This is an overview:
Sub Range_with_Variable_Row_Number()
First_Cell = InputBox("Enter the First Cell of the Range: ")
Row_Number = Str(Range(First_Cell).Row)
Number_of_Rows = InputBox("Enter the Total Number of Rows of the Range: ")
Set Rng = Range(First_Cell & ":" & Mid(First_Cell, 1, Len(First_Cell) - Len(Row_Number) + 1) & Mid(Str(Int(Number_of_Rows) + Int(Row_Number) - 1), 2, 10))
End Sub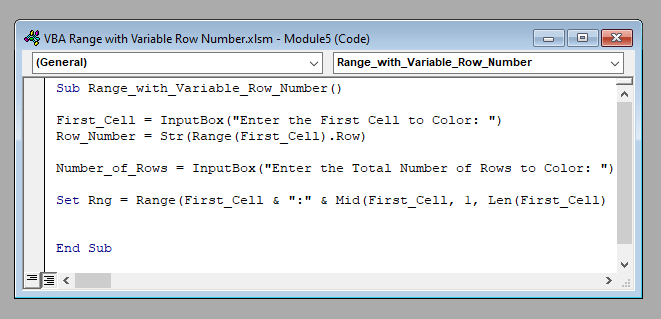
Code Breakdown
- The code takes two inputs, the first cell in the range, called First_Cell, and the total number of variable rows in the range, called Number_of_Rows.
- It creates a range of rows called Rng, starting from the First_Cell up to the total number of rows.
- If your First_Cell is B4 and the Number_of_Rows is 10, the output Rng is B4:B13.
- Use the relative cell reference of the First_Cell, not the absolute or the mixed cell reference (Use B4, not $B$4 or $B4).
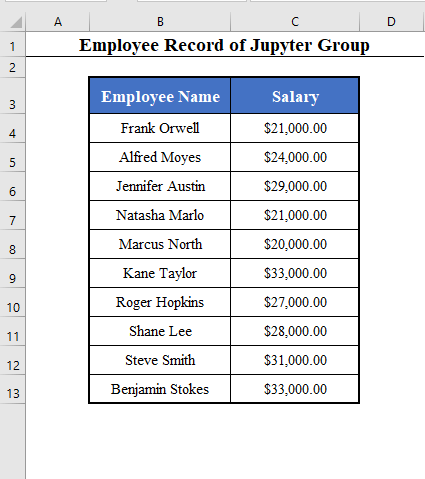
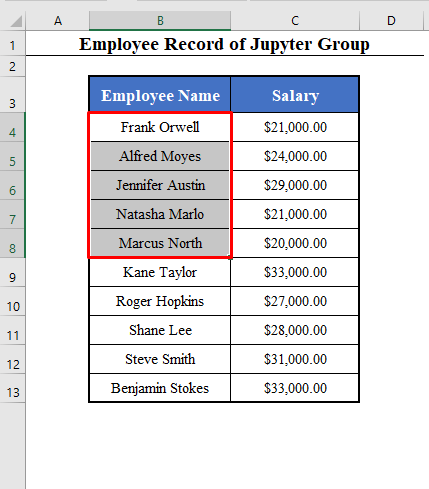
The dataset contains employees’ Names and Salaries.
Example 1 – Select a Range with a Variable Row Number with VBA
- Select the names of the 1st 5 employees.
