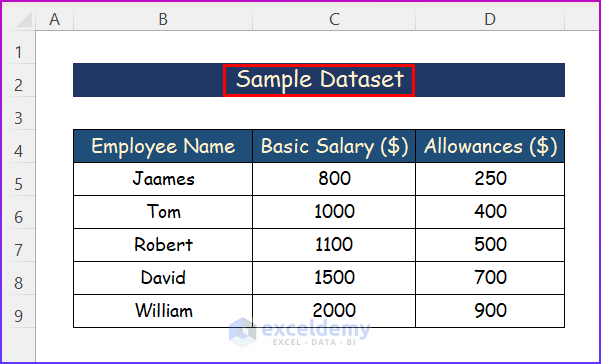
For illustration, we will search for the text “Sample Dataset” in multiple Excel files. One of the file’s texts is shown in the following image.
Method 1 – Utilizing File Explorer to Search Text in Multiple Files
Steps:
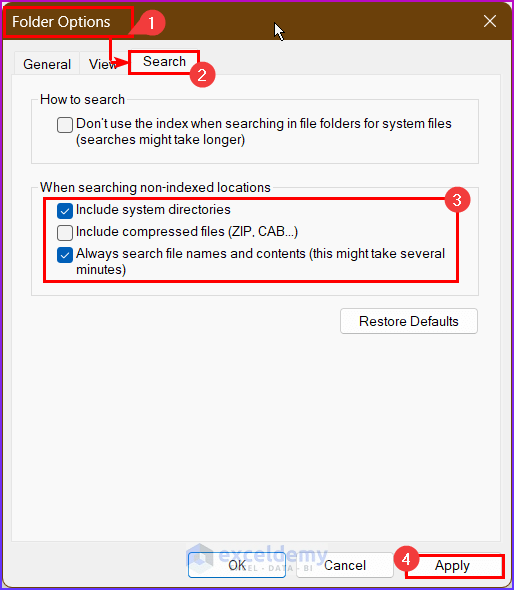
- Navigate to the folder where you want to search for the text.
- Go to Search from the Folder Option and select “Always search file names and contents”.
- Click on the Apply button.
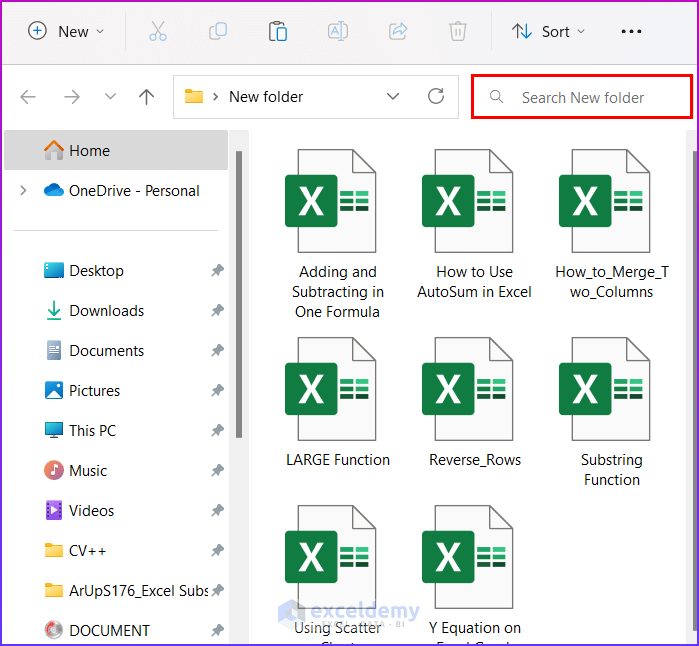
- From the upper right corner of the folder, click on the Search bar.
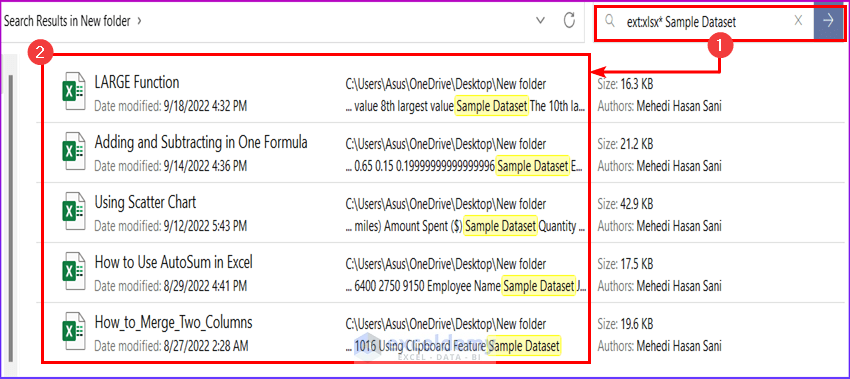
- Write your text in the search bar. For example, we have searched for the text “Sample Dataset” in all the Excel workbooks.
ext:xlsx* Sample Dataset
- This will show all the Excel workbooks containing the text you have searched for.
