In this article, we’ll demonstrate how to pull data from multiple worksheets into one worksheet with Visual Basic of Applications (VBA) in Excel.
Code Overview
Sub Pull_Data_from_Multiple_WorkSheets_Horizontally()
Dim Sheet_Names() As Variant
Sheet_Names = Array("January", "February", "March")
Destination_Sheet = "Combined Sheet (Horizontally)"
Gap = 1
Set Destination_Cell = Worksheets(Sheet_Names(0)).UsedRange.Cells(1, 1)
Starting_Row = Destination_Cell.Row
Starting_Column = Destination_Cell.Column
For i = LBound(Sheet_Names) To UBound(Sheet_Names)
Worksheets(Sheet_Names(i)).Activate
Row_Width = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Columns.Count
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Copy
Worksheets(Destination_Sheet).Activate
ActiveSheet.Cells(Starting_Row, Starting_Column).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteAll
Starting_Column = Starting_Column + Row_Width + Gap
Next i
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End Sub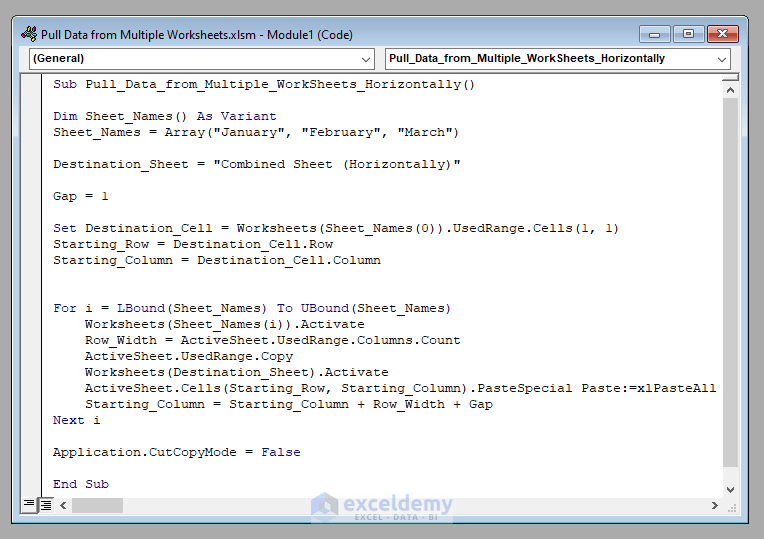
Suppose we have an Excel workbook that contains three worksheets titled January, February, and March respectively. Each contains the sales of some books for three different months in a bookstore.
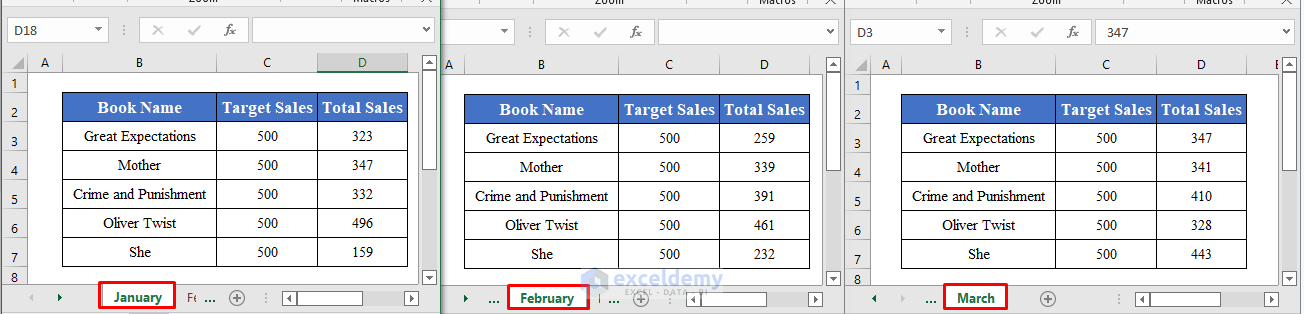
We’ll develop a Macro to pull data from these multiple sheets into one worksheet, using 3 different methods.
Method 1 – Pull Data from Multiple Worksheets into One Worksheet Horizontally
Open a new workbook and select the worksheet where you want to merge these files.
Here we named a new worksheet “Combined Sheet (Horizontally)”.
Now let’s enter the VBA code to develop the Macro.
Step 1 – Entering the Source Files and the Destination File
First we require the inputs into the code. These are the names of the sheets that we’ll combine (January, February, and March), the name of the destination worksheet (Combined Sheet (Horizontally)), and the gap between the data sets from the different worksheets to be placed into the combined sheet (1 here, set it according to your need).
Dim Sheet_Names() As Variant
Sheet_Names = Array("January", "February", "March")
Destination_Sheet = "Combined Sheet (Horizontally)"
Gap = 1Step 2 – Setting the Destination Cell, Starting Row, and Starting Column
The starting row and column will be the same as the starting cell of the first worksheet.
