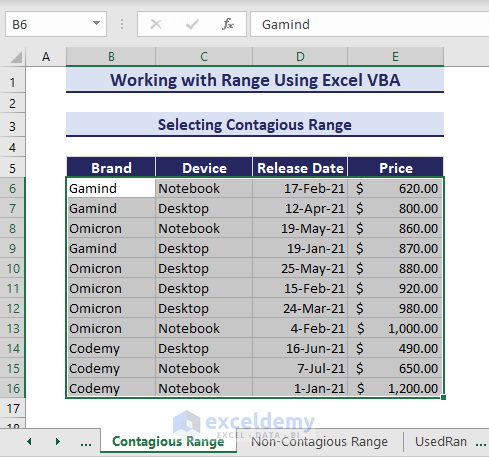
You can also select all the contagious cells at once. Consider the below VBA code:
Sub SelectingContagiousRange()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("B6", "E16").Select
End SubThe code selects every contagious cell of B6:E16.
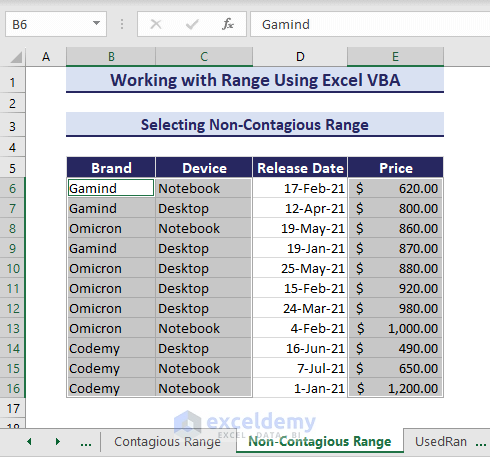
5. Selecting Non-Contagious Range
Now, let’s select the non-contagious cells of the same dataset. Use the below VBA code:
Sub SelectingNonContagiousCells()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("B6:C16, E6:E16").Select
End SubAfter running the code, two mentioned areas in the code were selected.
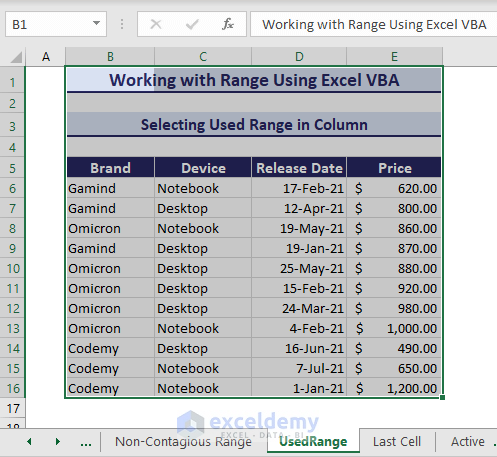
6. Selecting Used Range
You can select the used range of your active sheet using the Used Range property in VBA. Use the following VBA code:
Sub SettingUsedRangeinColumn()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Select
End SubThus, you select the whole used range of the active sheet.
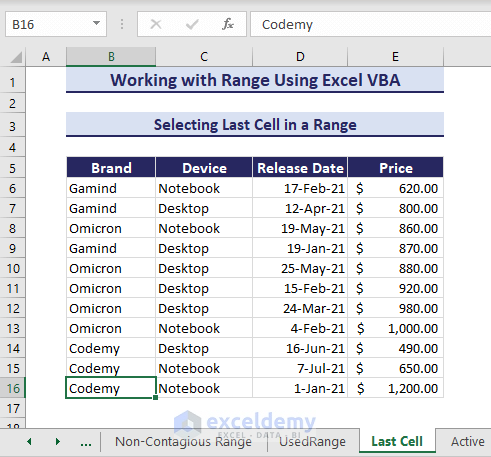
7. Selecting Last Cell in a Range
If you want to select the last cell of a large column without scrolling, you can use the below VBA code:
Sub SelectingLastCellInRange()
Range("B6").End(xlDown).Select
End SubThe last cell of the column B is selected.
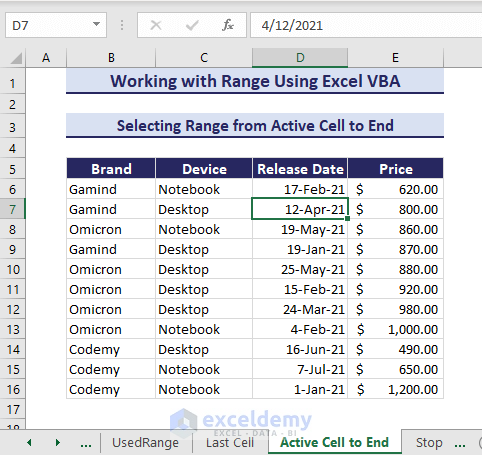
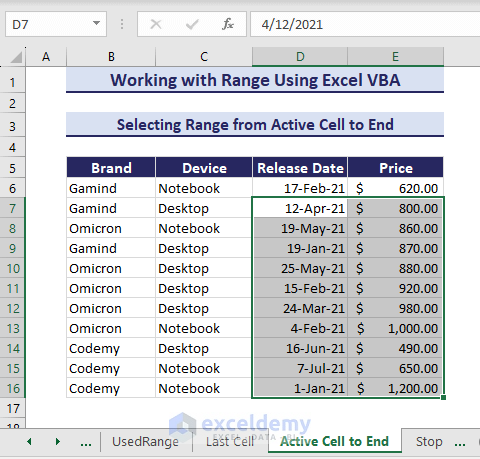
8. Selecting Range from Active Cell to End
Let’s say you have a selected cell in the dataset.
You can select range from the active cell in Excel with VBA Range Object to the end. Here is the VBA code:
Sub SelectfromActiveCelltoEnd()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range(ActiveCell.End(xlDown), ActiveCell.End(xlToRight)).Select
End SubHence, the code selects the range upto the last cells.
Read More: How to Select Range Based on Cell Value VBA
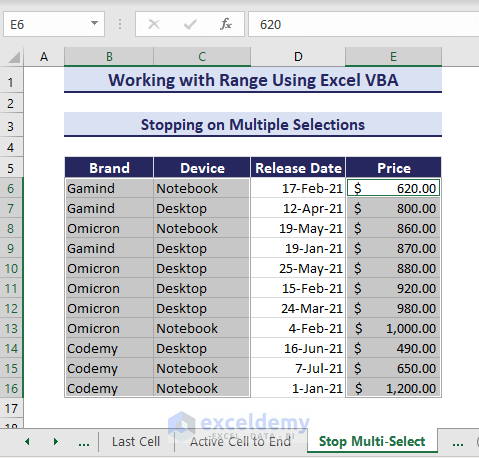
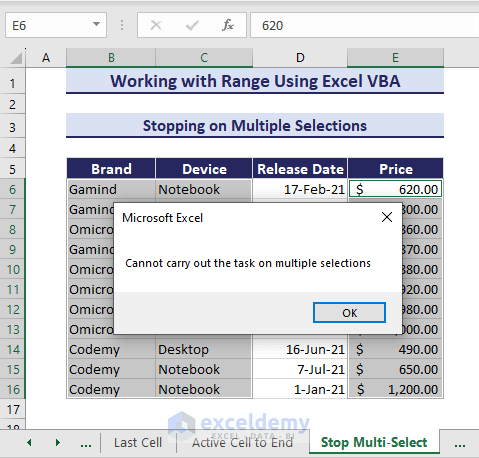
9. Stopping on Multi-Select Using VBA in Excel
You can stop an operation when you have multiple selections in your data using Range Object in VBA. See the dataset where we have multiple selections of different areas.