Method 2 – Applying VBA to Search Text in Multiple Excel Files
Steps:
- Open the worksheet where you want the text to be split.
- Hold the Alt+F11 keys in Excel, which opens the Microsoft Visual Basic Applications window.
- Click the Insert button.
- Click on Module from the menu to create a module.
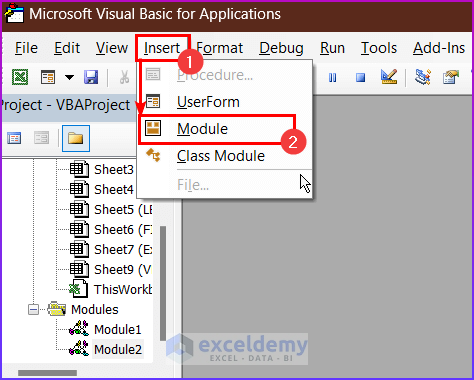
- A new window will open. Enter the following VBA macro in the Module window.
Sub SearchFolders()
'ExcelDemy Publications
'Declaring Variables
Dim xDgl As Object
Dim xFld As Object
Dim xBnkSearch As String
Dim xBnuPath As String
Dim xGnuPath As String
Dim xHty As Worksheet
Dim xTn As Workbook
Dim xRw As Worksheet
Dim xVoi As Long
Dim xGenerate As Range
Dim xGbrPosition As String
Dim xNewBox As FileDialog
Dim xNew As Boolean
Dim xCalculate As Long
Dim xJTQ As Workbook
Dim xJTQStrPath As String
Dim xBln As Boolean
Set xJTQ = ActiveWorkbook
xJTQStrPath = xJTQ.Path & "\" & xJTQ.Name
On Error GoTo FaultService
Set xNewBox = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFolderPicker)
xNewBox.AllowMultiSelect = False
xNewBox.Title = "Select a Folder"
If xNewBox.Show = -1 Then
xBnuPath = xNewBox.SelectedItems(1)
End If
If xBnuPath = "" Then Exit Sub
xBnkSearch = "Sample Dataset"
xNew = Application.ScreenUpdating
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Set xHty = Worksheets.Add
xVoi = 4
With xHty
.Cells(xVoi, 2) = "Workbook"
.Cells(xVoi, 3) = "Worksheet"
.Cells(xVoi, 4) = "Cell"
.Cells(xVoi, 5) = "Text in Cell"
Set xDgl = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set xFld = xDgl.GetFolder(xBnuPath)
xGnuPath = Dir(xBnuPath & "\*.xls*")
Do While xGnuPath <> ""
xBln = False
If (xBnuPath & "\" & xGnuPath) = xJTQStrPath Then
xBln = True
Set xTn = xJTQ
Else
Set xTn = Workbooks.Open(Filename:=xBnuPath & "\" & xGnuPath, UpdateLinks:=0, ReadOnly:=True, AddToMRU:=False)
End If
For Each xRw In xTn.Worksheets
If xBln And (xRw.Name = .Name) Then
Else
Set xGenerate = xRw.UsedRange.Find(xBnkSearch)
If Not xGenerate Is Nothing Then
xGbrPosition = xGenerate.Address
End If
Do
If xGenerate Is Nothing Then
Exit Do
Else
xCalculate = xCalculate + 1
xVoi = xVoi + 1
.Cells(xVoi, 2) = xTn.Name
.Cells(xVoi, 3) = xRw.Name
.Cells(xVoi, 4) = xGenerate.Address
.Cells(xVoi, 5) = xGenerate.Value
End If
