In this article, we will discuss the Excel Solver. We will go through some easy easy examples so that you thoroughly understand the topic.
The Solver is beneficial for various reasons. It helps to find optimal solutions for business problems; solve linear programming, nonlinear programming, and integer programming; define multiple constraints; and perform what-if analysis by quickly testing different scenarios and evaluating the outcomes.
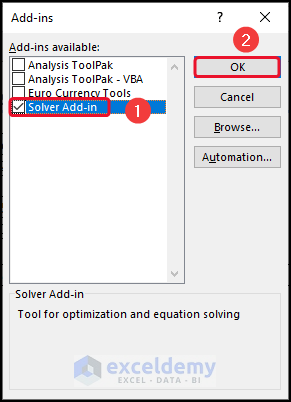
In the following overview image, you can see that we have enabled Solver Add-in. Now, let’s dive into the following article to explore more about this tool.]
Download Practice Workbook
What is an Excel Solver?
The Excel Solver is an add-in tool in Microsoft Excel that helps you find an optimal solution for complex problems involving mathematical equations and constraints. It is primarily used for optimization and solving linear programming problems.
Below we are describing definitions for the terms:
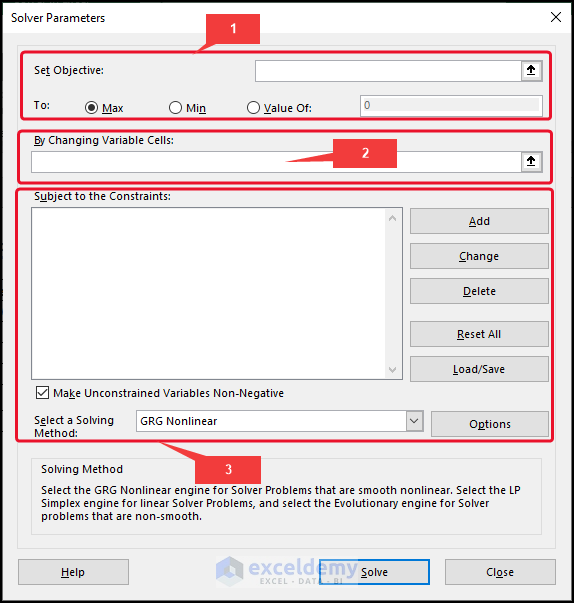
Objective Cell: It is simply a single cell with something like a formula in it. The constraint cells’ limitations are applied to the decision-based formula in the cell. The objective cell’s value can be decreased, increased, or fixed at the provided threshold.
Variable Cells: Variable cells are made up of variable data that the Solver modifies to accomplish the goal.
Constraint Cells: These are the constraints that the solution to the situation at hand must adhere to. On the other hand, these are the prerequisites that must be met.
How to Add Solver in Excel?
- To add Solver, go to the File tab >> select Options.
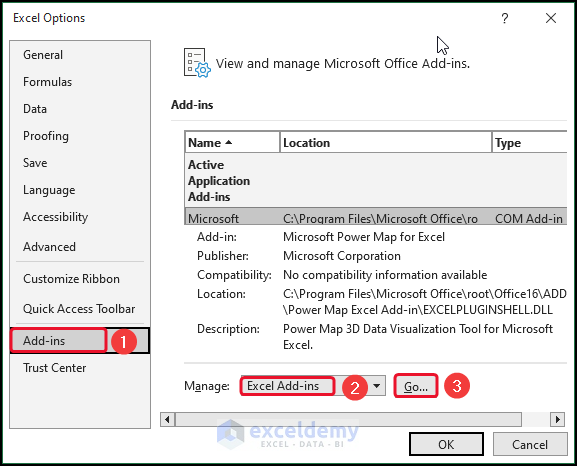
- From Add-ins >> select Excel Add-ins >> select Go.