The following VBA code stops any operations on multiple selections:
Sub StoppingOnMultiSelection()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
selected_area_count = Selection.Areas.Count
If selected_area_count > 1 Then
MsgBox "Cannot carry out the task on multiple selections"
End If
End SubAs a result, the code stops any activity on multiple selections.
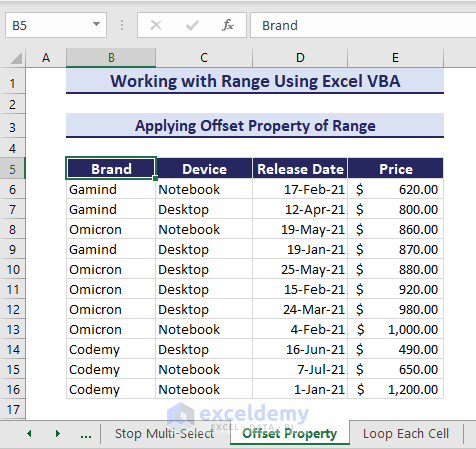
How to Apply Offset Property of Range in Excel VBA
You can apply the active cell Offset Property in VBA Range object to offset a range selection. The Offset property shifts the position of the range and the Resize property enlarges the size of the range to the specified range. Let’s say, you have an active cell B5 in your dataset.
The following VBA code offsets your selection to one row and one column and resizes the selection to cover 11 rows and 1 column:
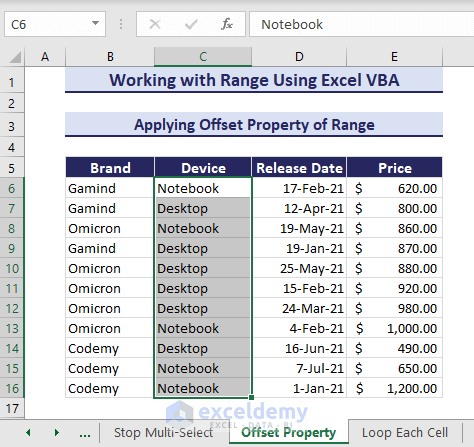
Sub ApplyOffsetProperties()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 1).Resize(11, 1).Select
End SubRunning the code results in the range B8:B16 being selected.
Read More: How to Use VBA Range Offset
How to Loop Through a Range in Excel VBA
To loop through a range in VBA, you can use the For Each loop. Here are some uses of For Each loop:
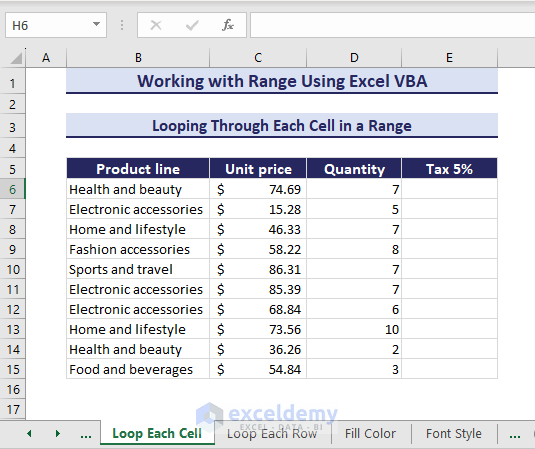
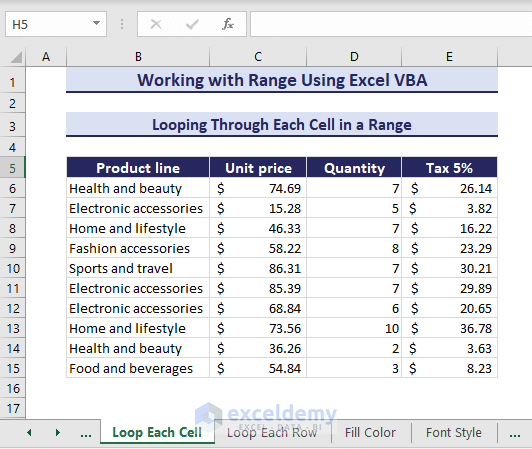
1. Looping Through Each Cell in a Range
This procedure shows how VBA For Each loops through each cell in range C6:D15. In this example, you will loop through the product’s unit price and quantity of the specified range and calculate the tax in the corresponding E column.
Within the loop, the VBA code calculates the tax values and enters them in E6:E15. Here is the VBA code:
Sub LoopingForEachCell()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Set target_range = Range("E6:E15")
tax_value = 0.05
For Each cell In target_range
cell.Value = cell.Offset(0, -2).Value * cell.Offset(0, -1).Value * tax_value
Next cell
End SubAs a result, the tax values appear in E6:E15.
Read More: VBA for Each Cell in Range in Excel
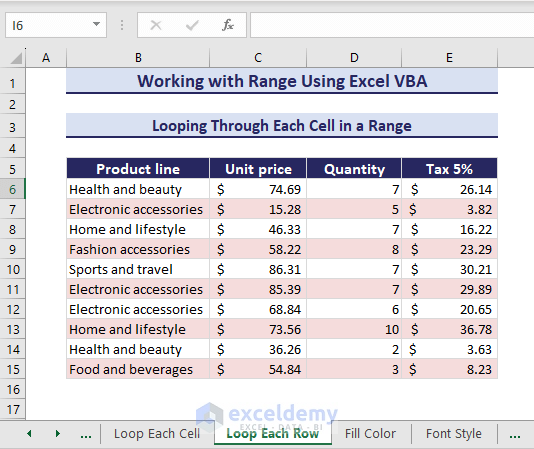
2. Looping Through Each Row in a Range
Now, we want VBA For Each loop to loop through each row 6 to 15. In the loop, we will look for odd or even rows and highlight the odd rows. Use the below VBA code:
Sub LoopingForEachRow()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Set working_range = Range("B6:E15")
For i = 1 To working_range.Rows.Count
If i Mod 2 = 0 Then
working_range.Rows(i).Interior.Color = RGB(245, 220, 220)
Else
working_range.Rows(i).Interior.Color = xlNone
End If
Next i
End SubThe code highlights the odd rows and the even rows remain the same.
Read More: Loop through a Range for Each Cell with Excel VBA
How to Work with VBA Range Properties in Excel
In this section, you will have a closer look at some useful Range properties in VBA. The Range Property represents cells, rows, and columns and manipulates cell formattings. Here are a few examples of Range Property in Excel VBA.
