1. Turning Off Gridline in an Excel Worksheet
- Go to the View tab.
- Uncheck the Gridlines option to disable it.
The gridlines will turn off from the worksheet.
Method 2 – Formatting Title in Excel Worksheet
2.1 Using Merge & Center Command
To apply the Merge & Center feature to format the title, apply the following steps:
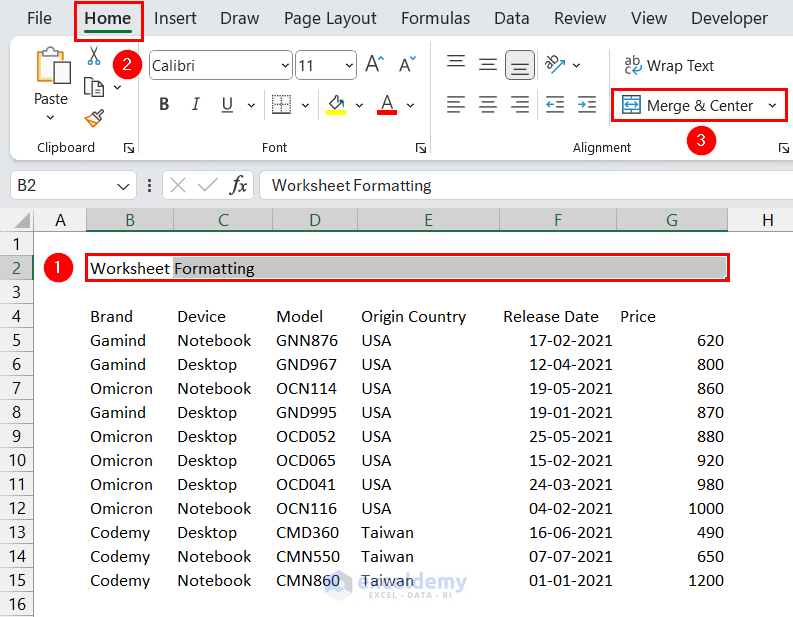
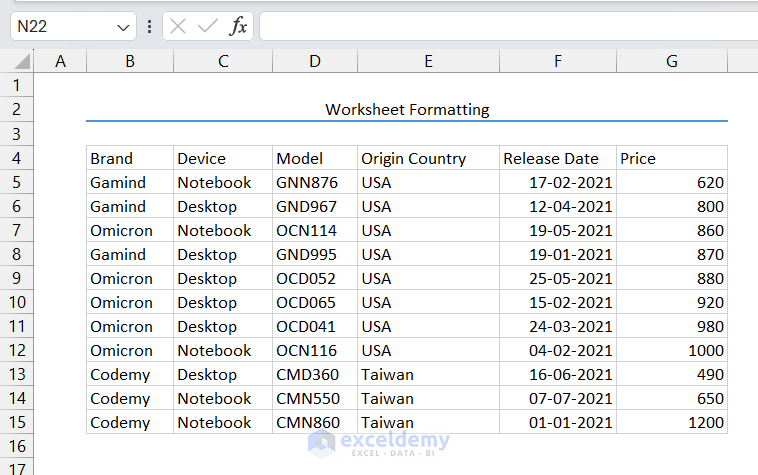
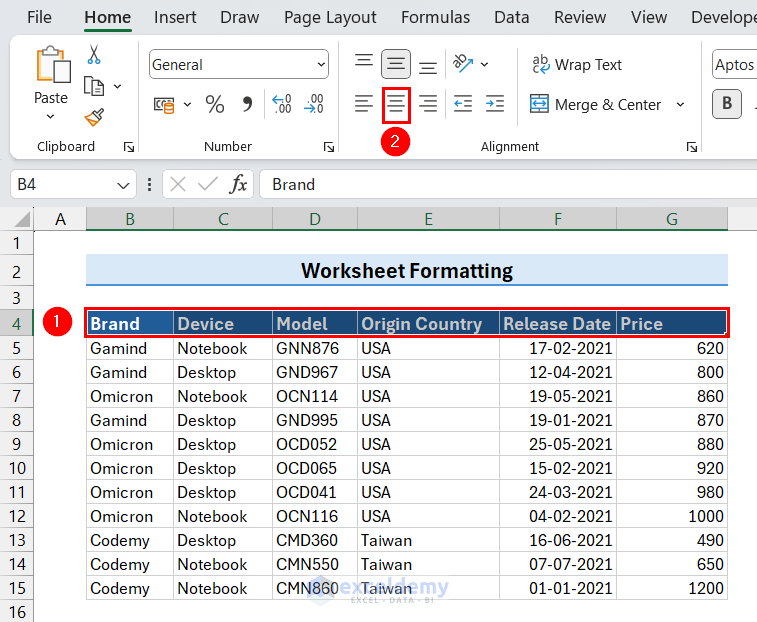
- Select the row of the title.
We selected the range B2:G2. - Go to Home tab > Alignment group > Merge & Center command.
This will merge all the selected cells and bring the title to the center of the merged cell.
2.2 Using Center Across Selection Option
Merging cells often creates problems in formula-based operations in Excel. To avoid such issues, you can use the Center Across Selection option as an alternative. This option only displays the value as center-aligned. But the value is stored in a single cell only.
To format the title with the Center Across Selection option, follow the steps below:
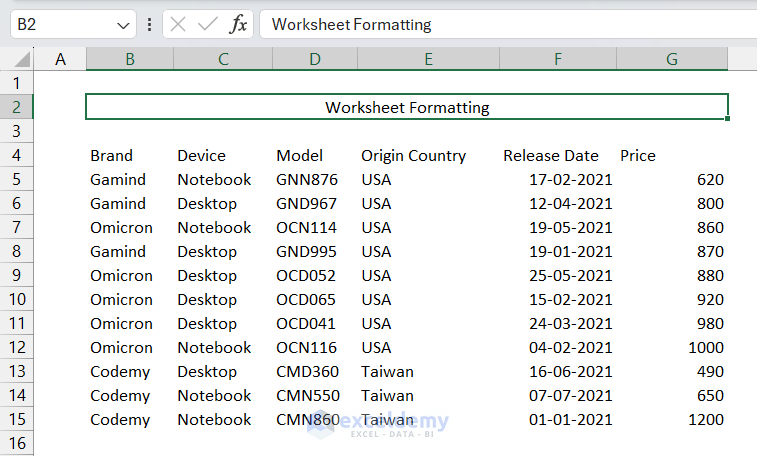
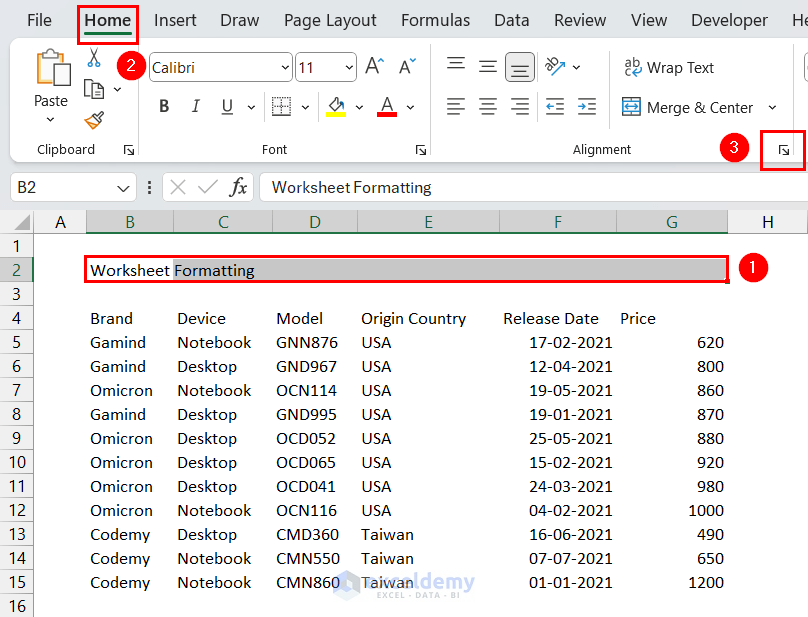
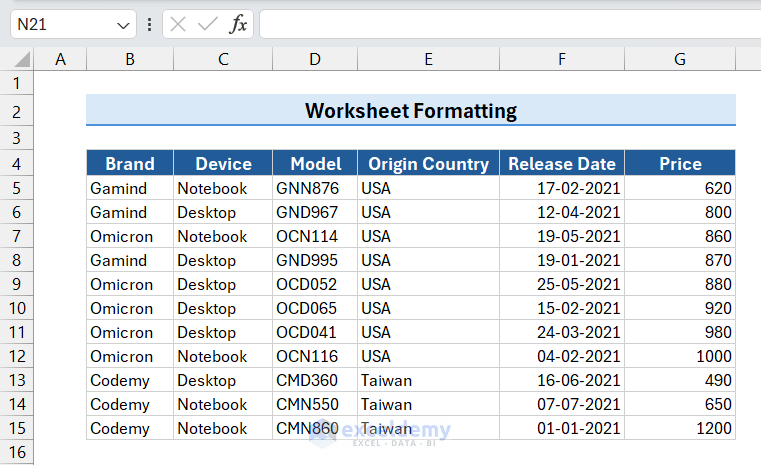
- Select the row of the title.
