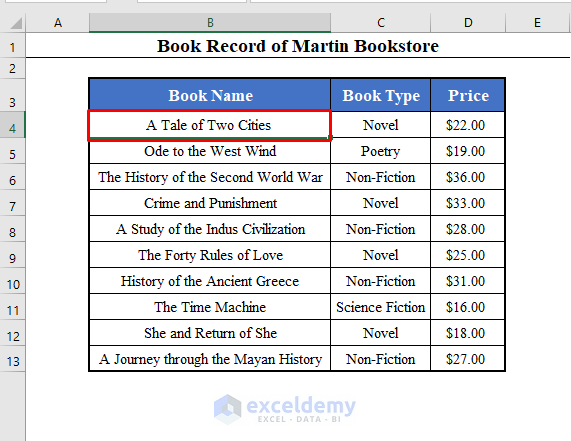
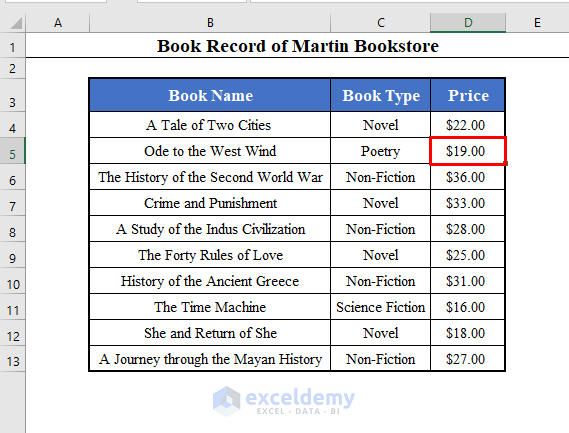
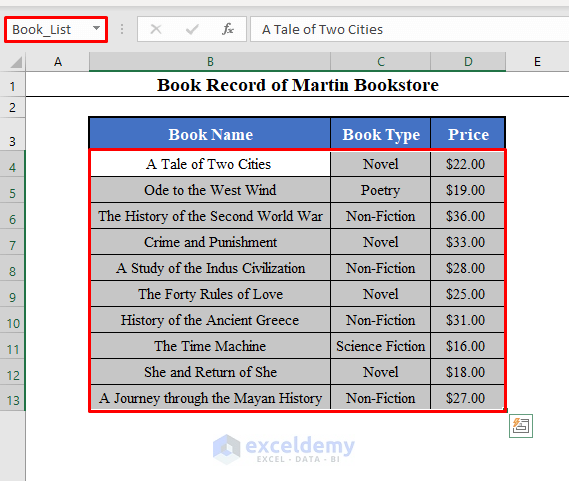
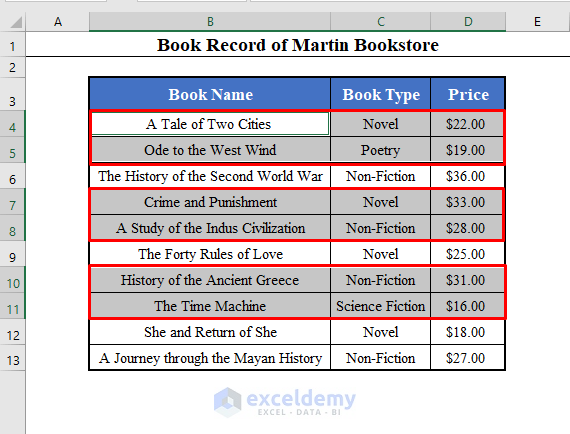
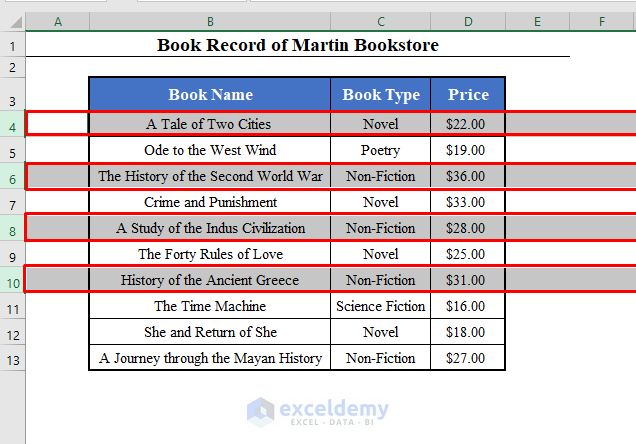
We’ll use a data set with the Book Name, Book Types, and Price of some books of a bookshop called Martin Bookstore. The data set lies in the range B4:D13 of the worksheet.
Method 1 – Refer to a Cell Reference by Using the Range Object in VBA in Excel
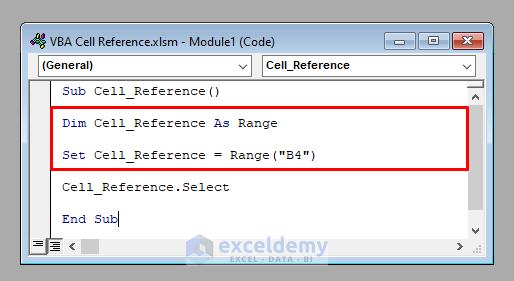
- To access the single-cell B4, use this line of code:
Dim Cell_Reference As Range
Set Cell_Reference = Range("B4")
- The following code selects cell B4.
- It’ll select cell B4 in the active worksheet.