- Use the following VBA code:
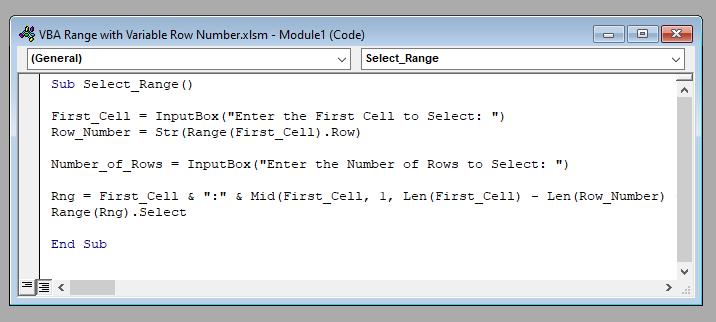
Sub Select_Range()
First_Cell = InputBox("Enter the First Cell to Select: ")
Row_Number = Str(Range(First_Cell).Row)
Number_of_Rows = InputBox("Enter the Number of Rows to Select: ")
Rng = First_Cell & ":" & Mid(First_Cell, 1, Len(First_Cell) - Len(Row_Number) + 1) & Mid(Str(Int(Number_of_Rows) + Int(Row_Number) - 1), 2, 10)
Range(Rng).Select
End SubOutput:
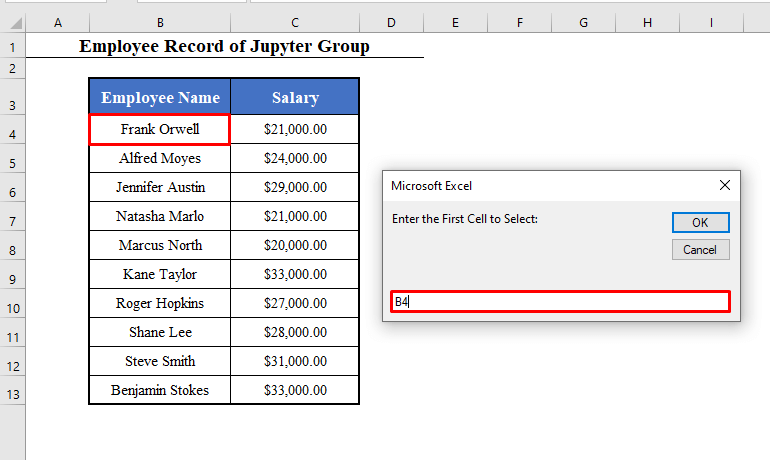
- Run the Macro (Select_Range). You’ll get two input boxes.
- The first box will ask you to enter the first cell of the range you want to select. Here, B4, the cell with the first employee.
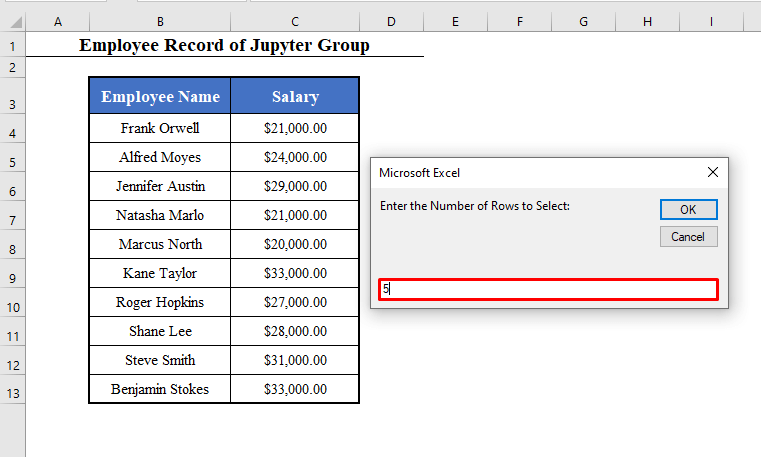
- Click OK. The second Input box will ask you the number of rows you want to select. Here, 5.
- Again, click OK. And you’ll get the names of the first 5 employees selected in your dataset.
Example 2 – Insert Numbers into a Range with a Variable Row Number in Excel
- Number the 1st 5 employees from 1 to 5.