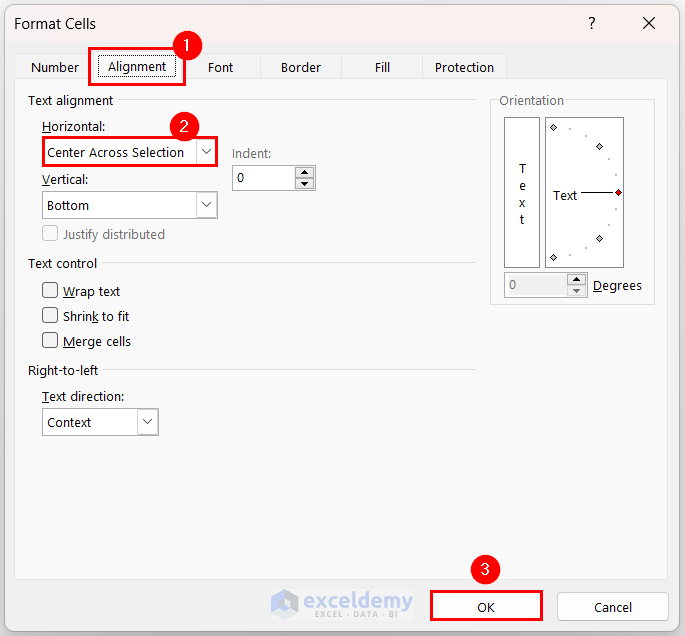
We selected the range B2:G2. - Click the Format Cells dialog box launcher from the Alignment group.
The Format Cells dialog box will appear. - In the Format Cells dialog box:
- Go to the Alignment tab.
- Set the Horizontal Text Alignment to the Center Across Selection option.
- Click OK.
This will display the title center-aligned to the row. You can notice that the title value is in a single cell (cell B2 in this case).
Method 3 – Applying Cell Borders in an Excel Worksheet
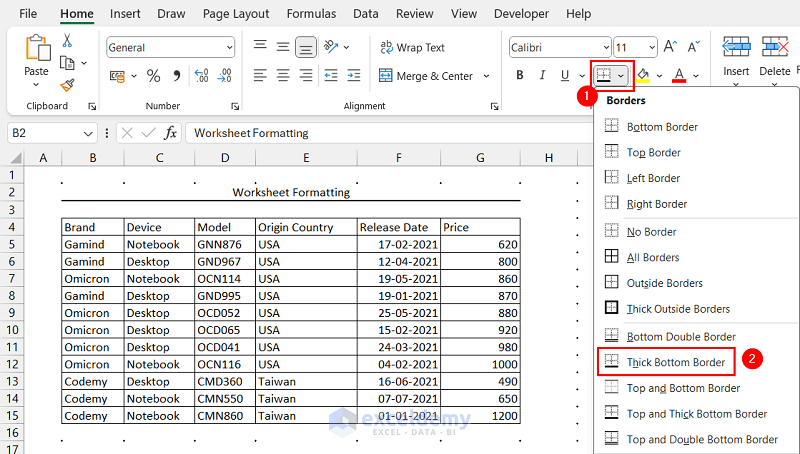
3.1 Apply Thick Bottom Border to Title
The Thick Bottom Border option is useful for differentiating between sections. Thus, applying this border to the title will visually separate it from the data table.
To apply the Thick Bottom Border option in the title, follow the steps below:
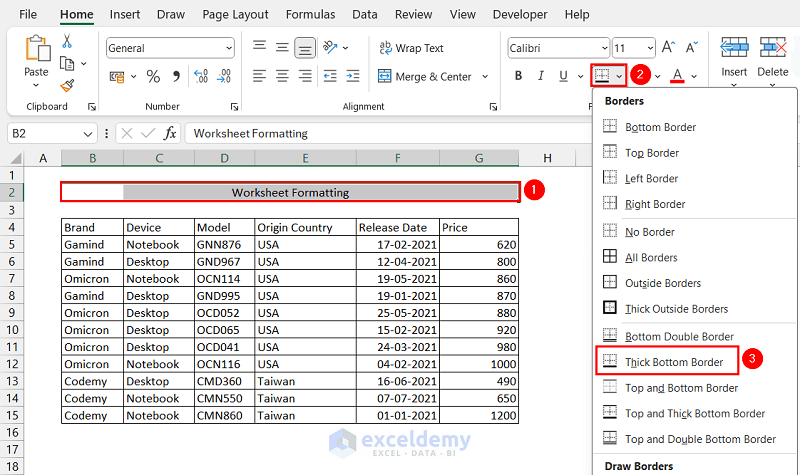
- Select the row where the title is displayed.
- Click the Borders dropdown from the Font group.
- Select the Thick Bottom Border option.
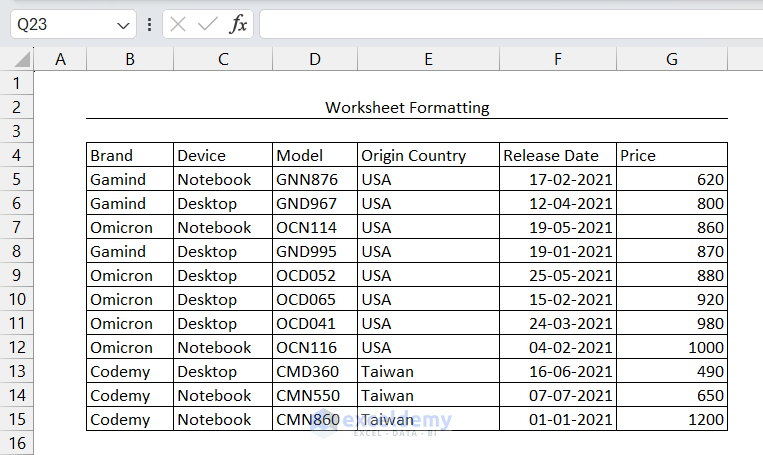
There is a thick bottom border in the title row.
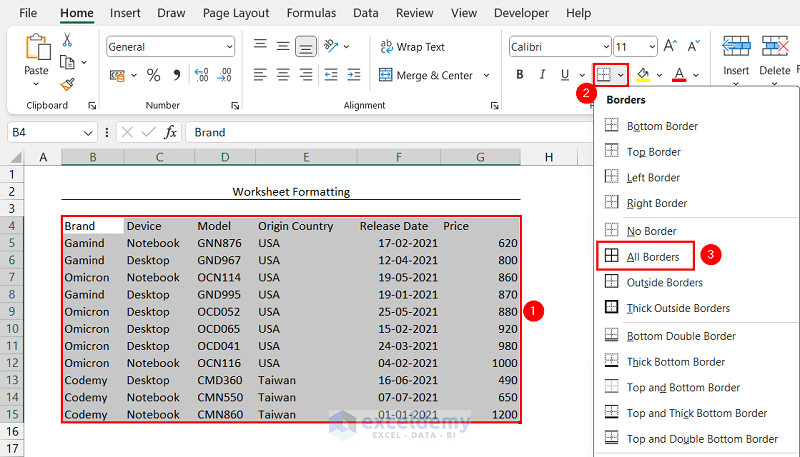
3.2 Apply All Borders Command
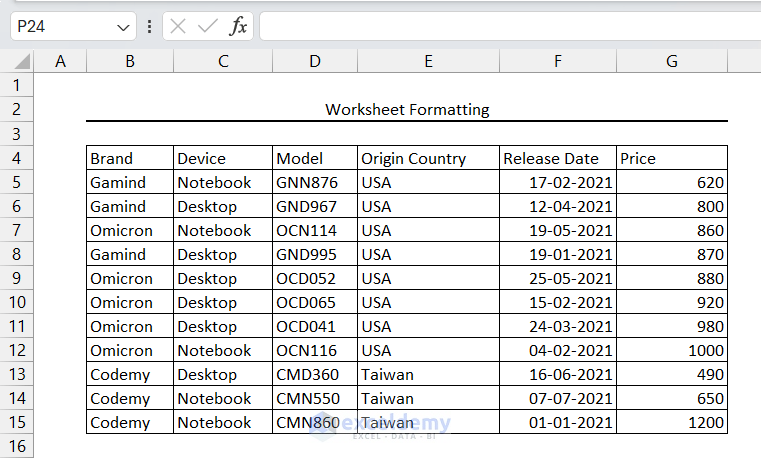
- Select the data table.
