In Excel, we apply basic to complex formulas. Depending on the scenario use of the formula changes. In case you have any formula dependent on multiple variables, and you want to see how the changes occur with the change of the inputs. You may change all variables individually which is time-consuming. So you can use the Data Table feature from the Excel ribbon. You can use the What-If Analysis tool to observe all values outcomes at a glance. In this article, I’m going to show you an example(s) of an Excel data table
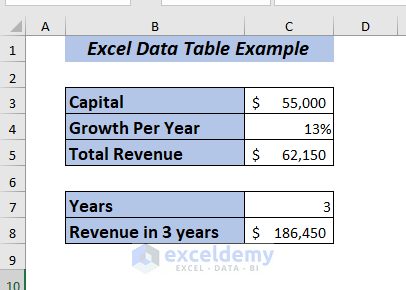
To make the explanation of the examples clearer, I’m going to use the information of any company, Capital, Growth Per Year, Total Revenue, Years, and Revenue in Years.
Information of Excel Data Table
Before diving into the examples, I want to give some basic ideas of the data table. There are 2 types of data tables.
➤ One-Variable Data Table
One variable data table allows testing a series of values for a single input cell; it can be either the Row input cell or Column input cell and shows how those values change the result of a related formula.
It is best suited when you want to see how the eventual result changes when you change the input variables.
➤ Two-Variable Data Table
A two-variable data table allows testing a series of values for a double input cell; You can use both the Row input cell and Column input cell and shows how changing two input values of the same formula changes the output
It is best suited when you want to see how the eventual result changes when you change two input variables.
Example of Excel Data Table: 6 Criteria
1. One Variable Data Table Example – Generating Total Revenue
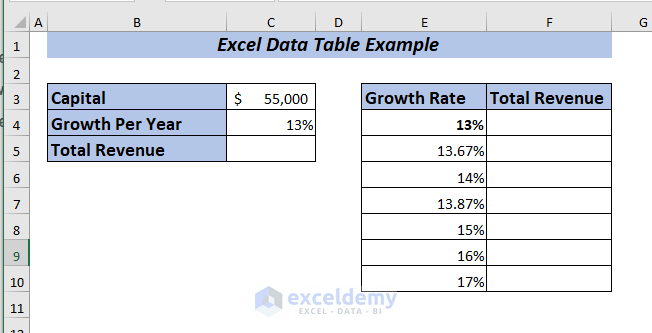
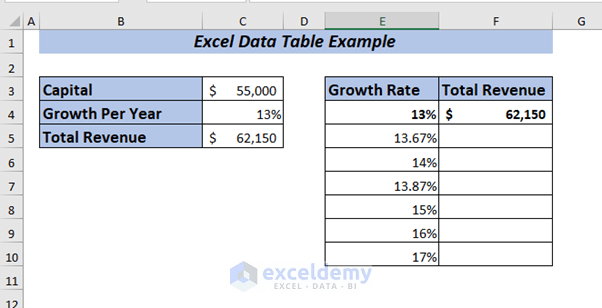
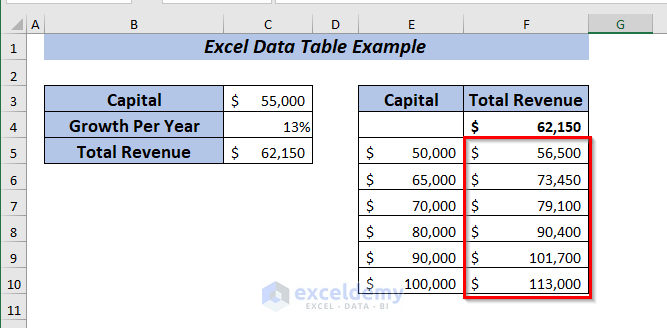
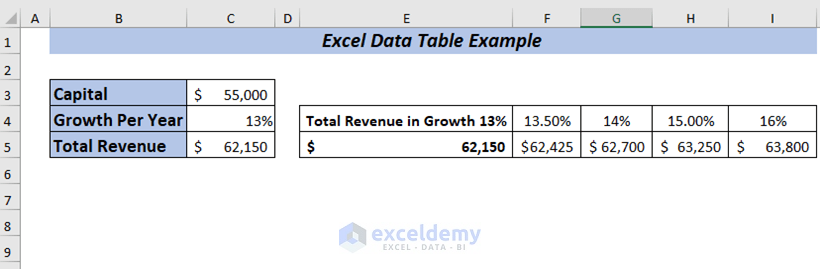
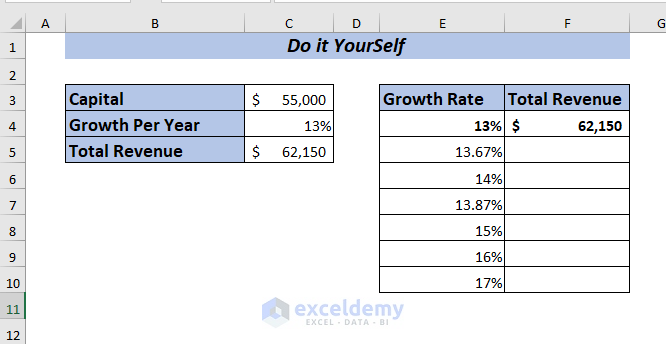
I’m going to show you an example of an Excel data table by using one variable data of a company. I want to observe the total revenue changes if I use different growth percentages.
As I have the information of Capital and Growth Per Year of the company. Now, I want to know how the Total Revenue will change for the given percentages.
First, by using the value of Capital and Growth Per Year I’ll determine the Total Revenue.
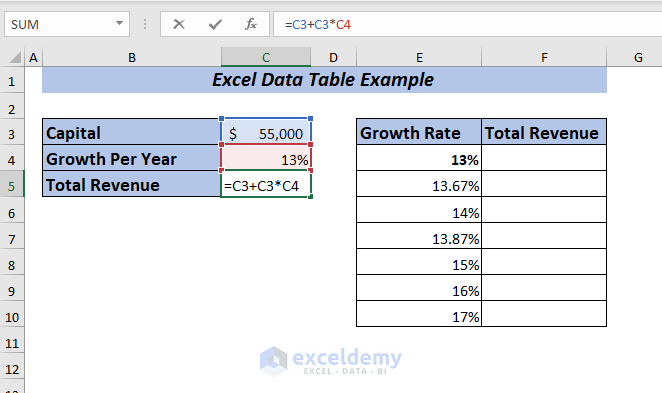
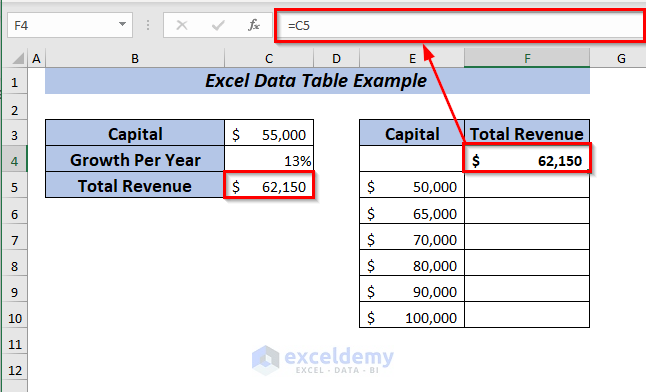
⏩ In cell C5, type the following formula.
