Method 1 – Perform Interpolation of Linear 2D Data in Excel
1.1 Apply Mathematical Equation for Linear Interpolation
There is an established mathematical equation for linear equations we will use.
y= y1 + (x-x1)⨯(y2-y1)/(x2-x1)STEPS:
- Find out the coefficients of this equation.
- Place the values of x1, x2, y1, y2, and x in the Excel sheet.
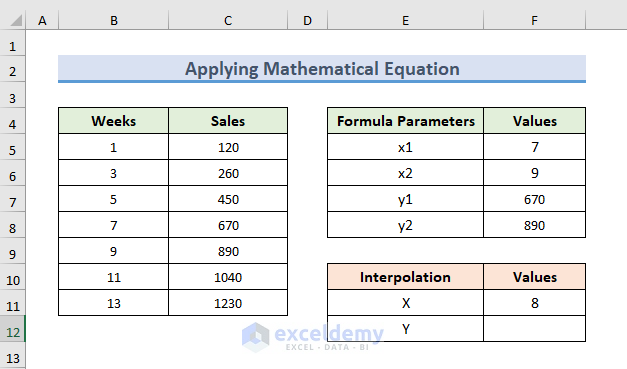
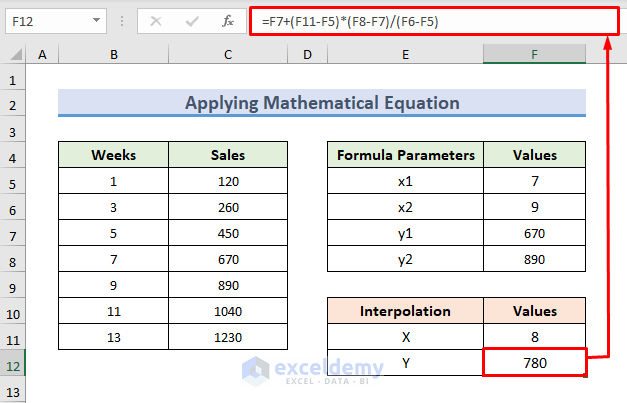
- Use the following formula in the F12 cell:
=F7+(F11-F5)*(F8-F7)/(F6-F5)- Press Enter to observe the interpolated result.
1.2 Interpolate Using a Trendline
STEPS:
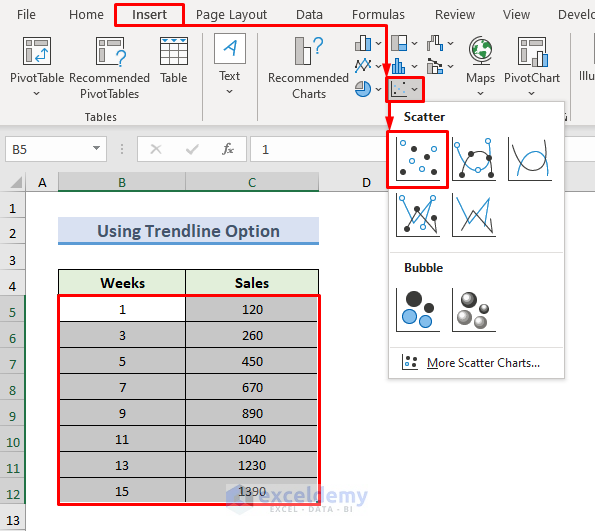
- Insert a plot from the dataset.
- Click on the Insert tab.
- Click on the drop-down menu of the Insert Scatter (X, Y) or Bubble Chart from the Charts group.
- A wizard will open.
- From the wizard, select the Scatter chart.
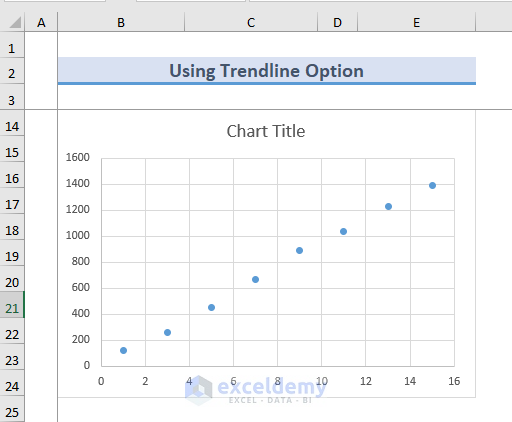
- The following chart is shown on the Excel Sheet.
- Click on the chart.
- You can see a plus (+) icon.
- Click on this icon and check Trendline.
