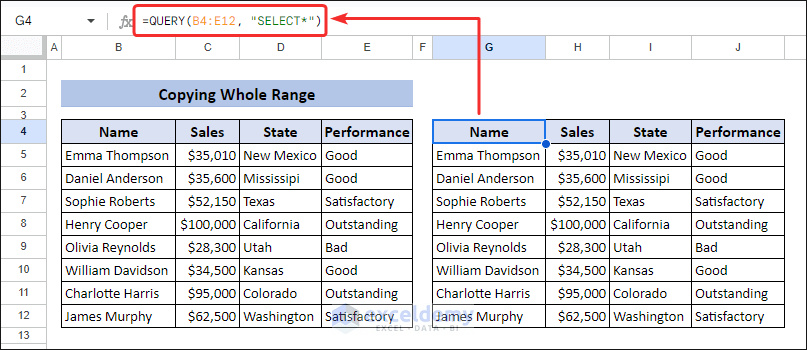
Method 1 – Excel Equivalent of QUERY Function: Copy Whole Range
We have some sales information in the range B4:E12 and want to copy the whole range somewhere else in the sheet. Using copy-paste, you can use the Google Sheets QUERY function to select all columns. The following QUERY function copies the whole data range.
=QUERY(B4:E12, "SELECT*")The query statement is enclosed in double quotation marks. The asterisk (*) is a wildcard that represents all columns in the selected range. This statement requests all columns from the specified range.
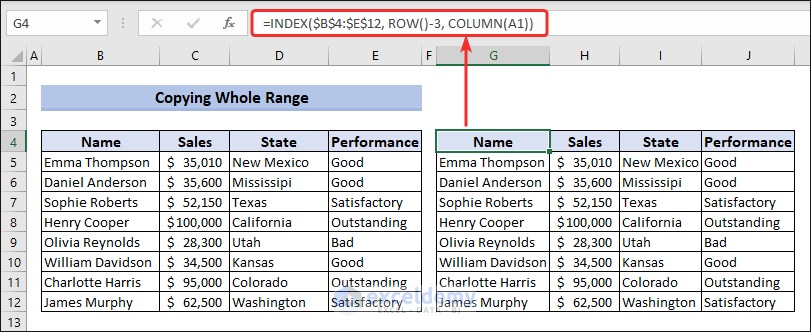
If you want to select all the columns in Excel, use a combination of INDEX, ROW, and COLUMN functions. The following formula will act like the above QUERY function in Google Sheets. Apply it in cell G4 and then drag the Fill Handle through the rows and columns to get your desired output.
=INDEX($B$4:$E$12, ROW()-3, COLUMN(A1))💡 Formula Breakdown
- ROW()-3: returns the current row number of the cell where the formula is entered, and subtracting 3 from it adjusts the row number to be relative to the range B4:E12. For example, if the formula is in row 4, the result of ROW()-3 would be 1, corresponding to the fourth row (B4:E4) of the specified range.
- COLUMN(A1): returns the column number of the reference provided. In this case, the reference is A1, the first column of the range B4:E12. The result of COLUMN(A1) is 1.
Method 2 – Excel Equivalent of QUERY Function: Select Specific Column
Select specific columns in the QUERY function; you have to define the column names in the SELECT statement. For the dataset below, if we want to select columns B, D, and F, we must use the following QUERY formula.