Set xGenerate = xRw.Cells.FindNext(After:=xGenerate)
Loop While xGbrPosition <> xGenerate.Address
End If
Next
If Not xBln Then
xTn.Close (False)
End If
xGnuPath = Dir
Loop
.Columns("A:D").EntireColumn.AutoFit
End With
MsgBox xCalculate & " cells have been found", , "ExcelDemy for Excel"
ExitHandler:
Set xHty = Nothing
Set xRw = Nothing
Set xTn = Nothing
Set xFld = Nothing
Set xDgl = Nothing
Application.ScreenUpdating = xNew
Exit Sub
FaultService:
MsgBox Err.Description, vbExclamation
Resume ExitHandler
End Sub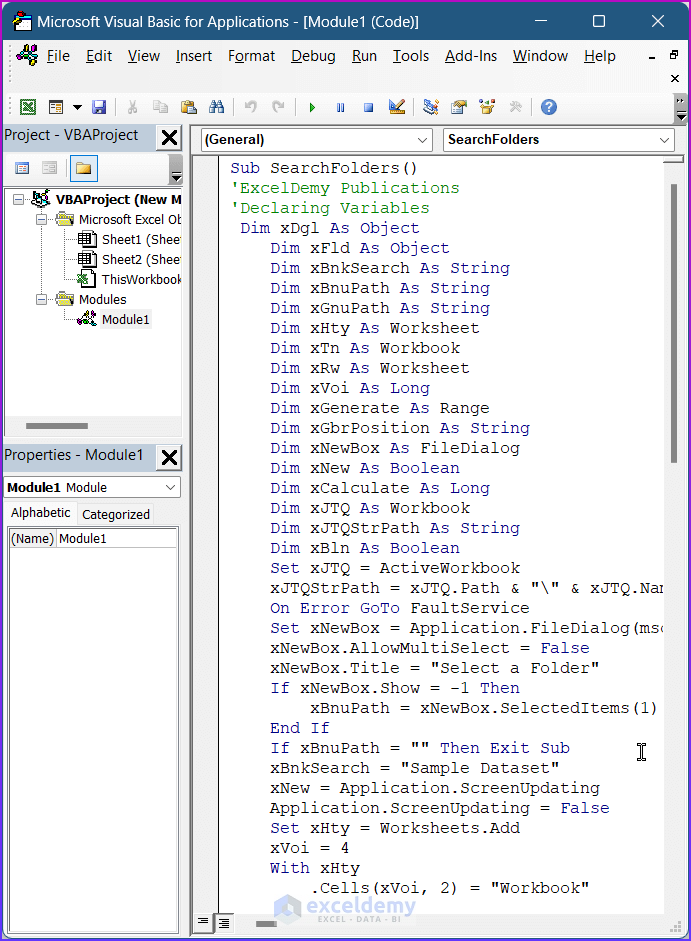
VBA Code Breakdown
- Create a new procedure Sub in the worksheet using the below statement
Sub SearchFolders()- Declare variables as
'Declaring Variables
Dim xDgl As Object
Dim xFld As Object
Dim xBnkSearch As String
Dim xBnuPath As String
Dim xGnuPath As String
Dim xHty As Worksheet
Dim xTn As Workbook
Dim xRw As Worksheet
Dim xVoi As Long
Dim xGenerate As Range
Dim xGbrPosition As String
Dim xNewBox As FileDialog
Dim xNew As Boolean
Dim xCalculate As Long
Dim xJTQ As Workbook
Dim xJTQStrPath As String
Dim xBln As Boolean- Activate the VBA sheet and set xJTQ, xNewBox to open a dialog box.
Set xJTQ = ActiveWorkbook
xJTQStrPath = xJTQ.Path & "\" & xJTQ.Name
On Error GoTo FaultService
Set xNewBox = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFolderPicker)
xNewBox.AllowMultiSelect = False
xNewBox.Title = "Select a Folder"- Apply two if loops. Add the text you want to search for in the xBnuSearch.
If xNewBox.Show = -1 Then
xBnuPath = xNewBox.SelectedItems(1)
End If
If xBnuPath = "" Then Exit Sub
xBnkSearch = "Sample Dataset"
xNew = Application.ScreenUpdating
Application.ScreenUpdating = False- Set xHty, xDgl, xFld, xTn.
Set xHty = Worksheets.Add
xVoi = 4
With xHty
.Cells(xVoi, 2) = "Workbook"
.Cells(xVoi, 3) = "Worksheet"
.Cells(xVoi, 4) = "Cell"
.Cells(xVoi, 5) = "Text in Cell"
Set xDgl = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set xFld = xDgl.GetFolder(xBnuPath)
xGnuPath = Dir(xBnuPath & "\*.xls*")
Do While xGnuPath <> ""
xBln = False
If (xBnuPath & "\" & xGnuPath) = xJTQStrPath Then
xBln = True
Set xTn = xJTQ
Else
Set xTn = Workbooks.Open(Filename:=xBnuPath & "\" & xGnuPath, UpdateLinks:=0, ReadOnly:=True, AddToMRU:=False)- Start an END If function and activate the cells according to the strings to get the result.
