Certainly, Microsoft Excel has a wide range of professional applications. In fact, we use Excel to manage data, process it, and get valuable information from that data. At times, we need to process raw data from a source file, and this may introduce errors like extra spaces in the data. Keeping this in mind, this article describes 5 ways how to remove extra spaces in Excel with suitable examples and explanations.
The animated GIF shown below is an overview of this article, which represents the removal of extra spaces.
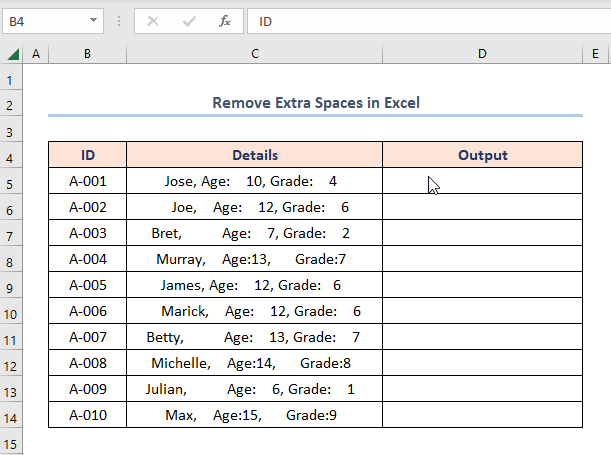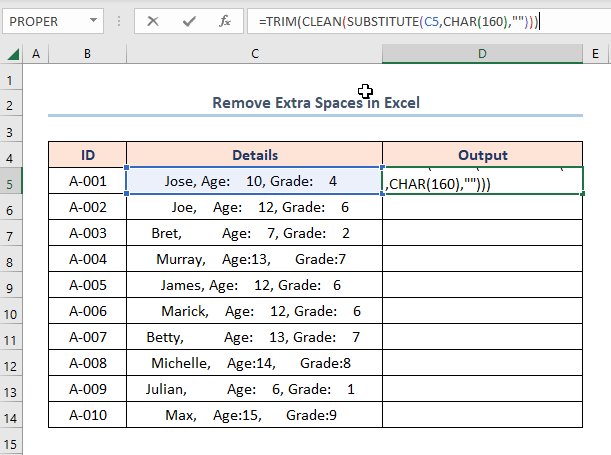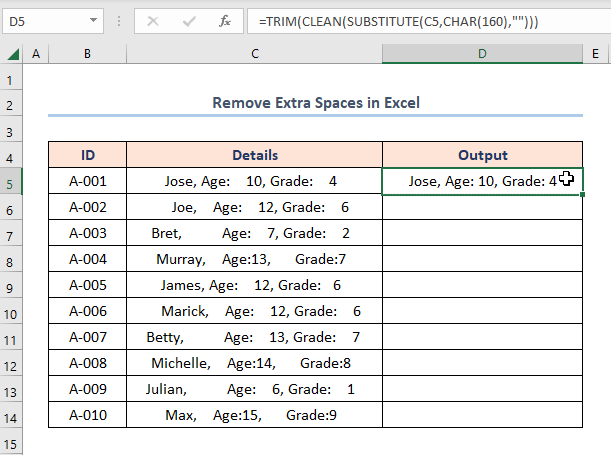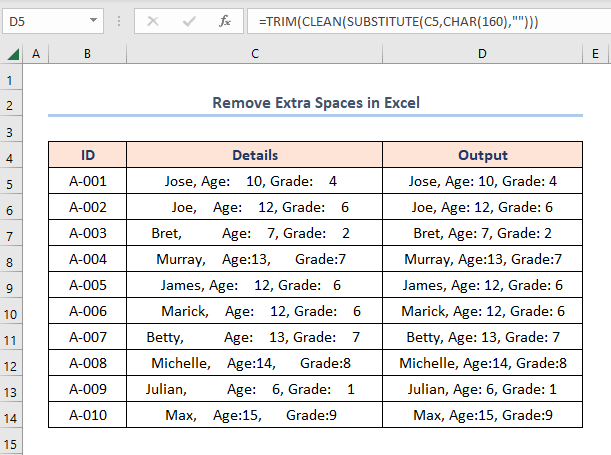
In the following sections, we’ll learn more about the dataset and observe each method in detail.