=QUERY(B4:F14, "SELECT B, D, F")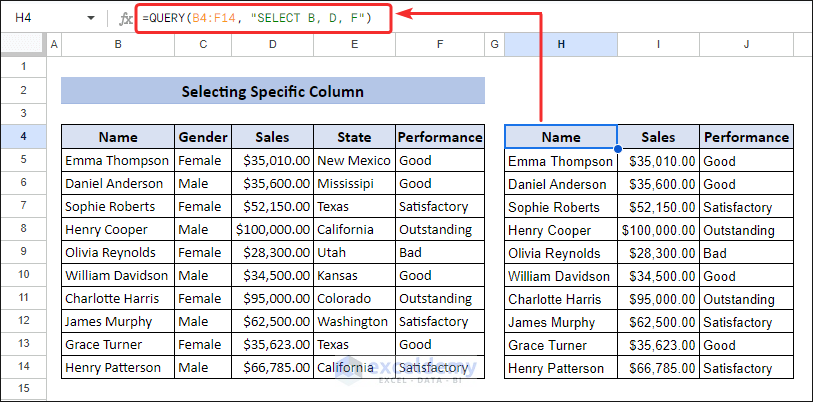
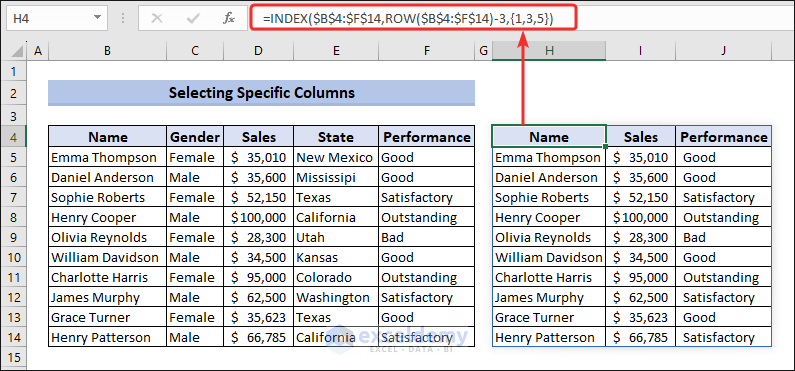
To perform the same operation in Excel for specific columns, apply the following array formula.
=INDEX($B$4:$F$14,ROW($B$4:$F$14)-3,{1,3,5})This formula will select columns 1,3,5 from the specific range $B$4:$F$14.
Method 3 – Excel Equivalent of QUERY Function: Extracting Values Based on Condition
In the dataset, both “Male” and “Female” persons are included. If we apply a condition, we only want data for “Male” sellers only, the Google Sheets QUERY function can easily extract data based on this condition. The function uses the “WHERE” statement.
=QUERY(B4:E14, "SELECT * WHERE C = 'Male'")This formula finds the text string “Male” in column C and returns all the corresponding row data.
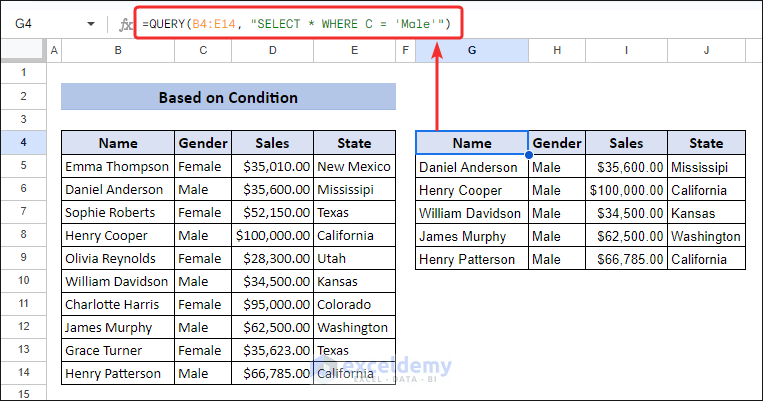
Excel has a unique feature that can perform the same task as Google Sheets QUERY function with the “Where” statement: Filter feature.
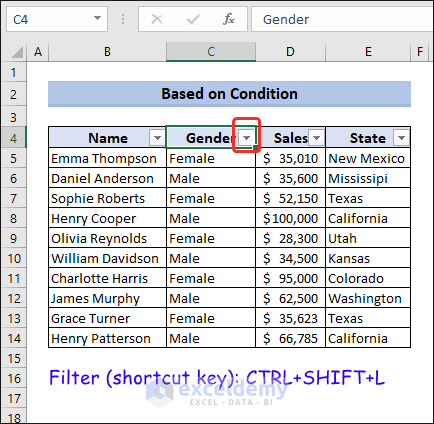
- Click on the header row and press CTRL+SHIFT+L. That will insert Filter in the header.
- Click on the dropdown arrow of the desired column where you want to apply the condition (i.e., Gender).
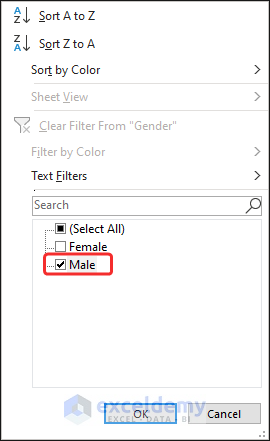
- Select the desired filter (i.e., Male).
- Click OK.