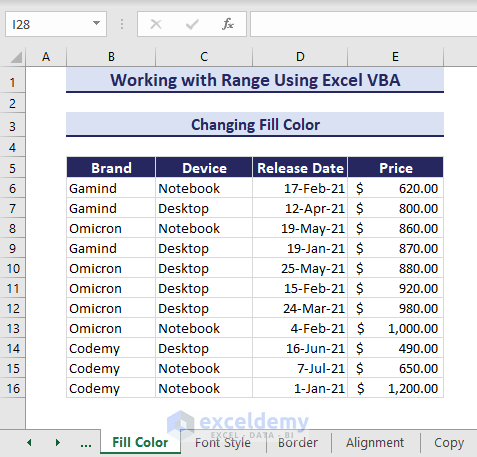
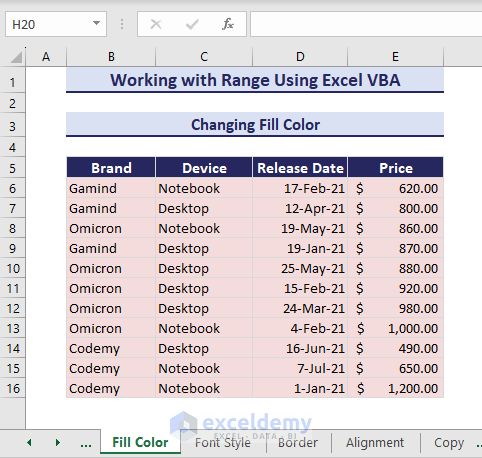
1. Changing Fill Color
Consider the below dataset where we want to change the fill color of the range B6:E16.
Sub ChangingFillColor()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("B6:E16").Interior.Color = RGB(245, 220, 220)
End SubThe fill color of the mentioned range changes.
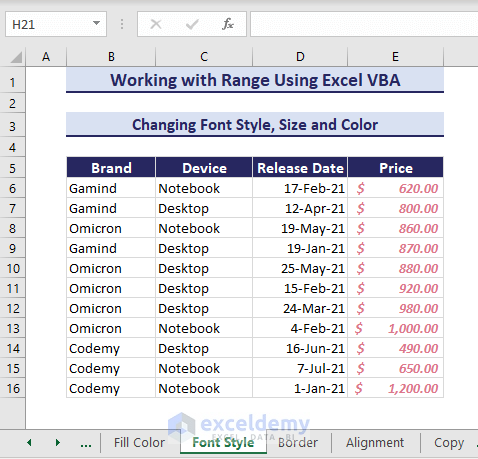
2. Changing Font Style, Size and Color
Similarly, you can change the font style, size and color using the Range Property. Let’s change the formatting of range E6:E16. Use the following VBA code:
Sub ChangeFontStyle()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Dim myRange As Range
Set myRange = Range("E6:E16")
With myRange.Font
.Size = 11
.Bold = True
.Italic = True
.Color = RGB(220, 120, 140)
End With
End SubThe new formatting appears in the desired range.
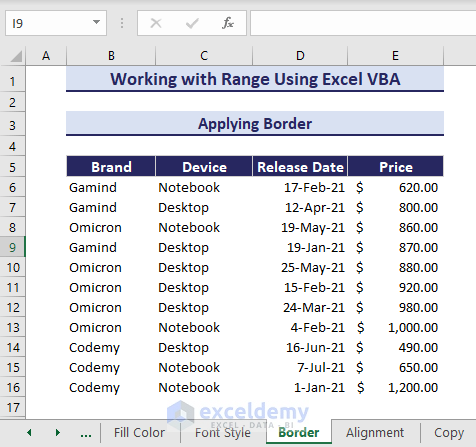
3. Applying Border
If you have borderless data in your sheet as given below, you can apply borders using VBA with Range Property.
Use the following VBA code to apply borders:
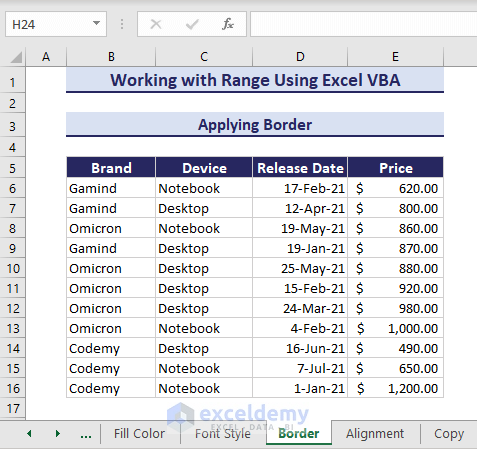
Sub ApplyingBorders()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Dim myRange As Range
Set myRange = Range("B5").CurrentRegion
With myRange.Borders
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Color = RGB(208, 206, 206)
.TintAndShade = 0
.Weight = xlThin
End With
End SubThus, you obtain the borders in the range.
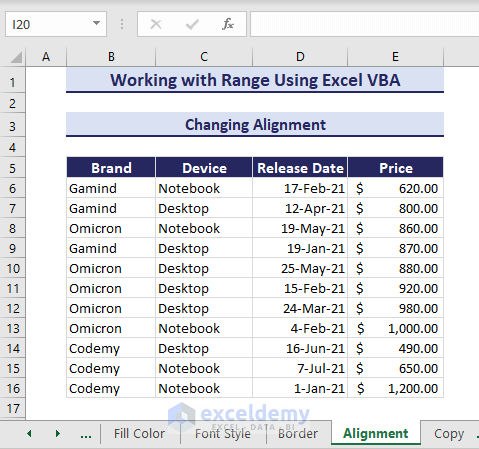
4. Changing Alignment
Finally, you can customize the cell alignment using this property. To change the alignment of the range, use the following VBA code:
Sub ChangingAlignment()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Dim myRange As Range
Set myRange = Range("B6:E16")
With myRange
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
.VerticalAlignment = xlVAlignCenter
End With
End SubThe cell alignments of the range B6:E16 move to the center both vertically and horizontally.
How to Work with VBA Range Methods in Excel
In VBA, methods are built-in functions that belong to specific objects and perform actions on them. The Range object in VBA provides various of methods, each with its own specific purpose. Here are some of the most commonly used methods: Value, Clear, Copy, Delete, etc.
