Method 1 – Use of SORT Function to Auto Sort in Excel
Introduction to the SORT Function
The SORT function in Excel returns a sorted range of data or array in an ascending or descending order. This function helps us sort data by one or more columns. It takes several arguments.
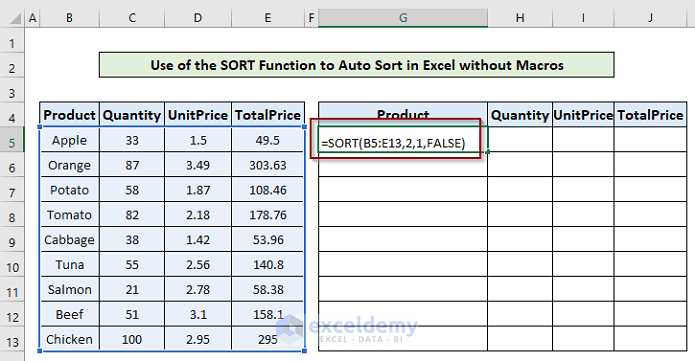
=SORT(array, [sort_index], [sort_order], [by_col])
array – range of data or array to sort.
[sort_index] – the column index that is used for sorting. The default value is 1 if omitted.
[sort_order] – use 1 for ascending (default) and -1 for descending order.
[by_col] – to sort data by column use TRUE and use FALSE to sort by row (default).
Task:
We want to auto-sort the dataset according to its quantity (column index=2) in ascending order without macros.
Solution:
To solve the task, we need to configure the arguments like this-
array=range B5:E13, the whole dataset.
[sort_index]= 2, column 2 holds the quantity values.
[sort_order]=1, sorting is in ascending order.
[by_col]= FALSE, sorting will be done by default, i.e., by row.
Steps:
Follow the steps below.
- Create an empty table with the same column header.
- In cell G5, write the following formula.
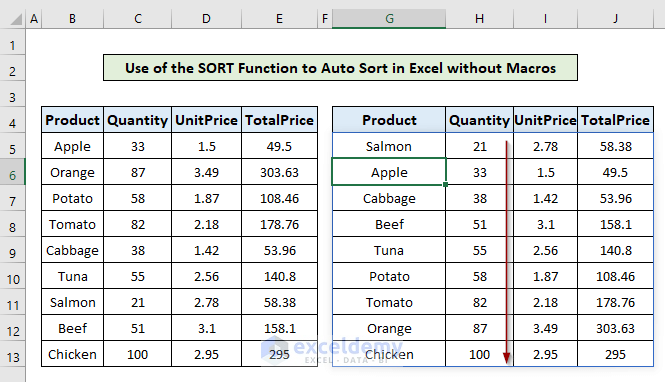
- Hit Enter to apply the formula.
Check the Auto Sort:
Let’s change the quantity of Apple from 33 to 60 in the source table.
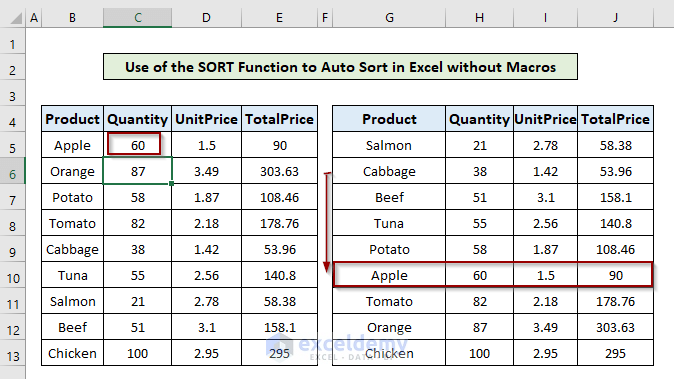
The position of Apple falls from 2nd to 6th in the auto-sorted table.
Method 2- Apply VLOOKUP Function to Auto Sort in Excel
Introduction to the VLOOKUP and RANK Function
The VLOOKUP function in Excel is used to look for data vertically in a table by matching it to the first column. The function takes several arguments-
=VLOOKUP(loopup_value, table_array,column_inded_num, [range_lookup])
lookup_value- the value we are looking for should be in the first column of the table.
table_array– the source data from where we want to retrieve a value.
Column_index_num – the column in the source table from where we want to retrieve a value.
range_lookup– FALSE for an exact match and TRUE for an approximate match.