- Use the following VBA code:
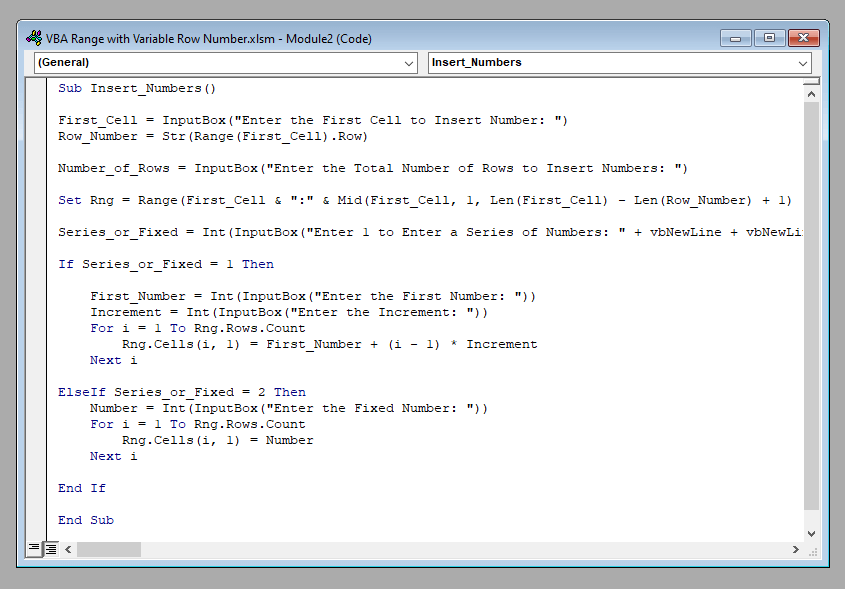
Sub Insert_Numbers()
First_Cell = InputBox("Enter the First Cell to Insert Number: ")
Row_Number = Str(Range(First_Cell).Row)
Number_of_Rows = InputBox("Enter the Total Number of Rows to Insert Numbers: ")
Set Rng = Range(First_Cell & ":" & Mid(First_Cell, 1, Len(First_Cell) - Len(Row_Number) + 1) & Mid(Str(Int(Number_of_Rows) + Int(Row_Number) - 1), 2, 10))
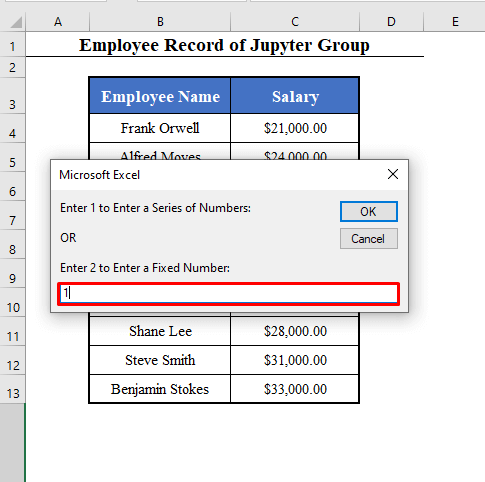
Series_or_Fixed = Int(InputBox("Enter 1 to Enter a Series of Numbers: " + vbNewLine + vbNewLine + "OR" + vbNewLine + vbNewLine + "Enter 2 to Enter a Fixed Number: "))
If Series_or_Fixed = 1 Then
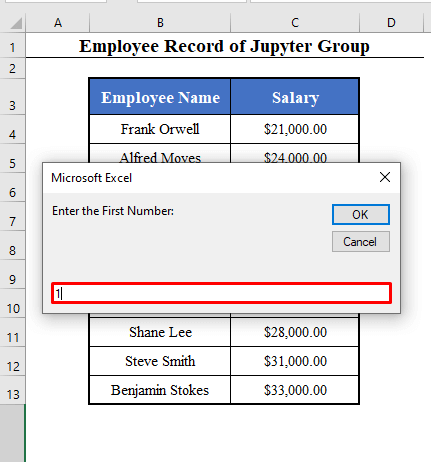
First_Number = Int(InputBox("Enter the First Number: "))
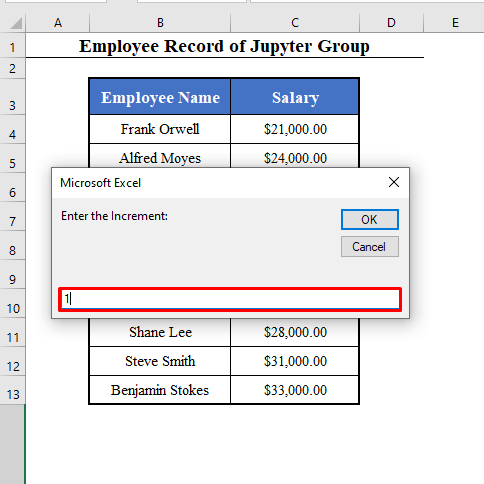
Increment = Int(InputBox("Enter the Increment: "))
For i = 1 To Rng.Rows.Count
Rng.Cells(i, 1) = First_Number + (i - 1) * Increment
Next i
