Method 1 – Use the VBA Left Function to Extract Text from the Left Side of the Cell and Display it in a Message Box
Step 1:
- Go to the Sheet Name at the bottom of each sheet, e.g; the sheet name is “Left Cell”.
- Press the right button of the mouse.
- Click View Code from the Context Menu.
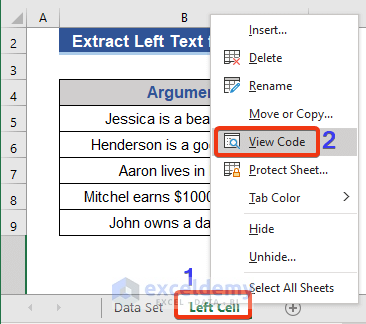
A VBA window will appear. We have to open a new module to write the code.
Step 2:
- Click on the Module option from the Insert tab.
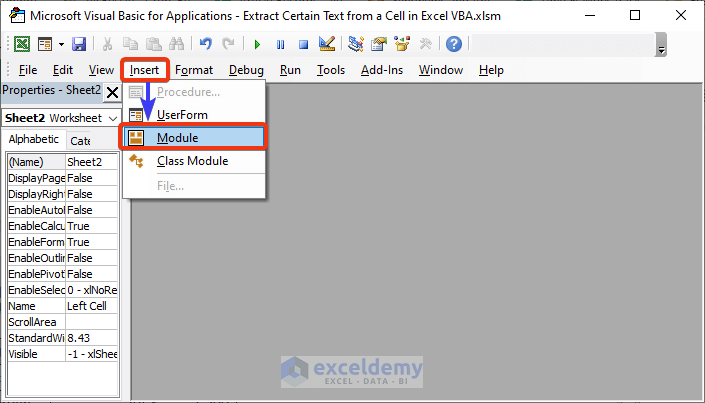
A new module appears now where we will write the code.
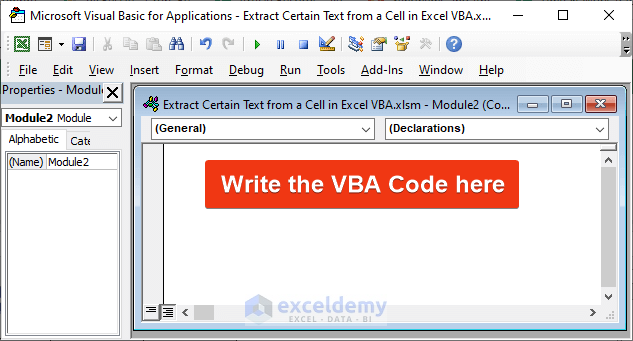
Step 3:
- Copy and paste the following VBA code into this module.
Sub extract_text1()
Dim cell_1 As Range
Dim value_1 As Variant
Set cell_1 = Range("B5")
value_1 = Left(cell_1, 7)
MsgBox value_1
End Sub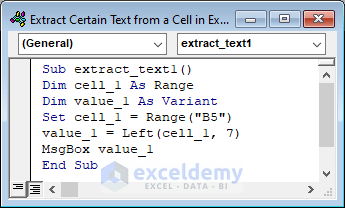
In this VBA code, the Left function has two arguments.
- cell_1 is the reference data.
- The 2nd one is a number, e.g; it is 7 which indicates that the Left function will return 7 characters from the left of the reference string.
Step 4:
- Press the F5 button to run this code or press the Run Sub/UserForm button from the Run tab.
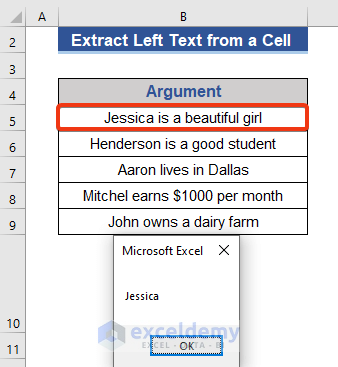
We get the 7 characters from the left side.
Code Explanation
Dim cell_1 As Range
Dim value_1 As VariantDeclaring the variable.
Set cell_1 = Range("B5")Store a range value in the cell_1 variable
value_1 = Left(cell_1, 7)Performs the Left operation and stores the value in the value_1 variable.
MsgBox value_1View the result of the value_1 variable.
Method 2 – Use the VBA Right Function to Extract Text from the Right Side of the Cell and Display
Step 1:
- Press Alt+F11 to enter the Excel VBA command window and insert a new module.