How to Remove Extra Spaces in Excel: 5 Simple Ways
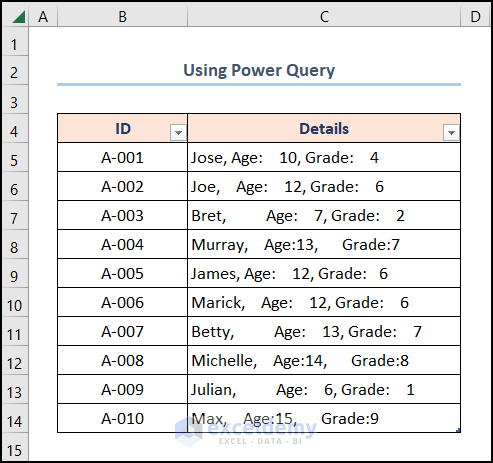
First and foremost, let’s assume the List of Student Information dataset shown in the B4:C14 cells containing the “ID” and “Details” columns respectively. Here, we want to get rid of the extra spaces present in the “Details” column using Excel functions and features. So, let’s glance at each method with the necessary illustrations.
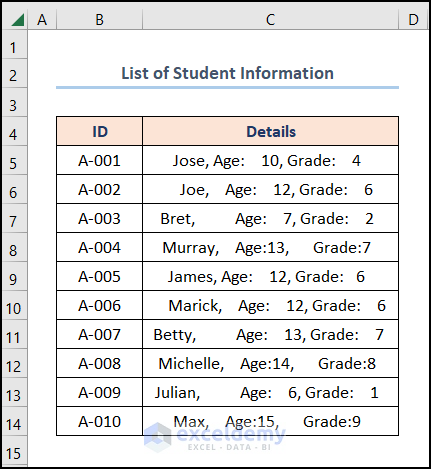
Here, we have used the Microsoft Excel 365 version; you may use any other version at your convenience.
1. Removing Extra Spaces with Excel Functions
Now, functions are the heart and soul of a spreadsheet, so let’s see how to remove extra spaces in Excel by utilizing functions.
1.1 Using TRIM Function to Remove All Extra Spaces
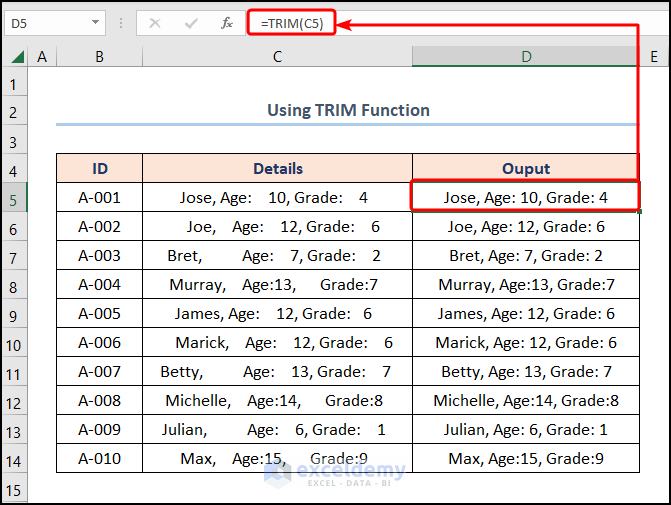
In the first place, we’ll apply the TRIM function that removes additional spaces within a text.
📌 Steps:
- Initially, go to the D5 cell >> enter the formula given below >> press ENTER.
=TRIM(C5)
Here, the C5 cell refers to the “Details” text regarding the “ID A-001”.
1.2 Combining TRIM, MID, FIND & LEN Functions to Remove Only Leading Spaces
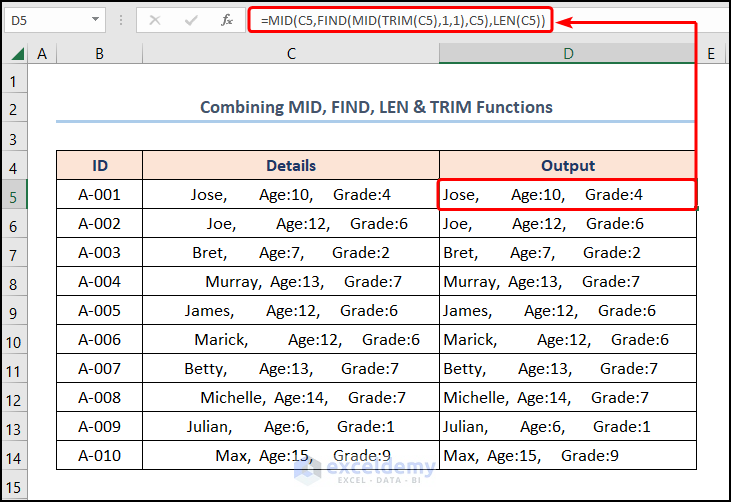
Besides, we may combine the TRIM, MID, FIND, and LEN functions to remove the leading spaces in a string of text. Here, the combination of these functions helps identify the starting position of the text characters and erase the leading space.
