This article illustrates how to calculate the Confidence Interval in Excel for a difference in Means. Various statistical functions and tools in Excel allow us to perform numerous statistical operations saving time and labor. You can calculate confidence interval using the statistical functions or the Data Analysis tool in Excel. The following picture shows a sample result obtained from such operations. Follow the article to learn how it’s done.
What Is Confidence Interval?
Confidence Interval (CI) is a statistical term referring to a range of values that include a population with an assumed confidence level. It is often used to analyze the statistical significance of a certain estimation. It depends on the sample size, sample variance, and confidence level. Statisticians normally use a 95% confidence level to calculate the confidence interval. People often misunderstand or misinterpret it saying that 95% of the sample values lie within the confidence interval though it may not be the case.
How to Calculate Confidence Interval in Excel for Difference in Means: 2 Possible Ways
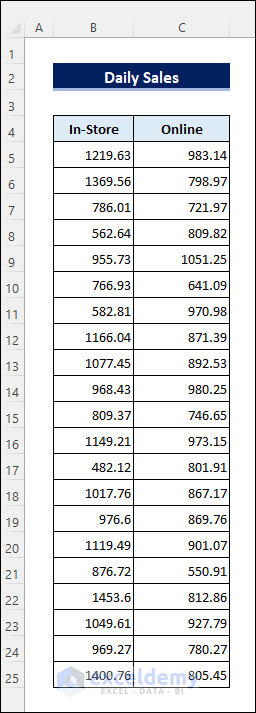
Assume you are the manager of a bookstore with an online extension. You are wondering if the average daily sales through the website of the store are any different than the in-store sales. So you have collected the sales data for 3 weeks both from the in-store and online sales.
Now you want to calculate the confidence interval based on this dataset to come to a conclusion. Follow the methods below to be able to do that in Excel.
1. Calculate Confidence Interval for Difference in Means Using Formulas
Follow the steps below to calculate the Confidence Interval for Difference in Means Using formulas in Excel.
📌 Steps:
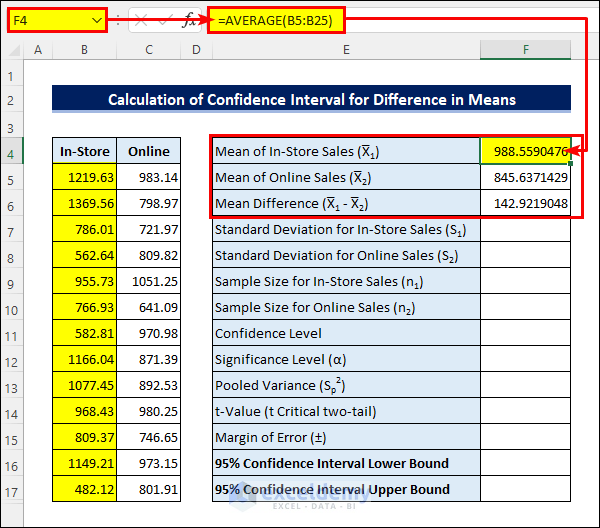
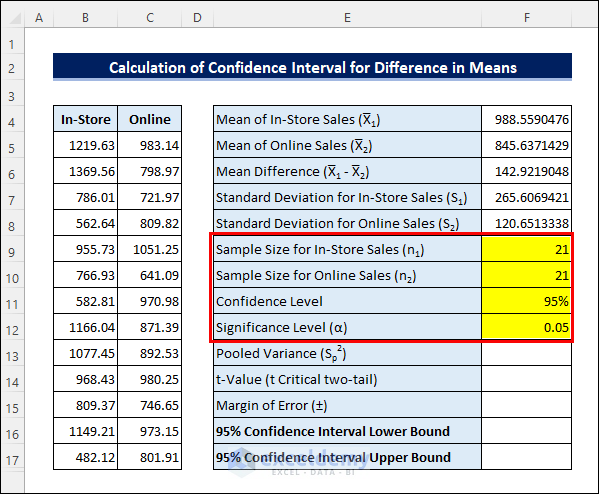
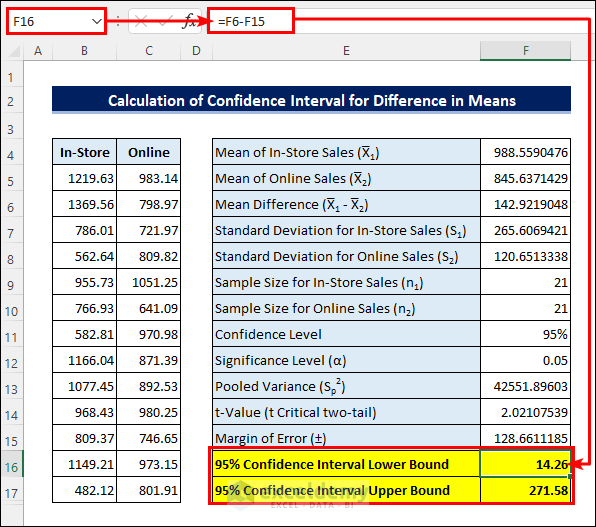
- First, enter the following formula in cell F4 to calculate the Mean of In-Store sales. Then, calculate the Mean of Online sales in a similar way. Next, subtract the two Means to get the Mean Difference.