ElseIf Series_or_Fixed = 2 Then
Number = Int(InputBox("Enter the Fixed Number: "))
For i = 1 To Rng.Rows.Count
Rng.Cells(i, 1) = Number
Next i
End If
End SubOutput:
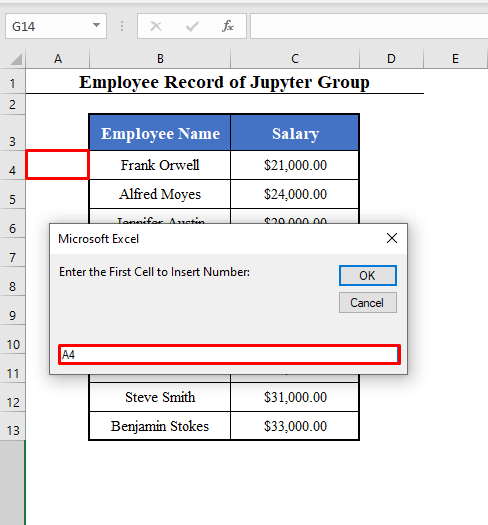
- Run the Macro (Insert_Numbers). You’ll see Input boxes.
- The 1st box will ask you to enter the first cell to insert the numbers. Here, A4.
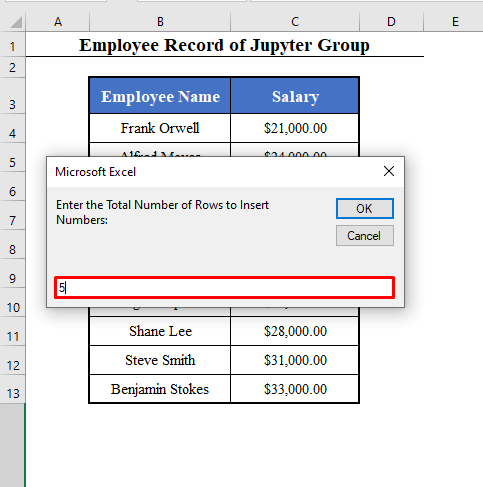
- Click OK. The 2nd box will ask you to enter the total number of rows to insert numbers. Here, 5.
- The 3rd box will ask you whether you want a series of numbers or a fixed number:
Enter 1 for a series of numbers.
Enter 2 for a fixed number.
- Here, a series of numbers.
- The 4th box will ask you the first number of the series: 1.
- The final box will ask you to enter the increment. In a series of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, it’s 1.
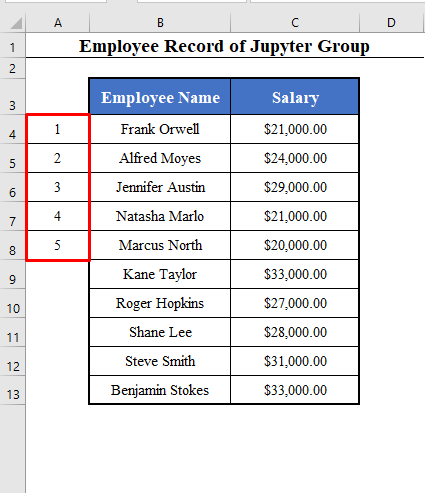
- Click OK. And you’ll get a series of 1 to 5 in A4:A8.