📌 Steps:
- First of all, move to the D5 cell >> enter the formula given below >> click ENTER.
=MID(C5,FIND(MID(TRIM(C5),1,1),C5),LEN(C5))
- LEN(C5) → returns the number of characters in a string of text. Here, the C5 cell is the text argument that yields the value 32.
- Output → 32
- MID(TRIM(C5),1,1) → returns the characters from the middle of a text string, given the starting position and length. Here, the C5 cell is the text argument, 1 is the start_num argument, and 1 is the num_chars argument such that the function returns the first character from the left side.
- Output → “J”
- FIND(MID(TRIM(C5),1,1),C5) → becomes
- FIND(“J”,C5) → returns the starting position of one text string within another text string. Here, “J” is the find_text argument while C5 is the within_text argument. Here, the FIND function returns the position of the numeric values in the string of text.
- Output → 1
- MID(C5,FIND(MID(TRIM(C5),1,1),C5),LEN(C5)) → becomes
- MID(C5,1,32) → Here, the C5 cell is the text argument, 1 is the start_num argument, and 32 is the num_chars argument such that the function returns the first character from the left side.
- Output → “Jose, Age:10, Grade:4”
1.3 Implementing CLEAN, SUBSTITUTE, and CHAR Functions to Eliminate Line Breaks
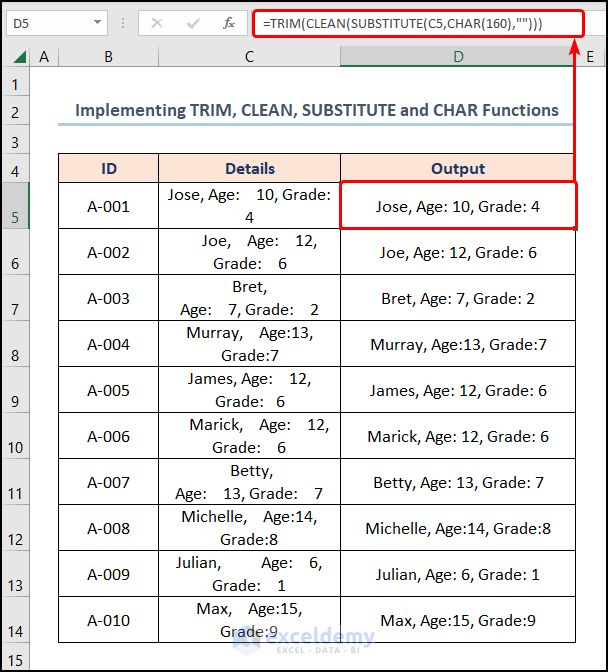
In addition, we can also fuse the TRIM, CLEAN, SUBSTITUTE, and CHAR functions to eliminate line breaks.
📌 Steps:
- In the first place, enter the D5 cell >> type the following expression >> hit ENTER.
=TRIM(CLEAN(SUBSTITUTE(C5,CHAR(160),"")))
- CHAR(160) → returns the character specified by the code number from the character set from your computer. Here, the 160 cell is the number argument that represents the white space character.
- Output → ” “
- SUBSTITUTE(C5,CHAR(160),””) → replaces existing text with new text in a text string. Here, the C5 refers to the text argument while the CHAR(160) represents the old_text argument, and the “” points to the new_text argument. Here, the function substitutes white spaces with blanks.
- Output → “Jose, Age: 10, Grade: 4 “
- CLEAN(SUBSTITUTE(C5,CHAR(160),””)) → becomes
- CLEAN(“Jose, Age: 10, Grade: 4”) → removes all nonprintable characters from text. Here, “Jose, Age: 10, Grade: 4” is the text argument.
- Output → “Jose, Age: 10, Grade: 4 “
- TRIM(CLEAN(SUBSTITUTE(C5,CHAR(160),””))) → becomes
- TRIM(“Jose, Age: 10, Grade: 4”) → here, the “Jose, Age: 10, Grade: 4” is the text argument and the function gets rid of excess spaces after the text.