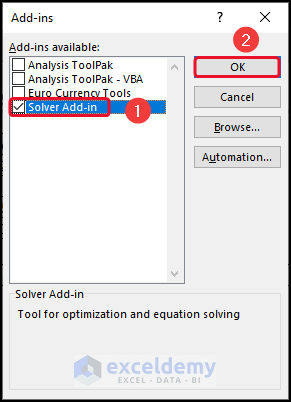
- Select Solver Add-in >> click OK.
Types of Solving Methods
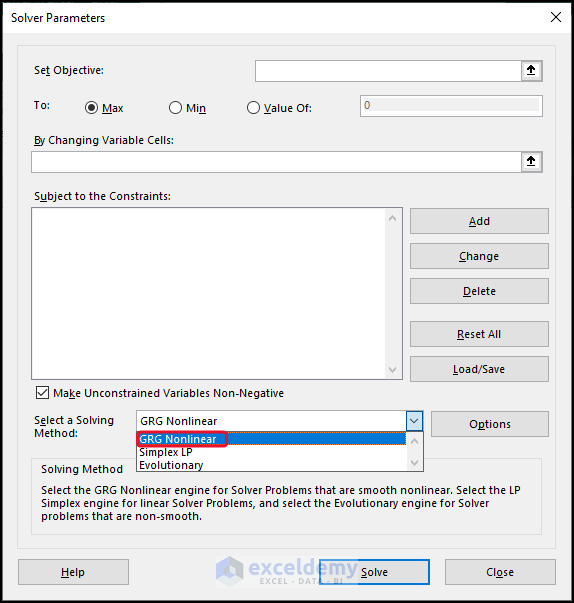
1. GRG Nonlinear
The acronym “GRG” stands for “Generalized Reduced Gradient Nonlinear.” This method is utilized to address nonlinear problems by optimizing their solutions.
Nonlinear problems can exhibit multiple feasible regions or a range of variable values that satisfy all the constraints.
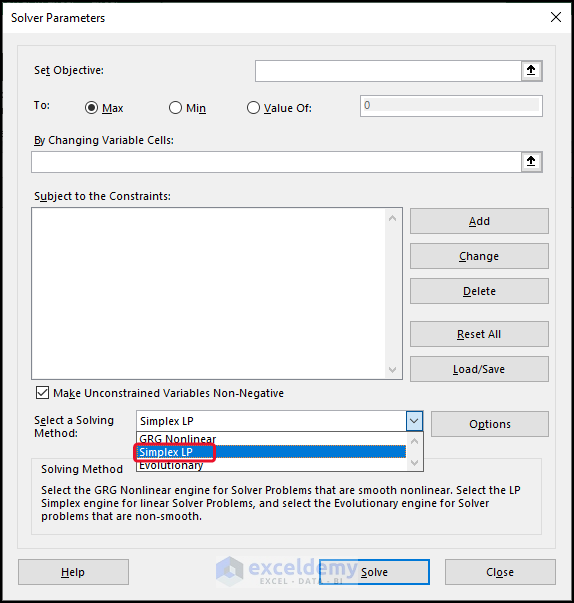
2. Simplex LP
The acronym “LP” stands for Linear Problems. This method assists in solving linear programming problems and is faster compared to the GRG nonlinear method.
In a linear programming problem, there is a need to maximize or minimize a single objective while considering specific conditions.
Both the simplex LP and GRG nonlinear methods are employed for smooth problems.
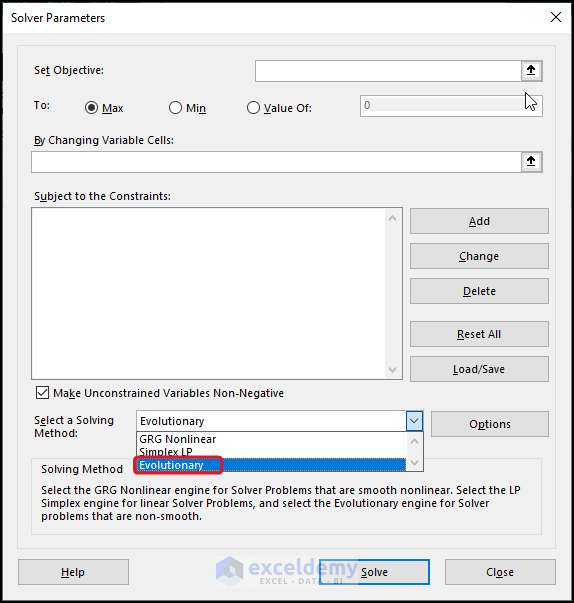
3. Evolutionary
This approach is useful for resolving problems with jagged patterns, which involve functions that have breaks. The jagged problems are the most difficult optimization models to tackle.