Use The RANK function before using the VLOOKUP function in this example. The RANK function ranks a number against a given set of numbers from smallest to largest and in reverse. The syntax for the function is-
=RANK(number,ref,[order])
number- the number that we want to rank.
ref- the set of numbers to rank against.
[order]- the order is either ascending or descending.
Task:
Auto-sort the dataset according to its quantity (column index=2) in ascending order without macros.
Solution:
Follow a two-part solution in this example.
Part 1:
Rank the quantity of each product against the quantity column itself. For this,
- Create a new column named Rank in the source table.
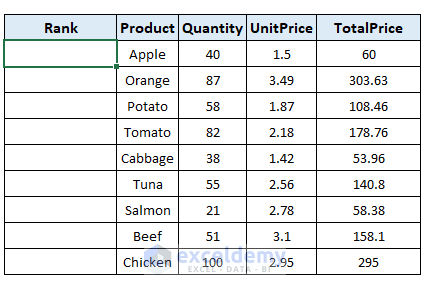
- In cell B5, write down the following formula.
=RANK.EQ(D5,$D$5:$D$13,1)With this formula, we ranked the value 40 at cell D5 in the range $D$5:$D$13, i.e., the Quantity column in ascending order.
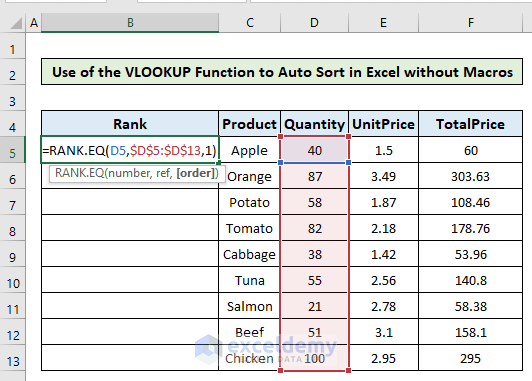
- Hit Enter and then copy the formula to the rest of the column.
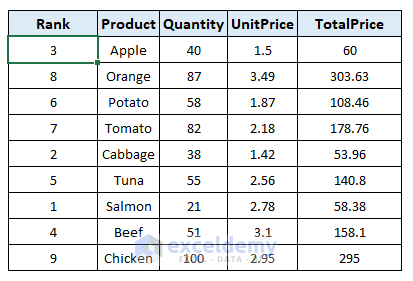
The rank column shows the ranking of each quantity in ascending order.
Part 2:
Use The VLOOKUP function to auto-sort the source data. Follow the steps below:
- Create an empty table with the same header as the source table.
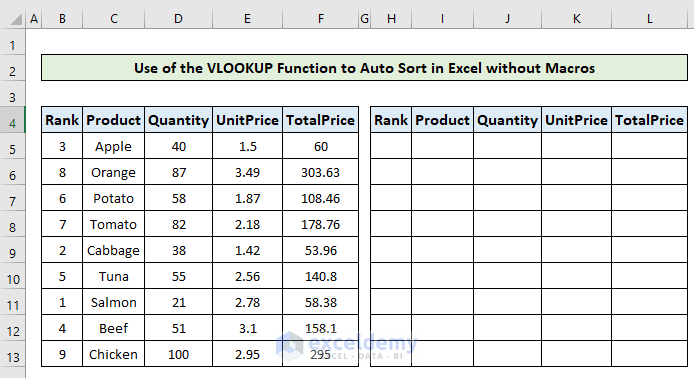
- Write down numbers 1-9 in the Rank column of the new table, as we want to auto-sort in ascending order.
- In cell I5, put the following formula.
=VLOOKUP($H5,$B$5:$F$13,2,FALSE)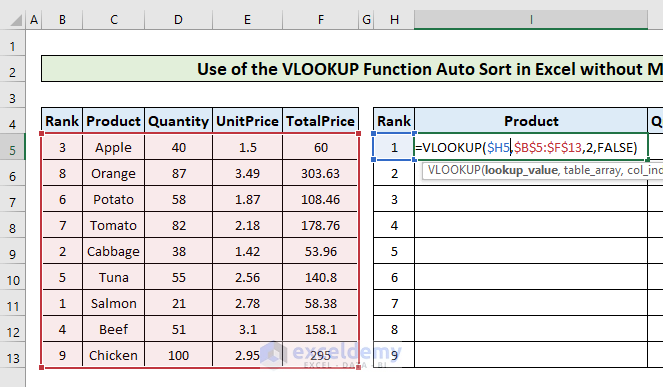
- Press Enter to apply the formula. The first ranked product, Salmon, is the output.
