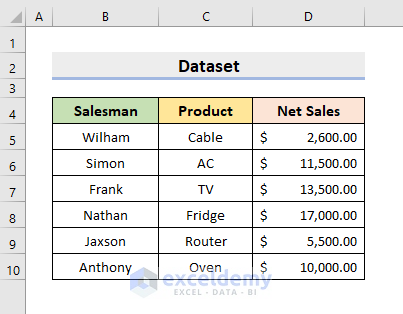
To illustrate how to Save as in various ways using VBA, we’ll use the following dataset containing the Salesman, Product, and Net Sales data of a company.
Example 1 – Save as Excel File
Let’s start with a simple VBA Code to save an Excel file.
STEPS:
- Go to the Developer tab.
- Select Visual Basic.
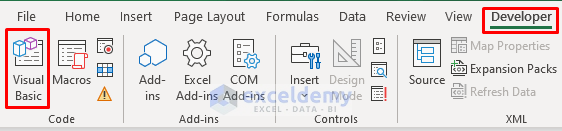
As a result, the VBA window will pop out.
- Click Insert.
- Select the Module.
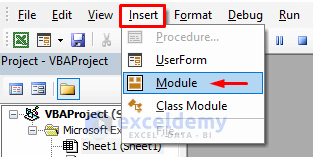
The Module window will appear.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the box:
Sub Example_1()
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs
End Sub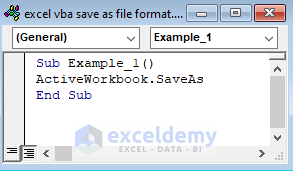
- Run the code by pressing F5.
- Input the file name, format, and other info as requested.
The file will be saved in your specified location.
Read More: Excel VBA to Save as File Using Path from Cell
Example 2 – Specify the File Extension
In the previous example, we had to manually specify the File Format after pressing the run command, but we can also specify the file extension after the file name in our code.
Insert the below code in the Module window:
Sub Example_2()
Dim location As String
location = "D:\SOFTEKO\excel vba save as file format.xlsm"
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=location
End Sub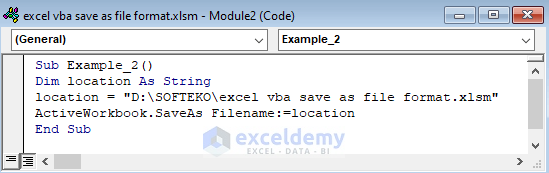
Run the code to save the file in the desired format and location.
To save the file in the xlsx Format, type xlsx instead of xlsm.
Read More: How to Use Macro to Save Excel File with New Name
Example 3 – Use File Format Code
We can input the File Format Code Number instead of specifying the file extension. Some useful codes are: .xlsx = 51, .xlsm = 52, .xlsb = 50, .xls = 56.
Copy the following code and paste it into the Module box:
Sub Example_3()
Dim location As String
location = "D:\SOFTEKO\excel vba save as file format"
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=location, FileFormat:=52
End Sub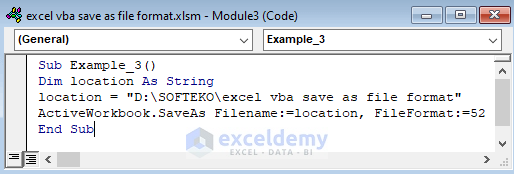
Read More: How to Save Excel Macro Files as Filename from Cell Value
Example 4 – Save in the Same Directory
It’s a simple process to Save into the Same Directory as the existing file.
Insert the following code in the Module window:
Sub Example_4()
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:="excel vba save as file format"
End Sub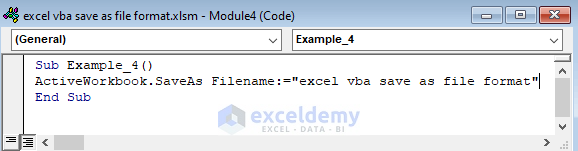
Example 5 – Save to a New Directory
Enter the following code in the Module box and run it.
Sub Example_5()
Dim location As String
location = "D:\SOFTEKO\excel vba save as file format"
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=location
End Sub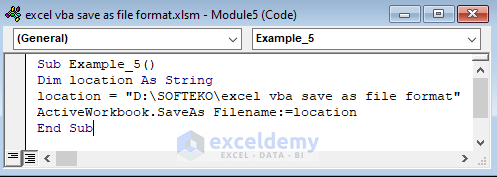
Example 6 – Ask for Password to Open Excel File
We can ask for a Password to Open Excel File.