- Output → “Jose, Age: 10, Grade: 4”
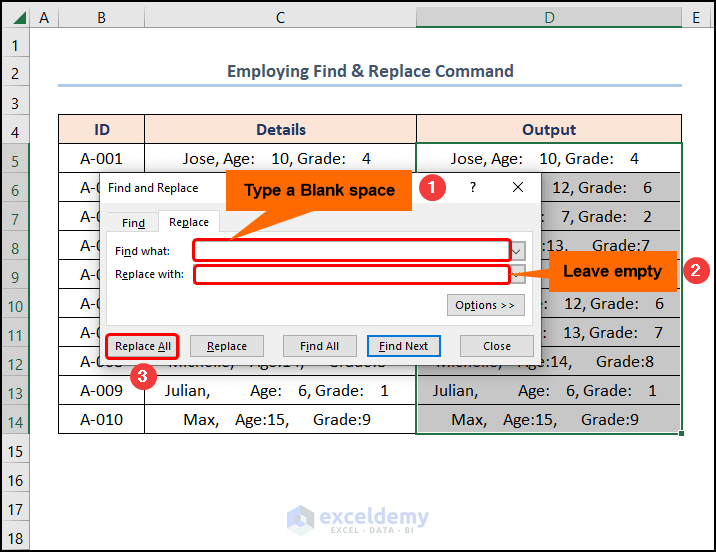
2. Removing Spaces Before Numbers Employing Find & Replace Feature
For one thing, if combining complex formulas and expressions does not suit you, then Excel’s Find and Replace command can help solve your problems.
📌 Steps:
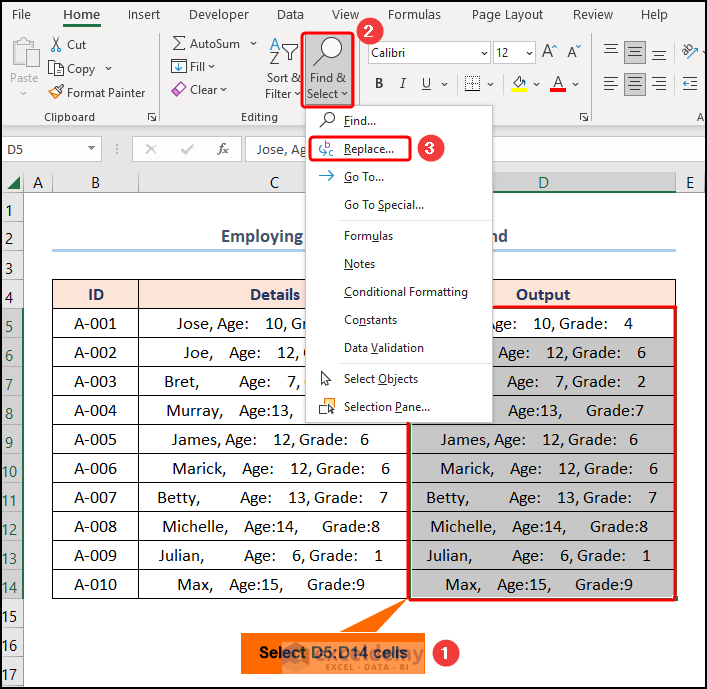
- At the very beginning, select the D5:D14 cells >> navigate to the Find & Select drop-down >> choose the Replace option.
- Next, in the Find what field, type a blank space >> leave the Replace with field empty >> press the Replace All button.
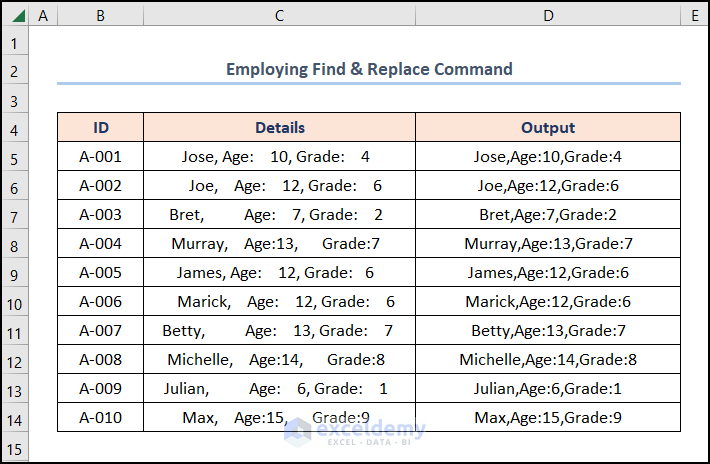
Ta-dah! That is how simple it is to remove spaces in Excel.