- Copy the formula to the rest of the column to get the auto-sorted product list.
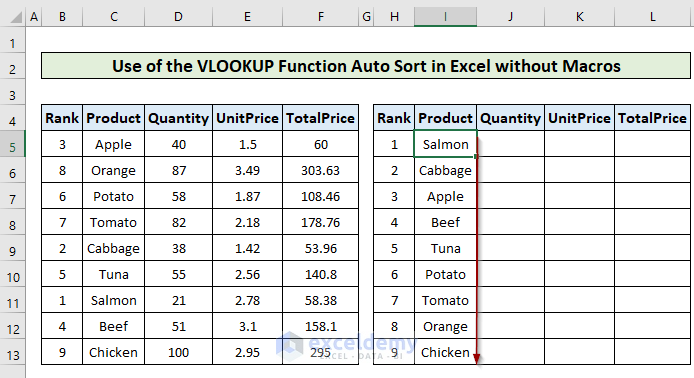
- Copy the following formula in cell J5 throughout the column to get the auto-sorted quantity column.
=VLOOKUP($H5,$B$5:$F$13,3,FALSE)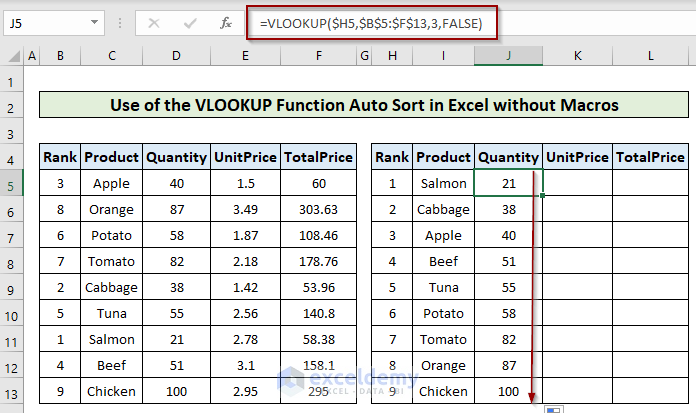
- Use the following formula to get the auto-sorted Unit Price column according to the rank.
=VLOOKUP($H5,$B$5:$F$13,4,FALSE)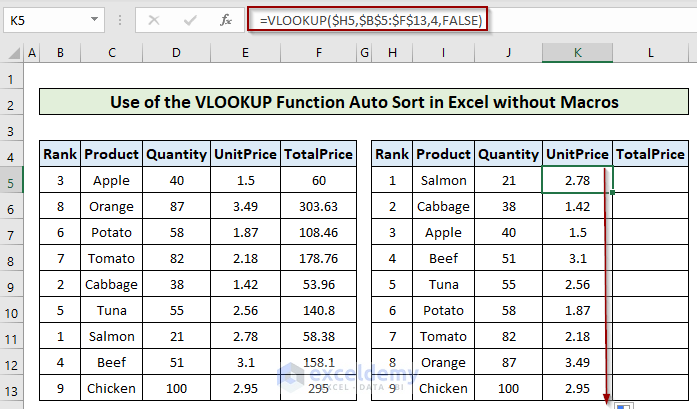
- The total price column is the product of the Quantity and Unit Price columns.
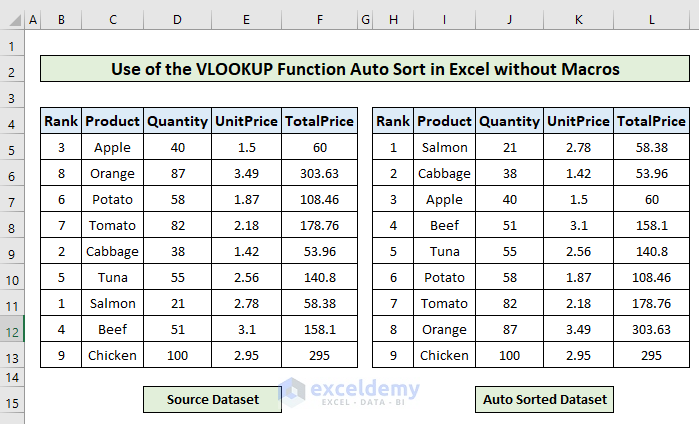
Check the Auto Sort:
Change the quantity of Apple from 40 to 60 in the source table.