=C3+C3*C4Here, I multiplied the Capital with the Growth Per Year and then added the result with the Capital to get the Total Revenue.
Press ENTER, and you will get the Total Revenue for the year with 13% growth.
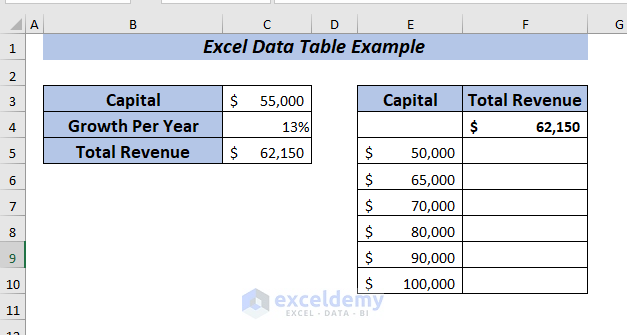
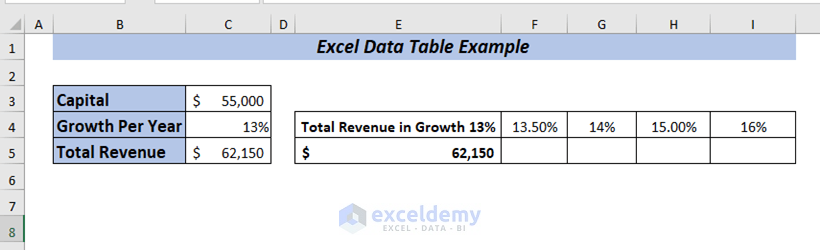
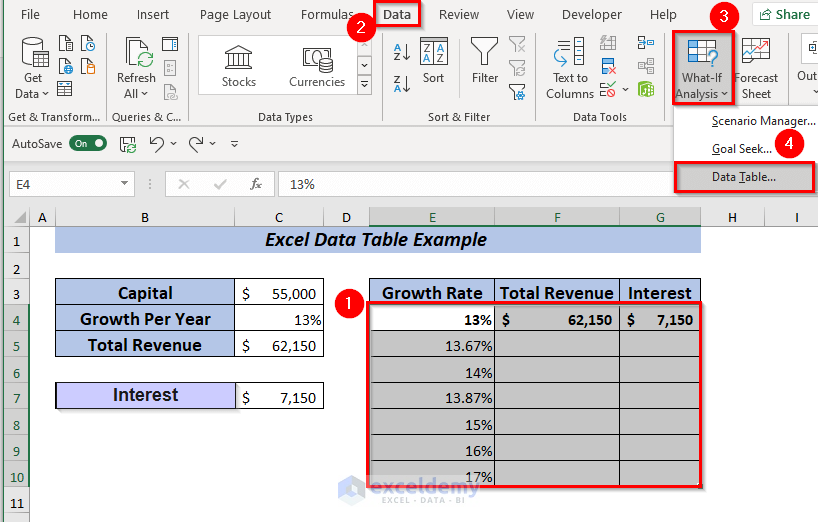
Now, I want to perform a What-If-Analysis to see how the Total Revenue will change if I use the Growth Per Year ranging from 13% to 17% depending on the Capital amount of the company.
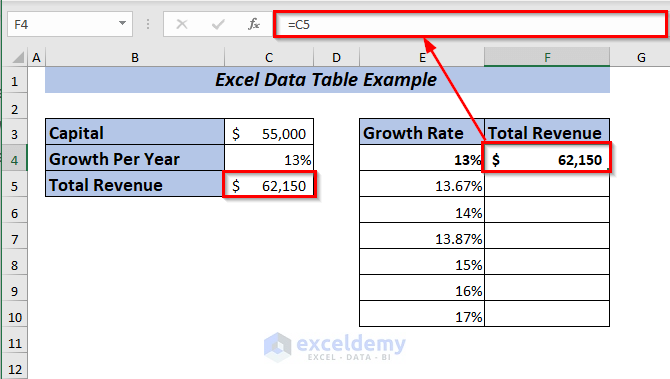
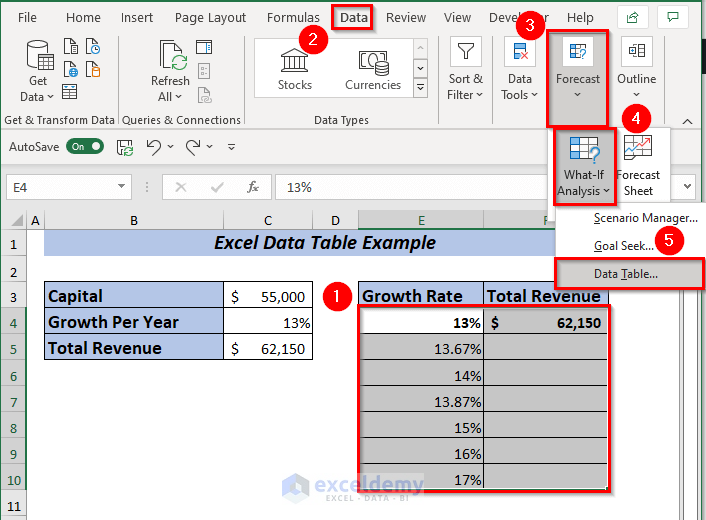
To apply one variable data table, place the formula of Total Revenue in cell F4.