Set Destination_Cell = Worksheets(Sheet_Names(0)).UsedRange.Cells(1, 1)
Starting_Row = Destination_Cell.Row
Starting_Column = Destination_Cell.ColumnStep 3 – Iterating Through a For-Loop to Combine All the Sheets into One Worksheet
This is the most important step.
For i = LBound(Sheet_Names) To UBound(Sheet_Names)
Worksheets(Sheet_Names(i)).Activate
Row_Width = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Columns.Count
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Copy
Worksheets(Destination_Sheet).Activate
ActiveSheet.Cells(Starting_Row, Starting_Column).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteAll
Starting_Column = Starting_Column + Row_Width + Gap
Next iStep 4 (Optional) – Turning Off the CutCopyMode
To complete the Macro, we’ll turn off the CutCopyMode of VBA. You can skip this step if you want.
Application.CutCopyMode = FalseTherefore, the complete VBA code is:
VBA Code
Sub Pull_Data_from_Multiple_WorkSheets_Horizontally()
Dim Sheet_Names() As Variant
Sheet_Names = Array("January", "February", "March")
Destination_Sheet = "Combined Sheet (Horizontally)"
Gap = 1
Set Destination_Cell = Worksheets(Sheet_Names(0)).UsedRange.Cells(1, 1)
Starting_Row = Destination_Cell.Row
Starting_Column = Destination_Cell.Column
For i = LBound(Sheet_Names) To UBound(Sheet_Names)
Worksheets(Sheet_Names(i)).Activate
Row_Width = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Columns.Count
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Copy
Worksheets(Destination_Sheet).Activate
ActiveSheet.Cells(Starting_Row, Starting_Column).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteAll
Starting_Column = Starting_Column + Row_Width + Gap
Next i
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End Sub
Output
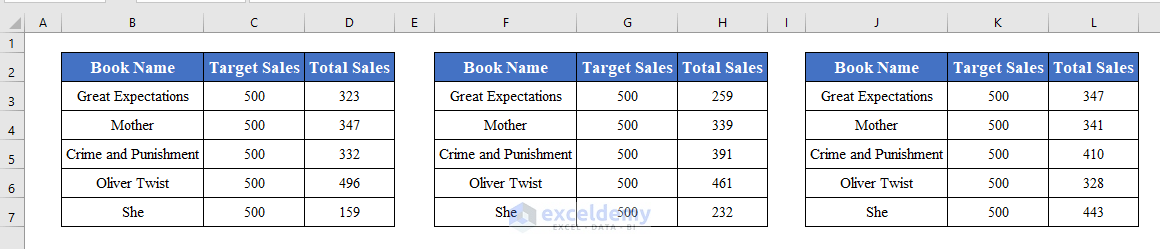
Run the code by pressing F5.
The macro will pull data from all the input worksheets horizontally into the destination worksheet (Combined Sheet (Horizontally)).
Read More: Extract Data from One Sheet to Another Using VBA in Excel
Method 2 – Pull Data from Multiple Worksheets into One Worksheet Vertically
Now we’ll develop a Macro to pull data from multiple Excel sheets into one worksheet vertically.
We follow the same steps as in Method 1.
First, insert the source worksheets (January, February, and March), the destination worksheet (a new worksheet called Combined Sheet (Vertically)), and the gap (again 1 here).
Then set the destination cell, starting row, and starting column.
And finally, combine the sheets with a For-loop.
The complete VBA code will be:
VBA Code
Sub Pull_Data_from_Multiple_Worksheets_Vertically()
Dim Sheet_Names() As Variant
Sheet_Names = Array("January", "February", "March")
Destination_Sheet = "Combined Sheet (Vertically)"
Set Destination_Cell = Worksheets(Sheet_Names(0)).UsedRange.Cells(1, 1)
Starting_Row = Destination_Cell.Row
Starting_Column = Destination_Cell.Column
Gap = 1
For i = LBound(Sheet_Names) To UBound(Sheet_Names)
Worksheets(Sheet_Names(i)).Activate
Row_Height = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Copy
Worksheets(Destination_Sheet).Activate
ActiveSheet.Cells(Starting_Row, Starting_Column).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteAll
Starting_Row = Starting_Row + Row_Height + Gap
Next i
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End Sub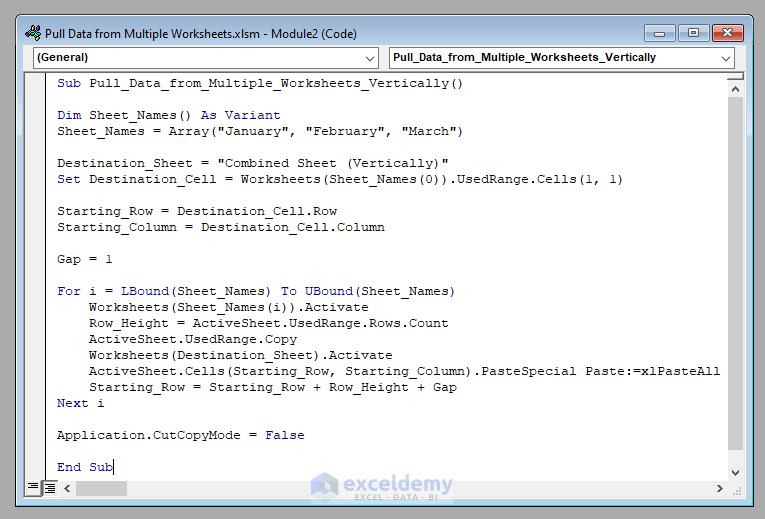
Output
Run the code. It’ll pull data from all the worksheets vertically into the destination worksheet (Combined Sheet (Horizontally)).