Example 3 – Perform a Mathematical Operation on a Range with a Variable Row Number in Excel
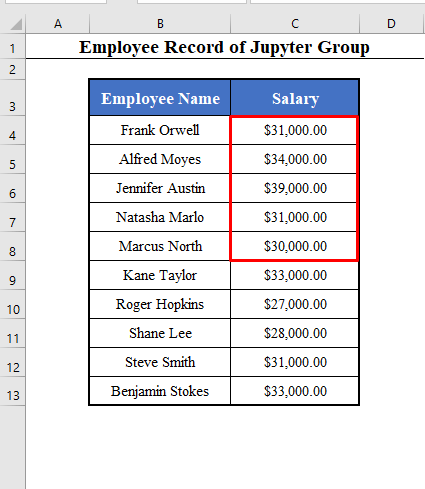
The salaries of the first 5 employees will be increased by $10,000.
Use the following VBA code:
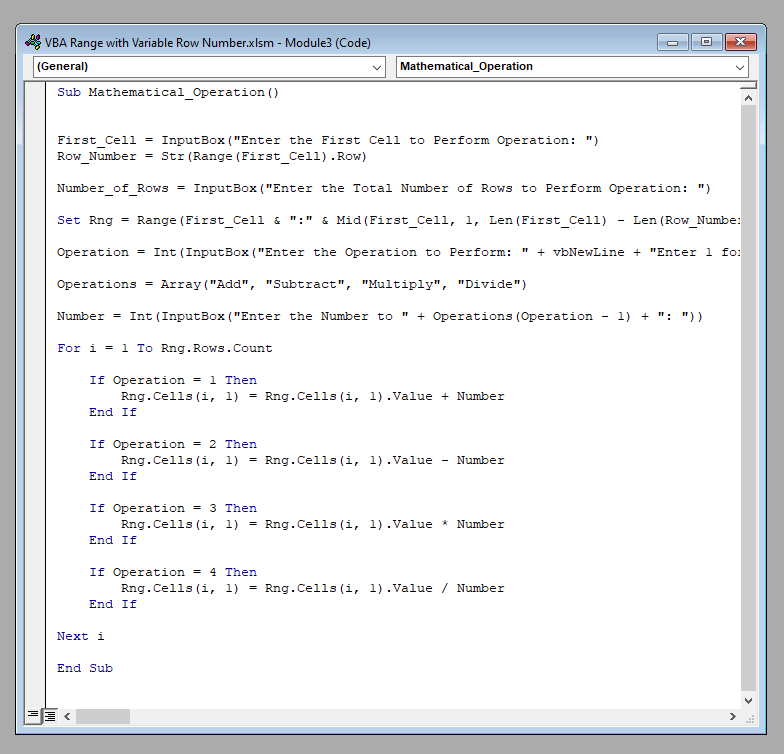
Sub Mathematical_Operation()
First_Cell = InputBox("Enter the First Cell to Perform Operation: ")
Row_Number = Str(Range(First_Cell).Row)
Number_of_Rows = InputBox("Enter the Total Number of Rows to Perform Operation: ")
Set Rng = Range(First_Cell & ":" & Mid(First_Cell, 1, Len(First_Cell) - Len(Row_Number) + 1) & Mid(Str(Int(Number_of_Rows) + Int(Row_Number) - 1), 2, 10))
Operation = Int(InputBox("Enter the Operation to Perform: " + vbNewLine + "Enter 1 for Addition: " + vbNewLine + "Enter 2 for Subtraction: " + vbNewLine + "Enter 3 for Multiplication: " + vbNewLine + "Enter 4 for Division: "))
Operations = Array("Add", "Subtract", "Multiply", "Divide")
Number = Int(InputBox("Enter the Number to " + Operations(Operation - 1) + ": "))