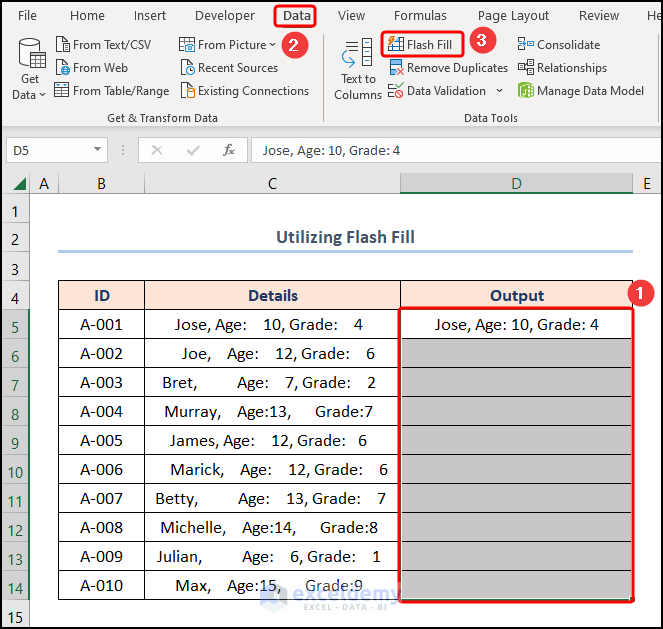
3. Utilizing Flash Fill to Remove Extra Spaces
Moreover, another smart feature of Excel is the Flash Fill option which recognizes a pattern and auto-fills the rest of the column without any formulas like magic! 🙃
📌 Steps:
- To begin with, type the desired output in the D5 cell >> choose the D5:D14 cells >> jump to the Data tab >> click Flash Fill.
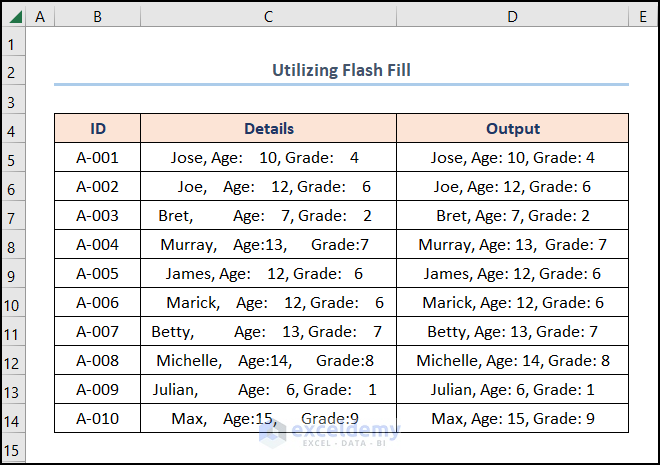
Boom! The end result appears in the image below.
4. Erasing Spaces with Power Query Tool