Copy-Pasting Range
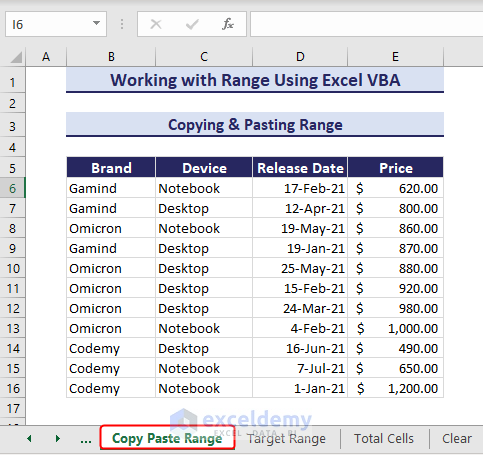
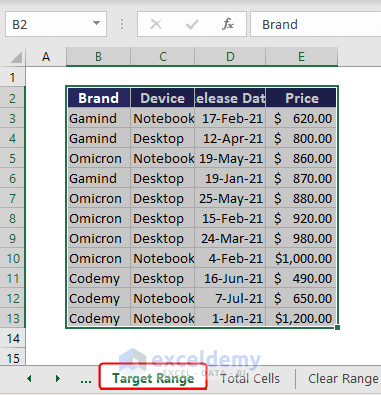
To copy and paste a range with VBA, you can use the Copy and Paste methods with Range object. See the below dataset where you will copy range B6:E16 of the Copy Paste Range worksheet.
- Run the below VBA code:
Sub CopyPasteRange()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Sheets("Copy Paste Range").Activate
Range("B5:E16").Select
Selection.Copy
Sheets("Target Range").Activate
Range("B2").Select
ActiveSheet.Paste
End SubAfter running the code, we get the copied value in the Target Range sheet.
Counting Total Cells in a Range
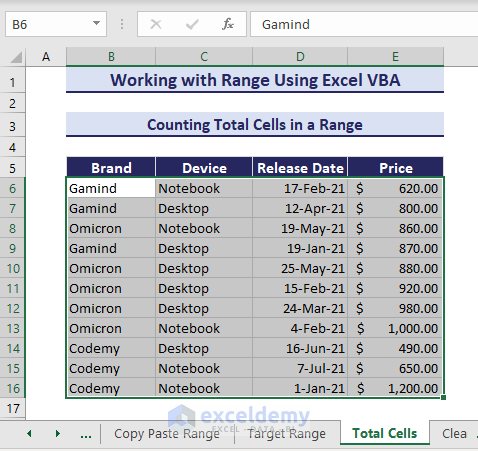
If you have a selected range as given below, you can count the total cells in that range using the Count method of VBA Range object.
- Consider the below VBA code where we have used the Count method:
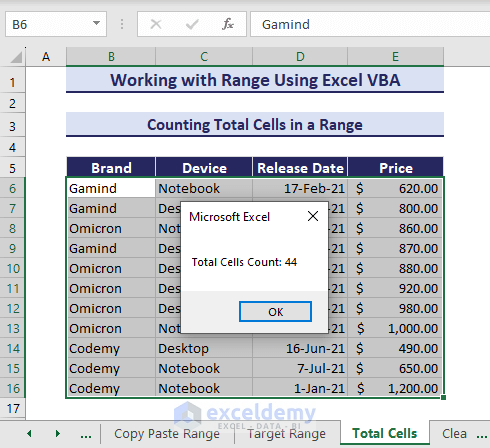
Sub CountTotalCellsInRange()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Set target_range = Selection
MsgBox "Total Cells Count: " & target_range.Cells.Count
End SubRunning the code will show you the total number of cells in a message box.
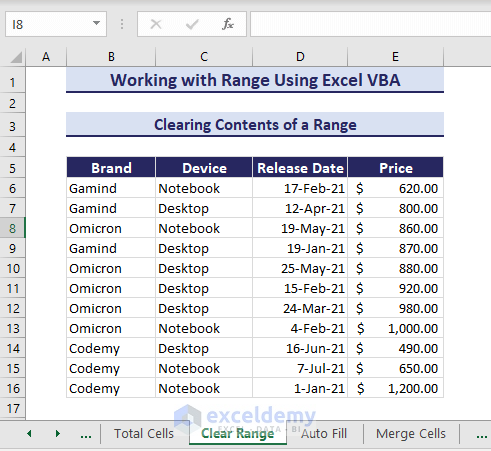
Clearing Contents of a Range
The Range object has ClearContents method to clear contents in VBA from the specified range E6:E16 of the below data.
So, use the following VBA code and run it.
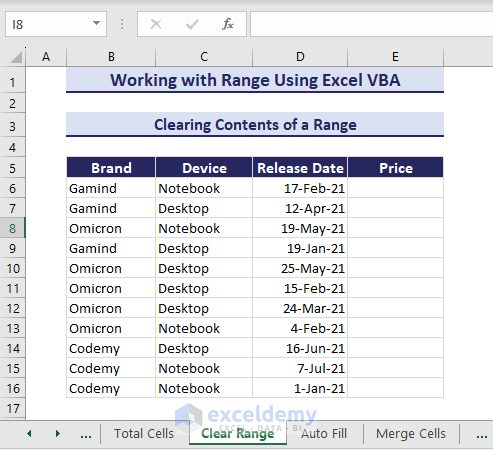
Sub ClearContentsofRange()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("E6:E16").ClearContents
End SubAs a result, the data of the specified range is cleared.
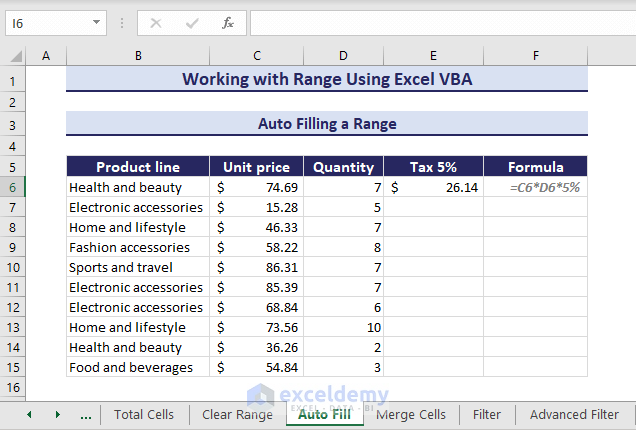
Autofill a Range
Let’s say, you have calculated a tax value in E6 based on the unit price and quantity using the given formula in F6. You can autofill the range in VBA using the AutoFill method.
Here is the VBA code to autofill the range E6:E15:
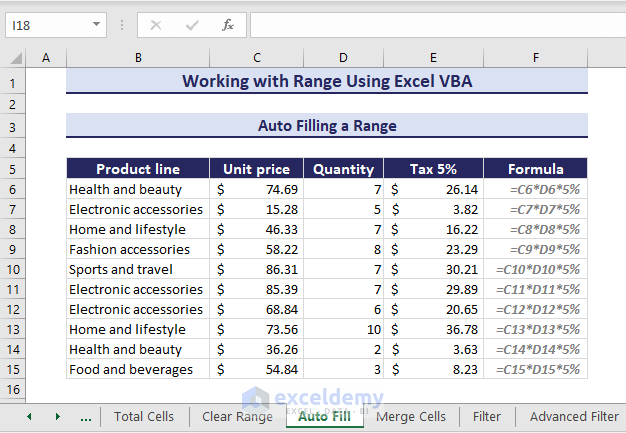
Sub AutoFillRange()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("E6").AutoFill Range("E6:E15")
End SubThus, you obtain the rest of the tax values.