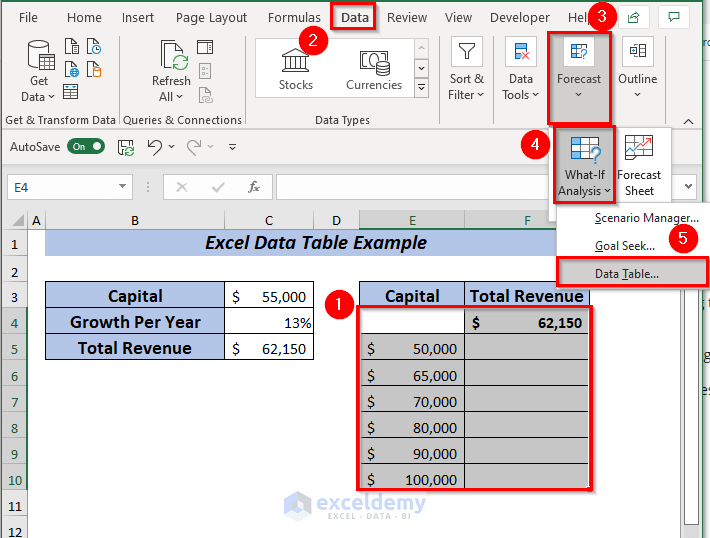
➤ Select range E4:F10 to apply the data table.
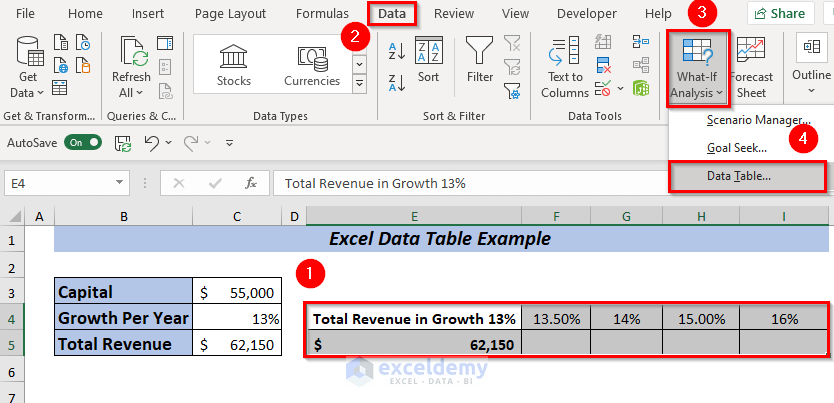
➤ Open Data tab >> Forecast >> Go to What-If-Analysis >> Select Data Table.
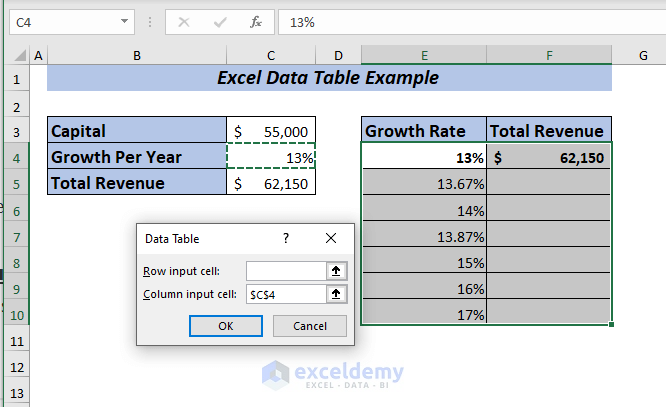
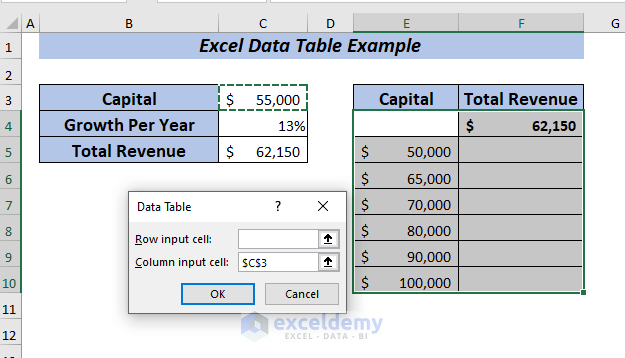
➤ A dialog box will pop up.
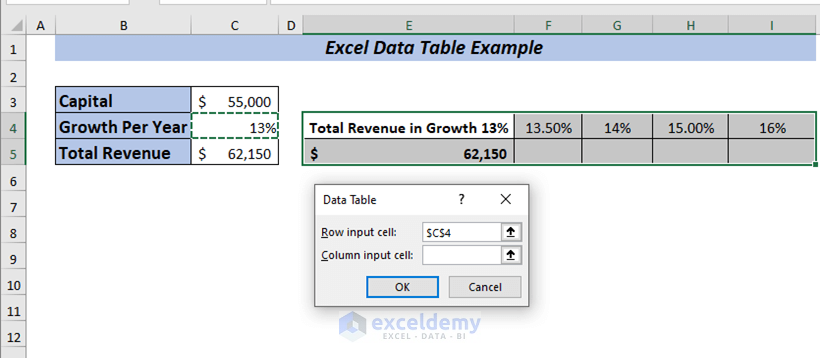
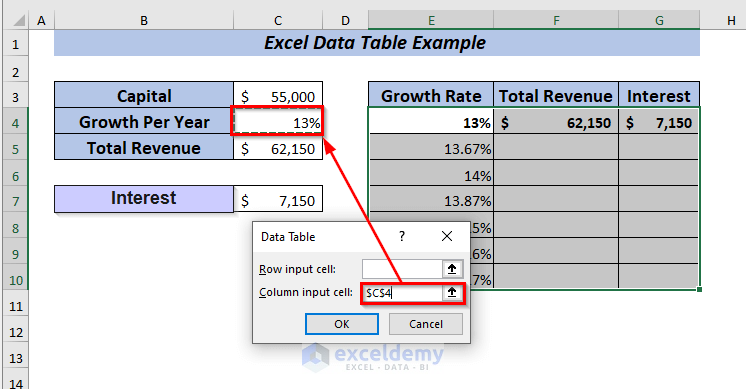
From there select any input cell. I want to see the changes in the column depending on growth per year.
➤ I selected C4 in the Column input cell box.
➤ Finally, click OK.