Read More: How to Pull Data From Another Sheet Based on Criteria in Excel
Method 3 – Pull Data from Multiple Worksheets into One Worksheet with an Operation
Now we’ll develop a Macro to pull data from these worksheets into one worksheet with a specific operation (Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, or Division).
Again, we’ll follow the same steps as in Methods 1 and 2.
First, insert the source worksheets (January, February, and March), the destination worksheet (a new worksheet called Combined Sheet (with Operation) here), the columns on which the operation will be applied (2 and 3 here), and the operation (Addition here).
Then set up the destination cell, starting row, and starting column.
And finally combine the files with a For-loop.
The complete VBA code will be:
VBA Code
Sub Pull_Data_from_Multiple_WorkSheets_with_Operation()
Dim Sheet_Names() As Variant
Sheet_Names = Array("January", "February", "March")
Destination_Sheet = "Combined Sheet (with Operation)"
Dim Operation_Columns() As Variant
Operation_Columns = Array(2, 3)
Operation = "Addition"
Set Destination_Cell = Worksheets(Sheet_Names(0)).UsedRange.Cells(1, 1)
Starting_Row = Destination_Cell.Row
Starting_Column = Destination_Cell.Column
Worksheets(Sheet_Names(0)).Activate
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Copy
Worksheets(Destination_Sheet).Activate
ActiveSheet.Cells(Starting_Row, Starting_Column).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteAll
For i = LBound(Sheet_Names) + 1 To UBound(Sheet_Names)
Worksheets(Sheet_Names(i)).Activate
For j = LBound(Operation_Columns) To UBound(Operation_Columns)
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Range(Cells(2, Operation_Columns(j)), Cells(ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count, Operation_Columns(j))).Copy
Worksheets(Destination_Sheet).Activate
If Operation = "Addition" Then
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Cells(2, Operation_Columns(j)).PasteSpecial Operation:=xlAdd
ElseIf Operation = "Subtraction" Then
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Cells(2, Operation_Columns(j)).PasteSpecial Operation:=xlSubtract
ElseIf Operation = "Multiplication" Then
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Cells(2, Operation_Columns(j)).PasteSpecial Operation:=xlMultiply
ElseIf Operation = "Division" Then
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Cells(2, Operation_Columns(j)).PasteSpecial Operation:=xlDivide
Else
MsgBox "Enter either Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, or Division as Operation."
End If
Next j
Next i
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End Sub
Output
Run the code. It’ll pull data from the input worksheets by adding data from columns 2 and 3, into the worksheet called Combined Sheet (with Operation).
Things to Remember
- Here, we’ve used the xlPasteAll property of the PasteSpecial method of VBA to copy everything from the source sheets to the destination sheets. Besides this property, the PasteSpecial method of VBA has 11 more properties.
- While pulling large data sets, the codes may take a bit of time to run. So have patience and wait until they run successfully.
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- Extract Filtered Data in Excel to Another Sheet
- How to Get Data from Another Sheet Based on Cell Value in Excel
- Pull Same Cell from Multiple Sheets into Master Column in Excel
- Excel Macro: Extract Data from Multiple Excel Files
- How to Pull Data from Multiple Worksheets in Excel
- How to Pull Values from Another Worksheet in Excel
<< Go Back To Extract Data Excel | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!


Create an excel Macro which performs below actions1. Load an excel file2. Show all the sheet names (10+ sheet) post loading3. User should have an privilege to select any of the sheet name from step 24. User should see all column names for the selected sheet5. User should have an privilege to select any of the columns from step 4 (multi select of columns)5. User should see the values (20+ rows with values) for all the selected columns
how can we do this??
Hello POOJA
Thanks for reaching out and sharing your requirements with such clarity. The problem you want a solution for can quickly be developed using several Excel VBA Sub-procedures, Event Procedures, and a UserForm.
Here is an algorithm you can follow:
OUTPUT Overview:
Regards
Lutfor Rahman Shimanto
Excel & VBA Developer
ExcelDemy