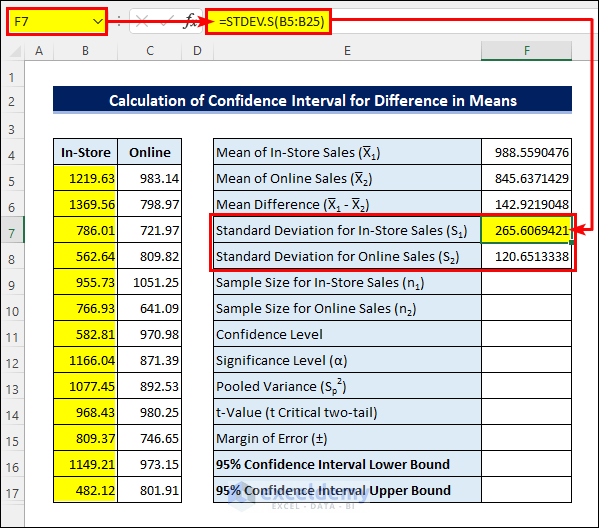
=AVERAGE(B5:B25)- After that, apply the formula in cell F7 to get the Standard Deviation for In-Store sales. Then calculate that for Online sales similarly.
=STDEV.S(B5:B25)- Next, input the sample sizes and Significance Level.
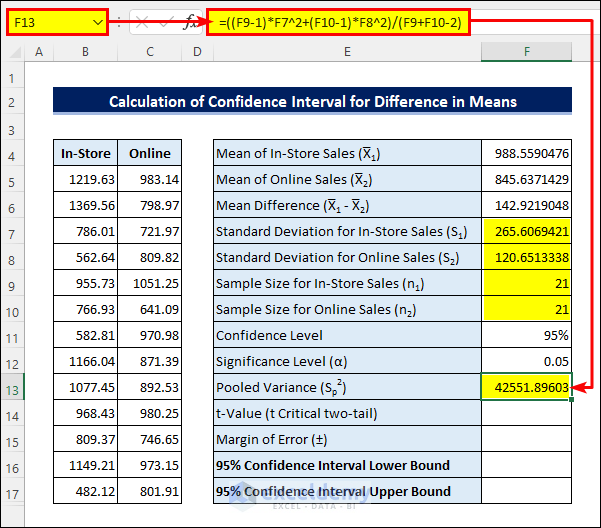
- After that, apply the following formula in cell F13 to calculate the Pooled Variance.