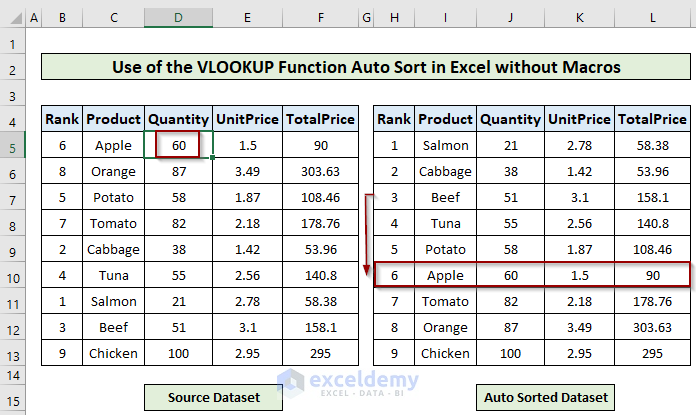
The position of Apple falls from 3rd to 6th in the auto-sorted table.
Method 3- Combine INDEX and MATCH Functions to Auto Sort in Excel
The INDEX function is used to find out the value of a specific location in a dataset. We used the MATCH function with the INDEX function. The MATCH function provides the location of the cell (row number) that fulfills both criteria.
The INDEX function takes the following arguments:
(array, row_num, [col_num])
We used the MATCH function to provide the row number argument of the INDEX function. The MATCH function checks the condition we specified and then outputs the row number of the cell data that fulfills the condition.
The syntax of the MATCH function is-
=MATCH(lookup_value, lookup_array, [match_type])
Task:
You want to auto-sort the dataset according to its quantity (column index=2) in ascending order without macros.
Solution:
Follow part 1 of the previous example to rank the dataset according to the product quantity.
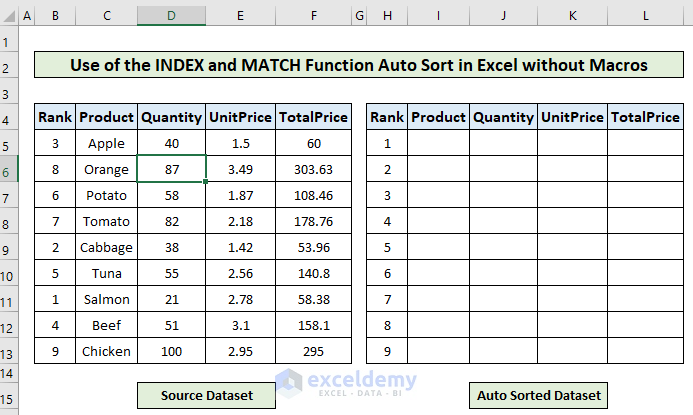
Part 2:
Configure the formula in cell I5. Do the following-
- Write the INDEX function, and select the whole source dataset $B$5:$F$13 as the array argument.
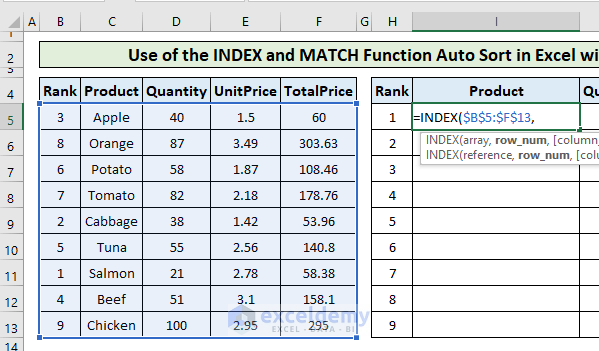
- You supplied the row_num argument of the INDEX function with the MATCH function as
MATCH($H5,$B$5:$B$13,0)Here,
lookup_value = 1, in cell H5.
lookup_array = $B$5:$B$13, Rank column in the source table.
match_type= 0, for exact match.