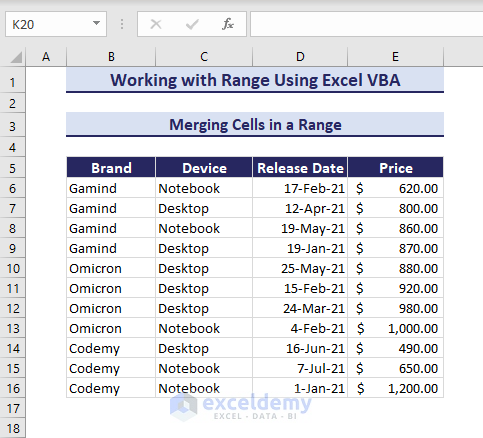
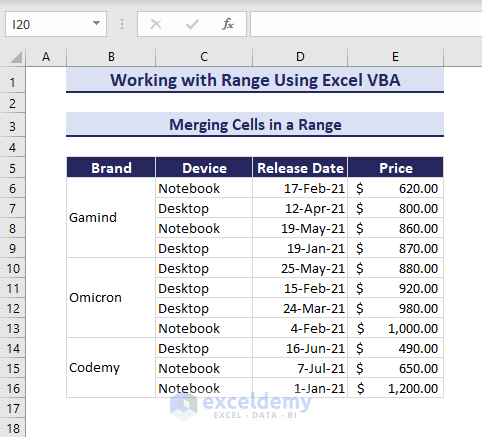
Merging Cells in a Range
Imagine the below scenario where the Brand column has similar values consecutively and you can merge the cells with similar values for better visibility.
Use the Merge method in the VBA code provided below and execute it.
Sub MergeCells()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Range("B6:B9").Merge
Range("B10:B13").Merge
Range("B14:B16").Merge
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End SubWe obtain cells with similar data merged.
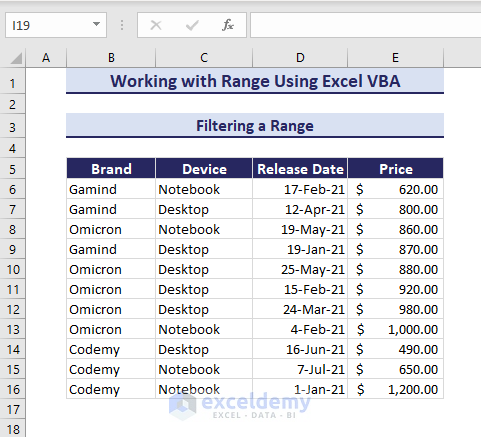
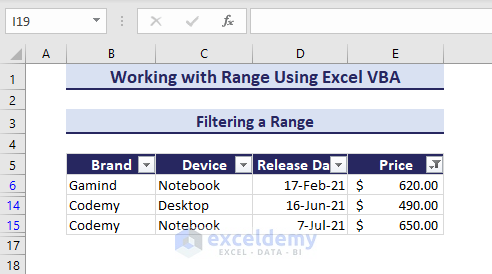
Filtering a Range Using Auto Filter
The AutoFilter method in the Range object can filter data based on criteria. In the below dataset, we will filter the range B5:E16 when the values of range E6:E16 are less than 800.
The following VBA code uses the .AutoFilter method to filter.
Sub FilteringRange()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("B5:E16").AutoFilter Field:=4, Criteria1:="<800"
End SubRunning the code gets us the filtered range based on the specified conditions.
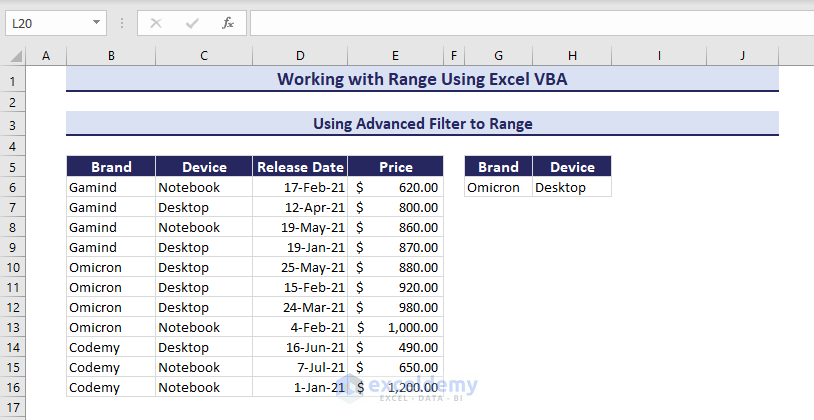
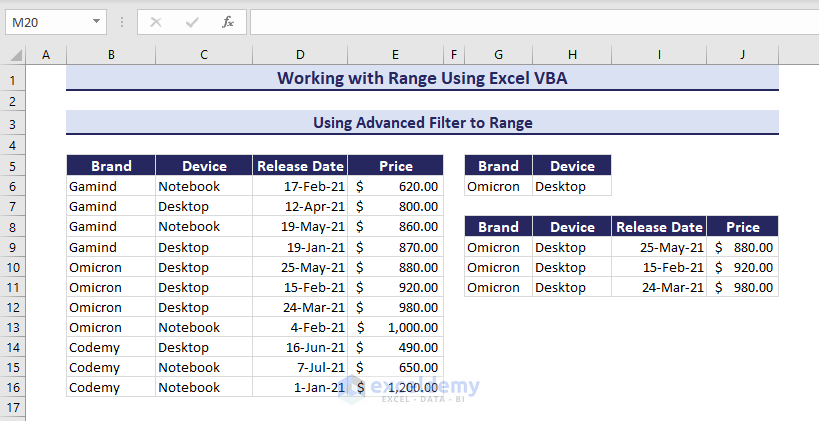
Using Advanced Filter Method
You can also use an auto filter and Advanced filter in VBA to filter range B5:E16 based on the criteria in range G5:H6. The Advanced Filter method copies the filtered range and pastes it to a specified location.
- Use the VBA code with the .AdvancedFilter method and run it.
Sub UsingAdvancedFiltertoRange()
' Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("B5:E16").AdvancedFilter _
Action:=xlFilterCopy, _
CriteriaRange:=Range("G5:H6"), _
CopyToRange:=Range("G8")
End SubThe filtered range appears after running the code.