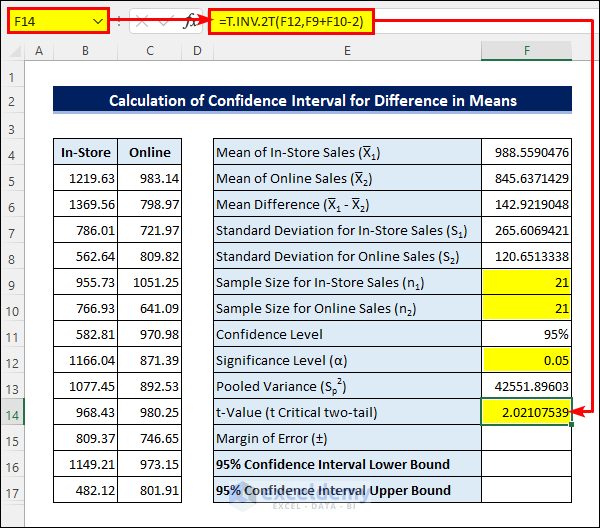
=((F9-1)*F7^2+(F10-1)*F8^2)/(F9+F10-2)- Then, enter the following formula in cell F14 to calculate the t-Value.
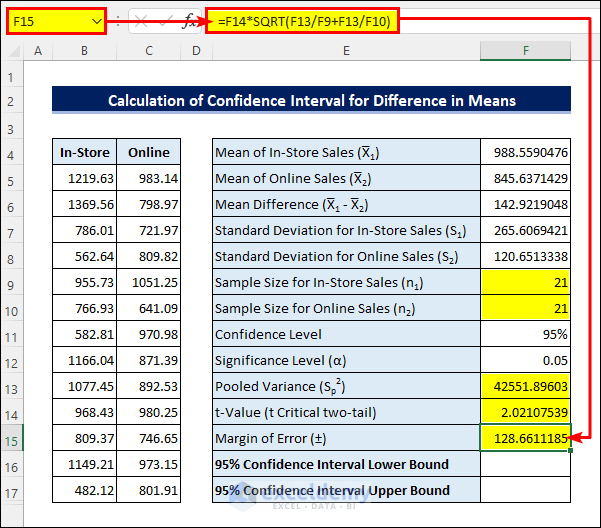
=T.INV.2T(F12,F9+F10-2)- Next, apply the following formula in cell F15 to get the Margin of Error.
=F14*SQRT(F13/F9+F13/F10)- Finally, subtract the Margin of Error from the Mean Difference to get the Confidence Interval Lower Bound. And add them to get the Upper Bound.
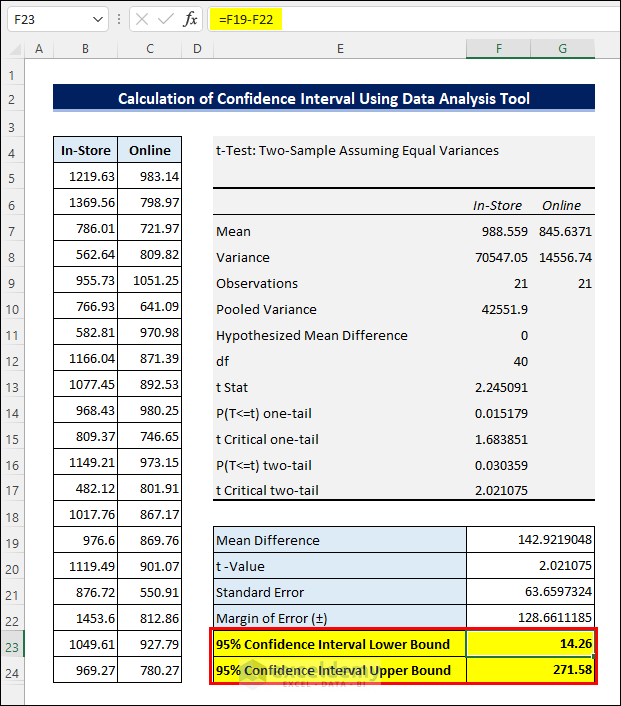
- The results suggest that there is a possibility that the Mean of daily In-Store sales will be $14.26 to $271.58 higher than Online sales.