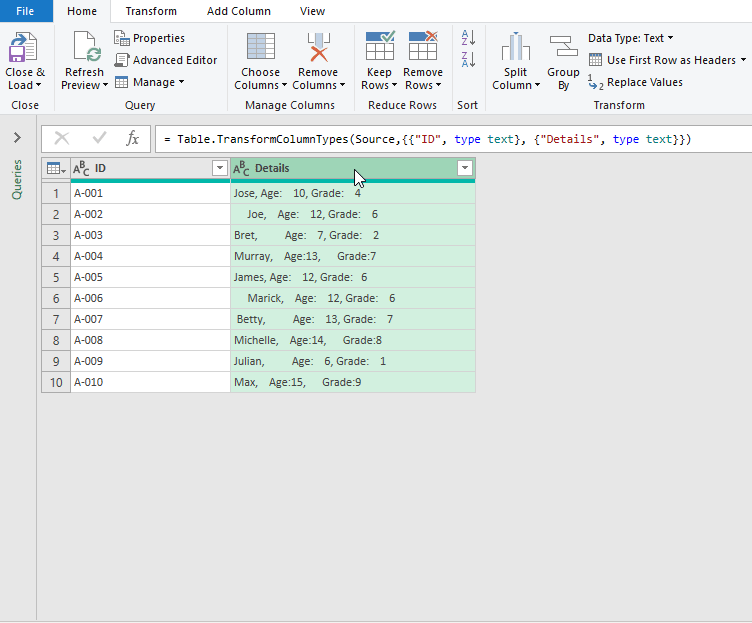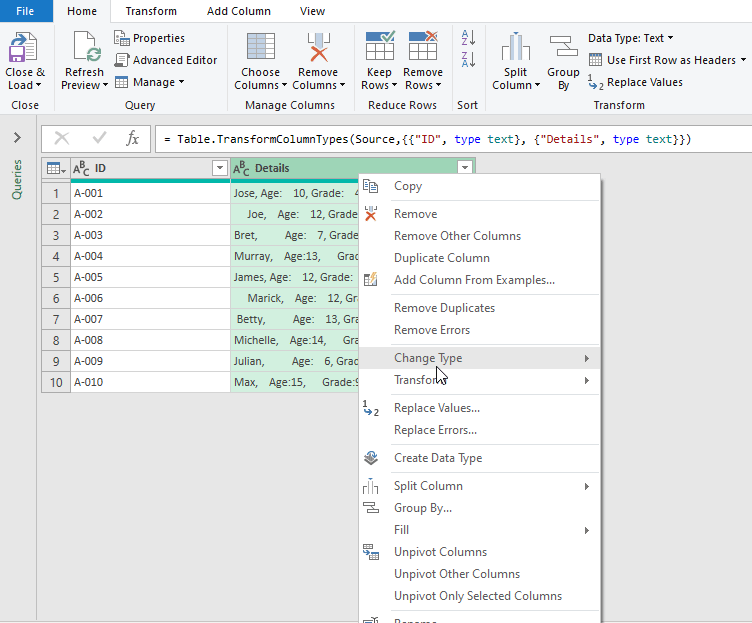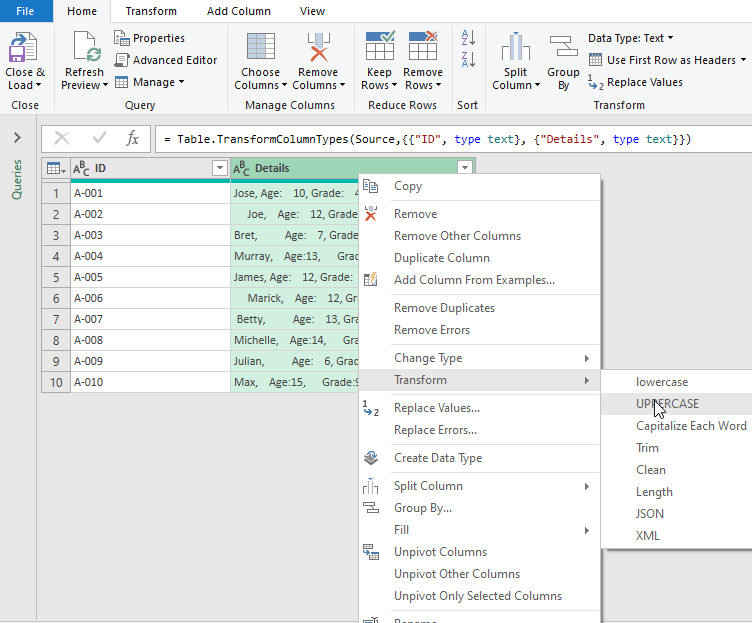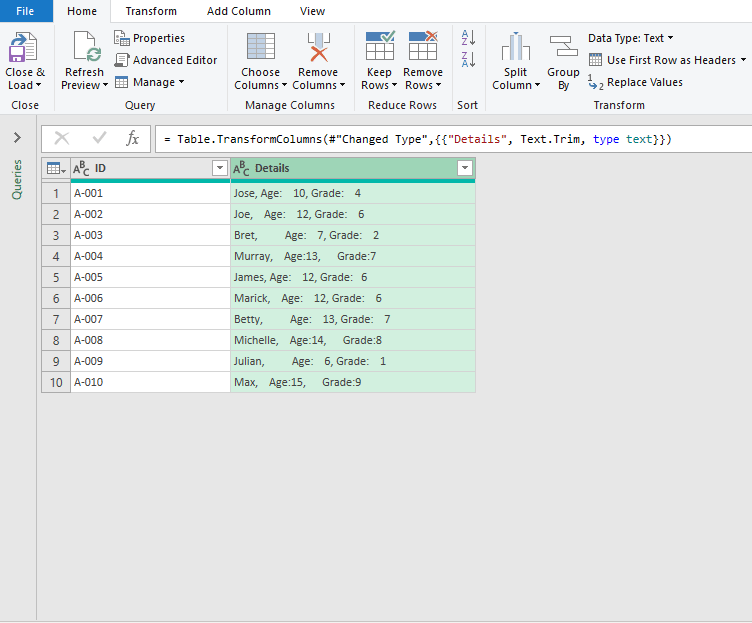
Conversely, the Power Query tool, an often overlooked feature of Excel, is quickly becoming my favorite tool for analyzing large sets of data. Since it is jam-packed with useful and handy features, let’s now see it in action.
📌 Steps:
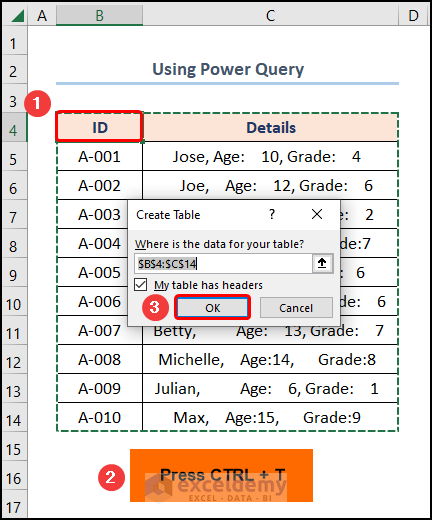
- To start with, move the cursor to the B4 cell >> press CTRL + T >> click on OK to insert an Excel Table.