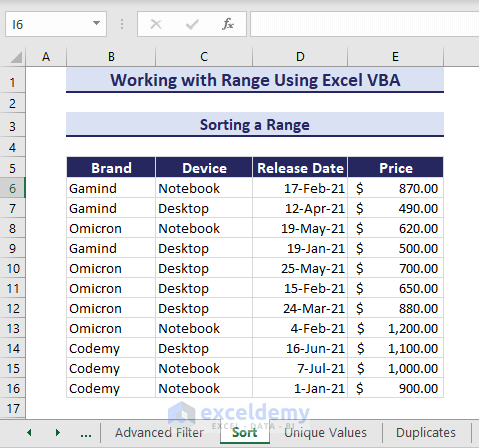
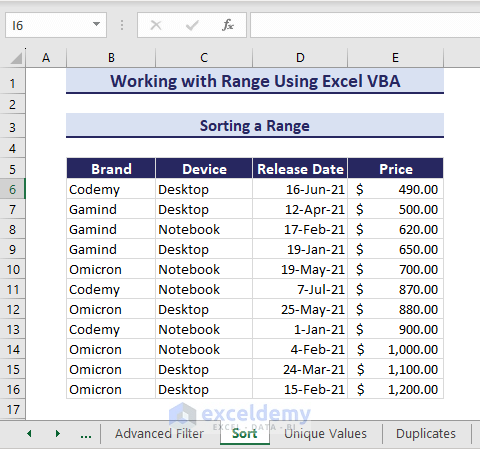
Sorting a Range
In the given dataset, we will sort range using VBA based on the range E6:E16 in ascending order.
- Use the given VBA code and run it.
Sub SortRange()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Dim rngToSort As Range
Set rngToSort = Range("B5:E16")
rngToSort.Sort key1:=rngToSort.Columns(4), _
order1:=xlAscending, _
Header:=xlYes
End SubThus, we get the sorted range based on the prices.
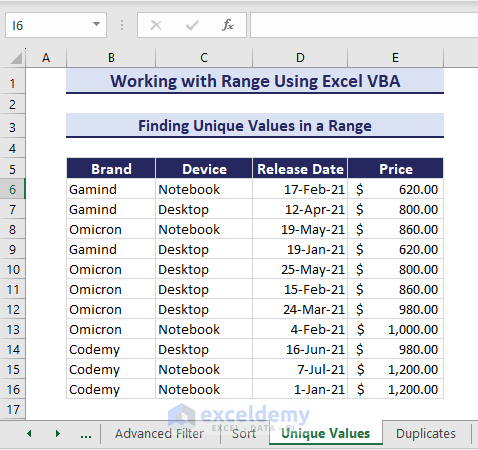
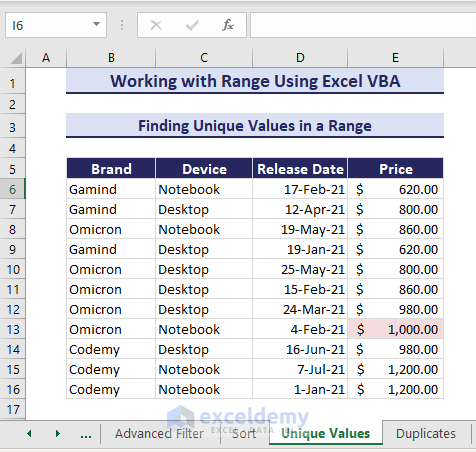
Finding Unique Values in a Range
In the given example, let’s highlight the unique values from range E6:E16 using the Range object.
Here is the VBA code to highlight the unique value of the range:
Sub FindUniqueValues()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Dim rng As Range
Dim cell As Range
Set rng = Range("E6:E16")
rng.Interior.ColorIndex = xlNone
For Each cell In rng
If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountIf(rng, cell.Value) = 1 Then
cell.Interior.Color = RGB(245, 220, 220)
End If
Next cell
End SubAfter running the code, it will highlight the unique value.
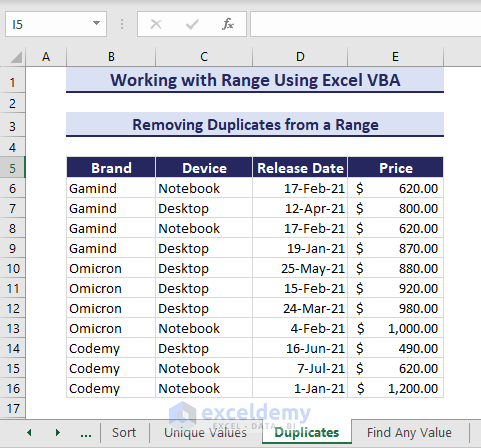
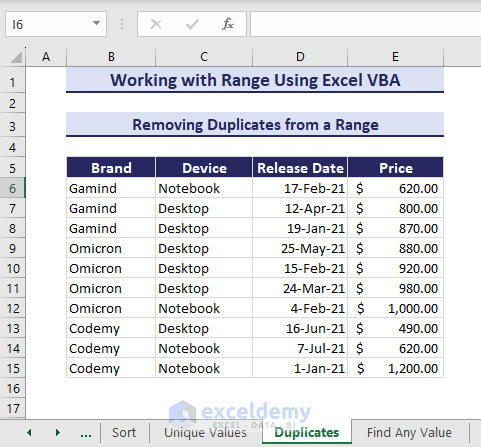
Removing Duplicates from a Range
Now, you will use a RemoveDuplicates method to remove duplicates in Excel VBA. See the below range E6:E16 that has duplicate values 620.
- Use the VBA code and run.
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
ActiveSheet.Range("B6:E16").RemoveDuplicates Columns:=Array(1, 2, 3, 4), Header:=xlNo
End SubAs you can see, there was one duplicate value and its entire row disappeared.
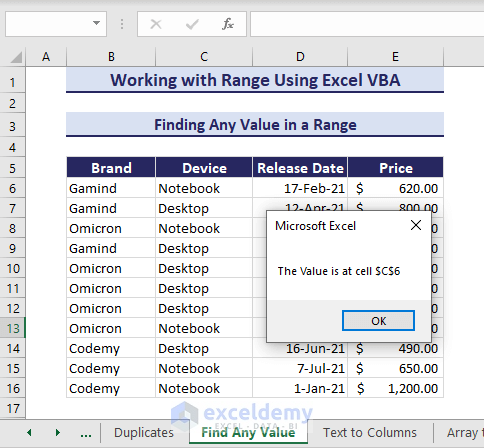
Finding Any Value in a Range
Now, you will search for “Notebook” in range B6:E16 using the Find Method in Excel VBA Range Object. The Find method searches any specified value and returns a message box showing its location if found. If there are multiple locations, the method will return the first location only. Use the following VBA to search:
Sub FindAnyValue()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Dim searchValue As Variant
Dim searchRange As Range
Dim foundCell As Range
searchValue = "Notebook"
Set searchRange = Range("B6:E16")
Set foundCell = searchRange.Find(What:=searchValue, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)
If Not foundCell Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "The Value is at cell " & foundCell.Address
Else
MsgBox "Value not found in the specified range."
End If
End SubThe code finds the value in C6.