- Paste the VBA code below into the module.
Sub extract_text2()
Dim cell_1 As Range
Dim value_1 As Variant
Set cell_1 = Range("B5")
value_1 = Right(cell_1, 4)
MsgBox value_1
End Sub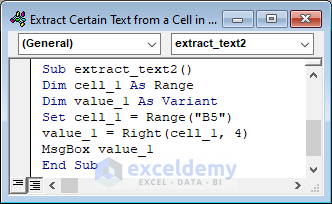
Cell B5 is specified as set as cell_1 range variable, and the length of string to return is set as 4 inside the Right function.
Step 2:
- Hit the F5 functional key from the keyboard to run the VBA code.
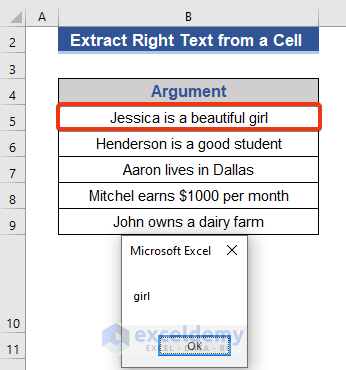
We’ve got 4 characters from the right-most side of cell B7.
Code Explanation
Dim cell_1 As Range
Dim value_1 As VariantDeclaring the variable.
Set cell_1 = Range("B5")Store a range value in the cell_1 variable
value_1 = Right(cell_1, 4)Performs the Right function operation and stores the value in the value_1 variable.
MsgBox value_1View the result of the value_1 variable.
Method 3 – Use VBA Mid Function to Extract Text from the Middle of an Excel Cell
Step 1:
- Press Alt+F11 and enter a new VBA command module.
- Write the following VBA code on the module.
Sub extract_text3()
Dim cell_1 As Range
Dim value_1 As Variant
Set cell_1 = Range("B7")
value_1 = Mid(cell_1, 7, 5)
MsgBox value_1
End Sub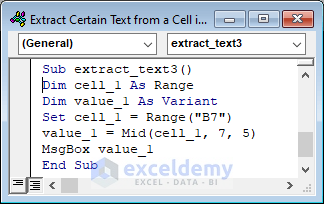
B7 is the reference cell set as cell_1 range variable, and the start position is 7 from the left of the reference string while 5 is the count of characters to return starting from the 7th position.
Step 2:
- Run the code by pressing the F5 button.
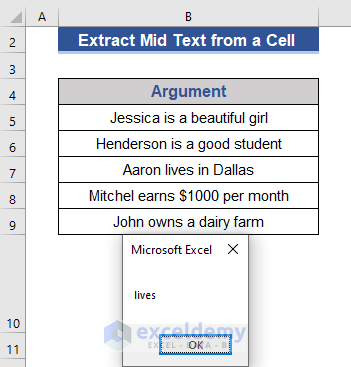
The message box shows the 5 characters from the 7th position of the reference string.
Code Explanation
Dim cell_1 As Range
Dim value_1 As VariantDeclaring the variable.
Set cell_1 = Range("B7")Store a range value in the cell_1 variable
value_1 = Mid(cell_1, 7, 5)Performs the Mid function operation and stores the value in the value_1 variable.
MsgBox value_1View the result of the value_1 variable.
Method 4 – Use a VBA Custom Function to Pick N-th Word from a Text String
Step 1:
- Press Alt+F11 to enter a new VBA command module.
- Copy and paste the following VBA code there.
Function Required_Text(value_1 As String, location As Integer)
Dim array_1() As String
array_1 = VBA.Split(value_1, " ")
xCount = UBound(array_1)
If xCount < 1 Or (location - 1) > xCount Or location < 0 Then
Required_Text = ""
Else
Required_Text = array_1(location - 1)
End If
End Function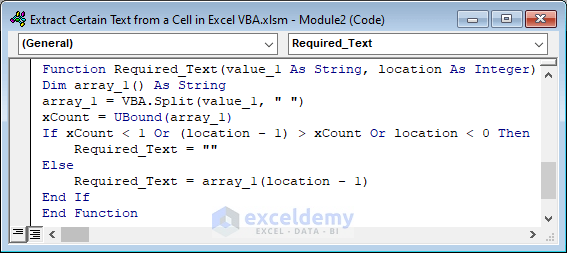
Step 2:
- Save the VBA code.
- Go to Cell D5 of the dataset. Put the following formula.