We selected the range B4:G15. - Click the Borders dropdown from the Font group.
- Select the All Borders option.
The borders have appeared around each cell of the data table.
3.3 Change Border Color
- Select the row with the title where the thick bottom border was applied.
- Click the Borders dropdown > Line Color > your preferred color. Dot symbols will appear at each corner of cells throughout the worksheet.
- Click the Borders dropdown again and select the Thick Bottom Border option.
This will change the border color of the row with the title.
- Change the border color of the data table as well.
Method 4 – Applying Cell Shading in an Excel Worksheet
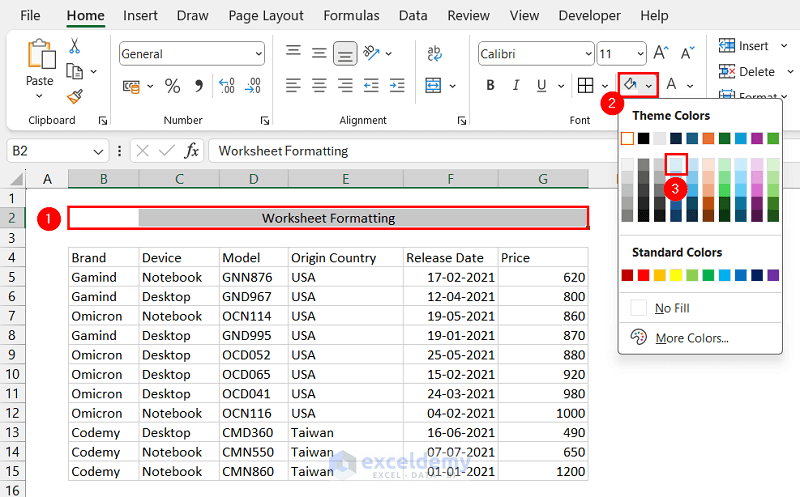
- Select the row with the title.
- Click the Fill Color dropdown from the Font group.
- Select a suitable color.
The selected cell shading will appear in the title row.
- Select the range with column headers.
We selected the range B4:G4. - Click the Fill Color dropdown again and select your preferred color.
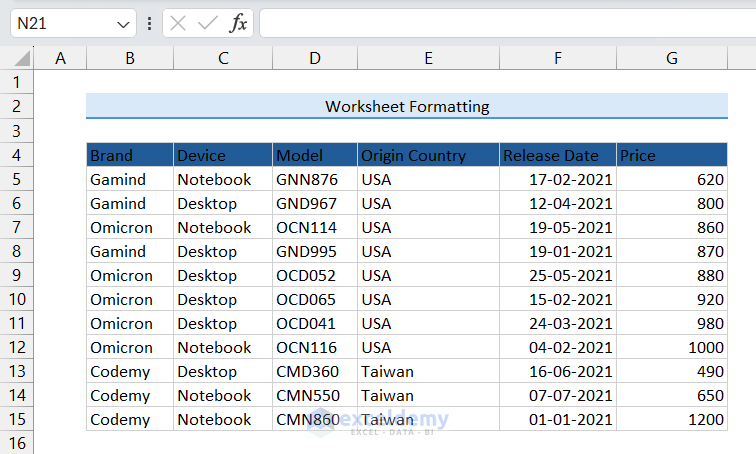
As a result, the title and column header rows will have a fill color like the following image. Using similar steps, you can apply cell shading to any range in a worksheet.
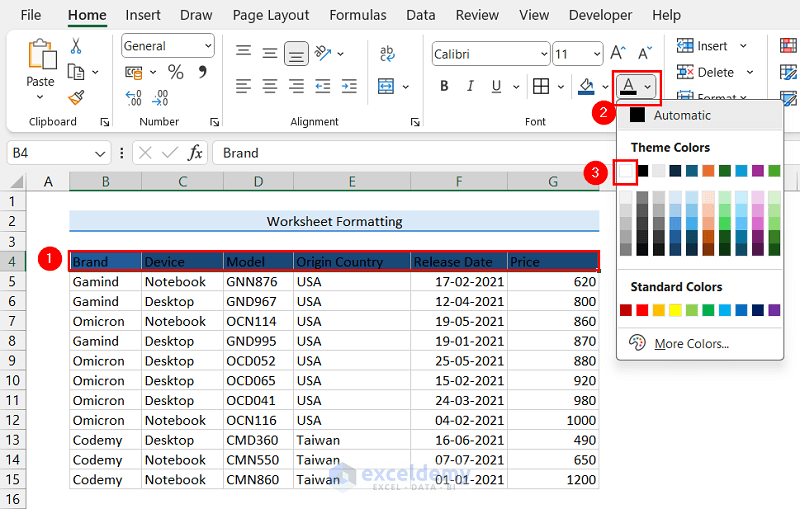
Method 5 – Changing Font Color in Excel
- Select the row with column headers.
- Click the Font Color dropdown from the Font group.
- Select your preferred color.
We selected the White color.
The font color of the column headers row has changed to White.
Method 6 – Changing Font in Excel
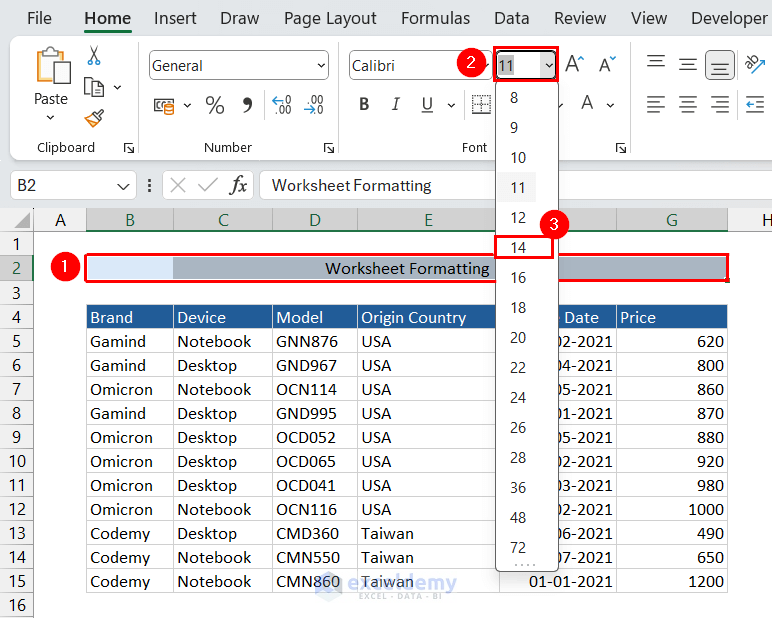
6.1 Change Font Size
- Select the range with the title.
- Click the Font Size dropdown and select 14.
- Select the column headers range and set the font size to 12.
