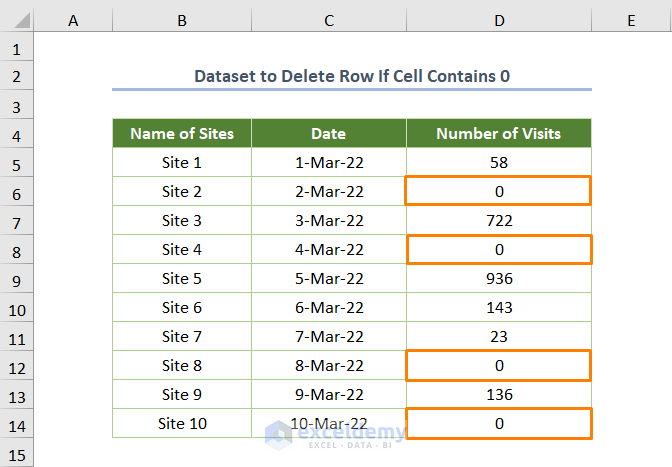
The dataset below shows the Number of Visits, the Names of the Sites, and the Dates. Some sites have a cell value (Number of Visits) of 0. In such a situation, you might want to delete rows with the cell value of 0.
Method 1 – Using Macro to Delete Certain Rows If Cell Contains 0
Step 1: Inserting a Module
- Open a module by clicking Developer > Visual Basic.
- Go to Insert > Module.
Step 2: Copying the VBA Code
- Enter the following code:
Sub Delete_CertainRows()
Dim Sht As Worksheet
Dim last as Long
Dim i As Long
Set Sht = ActiveSheet
last = Cells(Rows.count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
For i = last To 14 Step 1
If Cells(i, "D").Value = "0" Then
Cells(i, "D").EntireRow.Delete
End If
Next i
End Sub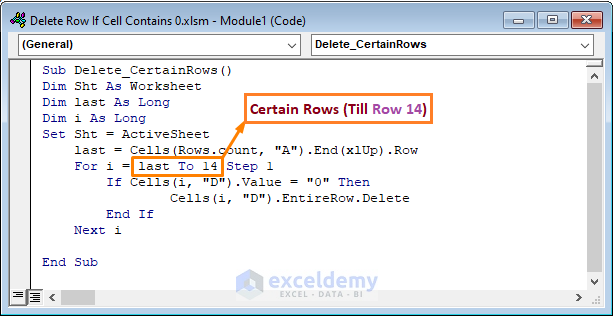
Code Breakdown
- I declared Sht as Worksheet to define the current worksheet. In addition, I also declared last and i as Long to store the row number.
- Then, I turned on the current sheet by setting the ActiveSheet.
- Immediately, I assigned the last to Cells(Rows.count, “A”).End(xlUp).Row to return the last row as the top cell of the bottom column.
- Later, I utilized For Loop where i was assigned as the last To 14 Step 1. That means the loop would run till Row 14 and the increment was 1 for every row.
- Lastly, I added an If statement to delete the row with a cell value of 0. The Delete function is attached to delete the entire row when the statement is true.
Step 3: Running the VBA Code
When you run the code (the keyboard shortcut is F5 or Fn + F5), you’ll get the following output.
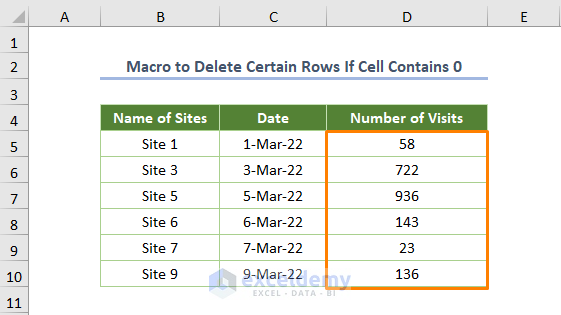
Read More: How to Use Macro to Delete Rows Based on Criteria in Excel
Method 2 – Deleting the Entire Row from the Defined Range When the Cell Value is Zero
- Enter the following code into the newly created module:
Sub DeleteRow_DefinedRange()
Dim Rng As Range
For Each Rng In Range("D5:D14")
If Rng.Value = "0" Then
Rng.EntireRow.Delete
End If
Next Rng
End Sub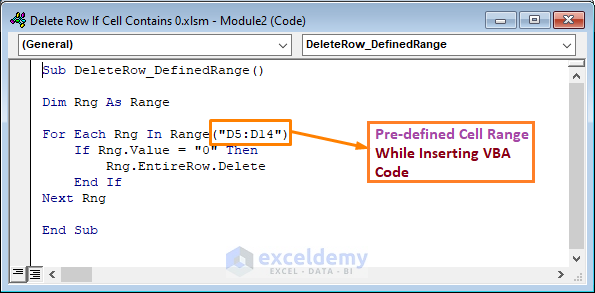
Code Breakdown
- I declared Rng as Range.