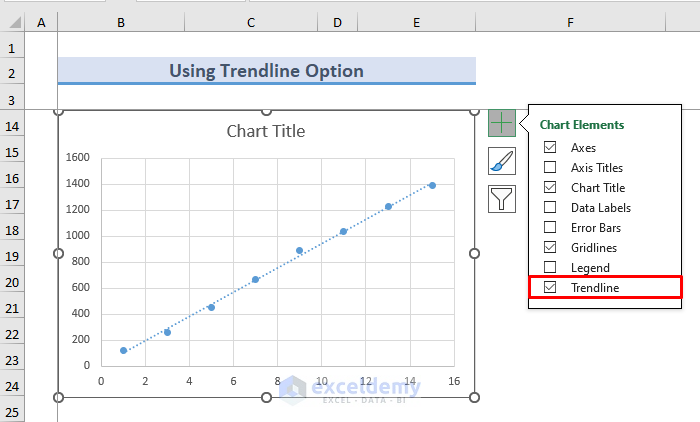
- A trendline can be seen on the chart.
- Double-click on the trendline.
- The Format Trendline window will appear on the right side of the Excel Sheet.
- Check Display Equation on the chart.
- You can see a floating equation.
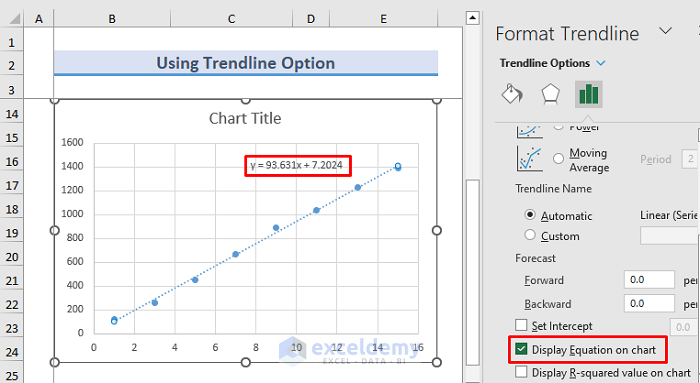
- Find the value of y from this equation.
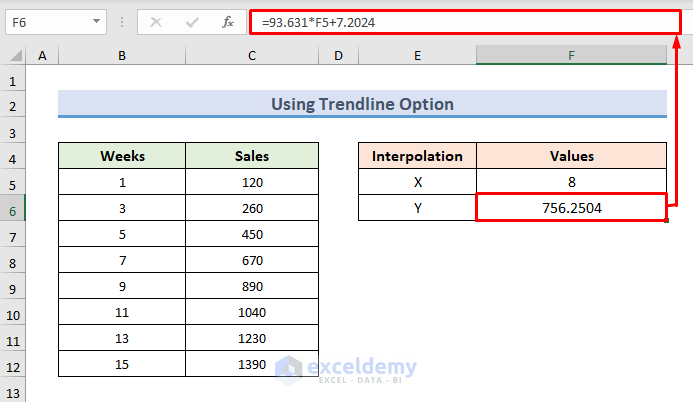
- Use the following formula in the F6 cell:
=93.631*F5+7.2024- Press Enter to observe the interpolated result of sales.
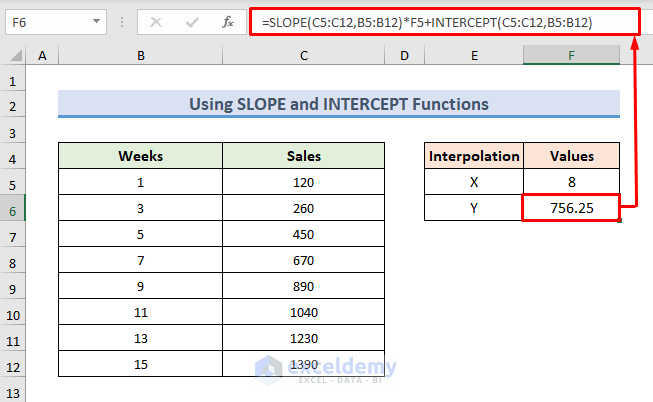
1.3 – Interpolate 2D Data Using SLOPE and INTERCEPT Functions
There is an established mathematical equation for linear equations.
y= mx+cSTEPS:
- Use the following formula in the F6 cell:
=SLOPE(C5:C12,B5:B12)*F5+INTERCEPT(C5:C12,B5:B12)- Press Enter to observe the interpolated result.