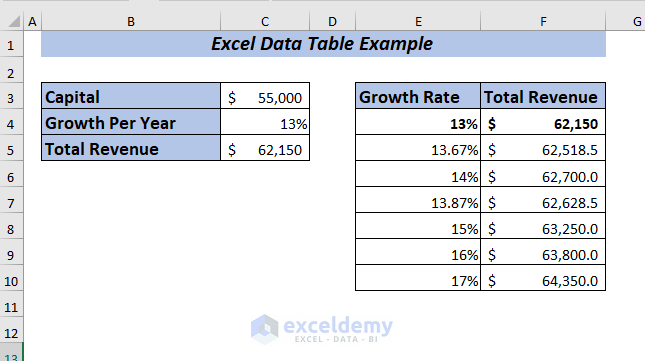
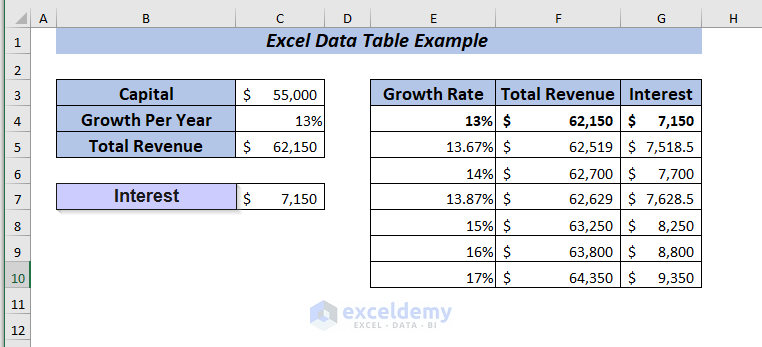
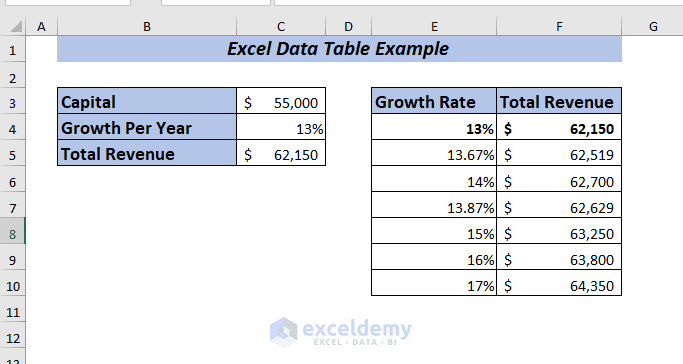
Result
Hence, you will get the Total Revenue for all the selected percentages at a glance.
2. One Variable Data Table Example – Observing Revenue Change
In the above example, I have shown you how the Total Revenue changes depending on different growth percentages.
Now, I will show you how the Total Revenue will change If I use Capital ranging from 50,000 to 100,000 while keeping the Growth Per Year at 13%.
To apply one variable data table, place the formula of Total Revenue in cell F4.
Insert the formula in cell F4.
➤ Select range E4:F10 to apply the data table.
➤ Open Data tab >> From Forecast >> Go to What-If-Analysis >> Select Data Table.
➤ A dialog box will pop up.
From there select any input cell. I want to see the changes in the column depending on capital.
➤ I selected C3 in the Column input cell and clicked OK.
Result
Therefore, you will get the Total Revenue for all the selected capitals at a glance.
3. Example of Row Oriented Data Table
If you want to use one variable data table horizontally then you also can do it.
First, place the formula in cell E5.
Then, type the values in a row while keeping one empty row below.
➤ Select range E4:I5 to apply the data table.
➤ Open Data tab >> From What-If-Analysis >> Select Data Table.
➤ A dialog box will pop up.
From there select any input cell. I want to see the changes in a row depending on percentages of growth per year.
➤ I selected C4 in the Row input cell and clicked OK.
Result
Now, you will get the Total Revenue for all the selected percentages.
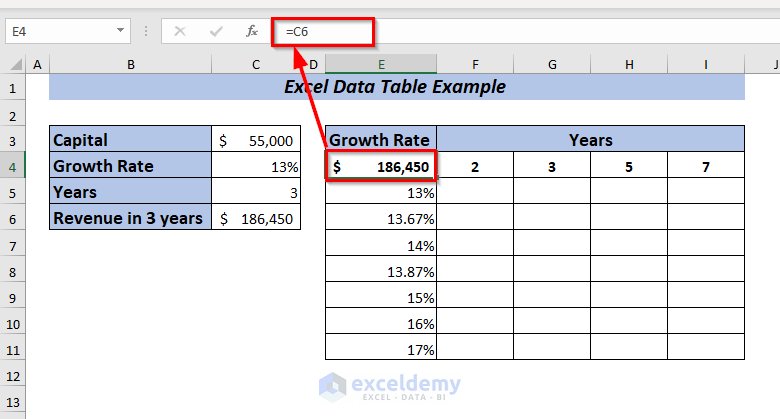
4. Two-Variable Data Table Example
The steps of two variable data tables are the same as one variable data table except that we enter two ranges of input values.
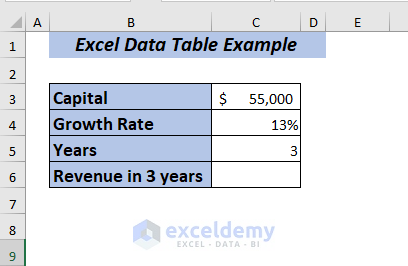
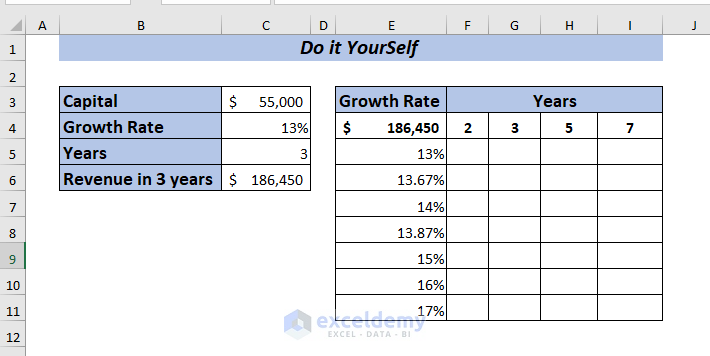
Here, I’ve modified the dataset a bit, given below.
To calculate Revenue in 3 years,
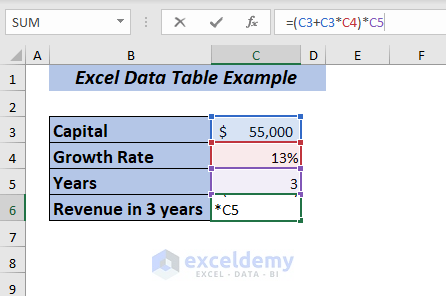
⏩ In cell C5, type the following formula.
=(C3+C3*C4)*C5Here, I have multiplied the Capital with the Growth Per Year and added the result with the Capital. Then multiplied it by Years to get the Revenue in 3 years.
Press ENTER, and you will get the Revenue in 3 years with 13% growth.