Insert and run the following code in the Module window:
Sub Example_6()
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs _
Filename:="D:\SOFTEKO\excel vba save as file format.xlsm", Password:="one"
End Sub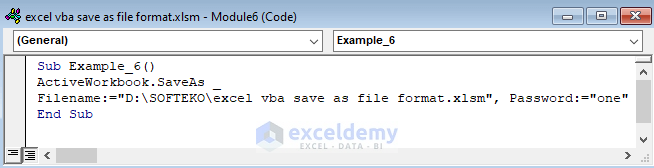
Example 7 – Add a Password for Editing
Moreover, you can ask for a Password for Editing when opening the saved file in Excel. Without the password, it’ll only open in read-only format.
Copy the following code and paste it in the Module window, then run the code:
Sub Example_7()
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs _
Filename:="D:\SOFTEKO\excel vba save as file format.xlsm", WriteRes:="one"
End Sub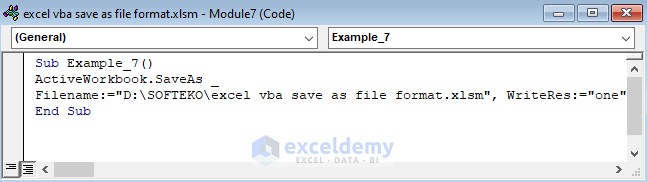
Example 8 – Open in Read-only Format
Enter the following code in the Module window and press F5 to run it:
Sub Example_8()
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs _
Filename:="D:\SOFTEKO\excel vba save as file format.xlsm", _
ReadOnlyRecommended:=True
End Sub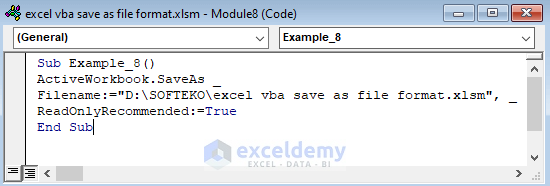
Example 9 – Generate a ‘Save As’ Dialog Box
Insert the following code in the Module window and run it:
Sub Example_9()
Application.GetSaveAsFilename
End Sub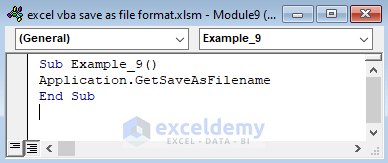
Example 10 – Create & Save a New Workbook
In addition to saving a file, we can also Create & Save New Workbook with VBA code.
Enter the following code in the Module window and press F5 to run it:
Sub Example_10()
Dim book As Workbook
Set book = Workbooks.Add
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
book.SaveAs Filename:="D:\SOFTEKO\excel vba save as file format.xlsm"
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End Sub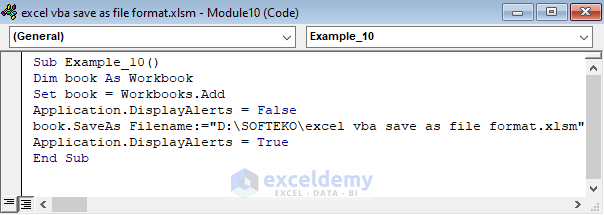
Example 11 – Save the Active Workbook
Likewise, we can save the active workbook where it’s already stored.
Simply insert the following very simple code in the Module window and press F5 to run it:
Sub Example_11()
ActiveWorkbook.Save
End Sub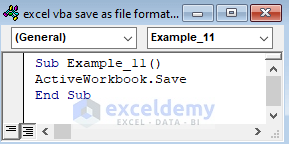
Example 12 – Save as PDF Format
We can use the PDF file extension to save in PDF Format.
Enter the following code in the Module window, and run it by pressing F5:
Sub Example_12()
ActiveSheet.SaveAs Filename:="excel vba save as file format.pdf"
End Sub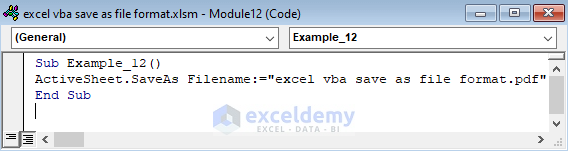
Read More: Excel Macro to Save as PDF
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- Create New Workbook and Save Using VBA in Excel
- Excel VBA to Save File with Variable Name
- Excel VBA: Save Workbook as New File in Same Folder
- Excel VBA to Save Workbook in Specific Folder with Date
- Excel VBA: Save Workbook in Specific Folder
- Excel VBA: Save Workbook Without a Prompt



Sorry for my limited knowledge. You should show the result for each VBA….Thanks.
Right now, I have some problem on excel in window 11.
‘Text to column’ is necessary after Copy & Paste.
I do not want to do ‘text to column’ manually.