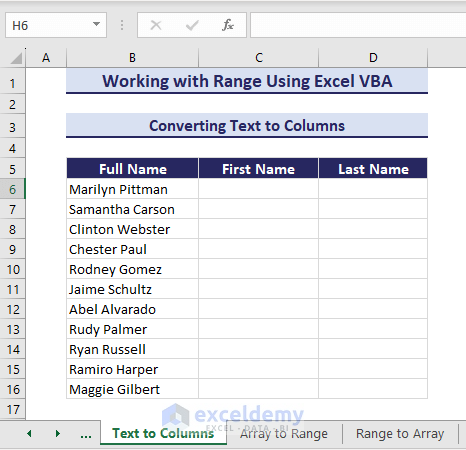
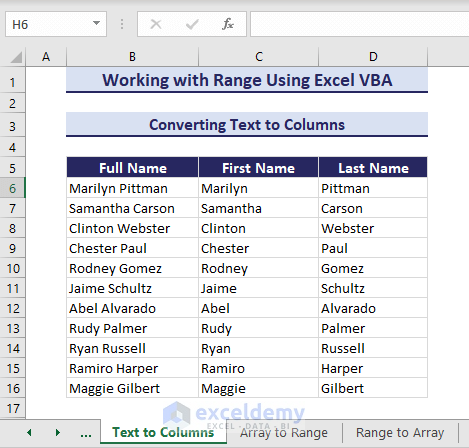
Converting Text to Columns
For data visualization, you might need to convert text to columns in VBA. See the below dataset where there is a list of full names in the range B6:B16. We will divide the full names into first and last names in separate columns using the TextToColumns method.
- The VBA code divides the names and places them in columns C & D:
Sub ConvertTextToColumns()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Range("B6:B16")
rng.TextToColumns Destination:=Range("C6"), _
DataType:=xlDelimited, _
TextQualifier:=xlTextQualifierNone, _
Tab:=False, _
Semicolon:=False, _
Comma:=False, _
Space:=True, _
Other:=False, _
FieldInfo:=Array(Array(1, 1), Array(2, 1)), _
DecimalSeparator:=".", _
ThousandsSeparator:=",", _
TrailingMinusNumbers:=True
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End SubRunning the code converts the text into columns and returns the first and last names.
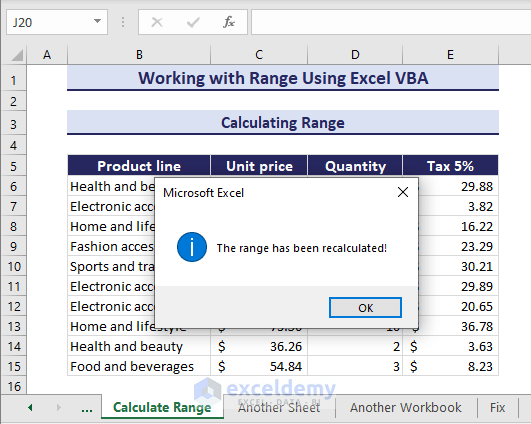
Calculating Range
Lastly, you can calculate a range in VBA using the Calculate method in VBA. The Calculate method allows you to compute values across all open workbooks, specific workbooks, or targeted worksheets, ranges, columns, or rows. If you have a formula range the Calculate method can recalculate or refresh that particular range. The following VBA recalculates the range.
Sub CalculateRange()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Range("E6:E15").Calculate
MsgBox "The range has been recalculated!", vbInformation
End SubAfter running the code, the specified range will be recalculated.
How to Convert Array to Range or Range to Array Using VBA in Excel
In this section, you will convert an array to range and range to an array using the Range object in Excel VBA.
1. Convert Array to Range
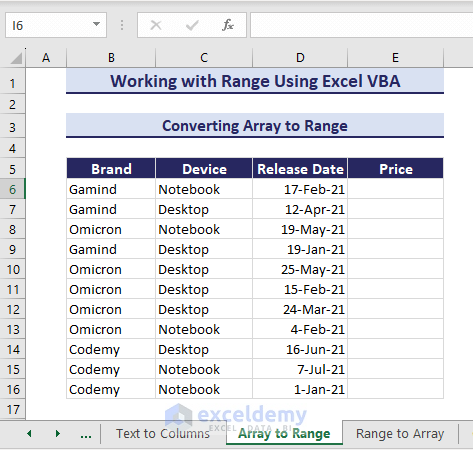
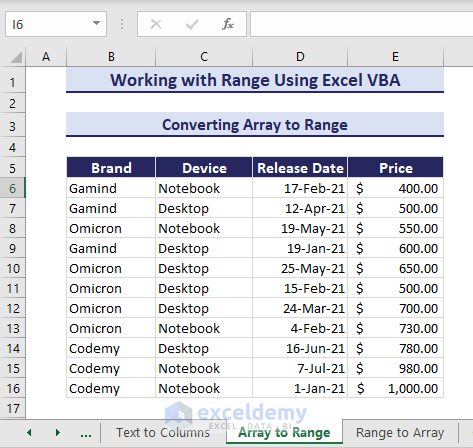
If you have an array, you can insert it in the VBA code and place it in range E6:E16 of the given dataset.
The VBA code uses the Range object to specify the range and uses the range to hold the array.
Sub ConvertArrayToRange()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Dim myArray As Variant
Dim myRange As Range
myArray = Array(400, 500, 550, 600, 650, 500, 700, 730, 780, 980, 1000)
Set myRange = Range("E6").Resize(UBound(myArray) + 1, 1)
myRange.Value = Application.Transpose(myArray)
End SubHence, you find the array stored in the specified range.
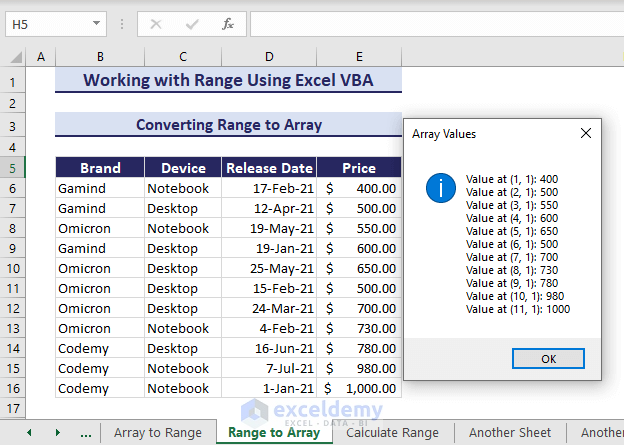
2. Convert Range to Array
Alternatively, you can use the same range and convert them into arrays using the Range object. The below VBA code will do the task using a message box.
Sub ConvertRangeToArray()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Dim myRange As Range
Dim dataArray As Variant
Dim i As Long, j As Long
Dim resultString As String
Set myRange = Range("E6:E16")
dataArray = myRange.Value
For i = LBound(dataArray, 1) To UBound(dataArray, 1)
For j = LBound(dataArray, 2) To UBound(dataArray, 2)
resultString = resultString & "Value at (" & i & ", " & j & "): " & dataArray(i, j) & vbCrLf
Next j
Next i
MsgBox resultString, vbInformation, "Array Values"
End SubThe above procedure returns a message box showing the array in the message box.