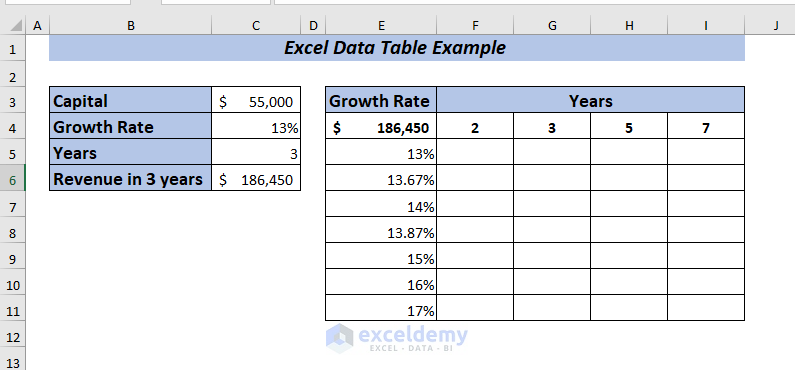
Now, I want to perform a What-If-Analysis to see how the Revenue will change in different Years with Growth Per Year ranging from 13% to 17% depending on the Capital amount of the company.
To apply a two-variable data table, place the formula of Total Revenue in cell E4.
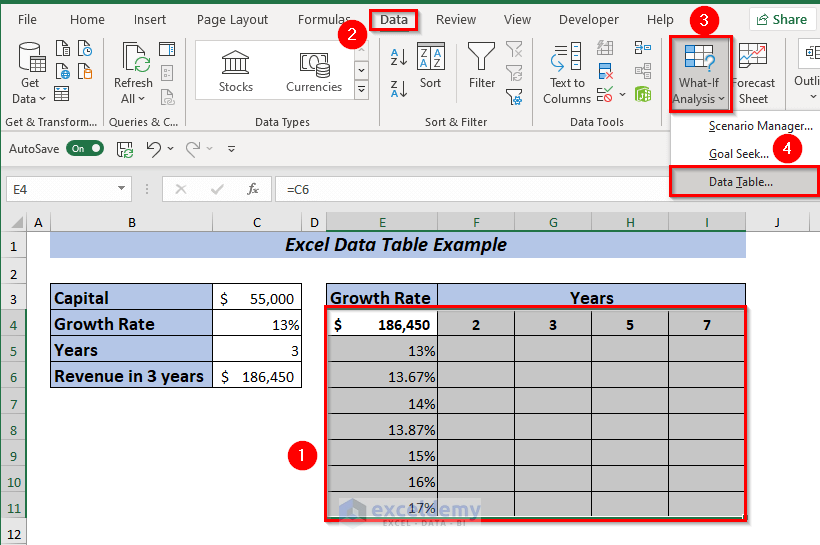
➤ Select range E4:I11 to apply the data table.
➤ Open Data tab >> From What-If-Analysis >> Select Data Table.
A dialog box will pop up.
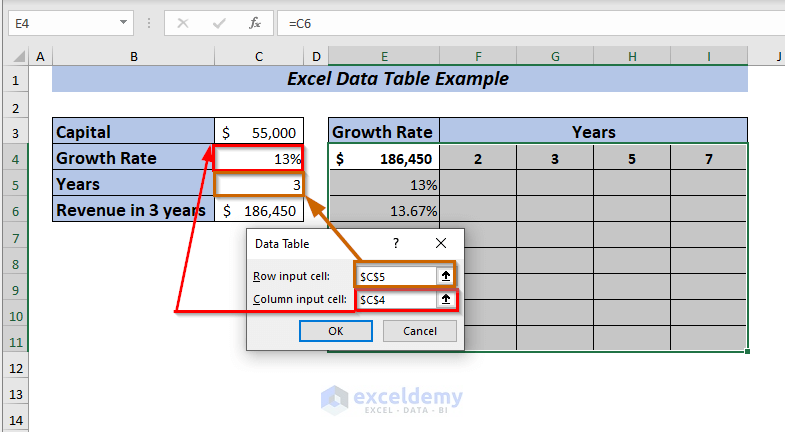
From there select two input cells.
➤ I selected C5 in the Row input cell because I kept the years in the row range F4:H4.
➤ I selected C4 in the Column input cell, as I kept the Growth Rate in a column range of E5:E11.
Finally, click OK.
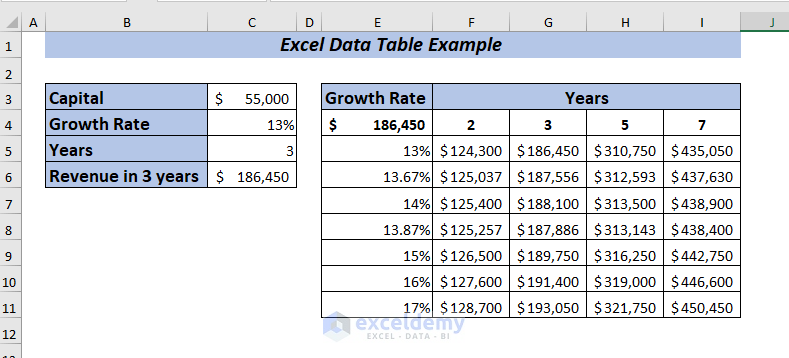
Result
Now, you will get the Revenue for all the selected percentages and years.
5. Compare Multiple Results Using Data Table
If you want you can compare multiple results using Data Table.
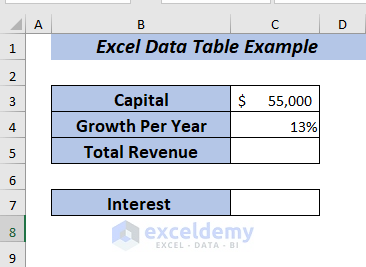
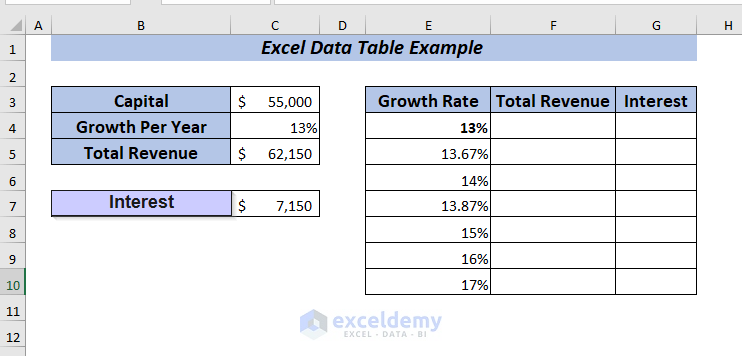
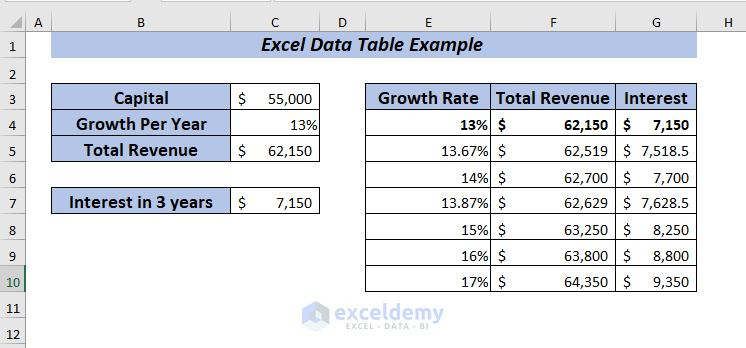
Let me show you a comparison between Revenue and Interest using Data Table. I’m going to use the information given in the dataset below.