Different Examples of the Excel Solver
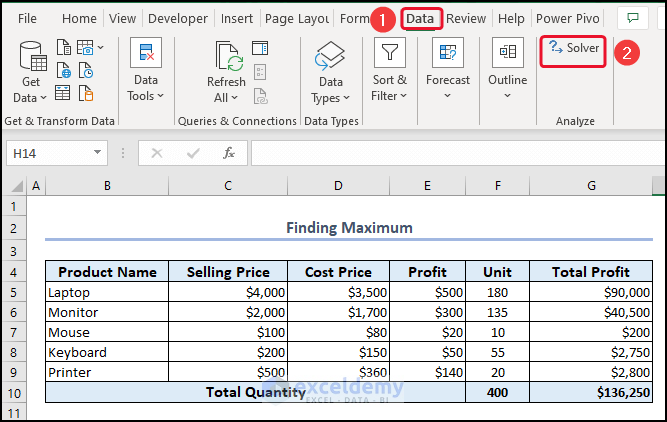
1. Finding Maximum (GRG Nonlinear)
- Go to the Data tab >> select Solver.
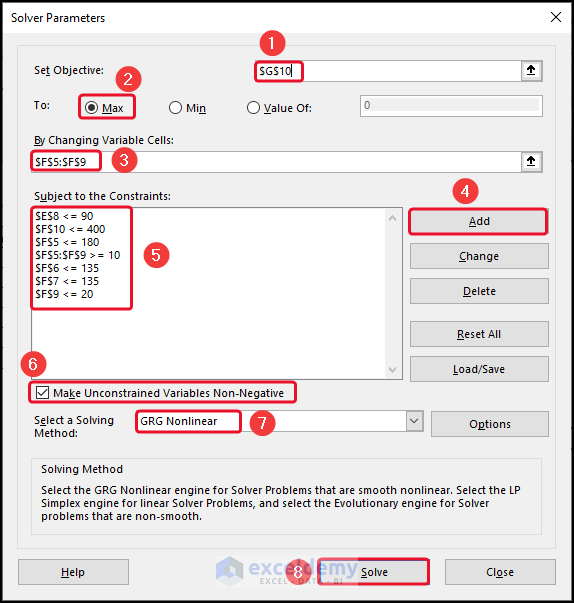
- In the Set Objective box, select cell G10 >> click on Max.
- Select cells F5:F9 in the By Changing Variables
- Click on Add >> give the Constraints.
- Click on Mark Unconstrained Variable Non-Negative >> select GRG Nonlinear.
- Click on Solve.
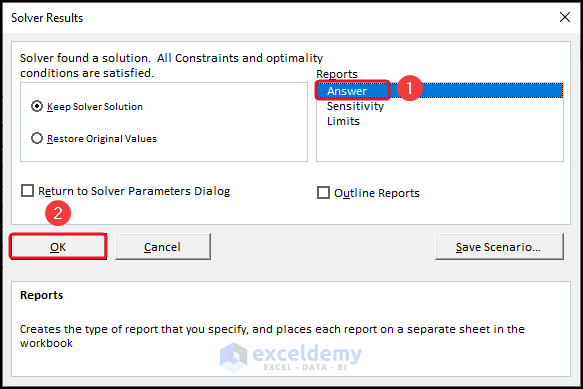
- In the Solver Result dialog box, select Answer >> click OK.