For i = 1 To Rng.Rows.Count
If Operation = 1 Then
Rng.Cells(i, 1) = Rng.Cells(i, 1).Value + Number
End If
If Operation = 2 Then
Rng.Cells(i, 1) = Rng.Cells(i, 1).Value - Number
End If
If Operation = 3 Then
Rng.Cells(i, 1) = Rng.Cells(i, 1).Value * Number
End If
If Operation = 4 Then
Rng.Cells(i, 1) = Rng.Cells(i, 1).Value / Number
End If
Next i
End SubOutput:
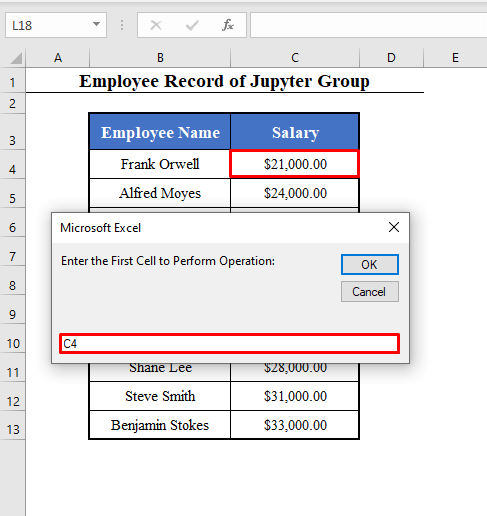
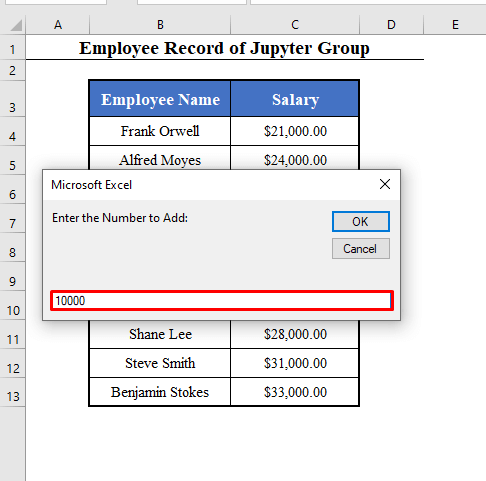
- Run the Macro (Mathematical_Operation). You’ll get 4 Input boxes.
- The 1st box will ask you to enter the first cell to perform the operation. Here, the salary of the 1st employee in C4.
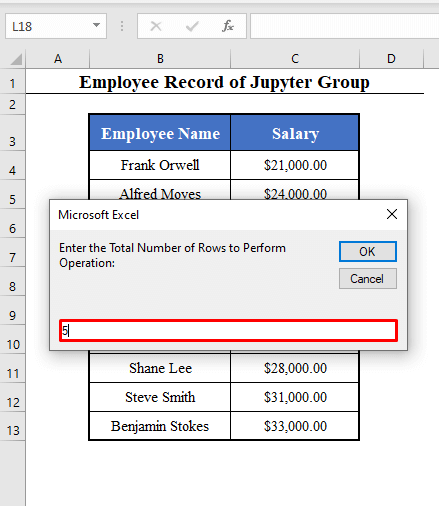
- The 2nd box will ask you the total number of rows to perform the operation.
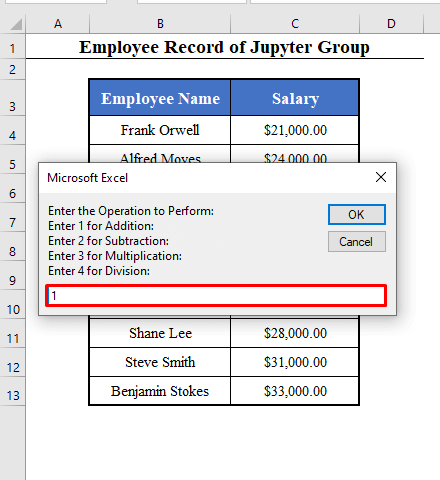
- The 3rd box will ask you to enter the operation you want to perform.
Enter 1 for addition.
Enter 2 for subtraction.
3 for Multiplication.
And 4 for a Division.
- Here, an addition.