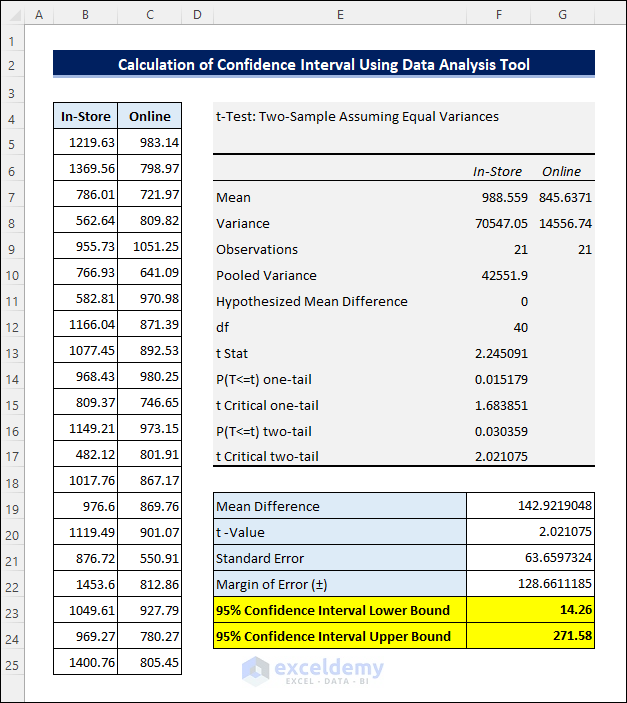
2. Calculate Confidence Interval for Difference in Means Using Data Analysis Tool
Follow the steps below to calculate the Confidence Interval for Difference in Means Using the Data Analysis tool in Excel.
📌 Steps:
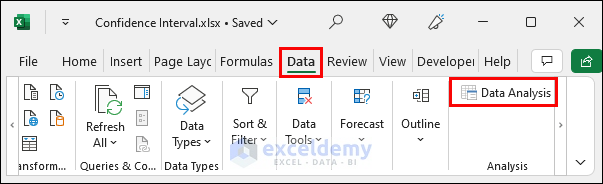
- First, select Data >> Data Analysis. You need to enable the Analysis Toolpak add-in to access it from there.
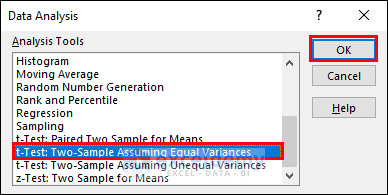
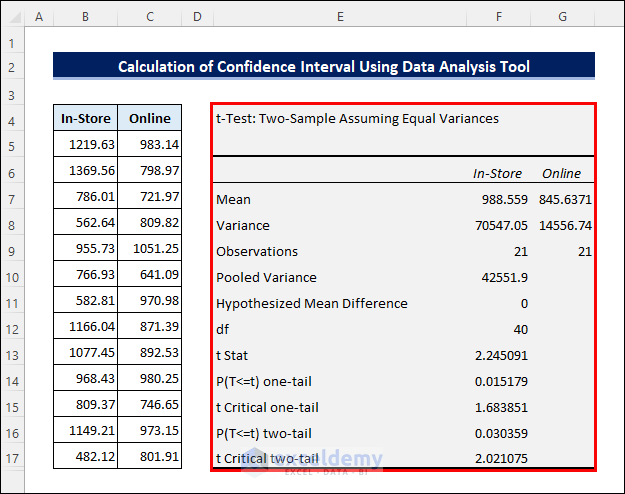
- Then, choose t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Equal Variances and click OK.
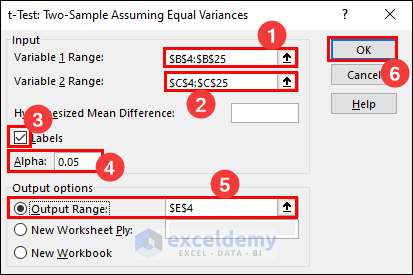
- Next, select the sample ranges as the Variable 1 Range and Variable 2 Range respectively. Then check the Labels checkbox and keep the Alpha value to 0.05. Now, enter the output range and click OK.
- After that, you will get the following result.