- Then I assigned For Each statement to define each element of the pre-defined range i.e. D5:D14.
- Along with that, I also added an If statement and Delete to delete the entire row when the statement is true.
However, the output will look as follows if you run the code.
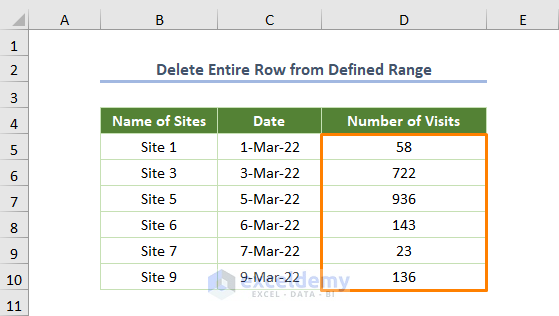
Read More: How to Apply VBA Code to Delete Rows Based on Multiple Cell Value
Method 3 – Using InputBox for Defining Range to Delete Entire Row
- Enter the following code:
Sub DeleteRow_UsingInputBox()
Set Rng = Application.Selection
Title = "Delete Row Using InputBox"
Set Rng = Application.InputBox("Please Select the Cell Range:", Title, Rng.Address, Type:=8)
Do
Set cell = Rng.Find("0", LookIn:=xlValues)
If Not cell Is Nothing Then
cell.EntireRow.Delete
End If
Loop While Not cell Is Nothing
End Sub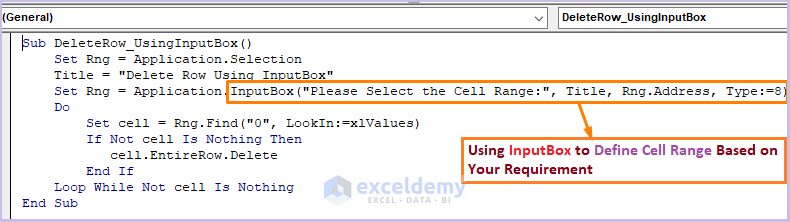
Code Breakdown
- Here, I set Rng utilizing InputBox
- Then I assigned Do Loop to repeat and transfer the control of the If Not statement.
- Meanwhile, I specified the cell using the Find to find 0.
- In addition, I added an If Not statement with the Delete to delete row when the statement is true.
- You’ll see the following dialog box to enter the range from where you want to delete rows with specific criteria.
- Enter $D$5:$D$14 manually or drag down the cursor from D5 to D14 cell.
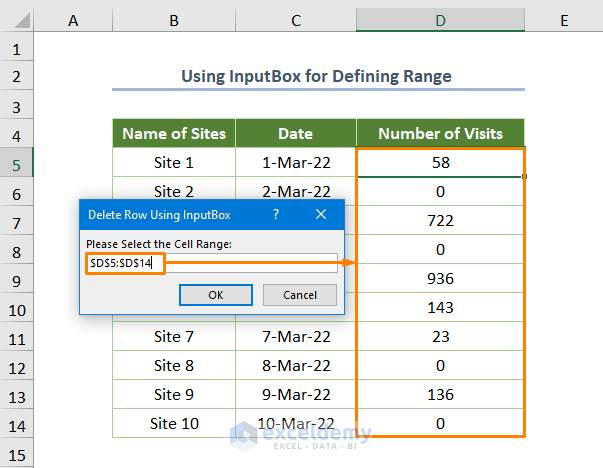
You’ll get the following output.