End If
For Each xRw In xTn.Worksheets
If xBln And (xRw.Name = .Name) Then
Else
Set xGenerate = xRw.UsedRange.Find(xBnkSearch)
If Not xGenerate Is Nothing Then
xGbrPosition = xGenerate.Address
End If
Do
If xGenerate Is Nothing Then
Exit Do
Else
xCalculate = xCalculate + 1
xVoi = xVoi + 1
.Cells(xVoi, 2) = xTn.Name
.Cells(xVoi, 3) = xRw.Name
.Cells(xVoi, 4) = xGenerate.Address
.Cells(xVoi, 5) = xGenerate.Value
End If
Set xGenerate = xRw.Cells.FindNext(After:=xGenerate)
Loop While xGbrPosition <> xGenerate.Address
End If- End and exit the Sub of the VBA macro as
Next
If Not xBln Then
xTn.Close (False)
End If
xGnuPath = Dir
Loop
.Columns("A:D").EntireColumn.AutoFit
End With
MsgBox xCalculate & " cells have been found", , "ExcelDemy for Excel"
ExitHandler:
Set xHty = Nothing
Set xRw = Nothing
Set xTn = Nothing
Set xFld = Nothing
Set xDgl = Nothing
Application.ScreenUpdating = xNew
Exit Sub
FaultService:
MsgBox Err.Description, vbExclamation
Resume ExitHandler
End Sub- Press the F5 key to run the VBA code. A dialog box named Select a Folder will appear.
- Select the folder where you want to search for and press OK.
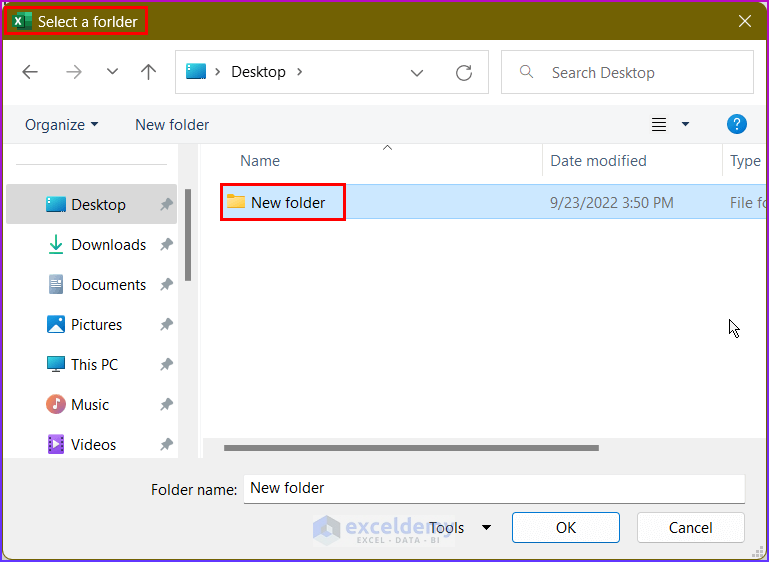
- Another dialog box will appear showing the number of cells found. Press OK.
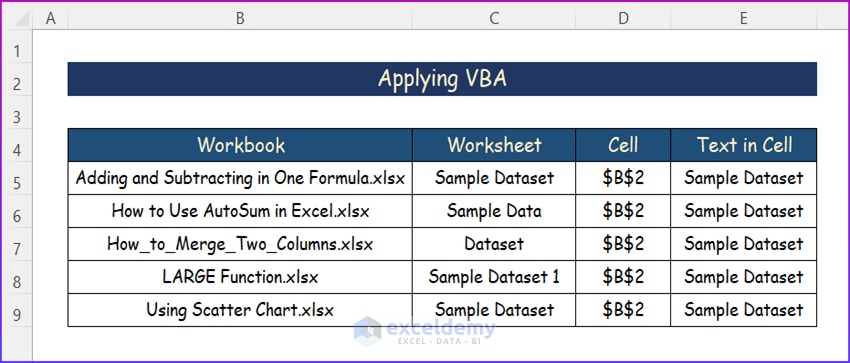
- You will find the name of the workbook, sheet number, and cell number of the searched text as in the following image.
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- How to Check If a Value is in List in Excel
- Lookup Value in Column and Return Value of Another Column in Excel
- How to Find Top 5 Values and Names in Excel
- Find Text in Excel Range and Return Cell Reference
- [Solved!] CTRL+F Not Working in Excel
- How to Get Top 10 Values Based on Criteria in Excel
- How to Create Top 10 List with Duplicates in Excel
<< Go Back to Find Value in Range | Excel Range | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