6.2 Change Font Style
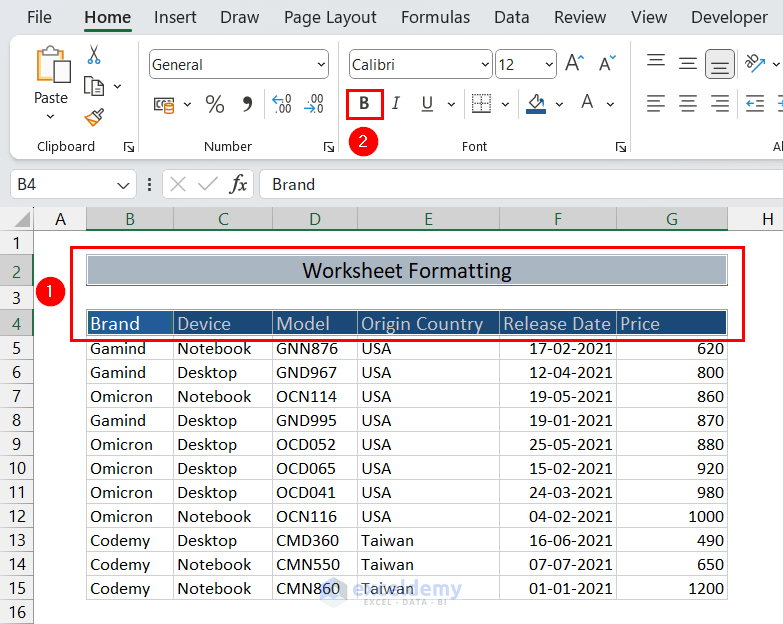
- Press and hold the Ctrl key while selecting the title range and column headers range (i.e. range B2:G2 and B4:G4).
- Click the Bold command button.
This will change the font style of the selected ranges to bold.
- Click the Select All button from the top-left corner of the worksheet.
- Click the Font dropdown and select your preferred font.
We selected the Aptos Narrow font.
The font in the worksheet has changed now.
Method 7 – Changing Data Alignment in Excel
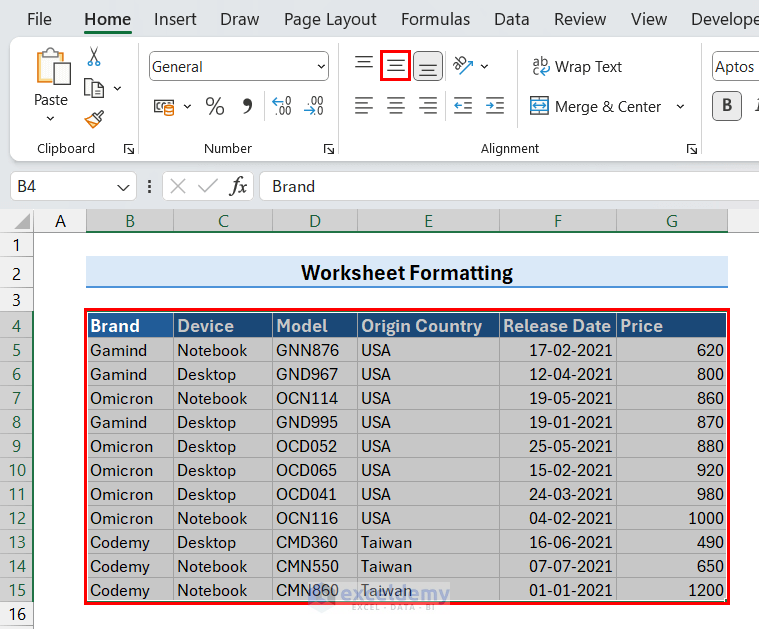
- Select the data table (i.e. range B4:G15).
- Click the Middle Align command from the vertical alignment options.
- Select the column headers (i.e. range B4:G4).
- Click the Center command from the horizontal alignment options.
The data alignment in your worksheet has changed now.
Method 8 – Changing Number Format in Excel
8.1 Modify Date Format
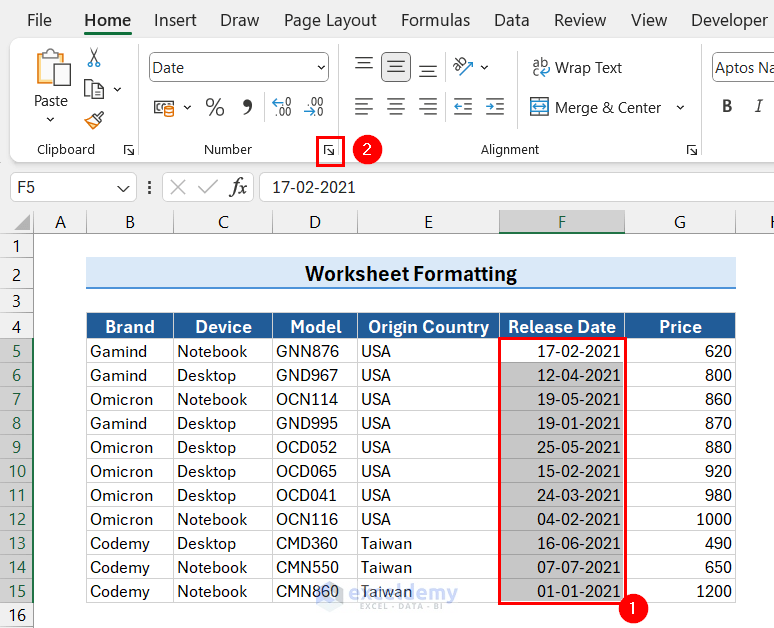
- Select the column with dates.
We selected the range F5:F15. - Click the Format Cells dialog box launcher.
The Format Cells dialog box will appear.
- In the Format Cells dialog box:
- Go to the Number tab.
- Select Date from Category.
- Choose your desired data format.
We selected the dd mmmm yyyy format. - Click OK.
The selected date format has appeared in the target column. You may notice ### symbols in some cells due to inadequate column width. We will discuss the process to fix this issue in the upcoming sections.
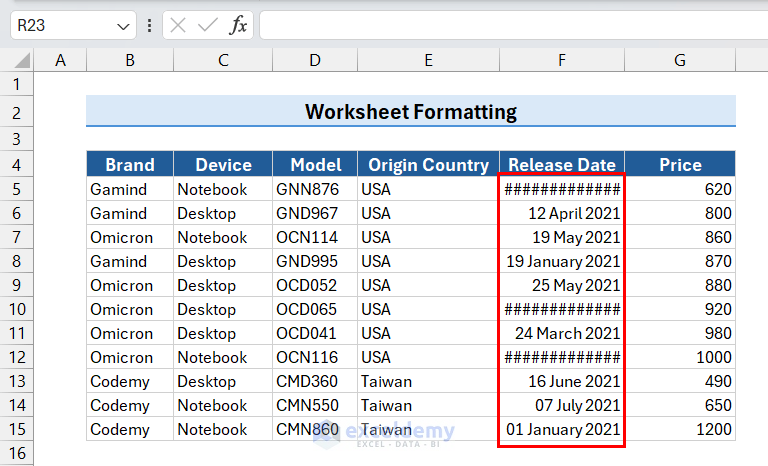
8.2 Apply Accounting Format
- Select the column with price values.
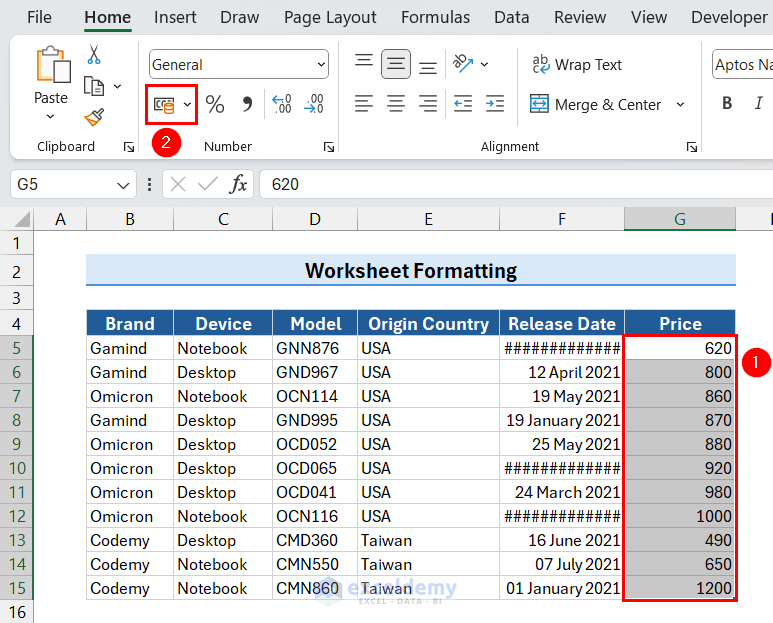
We selected the range G5:G15. - Click the Accounting format button.
This will display the data in Accounting format.
- If you want to change the number of decimal places, click the Increase Decimal or Decrease Decimal buttons.