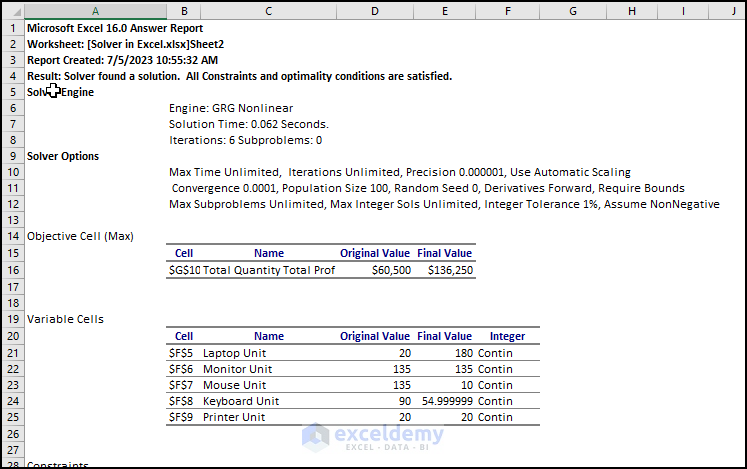
You can see the result in a different Excel sheet.
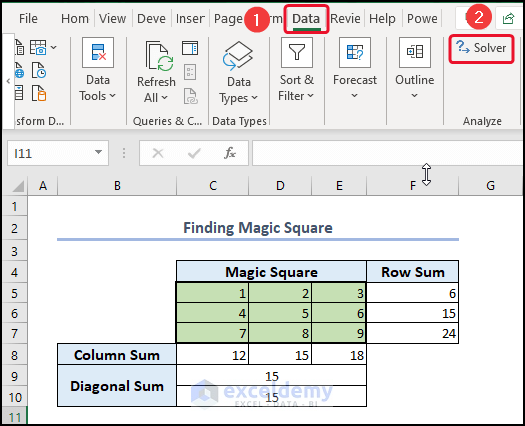
2. Finding Magic Square (GRG Nonlinear)
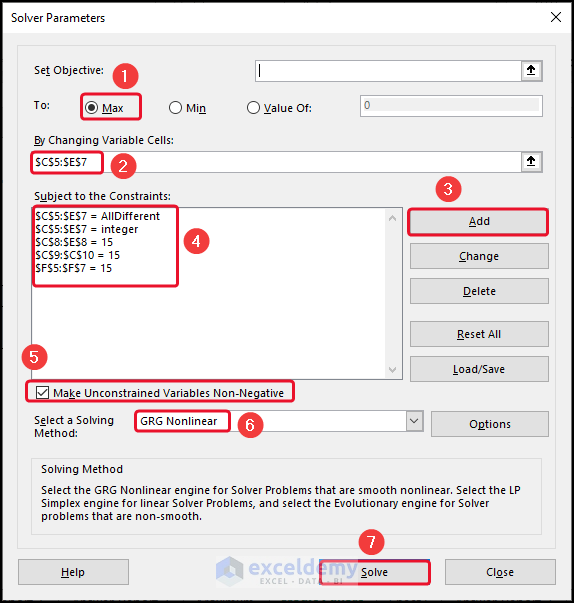
- To find a magic square, go to the Data tab >> select Solver.
- Keep the Set Objective box empty >> click on Max.
- Select cells C5:E7 in the By Changing Variables
- Click on Add >> give the Constraints.
- Click on Mark Unconstrained Variable Non-Negative >> select GRG Nonlinear.
- Click on Solve.
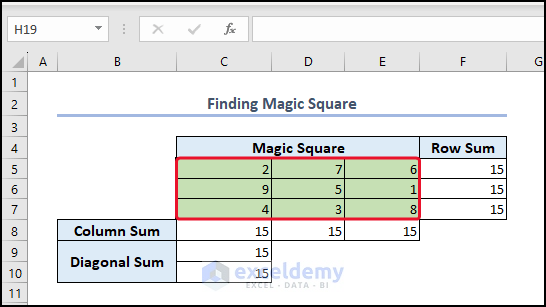
As a result, you can see the rearranged magic square.