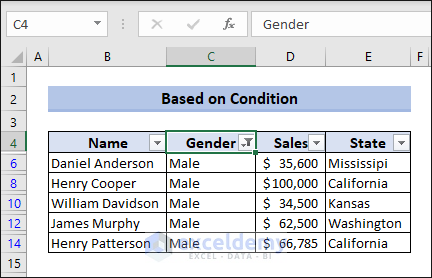
This will make only the data of “Male” persons visible.
Method 4 – Excel Equivalent of QUERY Function: Performing Mathematical Calculations
We can calculate Average, Minimum, and Maximum Values in Google Sheets with QUERY. To calculate those values from the “Sales” column (D), then you can use the following formula to get the maximum, minimum and average of sales.
=QUERY(B4:F14,"SELECT MAX(D), MIN(D), AVG(D)")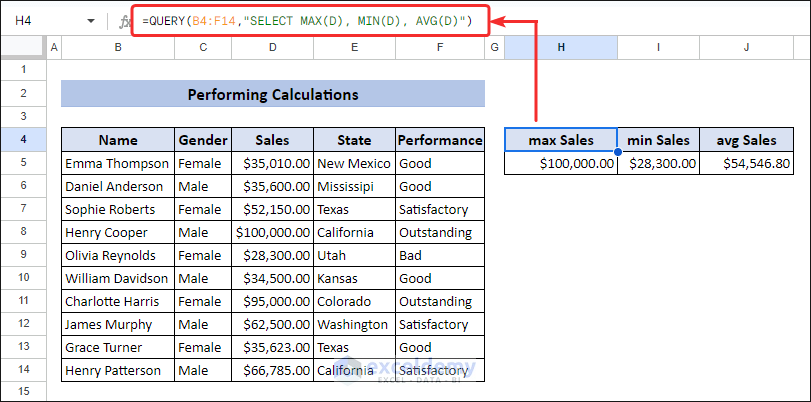
We can’t find these values in Excel with a single formula. Excel has MAX, MIN and AVERAGE functions for getting these values.
For the maximum value of sales:
=MAX(D5:D14)For the minimum value of sales:
=MIN(D5:D14)For the average value of sales:
=AVERAGE(D5:D14)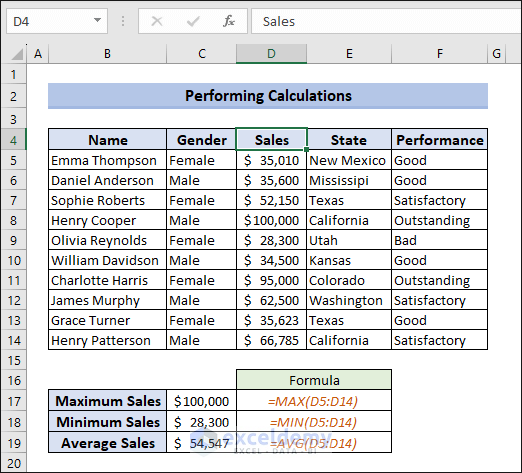
Method 5 – Excel Equivalent of QUERY Function: Sorting Data
By applying the QUERY function in Google Sheets, you can sort your data in ascending or descending order. For the dataset, to sort the data according to “Sales” column in descending order, apply the following formula with “desc” statement.