Method 9 – Changing Column Width in Excel
Sometimes you may ### symbols instead of actual values in some cells. It usually happens due to insufficient column widths. To fix this problem, you have to adjust the column width in Excel.
You can use the following 3 methods to adjust column width in Excel:
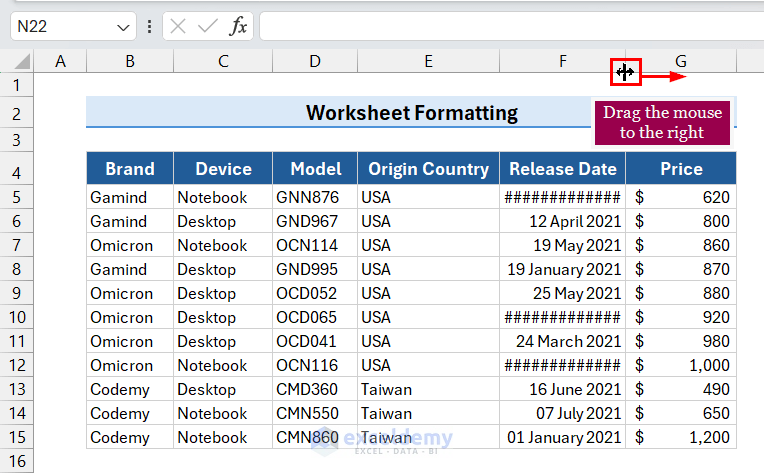
9.1 Use Mouse to Change Column Width
- Hover the mouse pointer at the column bar’s right side in the desired column.
The drag icon will appear. - Drag the column bar to the right until you get the desired width.
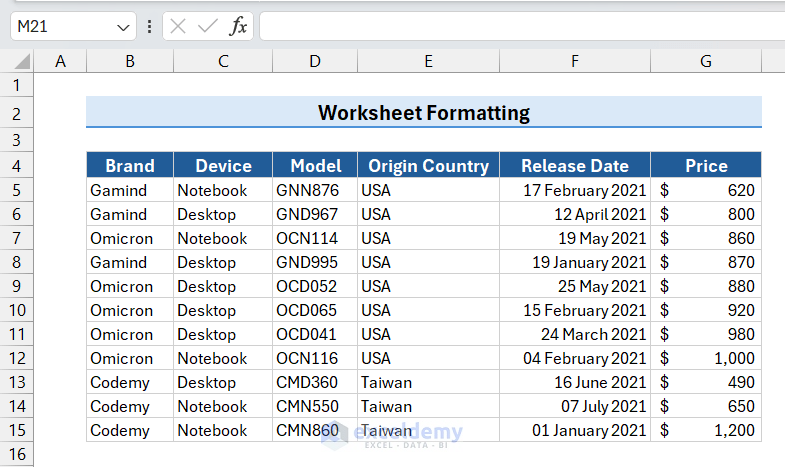
The column width is adjusted, and the dates appear.
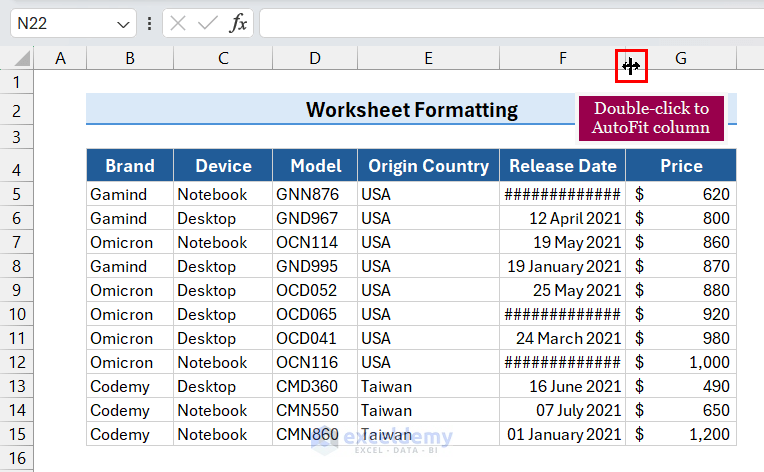
9.2 AutoFit Column
- Hover the mouse pointer at the column bar’s right side in the desired column.
- Double-click on the column bar’s right side.
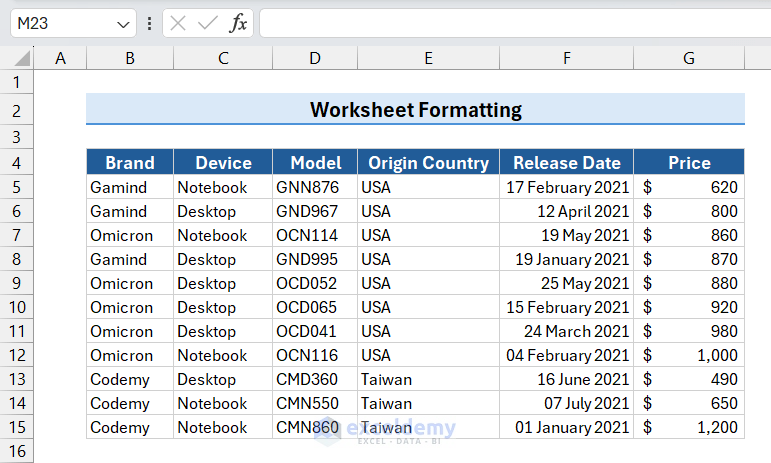
The column width will adjust automatically to fit the data in the column.
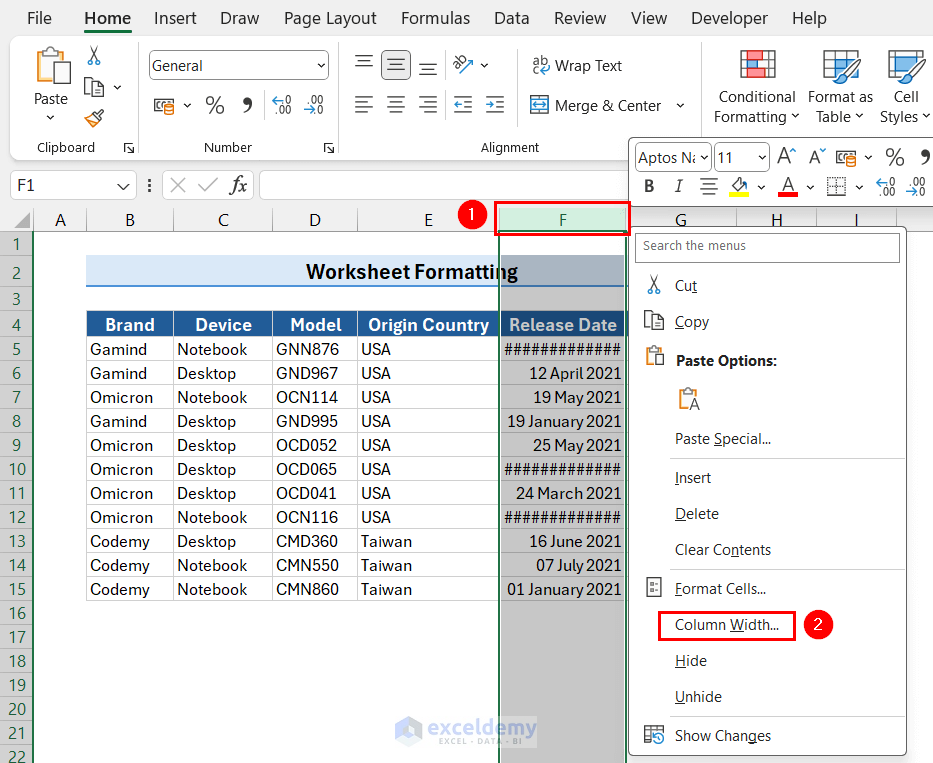
9.3 Set Column Width to a Specific Number
- Select the desired column by clicking on the column bar.
- Right-click on your mouse to open the context menu.
- Select the Column Width option.