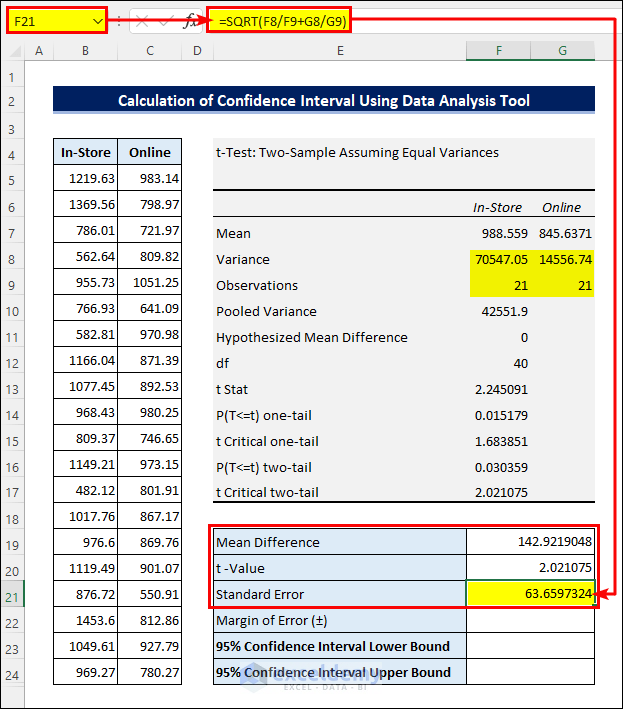
- Then calculate the Mean Difference by subtracting the two Means. You have the t-Value from the analysis. Now apply the following formula in cell F21 to calculate the Standard Error.
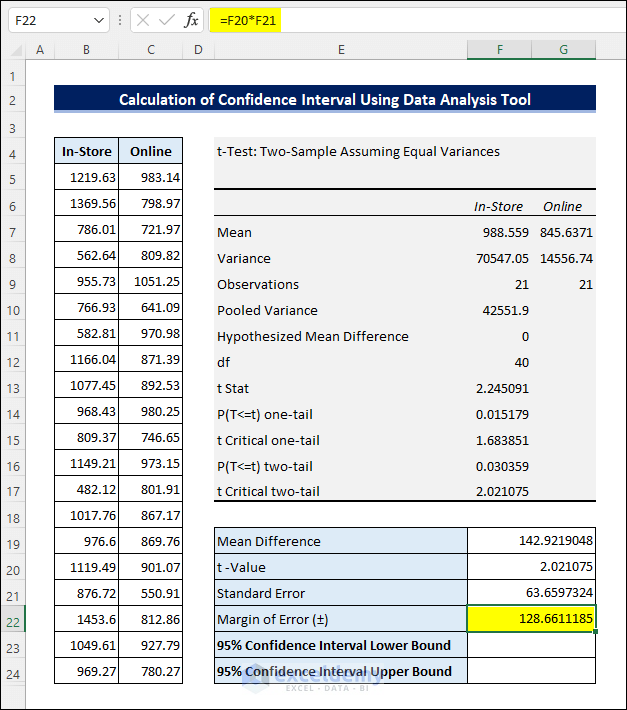
=SQRT(F8/F9+G8/G9)- Then multiply the t-Value with the Standard Error to get the Margin of Error.
- Finally, you can calculate the Confidence Interval by adding and subtracting the Margin of Error to and from the Mean Difference as earlier.
Things to Remember
- You can enable the Data Analysis tool from File >> Options >> Add-ins >> Go if it is not enabled already.
- You can use a different confidence level or assume unequal sample variances if required.
Download Practice Workbook
You can download the practice workbook from the download button below.
Conclusion
Now you know how to calculate the Confidence Interval for Difference in Means in Excel. Hope this helped. Do you have any further queries or suggestions? Please let us know in the comment section below. Stay with us and keep learning.
Related Articles
- How to Calculate P-Value from Confidence Interval in Excel
- How to Calculate Population Proportion in Excel
- How to Calculate Confidence Interval Without Standard Deviation in Excel
- How to Calculate Confidence Interval Proportion in Excel
- How to Add Confidence Interval Error Bars in Excel
- How to Calculate Confidence Interval for Population Mean in Excel
<< Go Back to Confidence Interval Excel | Excel for Statistics | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!