=Required_Text(B5,4)
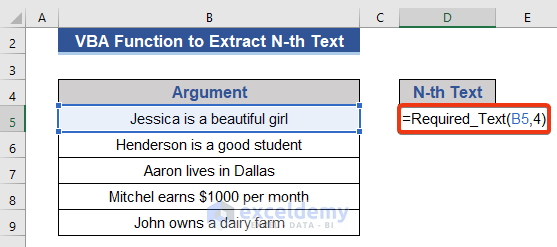
The 1st argument in Cell B5 is considered as the reference string, and the 2nd argument expresses the position of text in Cell B5.
Step 3:
- Press Enter.
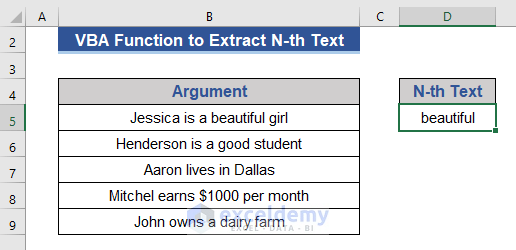
We get the 4th text from the string in Cell B5.
Code Explanation
Function Required_Text(value_1 As String, location As Integer)Declaring a function with arguments.
Dim array_1() As StringDeclaring an array variable.
array_1 = VBA.Split(value_1, " ")Split the value_1 variable based on space and store the values on array_1.
xCount = UBound(array_1)This finds the largest value of array_1 and stores it on xCount.
If xCount < 1 Or (location - 1) > xCount Or location < 0 Then
Required_Text = ""
Else
Required_Text = array_1(location - 1)
End IfAn IF condition is applied. This is a comparison between xCount and location variables.
Method 5 – Excerpt Substring from a Cell with VBA RegExp Object
Step 1:
- Hit Alt+F11 and enter the VBA command module.
- Copy the following VBA code on the command module.
Function Extract_Email(text_1 As String, sequence As String, Optional instance_n As Integer = 0, Optional match_n As Boolean = True)
Dim text_1_matches() As String
Dim matches_index As Integer
On Error GoTo ErrHandl
Extract_Email = ""
Set regex = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
regex.pattern = sequence
regex.Global = True
regex.MultiLine = True
If True = match_n Then
regex.ignorecase = False
Else
regex.ignorecase = True
End If
Set matches = regex.Execute(text_1)
If 0 < matches.Count Then
If (0 = instance_n) Then
ReDim text_1_matches(matches.Count - 1, 0)
For matches_index = 0 To matches.Count - 1
text_1_matches(matches_index, 0) = matches.Item(matches_index)
Next matches_index
Extract_Email = text_1_matches
Else
Extract_Email = matches.Item(instance_n - 1)
End If
End If
Exit Function
ErrHandl:
Extract_Email = CVErr(xlErrValue)
End Function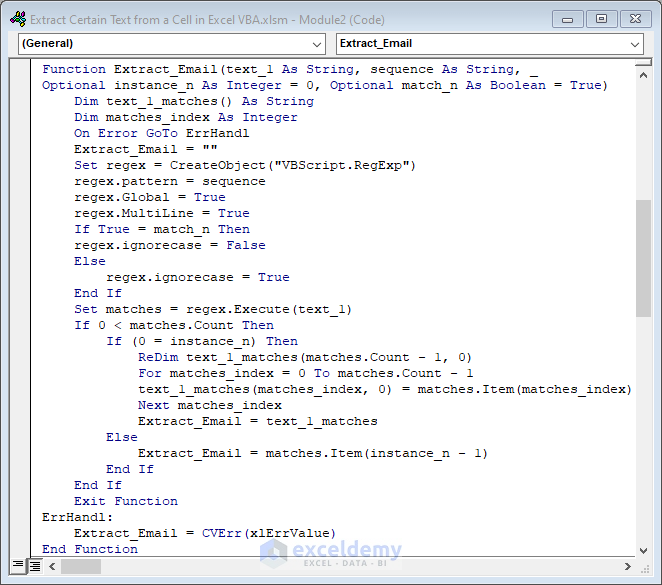
Step 2:
- Save the VBA code first.
- A pattern will be used as an argument for this function.