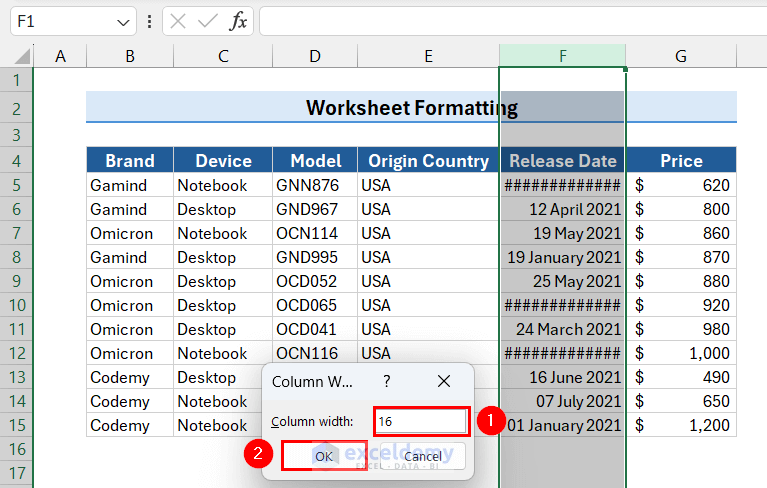
- Enter the desired column width value in the Column Width dialog box and click OK.
This will adjust the column width in your selected column.
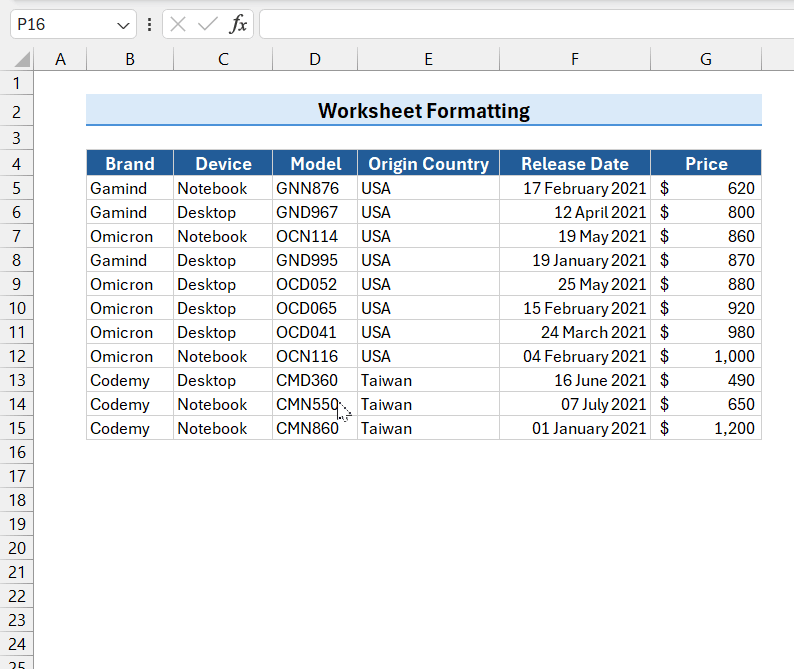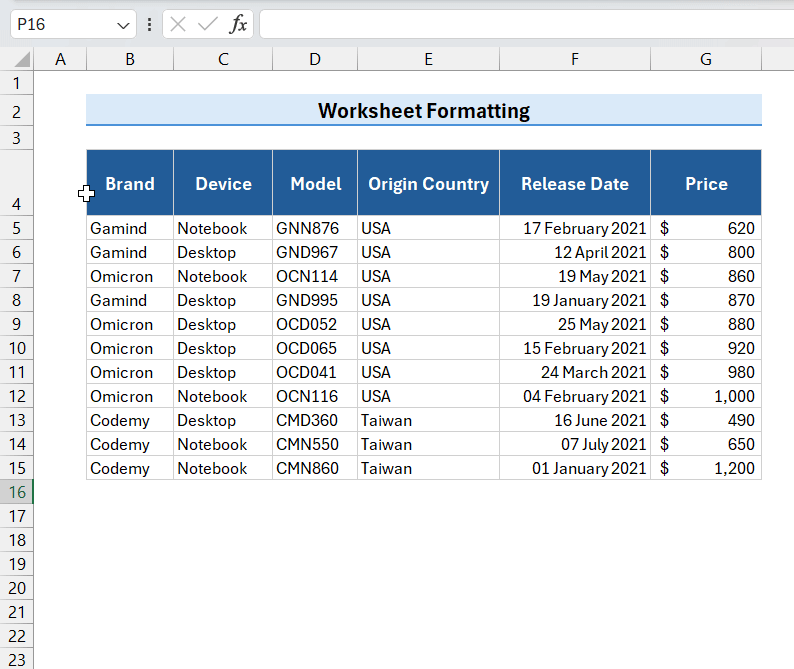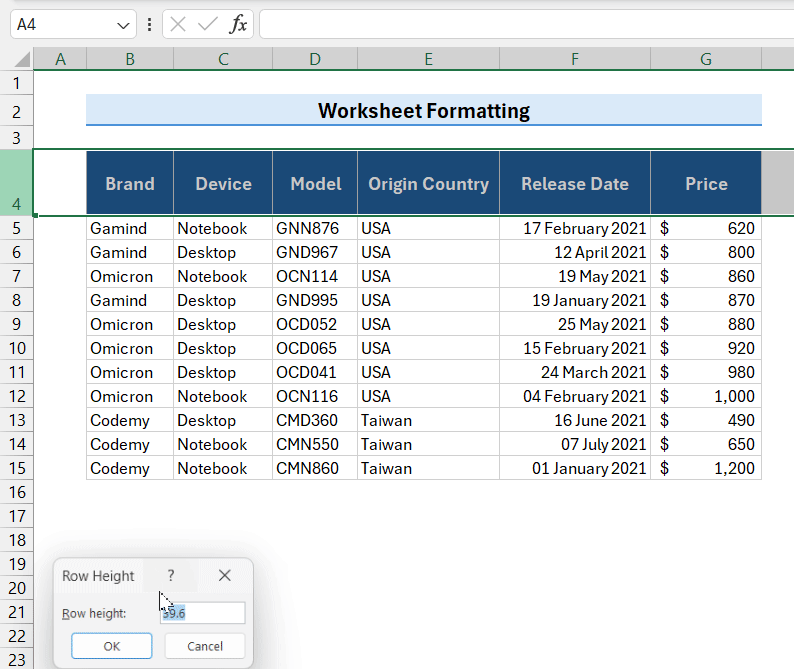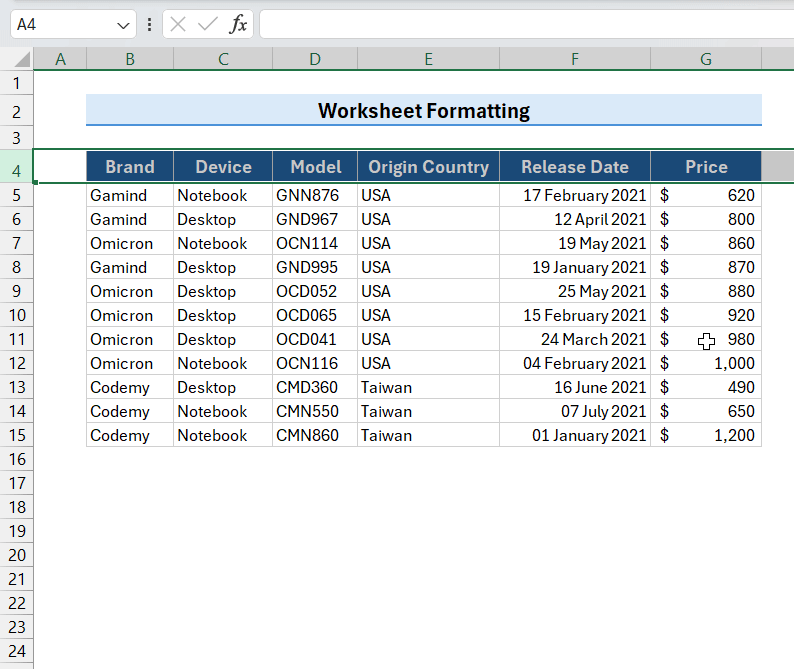
Method 10 – Changing Row Height in Excel
When you add multi-line texts with the Wrap Text feature, the entire data may not be displayed due to insufficient row height. To fix that, you can adjust row heights in your worksheet. You may adjust the row height to adjust the vertical spacing in a row as well simply.