First, calculate the Total Revenue.
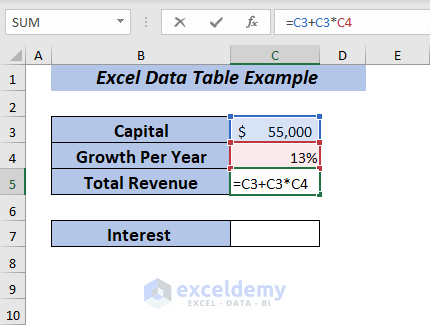
⏩ In cell C5, type the following formula.
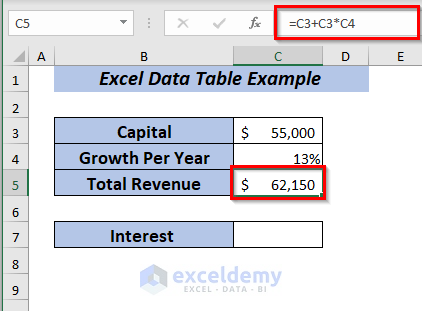
=C3+C3*C4Here, I multiplied the Capital with the Growth Per Year and then added the result with the Capital to get the Total Revenue.
Press ENTER, and you will get the Total Revenue for the year with 13% growth.
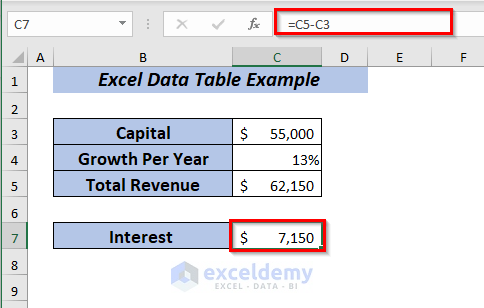
Now, to calculate the Interest,
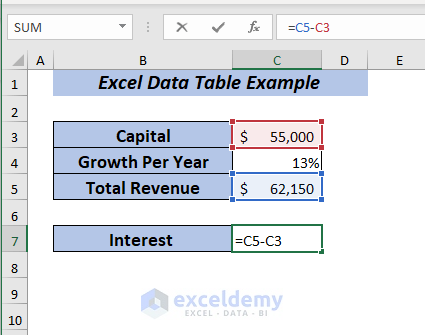
⏩ In cell C5, type the following formula.
=C5-C3Here, I subtracted the Capital from the Total Revenue to get the Interest.
Press ENTER and you will get the Interest.
Now, I will compare the Total Revenue and Interest using the data table. Change the Growth Per Year ranging from 13% to 17% while the Capital amount is $55,000.
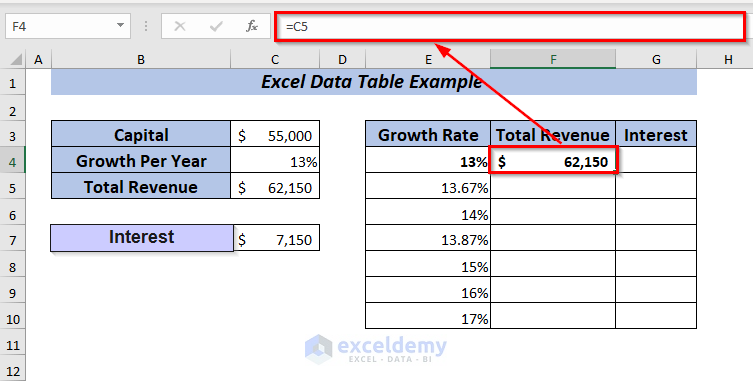
To apply one variable data table, place the formula of Total Revenue in cell F4.
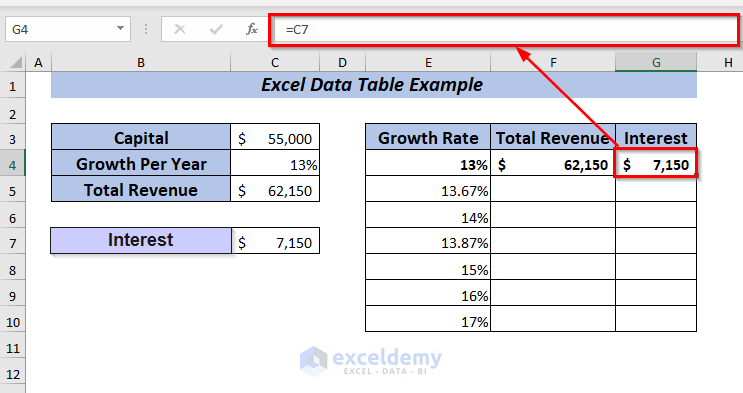
Again, place the formula of Interest in cell G4.
➤ Select range E4:G10 to apply the data table.
➤ Open Data tab >> From What-If-Analysis >> Select Data Table.
➤ A dialog box will pop up.
From there select any input cell. I want to see the changes in the column depending on growth per year.
➤ I selected C4 in the Column input cell and pressed OK.
Result
Hence, you will get the Total Revenue and Interest for all the selected percentages.
6. Example of Data Table Modification
You can modify a data table depending on your needs. In this section, I’m going to describe the table modification with examples.
6.1. Edit Data Table
If you want, you can edit the data table.