- The 4th box will ask you to enter the number to add. Here, 10000.
- Click OK. And you will find the salaries of the first 5 employees increased by $10,000.
Read More: Excel VBA: Set Range by Row and Column Number
Example 4 – Color Cells of a Range with a Variable Row Number in Excel
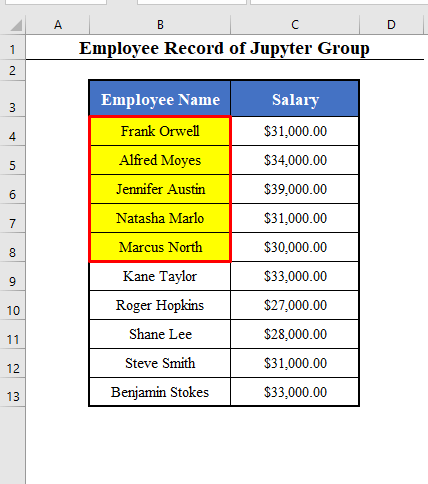
Color the names of the 1st five employees.
Use the following VBA code:
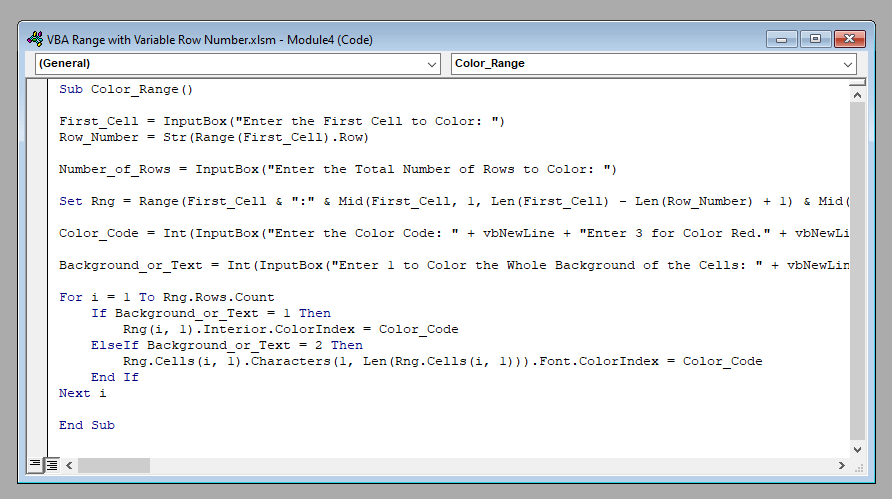
Sub Color_Range()
First_Cell = InputBox("Enter the First Cell to Color: ")
Row_Number = Str(Range(First_Cell).Row)
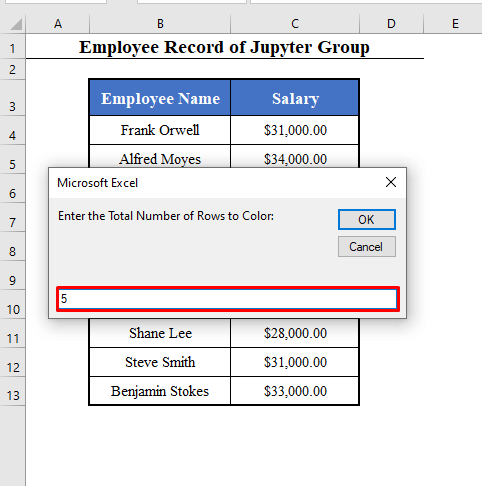
Number_of_Rows = InputBox("Enter the Total Number of Rows to Color: ")
Set Rng = Range(First_Cell & ":" & Mid(First_Cell, 1, Len(First_Cell) - Len(Row_Number) + 1) & Mid(Str(Int(Number_of_Rows) + Int(Row_Number) - 1), 2, 10))
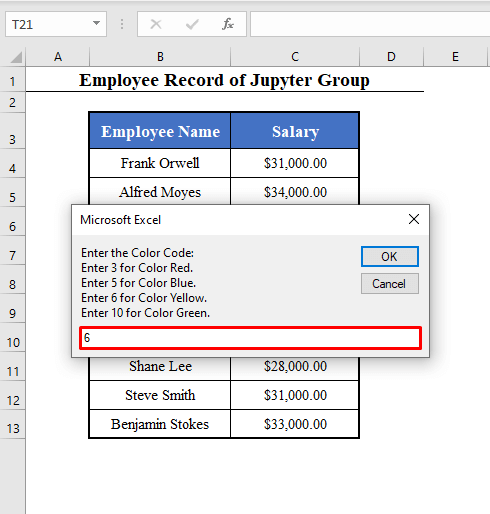
Color_Code = Int(InputBox("Enter the Color Code: " + vbNewLine + "Enter 3 for Color Red." + vbNewLine + "Enter 5 for Color Blue." + vbNewLine + "Enter 6 for Color Yellow." + vbNewLine + "Enter 10 for Color Green."))