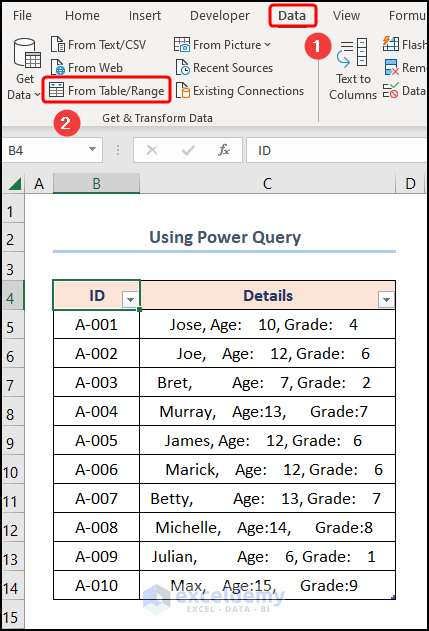
- Not long after, proceed to the Data tab >> choose From Table/Range option.
- At this point, this opens the Power Query editor, follow the steps shown in the GIF for a live demonstration.
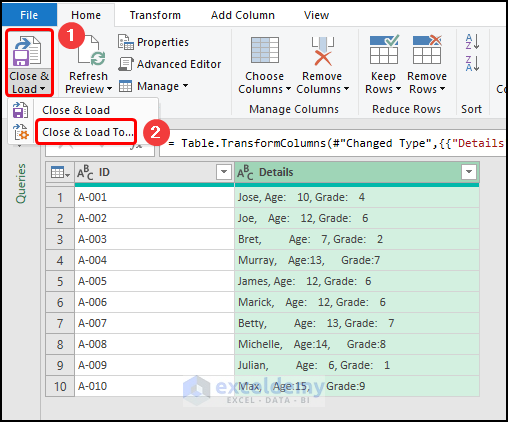
- Afterward, press the Close & Load drop-down >> choose the Close & Load To option.
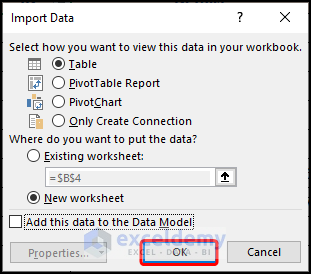
- Furthermore, in the Import Data window, press OK.
Voila! The final result should look like the screenshot shown below.
5. Applying VBA Code for Removing Extra Spaces
Last but not least, If you often need to remove extra spaces, then you may consider the VBA Code below. It’s simple & easy, just follow along.
📌 Steps:
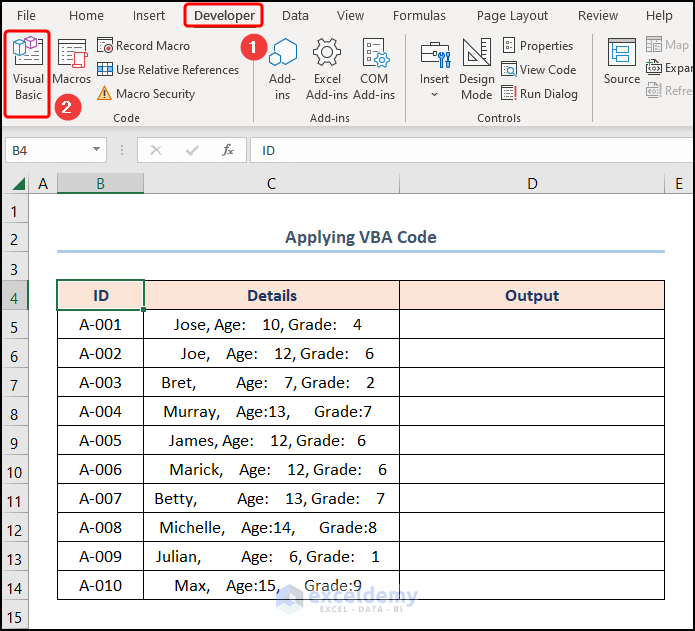
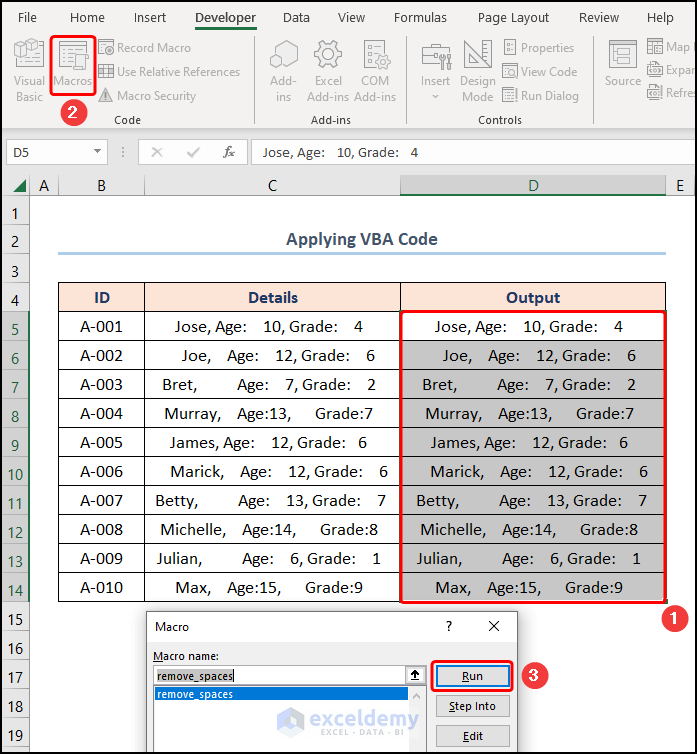
- First, navigate to the Developer tab >> click the Visual Basic button.