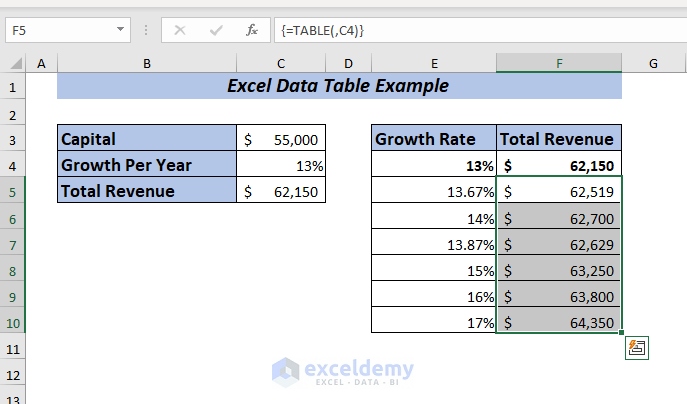
Here, I’ve taken a dataset where the data table is already applied to show you an example of editing an Excel data table.
➤ First, select the data table range from where you want to replace or edit data.
I selected the range F4:F10.
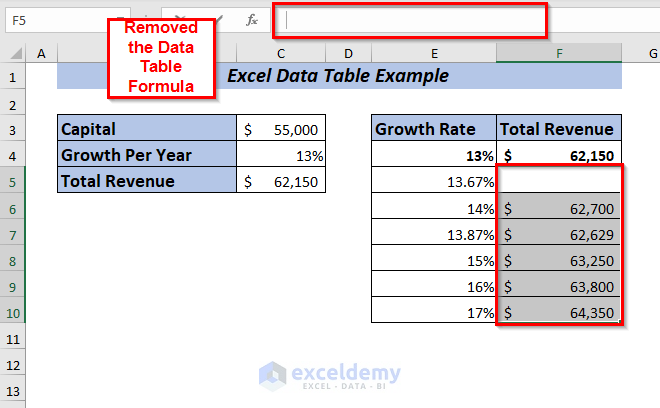
Now, remove the data table formula from any cell.
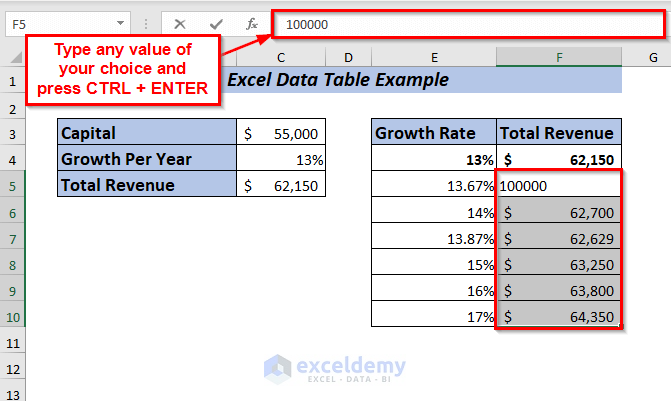
Insert the value of your choice and press CTRL + ENTER.
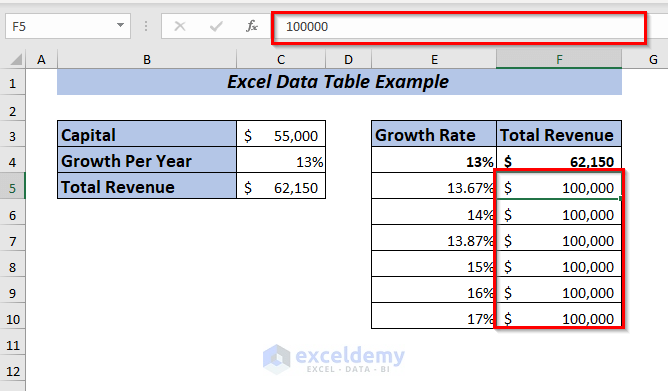
Result
Now, the inserted same value will be in all the selected cells.
As the Data Table formula is gone, you can edit any cell individually.
6.2. Delete Data Table
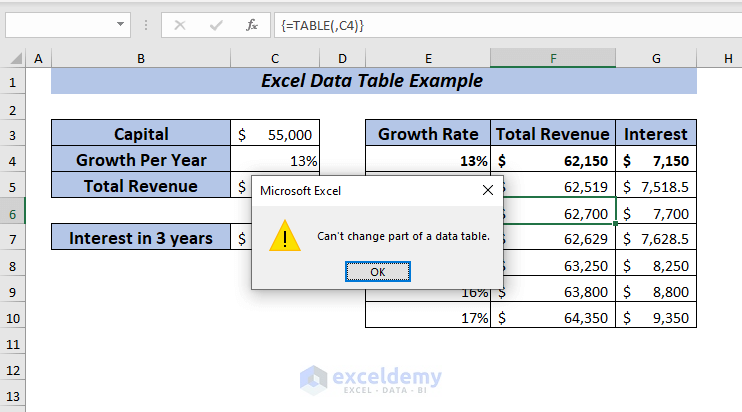
Naturally, you can’t delete any cell from the data table.
Let me show you an example of deleting an Excel data table. To perform the task, I’m going to use the dataset given below.
If you try to delete any cell from the data table then it will show you a warning message which is Can’t change part of a data table.
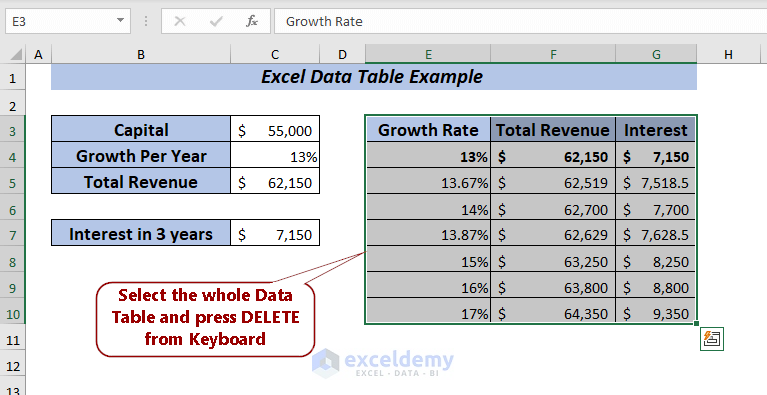
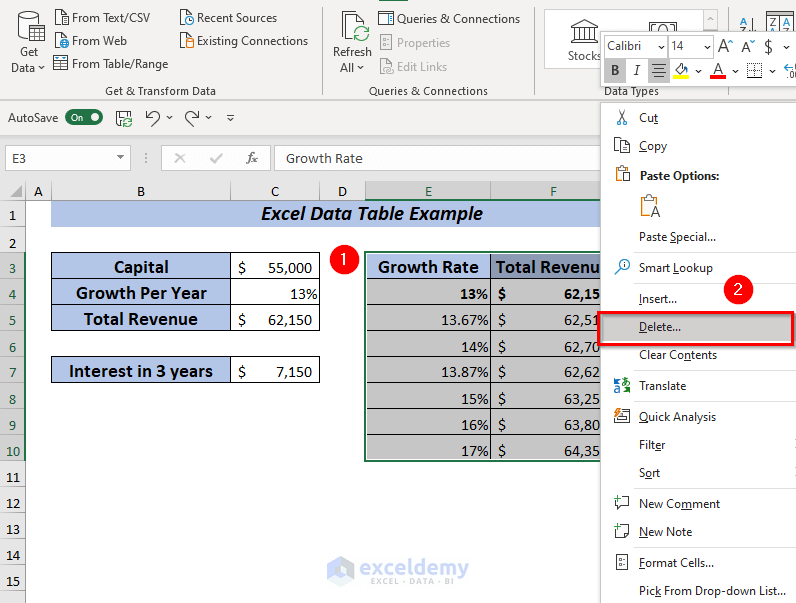
➤ To delete the data table, select the entire range of the data table.