Method 11 – Applying Conditional Formatting in Excel
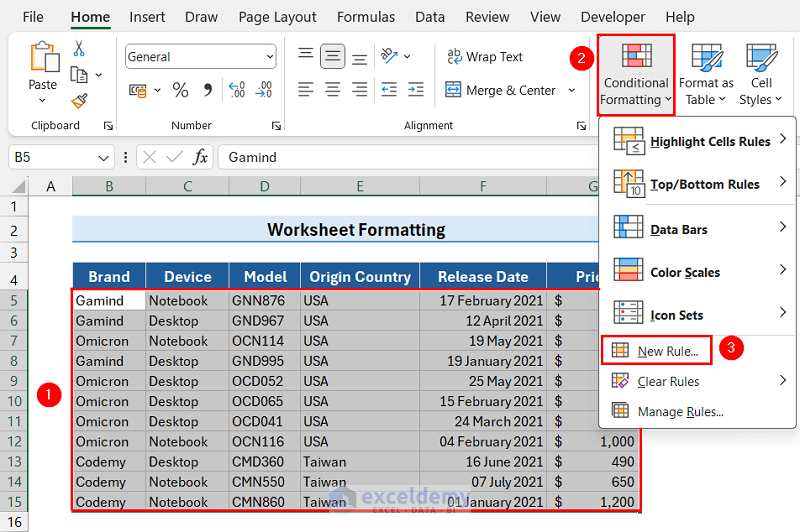
- Select the rows for which you want to set alternative row colors.
We selected the range B5:G15. - Click the Conditional Formatting dropdown and select the New Rule option.
The New Formatting Rule dialog box will appear.
- In the New Formatting Rule dialog box:
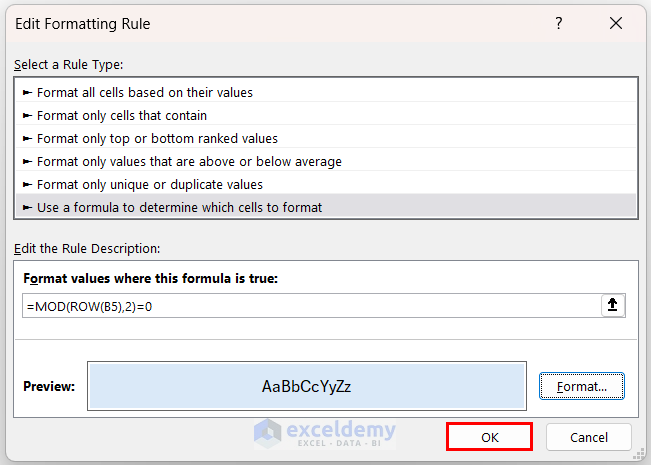
- Select the rule type Use a formula to determine which cells to format.
- Set the formatting rule to:
=MOD(ROW(B5),2)=0 - Click the Format button.
This will open the Format Cells dialog box.
- In the Format Cells dialog box:
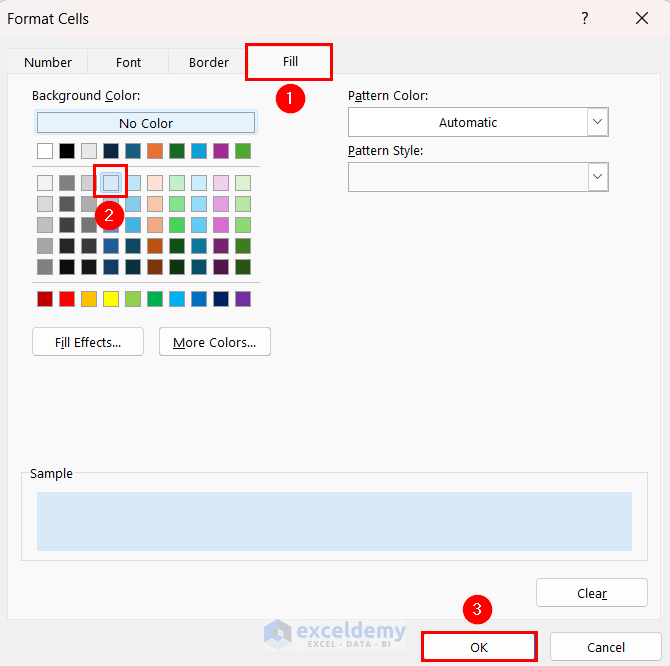
- Go to the Fill tab.
- Select your preferred background color.
- Click OK.
- Now, you can preview the selected format in the Edit Formatting Rule dialog box. Click OK in this dialog box as well.
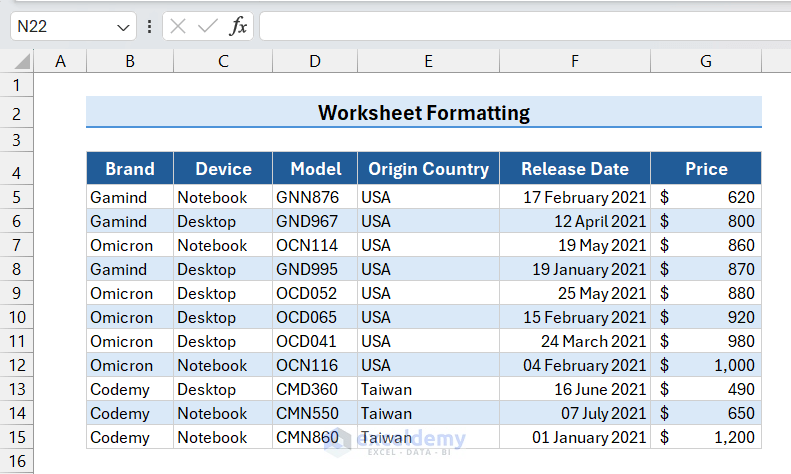
The alternative row colors are applied to the selected range in the worksheet.
Download Practice Workbook
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I quickly change the format of a worksheet?
Here are the steps to change the format of a worksheet quickly:
- Go to the Page Layout tab.
- Click the Themes dropdown.
- Hover the mouse pointer over various themes to see the change in the worksheet format.
- Select your preferred theme.
Can I copy formatting from one worksheet to another?
Yes, you can copy any worksheet format to other worksheets. Here are the steps to copy worksheet formatting to other sheets:
- Select the cell or range whose formatting you want to copy.
- Press the Ctrl+C keys to copy the cell.
- Go to the target worksheet.
- Select the cell or range where you want to paste the formatting.
- Right-click on the mouse to open the context menu.
- Select Formatting from the Paste Options.
How to freeze a row in a worksheet?
While working with worksheets containing a large dataset, we often need to freeze rows to keep specific rows visible when we scroll down. Consider a situation where you need to freeze the 5th row in a worksheet. Here are the steps to freeze that row:
- Click the row bar of the 6th row.
- Go to the View tab.
- From the Freeze Panes dropdown, click the Freeze Panes option.
<< Go Back to Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!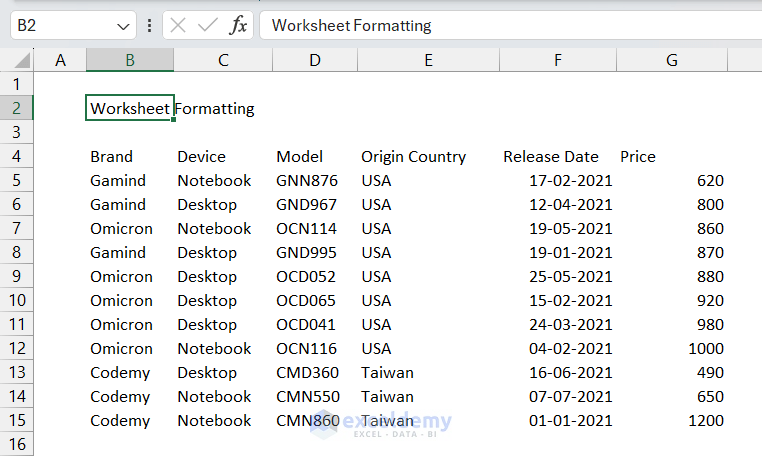
 This will change the border color of the row with the title.