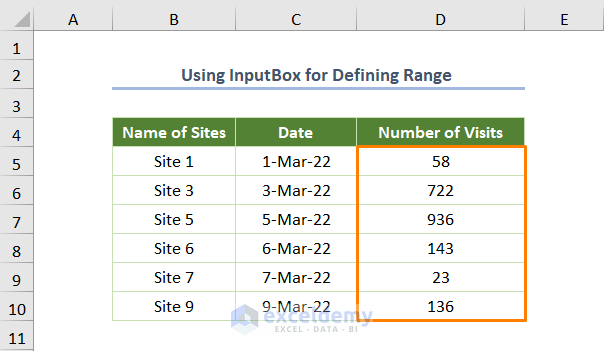
Read More: How to Use VBA to Delete Empty Rows in Excel
Method 4 – Deleting a Row If Cell Contains 0 across Multiple Sheets
For example, the dataset has 3 separate working sheets. Sheet 1 includes the same information as the dataset, but Sheet 2 has a slightly different Number of Visits.
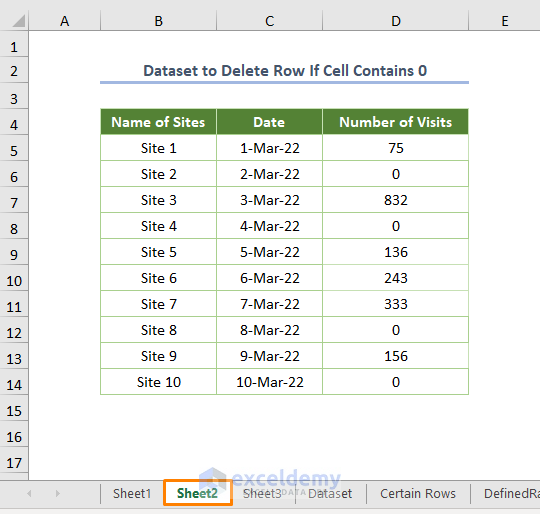
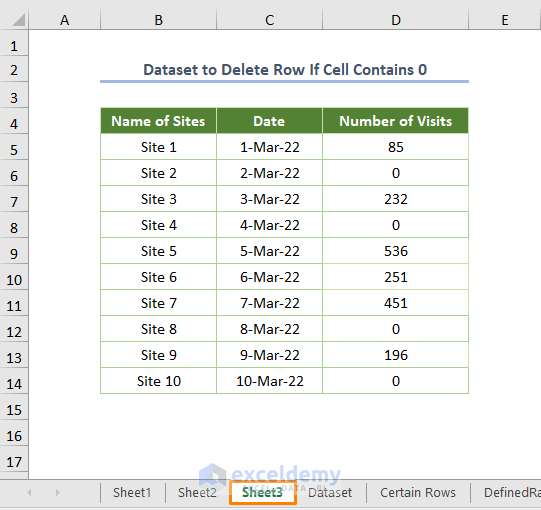
The following picture denotes the different information about Sheet3.
- Enter the following code:
Sub DeleteRows_MultipleSheets()
Dim Sht As Worksheet
Dim last As Long
Dim i As Long
For Each Sht In Worksheets(Array("Sheet1", "Sheet2", "Sheet3"))
Sht.Activate
last = Cells(Rows.count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
For i = last To 14 Step 1
If Cells(i, "D").Value = "0" Then
Cells(i, "D").EntireRow.Delete
End If
Next i
Next Sht
End Sub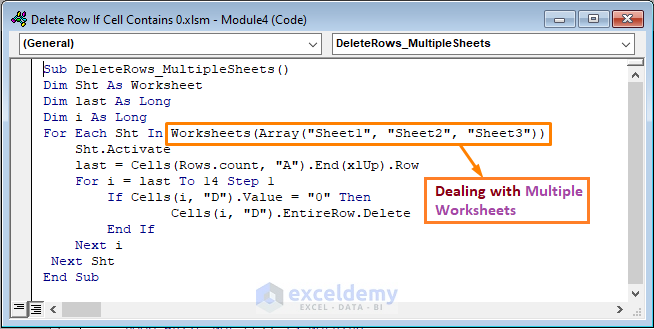
Code Breakdown
- I declared Sht as Worksheet. In addition, I also declared last and i as Long to store the row number.
- Then, I specified the 3 sheets with their name using the Worksheets, And Each statement is set to define each element.
- The rest are similar to the first method.