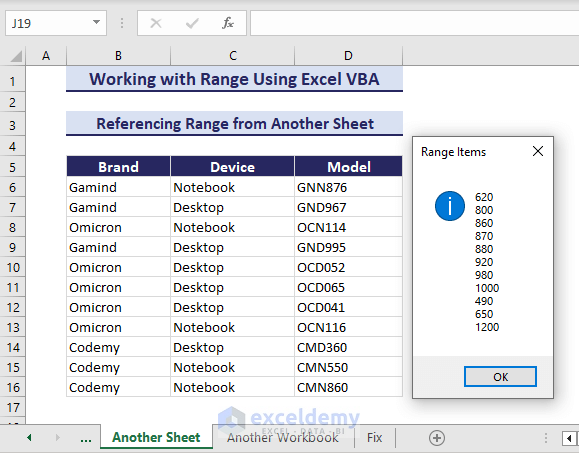
How to Reference Range from Another Sheet with Excel VBA
To reference a range from another sheet, use the Range object to specify the range in VBA. Here is the VBA code for referring to a range E6:E16 from the Calculate Range sheet.
Sub ReferRangefromAnotherSheet()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Dim myRange As Range
Set myRange = Worksheets("Calculate Range").Range("E6:E16")
Dim rangeValues As Variant
rangeValues = myRange.Value
Dim resultString As String
Dim i As Long, j As Long
For i = LBound(rangeValues, 1) To UBound(rangeValues, 1)
For j = LBound(rangeValues, 2) To UBound(rangeValues, 2)
resultString = resultString & rangeValues(i, j) & vbTab
Next j
resultString = resultString & vbCrLf
Next i
MsgBox resultString, vbInformation, "Range Items"
End SubAfter running the code, you will get a message box displaying the specified range from the specified worksheet.
Read More: How to Use Excel VBA to Copy Range to Another Excel Sheet
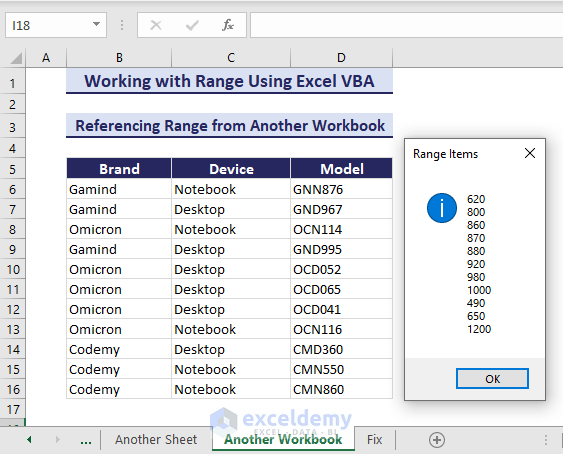
How to Reference Range from Another Workbook with Excel VBA
Similarly, the below procedure will specify a range from another workbook using the Range object in Excel VBA.
- Specify your file location in the VBA code and run it.
Sub ReferRangeFromAnotherWorkbook()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
Dim otherWorkbook As Workbook
Dim myRange As Range
Dim otherWorkbookPath As String
otherWorkbookPath = "C:\Users\YOUSUF\Desktop\Target File.xlsm"
Set otherWorkbook = Workbooks.Open(otherWorkbookPath)
Set myRange = otherWorkbook.Worksheets("Calculate Range").Range("E6:E16")
Dim rangeValues As Variant
rangeValues = myRange.Value
Dim resultString As String
Dim i As Long, j As Long
For i = LBound(rangeValues, 1) To UBound(rangeValues, 1)
For j = LBound(rangeValues, 2) To UBound(rangeValues, 2)
resultString = resultString & rangeValues(i, j) & vbTab
Next j
resultString = resultString & vbCrLf
Next i
otherWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=False
MsgBox resultString, vbInformation, "Range Items"
End SubIn this way, you can access a range of other workbooks.
What to Do When Macro Returns Subscript Out of Range Error in Excel VBA?
The Subscript Out of Range error can occur for mainly these reasons:
- Trying to access a cell beyond the range’s actual size.
- Using properties or methods of a non-existent Range object.
- Accidentally deleting definitions in a Named Range.
- The defined worksheet in VBA isn’t open or accessible on the user’s computer
- The worksheet or the range is nonexistent
- The provided worksheet name doesn’t match the actual name of the desired sheet, etc.
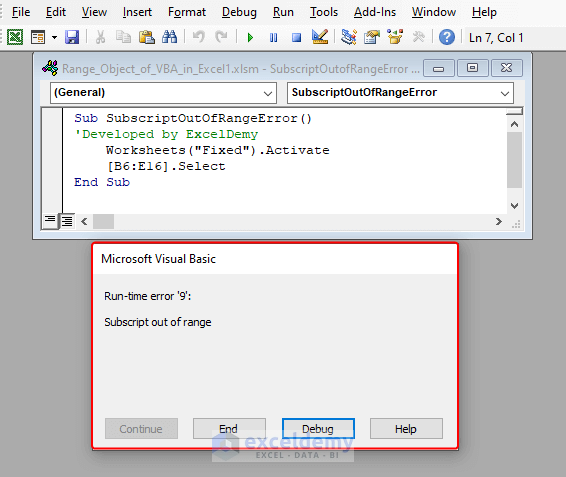
In the below scenario, the Range object could not find any range named Fixed. As a result, it shows the Run-time error ‘9’: Subscript out of range error.
To fix the situation, the most proper way is to put the correct sheet name in the code. You can add an error handler to avoid this error like the VBA code below.
Sub FixSubscriptOutOfRangeError()
'Developed by ExcelDemy
On Error Resume Next
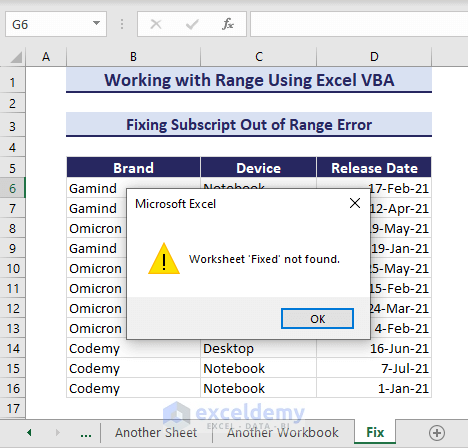
Worksheets("Fixed").Activate
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
MsgBox "Worksheet 'Fixed' not found.", vbExclamation
Err.Clear
Exit Sub
End If
On Error Resume Next
Range("E6:E16").Select
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
MsgBox "Range [E6:E16] not found on the 'Fixed' worksheet.", vbExclamation
Err.Clear
Exit Sub
End If
On Error GoTo 0
End SubRunning the code returns an error message box saying the worksheet is not found.
Download Practice Workbook
This has been a guide to working with Range using Excel VBA. It has covered how to set a range using Range object and manipulate range value using VBA methods and properties with practical examples. It has also shown possible range errors and how to handle them. Hopefully, you are now able to use the experience you have gained here and implement it in your VBA programming. Thanks for your read!
Related Readings
- How to Count Text in Excel
- End of a Range Using VBA in Excel
- Excel Subscript Out of Range Error in VBA
- VBA Range with Variable Row Number in Excel
- How to Use the UsedRange Property of VBA in Excel