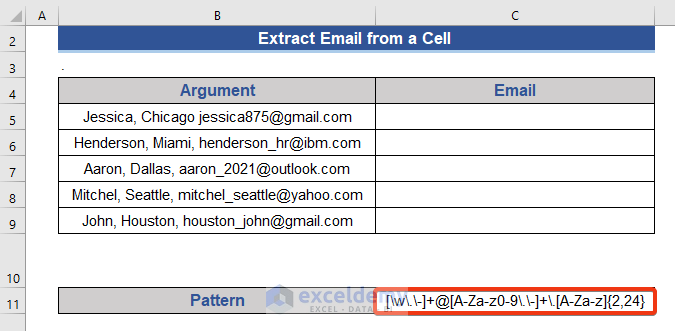
Step 3:
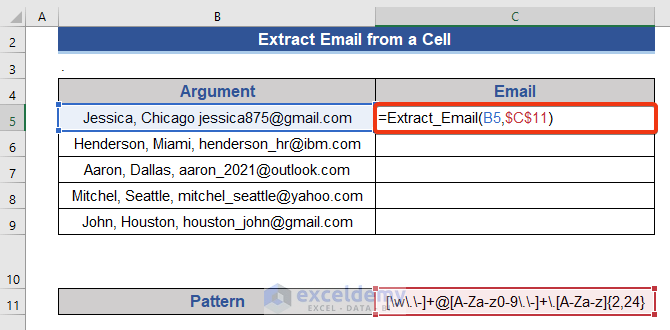
- Go to Cell C5 and put the following formula.
=Extract_Email(B5,$C$11)
Step 4:
- Press the Enter button and drag the Fill Handle icon downwards.
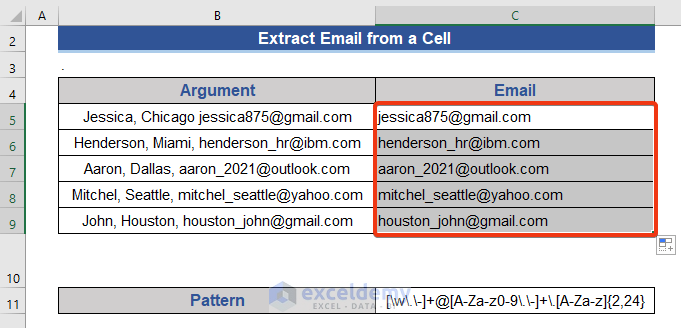
We extract only email addresses from a cell.
Code Explanation
Function Extract_Email(text_1 As String, sequence As String, Optional instance_n As Integer = 0, Optional match_n As Boolean = True)Declaring a function with arguments.
Dim text_1_matches() As String
Dim matches_index As IntegerDeclaring an array variable.
On Error GoTo ErrHandlWhen any error finds move to ErrHandl section.
Set regex = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")Create an object and store it at regex variable.
regex.pattern = sequence
regex.Global = True
regex.MultiLine = TrueDefines properties of regex.
If True = match_n Then
regex.ignorecase = False
Else
regex.ignorecase = True
End IfPerforms an IF operation.
Set matches = regex.Execute(text_1)Stores value of matches.
If 0 < matches.Count Then
If (0 = instance_n) Then
ReDim text_1_matches(matches.Count - 1, 0)
For matches_index = 0 To matches.Count - 1
text_1_matches(matches_index, 0) = matches.Item(matches_index)
Next matches_index
Extract_Email = text_1_matches
Else
Extract_Email = matches.Item(instance_n - 1)
End If
End IfTwo IF functions are applied here.
Extract_Email = CVErr(xlErrValue)Checks the error of the given argument and stores on variable Extract_Email.
We used a pattern to get the Email address, that is :
[\w\.\-]+@[A-Za-z0-9\.\-]+\.[A-Za-z]{2,24}
[\w\.\-]+ indicates the username of an email address. There may be any text, numbers, or special symbols.
@, We know this is a must-needed symbol of an email address. It separates the domain and user name.
[A-Za-z0-9\.\-]+, this is the domain name part. Numbers, texts, and some symbols are allowed here. But undercover is strictly prohibited.
\.[A-Za-z]{2,24}, this is for top-level domain. It consists of a Dot(.). Most top-level domains consist of 3 letters.
Download Practice Workbook
Download this practice workbook to exercise while you are reading this article.
Related Readings
- How to Extract Text after Second Comma in Excel
- How to Extract Text between Two Spaces in Excel
- How to Extract Text Between Two Characters in Excel
- How to Extract Text After a Character in Excel
<< Go Back to Extract Text in Excel | String Manipulation | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!