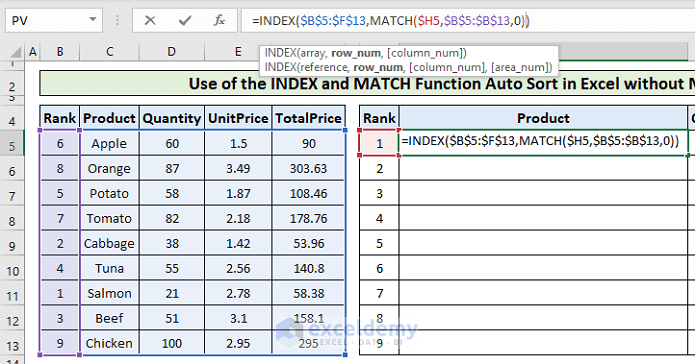
- Put 2 for the [col_num] argument in the INDEX function to show the product names. The column index 2 in the source dataset represents the product column.
=INDEX($B$5:$F$13,MATCH($H5,$B$5:$B$13,0),2)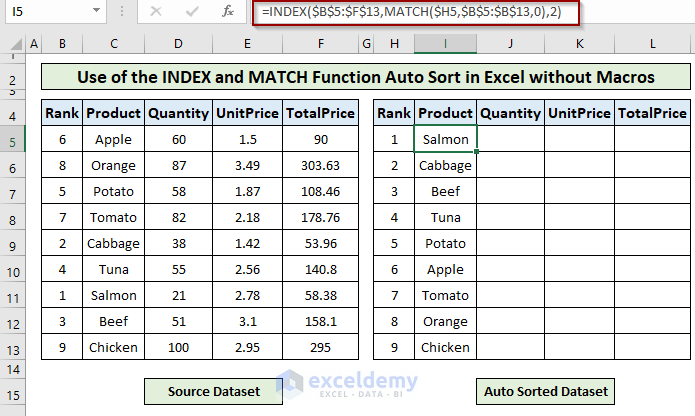
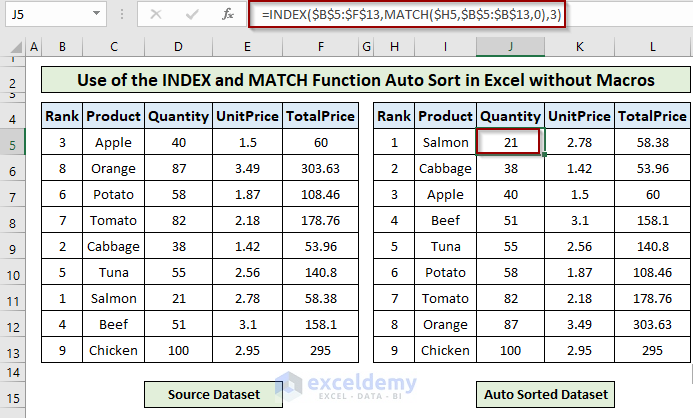
- To get the auto-sorted Quantity and Unit Price column, you need to change the [col_num] argument as 3 and 4, respectively, in the final formula.
Check the Auto Sort:
Change the quantity of Apple from 40 to 60 in the source table.
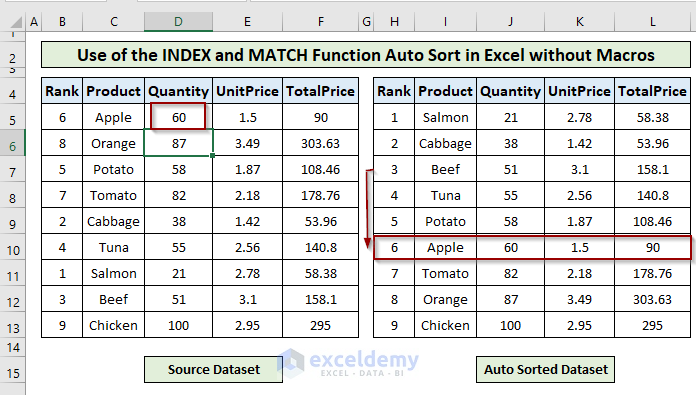
The position of Apple falls from 3rd to 6th in the auto-sorted table.
Things to Remember
- The SORT function is only available in Excel 365.
- We used absolute cell reference for selecting different arguments as they remain the same while copying the formula to other cells.
Download Practice Workbook
Download this practice workbook to exercise while you are reading this article.
Related Articles
<< Go Back to Auto Sort in Excel | Sort in Excel | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