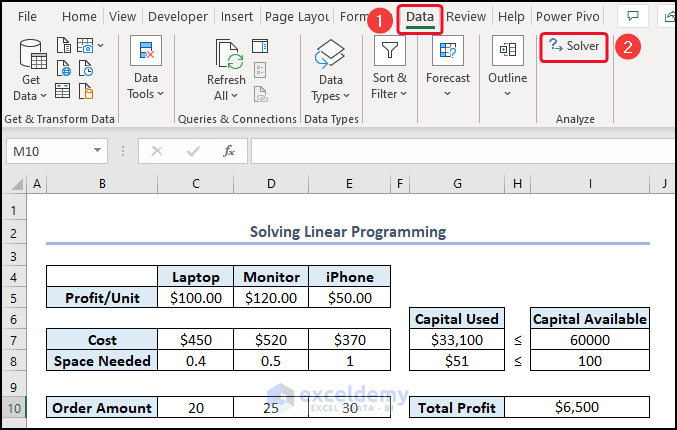
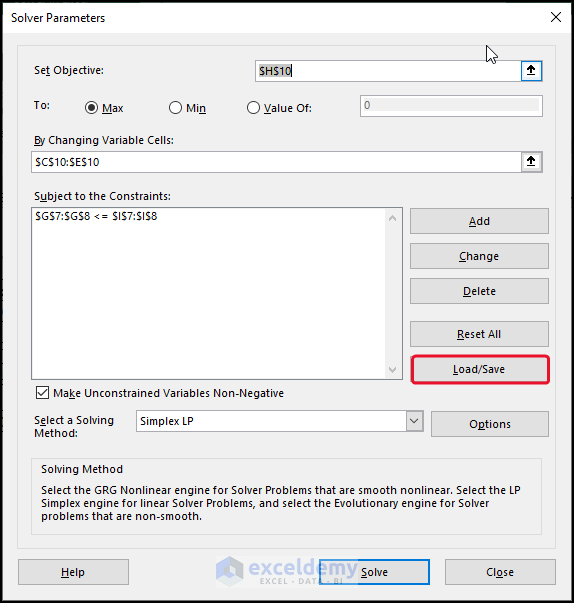
3. Interpreting Linear Programming (Simplex LP)
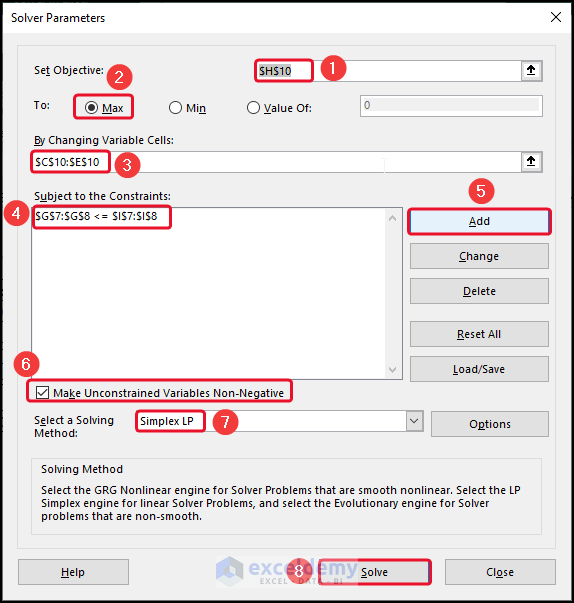
- To Interpret linear programming, select Solver from the Data
- In the Set Objective box, select cell H10 >> click on Max.
- Select cells C10:E10 in the By Changing Variables
- Click on Add >> give the Constrain.
- Click on Mark Unconstrained Variable Non-Negative >> select Simple LP..
- Click on Solve.