I selected the cell range E3:G10.
Now, press DELETE from the keyboard.
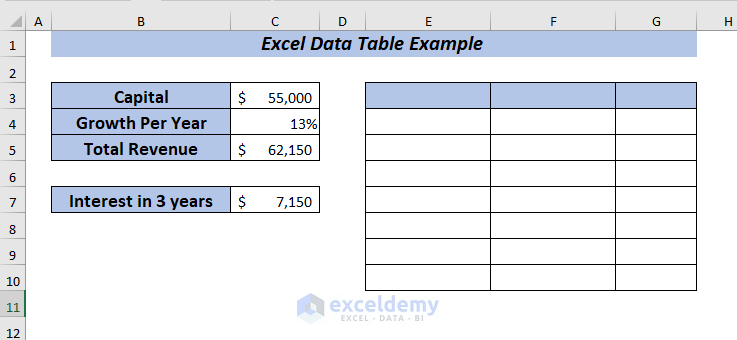
Here, the entire data is deleted.
You also can use the Context Menu to delete the data table.
➤ Select the entire range of the data table.
I selected the cell range E3:G10.
Now, right-click on the mouse.
➤ From the Context Menu select Delete.
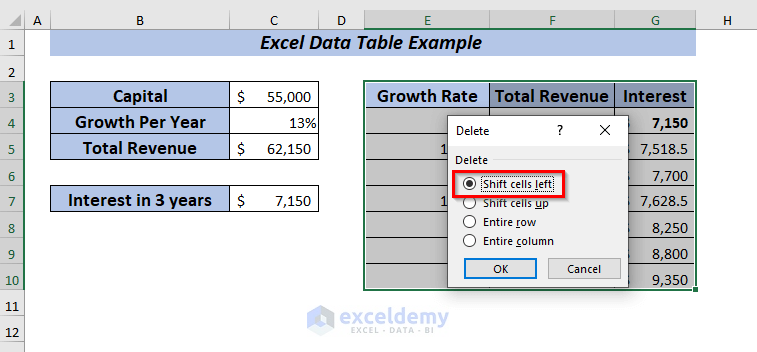
➤ Now, a dialog box will appear. Select any Delete option of your choice and click OK.
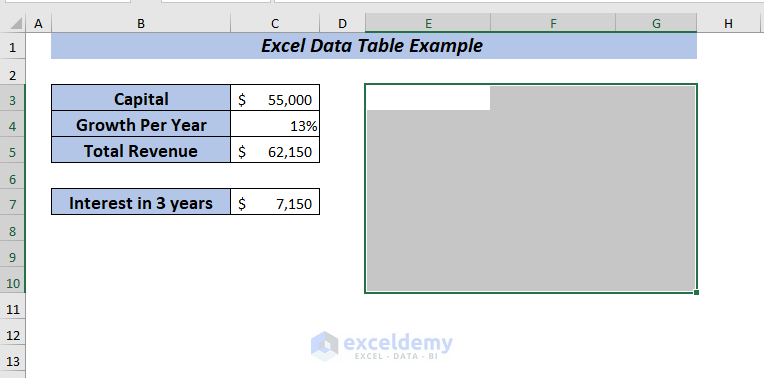
Here the data table is deleted.
Things To Remember
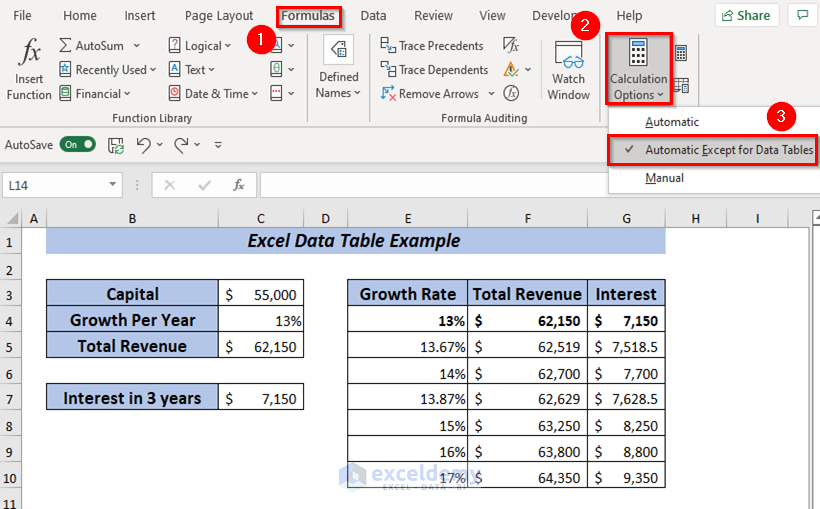
In your data table if you have multiple variable values and formulas that may slow down your Excel, then you can disable automatic recalculations in that and all other data tables which will speed up recalculations of the entire workbook.
Open Formulas tab >> From Calculation Options >> Select Automatic Except Data Tables.
🔺 If a data table is applied then you can’t undo the action.
🔺 Once What-If-Analysis is performed, and the values are calculated then it is impossible to change or modify any cell from the set of values.
Practice Section
I’ve provided practice sheets in the workbook to practice these explained examples.
Download to Practice
Conclusion
In this article, I have shown 6 examples of the Excel data table. Then, I also tried to mention things you need to remember while using the data table. Lastly, if you have any kind of suggestions, ideas, or feedback please feel free to comment down below.
Related Articles
- How to Create a Sensitivity Table in Excel
- One and Two Variables Sensitivity Analysis in Excel
- Data Table Not Working in Excel
- [Fixed] Excel Data Table Input Cell Reference Is Not Valid
<< Go Back to Data Table in Excel | What-If Analysis in Excel | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!