This will change the border color of the row with the title.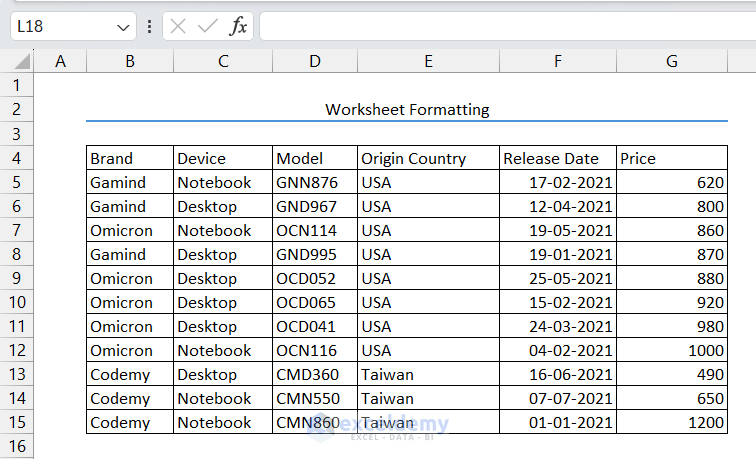
 The selected cell shading will appear in the title row.
The selected cell shading will appear in the title row.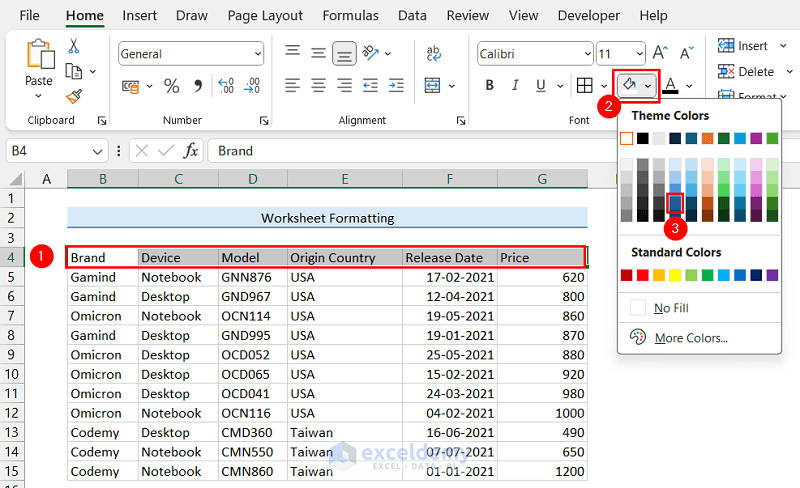
 This will change the font style of the selected ranges to bold.
This will change the font style of the selected ranges to bold.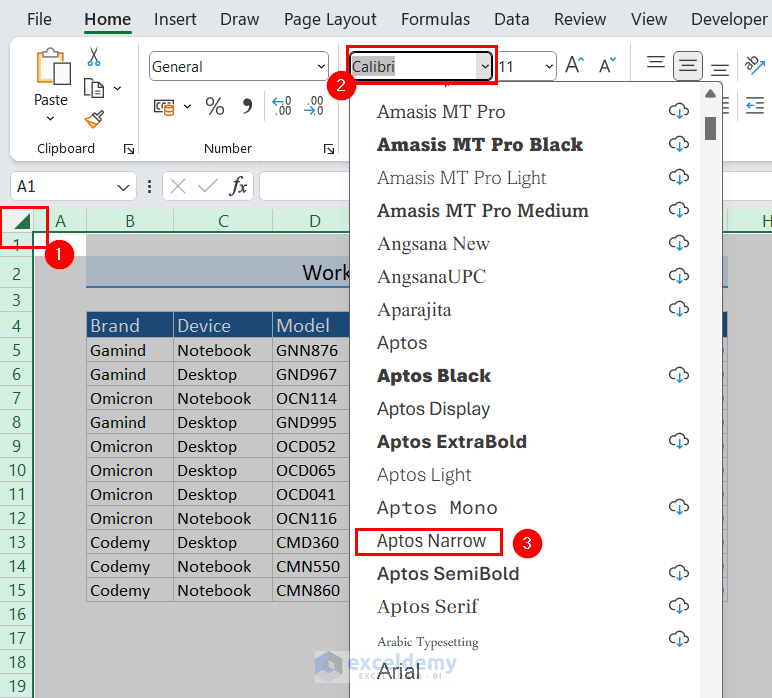
 The Format Cells dialog box will appear.
The Format Cells dialog box will appear.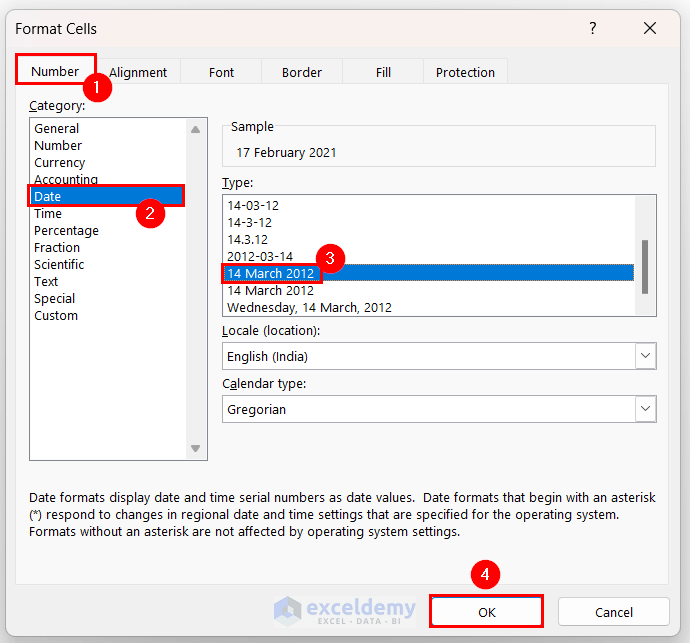
 This will display the data in Accounting format.
This will display the data in Accounting format.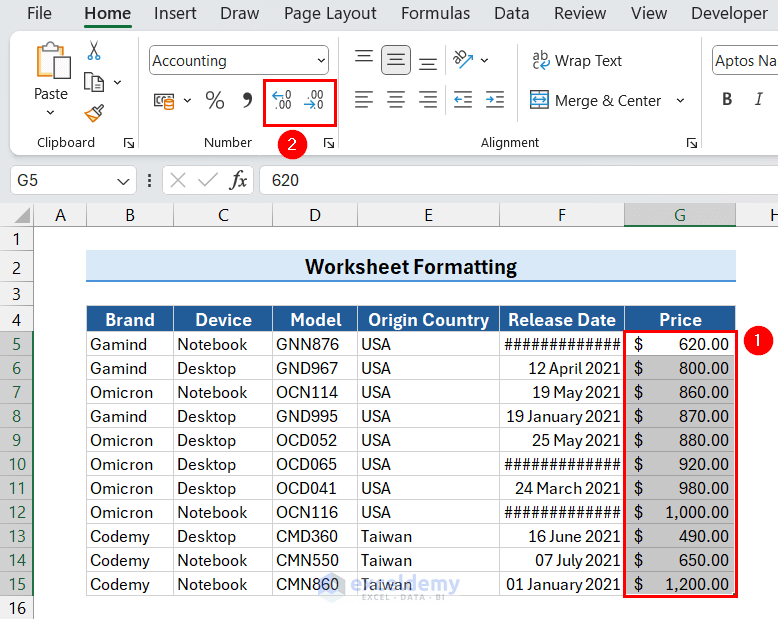
 The New Formatting Rule dialog box will appear.
The New Formatting Rule dialog box will appear.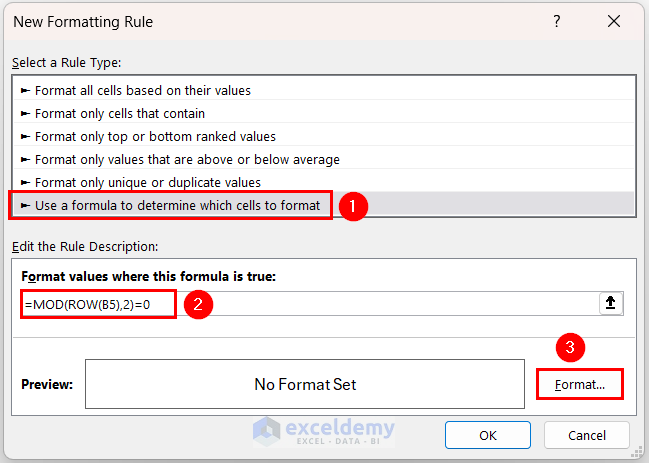 This will open the Format Cells dialog box.
This will open the Format Cells dialog box.