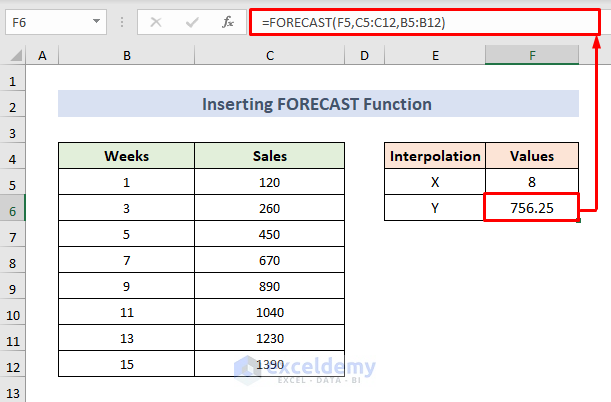
1.4 – Insert the FORECAST Function for Interpolation
STEPS:
- Use the following formula in the F6 cell:
=FORECAST(F5,C5:C12,B5:B12)- Press Enter to observe the interpolated result.
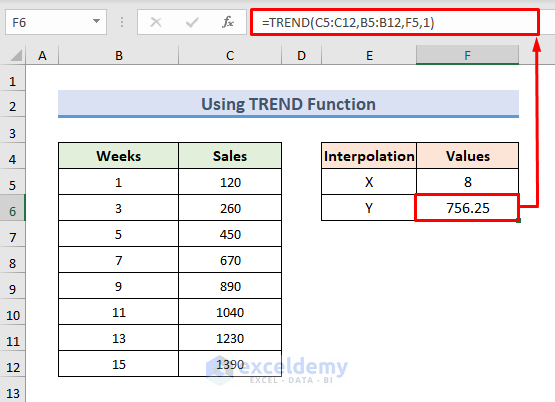
1.5 – Interpolation of 2D Data Using the TREND Function
STEPS:
- Use the following formula in the F6 cell:
=TREND(C5:C12,B5:B12,F5,1)- Press Enter to observe the interpolated result.
Method 2 – Perform Interpolation of Non-Linear 2D Data in Excel
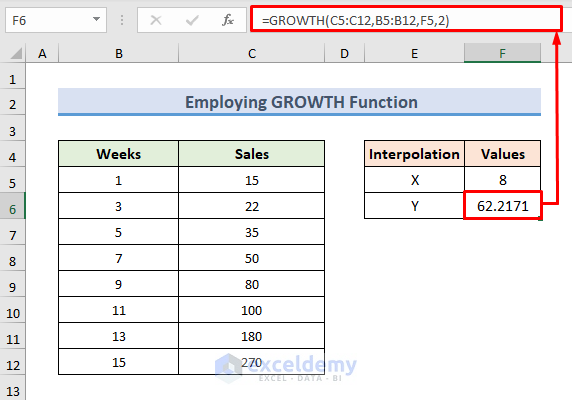
2.1 – Interpolation Using the GROWTH Function
STEPS:
- Use the following formula in the F6 cell:
=GROWTH(C5:C12,B5:B12,F5,2)- Press Enter to observe the interpolated result.
2.2 – Combine FORECAST, INDEX, and MATCH Functions for Non-Linear Interpolation
STEPS:
- Use the following formula in the F6 cell:
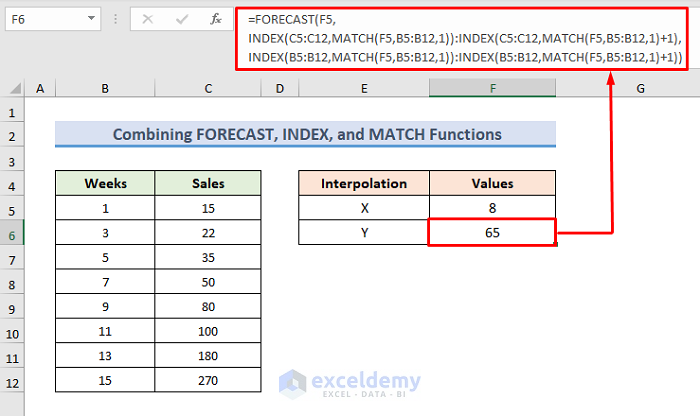
Download the Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- How to Calculate Logarithmic Interpolation in Excel
- 3D Interpolation in Excel
- How to Interpolate Time Series in Excel
- How to Perform Exponential Interpolation in Excel
- How to Do Polynomial Interpolation in Excel
- How to Apply Cubic Spline Interpolation in Excel
<< Go Back to Excel Interpolation | Excel for Statistics | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