=QUERY(B5:E14, "select * order by D desc")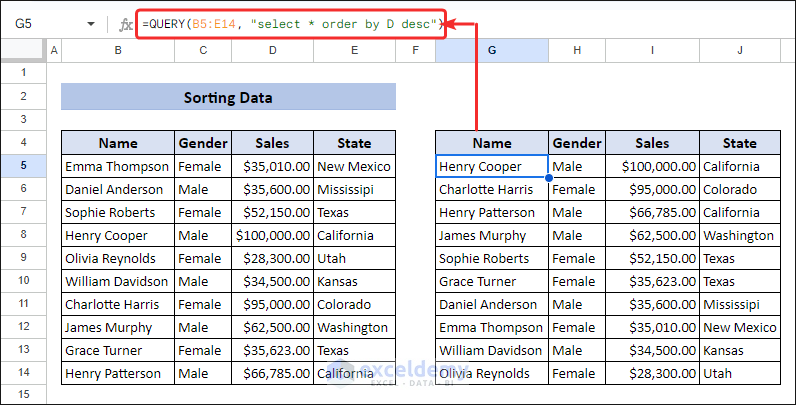
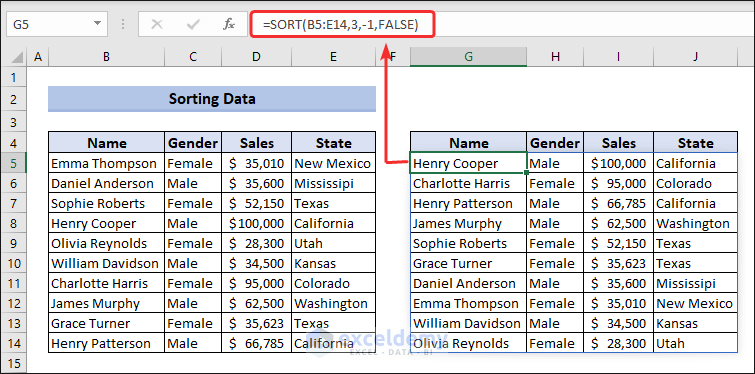
Excel has a built-in SORT function which is used to sort data both in ascending and descending order. The following formula will work out to serve your purpose.
=SORT(B5:E14,3,-1,FALSE)The second argument 3 means we want to sort column 3 and 3rd argument “-1” indicates we want to sort by descending order.
Method 6 – Excel Equivalent of QUERY Function: Counting Numbers of Rows Based on Specific Criteria
To count the number of rows on a specific criteria. We only want to count the data of “Male”. The following formula will count cell from column B that meets the criteria “Male” in column C.
=QUERY(B5:F14, "SELECT COUNT(B) WHERE C = 'Male'")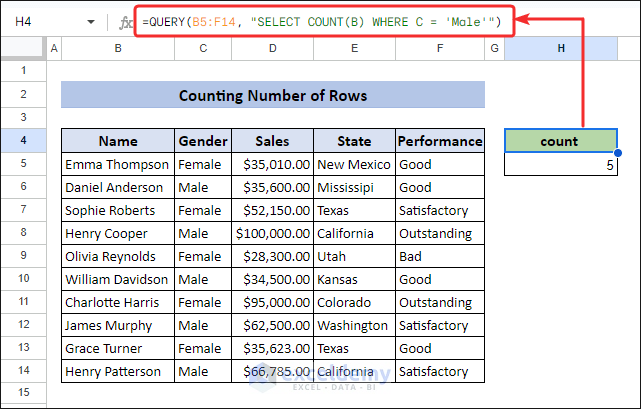
The COUNTIF function counts numbers on specific criteria. The following formula will perform a similar operation to Google Sheets.
=COUNTIF(B5:E14,"Male")Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are there any limitations or differences when using the QUERY function in Excel compared to Google Sheets?
Since the QUERY function is specific to Google Sheets, it is not directly available in Excel. The differences and limitations will depend on the alternative functions and methods you use in Excel to achieve similar results.
2. Can I use the same syntax and parameters in the QUERY function in Excel as in Google Sheets?
The syntax and parameters used in the QUERY function are specific to Google Sheets and are not directly applicable to Excel. When using alternative functions in Excel, you must refer to the documentation and syntax guidelines.
3. Are there any specific examples or use cases where the QUERY function in Excel is particularly useful?
Although the QUERY function is not available in Excel, there are various scenarios where alternative functions can be useful. For example, you can use the FILTER feature to extract specific rows based on conditions or the SORT function to sort your data. The choice of function will depend on the specific requirements of your data analysis task.
Takeaways from this Article
- The QUERY function is a powerful tool in Google Sheets that allows you to retrieve, filter, and manipulate data using SQL-like syntax.
- Unfortunately, the QUERY function is not available in Excel. However, there are alternative functions such as FILTER, SORT, SUMIFS, and COUNTIFS that can help you achieve similar results.
- When using Excel, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the available functions and their syntax to effectively filter, sort, and perform calculations on your data.
- While you can’t directly use the QUERY function in Excel, you can combine multiple functions and techniques to accomplish complex data analysis tasks.
- It’s essential to understand the limitations and differences between the QUERY function in Google Sheets and the alternative functions in Excel to choose the right approach for your data analysis needs.
Download Practice Workbook
You can download the practice book from the link below.
Related Articles
<< Go Back to Import Google Sheets to Excel | Importing Data in Excel | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