- Second, go to the Insert tab >> select Module.
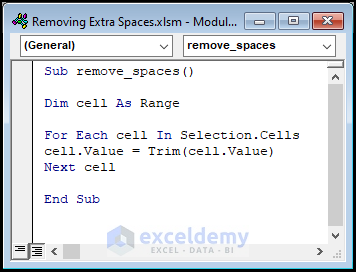
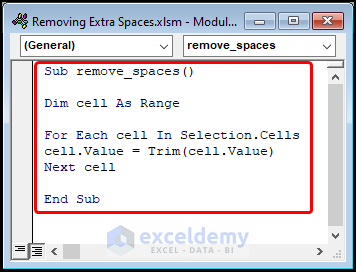
For ease of reference, copy the code from here and paste it into the window as shown below.
Sub remove_spaces()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Selection.Cells
cell.Value = Trim(cell.Value)
Next cell
End SubIn the following section, we’ll explain the VBA code used to erase extra spaces.
- In the first portion, the sub-routine is given a name, here it is remove_spaces().
- Next, define the variable cell as Range.
- Lastly, use a For Loop to iterate through each value and apply the Trim function to get rid of the spaces.
- Third, copy and paste the “Details” column into the “Output” column >> click the Macros button >> press Run.
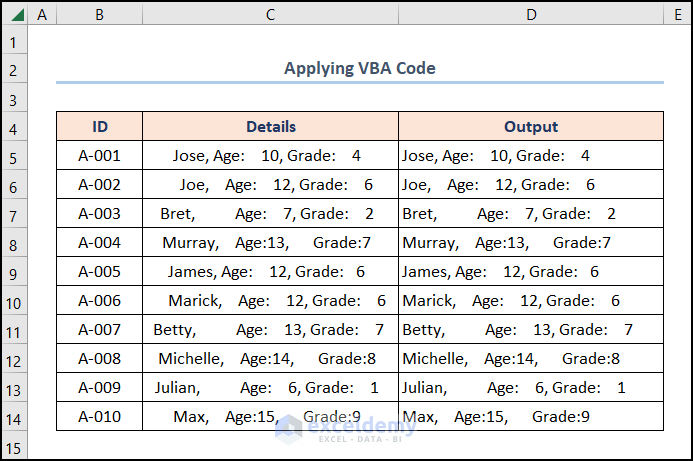
Consequently, the results should look like the figure given below.
Practice Section
We have provided a Practice section on the right side of each sheet so you can practice yourself. Please make sure to do it by yourself.
Download Practice Workbook
Conclusion
In essence, this article shows 5 effective methods on how to remove extra spaces in Excel. So, read the full article carefully and download the free workbook to practice. Now, we hope you find this article helpful and if you have any further queries or recommendations, please feel free to comment here.
Related Articles
- How to Remove White Space in Excel
- How to Remove Space after Number in Excel
- How to Remove Space in Excel after Text
- How to Remove Space between Rows in Excel
- How to Remove Tab Space from Excel
- How to Remove Space in Excel Before Numbers
- Remove the Trailing Spaces in Excel
- How to Find and Replace Space in Excel
- How to Remove Blank Spaces in Excel
- How to Remove Space Before Text in Excel
<< Go Back To Remove Space in Excel | Data Cleaning in Excel | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!