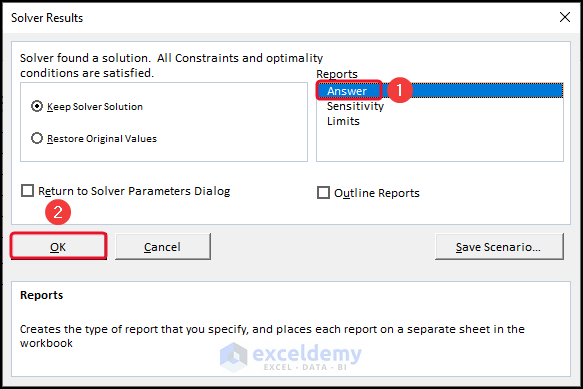
- Select Answer >> click OK.
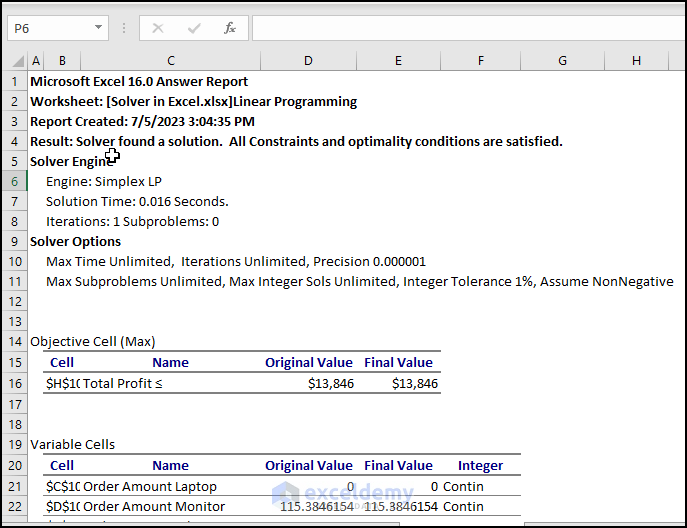
Therefore, you can see the answer report.
Read More: Where Is Solver in Excel – Find, Install & Use
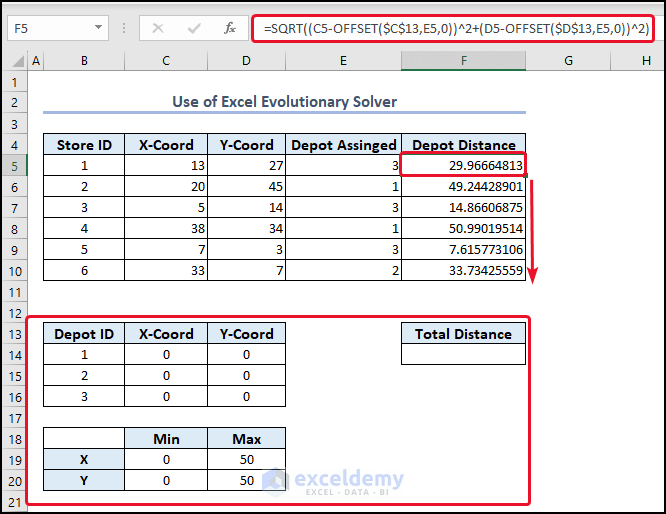
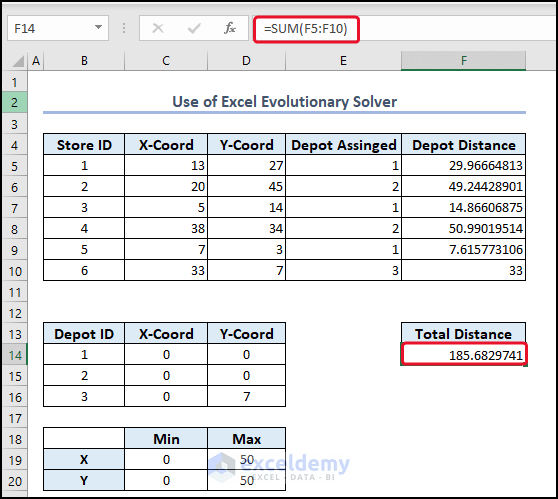
4. Coordinates and Mapping with Solver (Evolutionary Solver)
- Type the following formula in cell F5.