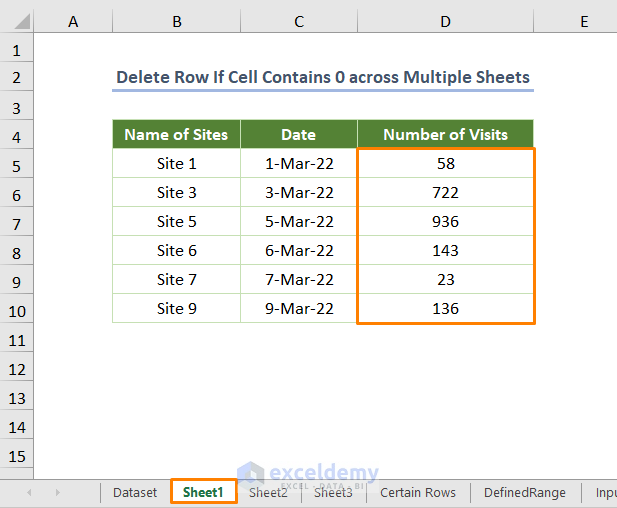
After running the code, you’ll get the output in the case of Sheet1.
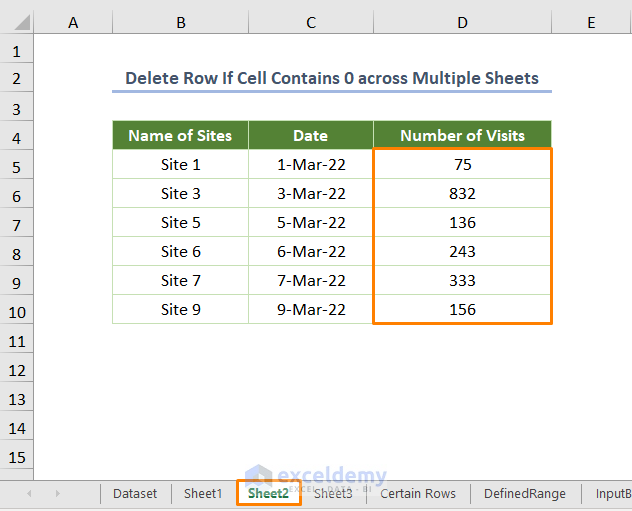
You’ll get the following output in the case of Sheet2.
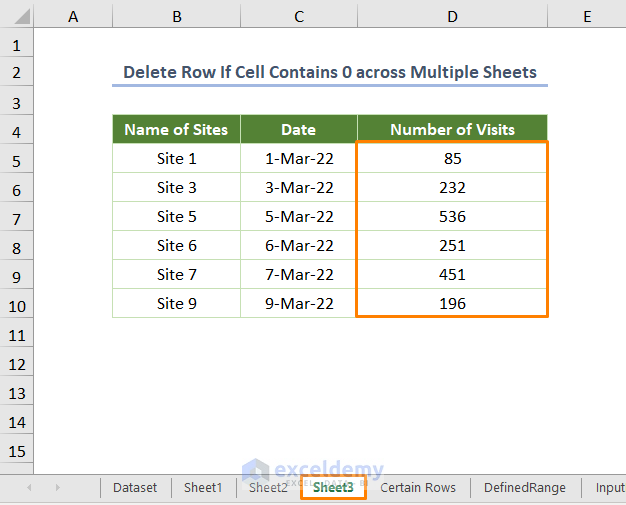
The output for Sheet3 will be as follows.
Read More: Excel VBA to Delete Row If Cell Contains Partial Text
Download the Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- How to Filter and Delete Rows with VBA in Excel
- How to Apply VBA to Delete Rows with Specific Data in Excel
- Excel VBA: Delete Row If Cell Is Blank



Hello Abdul,
I am struggling with my data set.
Using your macros (method 2 suits best) seems to miss deleting rows containing zero if they are adjacent (above / below) another row containing zero. Your example does not replicate this.
Hello T C Millichap,
It sounds like the macro might not be checking all rows properly when there are consecutive zeros. This could happen if the loop skips over rows after deleting one. You can modify the code to ensure it doesn’t skip rows by adjusting how the loop is set up.
By looping backwards, you prevent skipping rows after deletion. This should address the issue of consecutive zeros. Let me know if you need further adjustments!
Regards
ExcelDemy