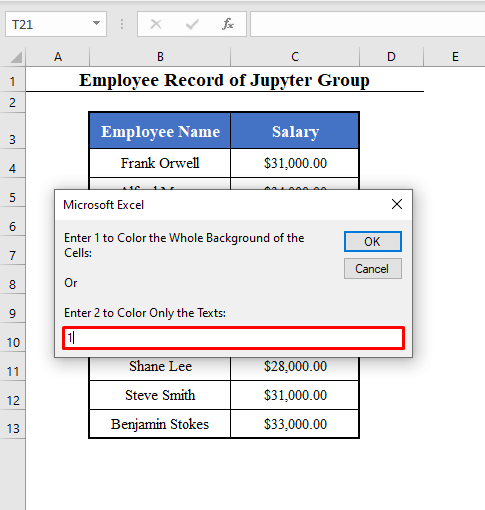
Background_or_Text = Int(InputBox("Enter 1 to Color the Whole Background of the Cells: " + vbNewLine + vbNewLine + "Or" + vbNewLine + vbNewLine + "Enter 2 to Color Only the Texts: "))
For i = 1 To Rng.Rows.Count
If Background_or_Text = 1 Then
Rng(i, 1).Interior.ColorIndex = Color_Code
ElseIf Background_or_Text = 2 Then
Rng.Cells(i, 1).Characters(1, Len(Rng.Cells(i, 1))).Font.ColorIndex = Color_Code
End If
Next i
End SubOutput:
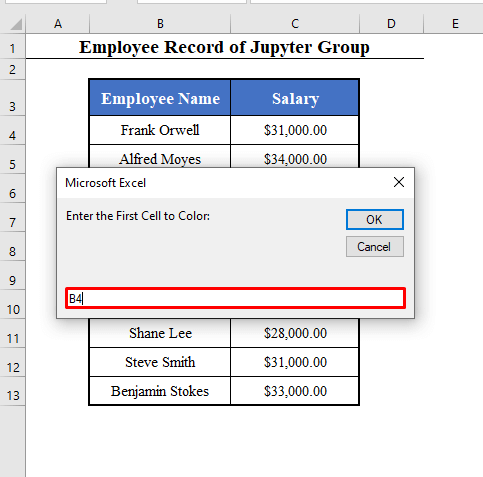
- Run the Macro (Color_Range). You’ll get 4 input boxes.
- The 1st box will ask you to enter the first cell to color. Here, the first employee, B4.
- The 2nd box will ask for the total number of rows to color: 5.
- The 3rd box will ask you to choose the color. Here, 6 – yellow.
- The final box will ask whether you want to color the whole background of the cells or the only text. Here, 1 (Whole background).
- Click OK. And you’ll get the whole background of the 1st 5 names highlighted in yellow.
Read More: How to Use Range with Variable Row and Column with Excel VBA
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- Excel VBA Range Function
- Excel VBA: Get Range of Cells with Values
- VBA to Set Range in Excel
- How to Use VBA to Set a Range Variable to Selection in Excel