- Type the following formula in cell F14.
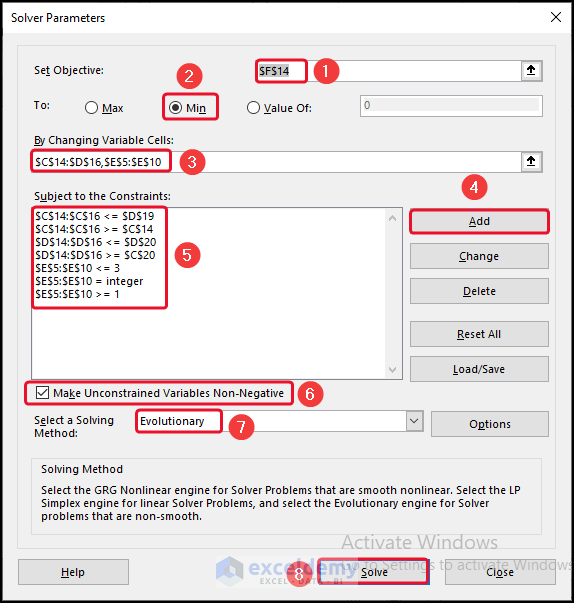
- From the Data tab >> select Solver.
- In the Set Objective box, select cell F14 >> click on Min.
- Select cells in the By Changing Variables
- Click on Add >> give the Constrain.
- Click on Mark Unconstrained Variable Non-Negative >> select Evolutionary.
- Click on Solve.
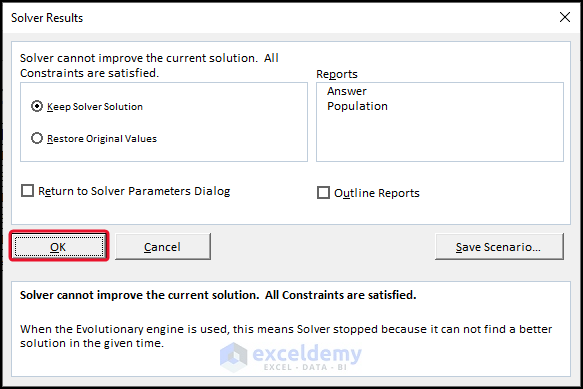
- Click OK.
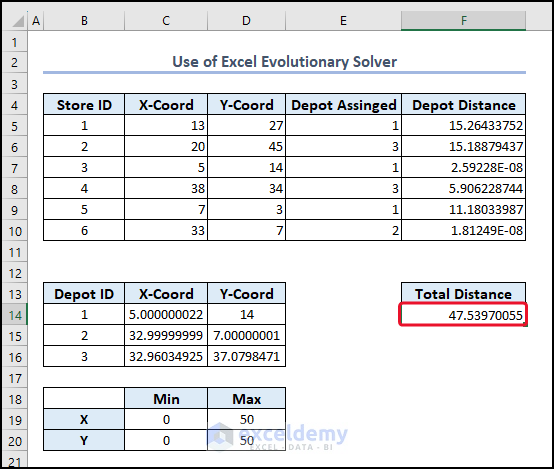
You can see the result in cell F14.
Read More: Optimization in Excel
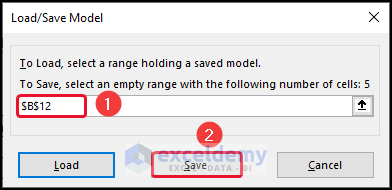
How to Load/Save Solver Solution in Excel
- To load/save a solver solution, select Load/Save in the Solver Parameters dialog box.
- Select a cell >> click on Save.
Conclusion
Here, we extensively describe Solver in Excel. We have described what the solver is in Excel, and how to add the solver. Also, we described different types of solving methods. In addition to this, we describe examples of solvers.
Thank you for reading this article. We hope you find this article beneficial. Please let us know in the comment section if you have any queries or suggestions.
Solver in Excel: Knowledge Hub
<< Go Back to Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!