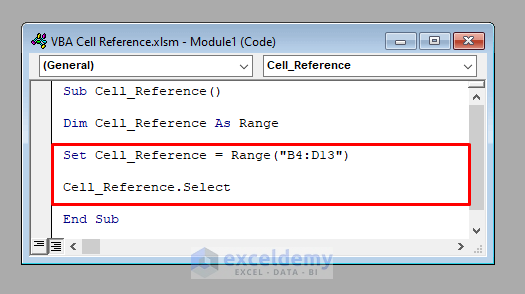
You can access a range of cells in this way.
Dim Cell_Reference As Range
Set Cell_Reference = Range("B4:D13")
- The following code selects the range B4:D13.
- It’ll select the range of cells B4:D13.
Note: You can use the Range object directly without declaring it first, like:
Range("B4:D13").Select- If you want to access any cell of a worksheet that’s not active, use the name of the worksheet before the Range object.
- To access the cell B4 of Sheet2, use:
Worksheets("Sheet2").Range("B4:D13")Method 2 – Refer to a Cell Reference by Using the Index Numbers in VBA in Excel
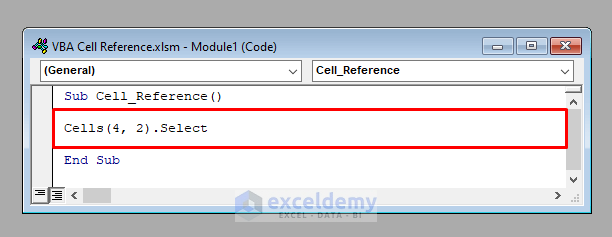
- To access the cell with row number 4 and column number 2 (B4), use:
Cells(4, 2))- The following code again selects cell B4 of the active worksheet.
- It’ll select cell B4.
Note: To access any cell of an inactive worksheet, use the name of the worksheet before the cell reference.
Worksheets("Sheet2").Cells(4, 2)Read More: How to Keep a Cell Fixed in Excel Formula
Method 3 – Refer to a Cell Reference Relative to Another Cell in VBA in Excel
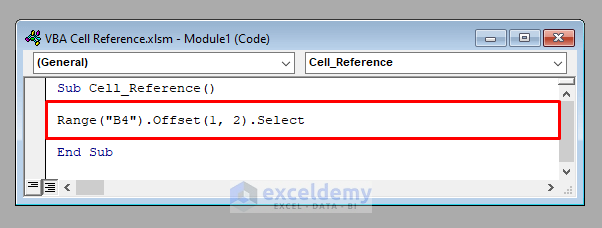
- To access the cell 1 row down and 2 columns right of the cell B4 (D5), use:
Range("B4").Offset(1, 2)The following code selects cell D5 of the active worksheet.
It’ll select cell D5.
Note: To refer to any cell of a worksheet that’s inactive, use the name of the worksheet before the cell reference.
For example:
Worksheets("Sheet2").Range("B4").Offset(1, 2)Method 4 – Refer to a Cell Reference by Using the Shortcut Notation in VBA in Excel
- To access cell B4, use:
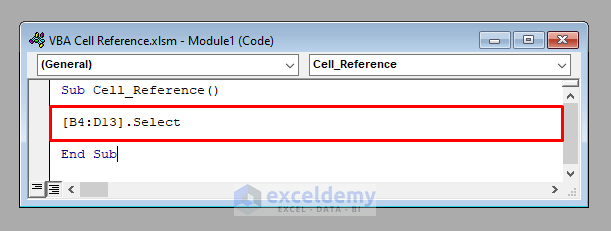
[B4] - To access the range B4:D13, use:
[B4:D13]
The following code selects the range B4:D13.
It’ll select the range B4:D13.
Note: To refer to any cell of an inactive worksheet, use the name of the worksheet before the cell reference.
For example:
Worksheets("Sheet2").[B4:D13]Method 5 – Refer to a Named Range in VBA in Excel
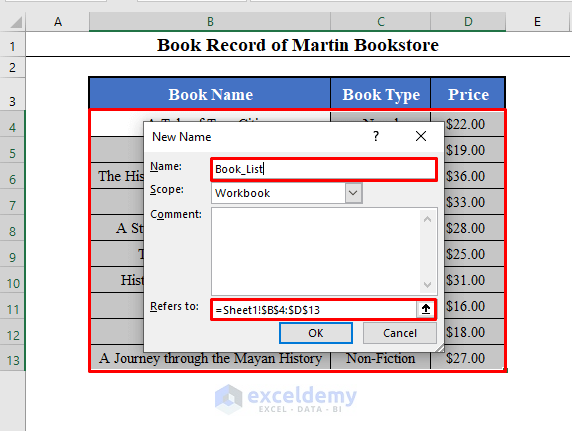
- Let’s name the range B4:D13 of the active worksheet as Book_List.
- We can refer to this Named Range by the line of code:
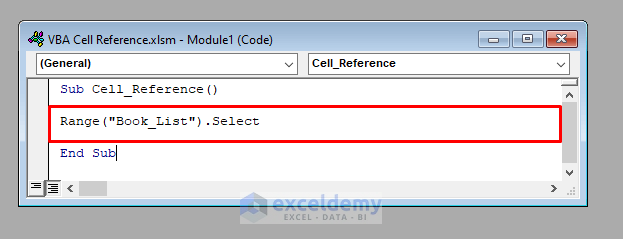
Range("Book_List")The following code selects the range Book_List (B4:D13).
It’ll select the range Book_List.
Note: To access any cell of an inactive worksheet, use the name of the worksheet before the cell reference.
For example:
Worksheets("Sheet2").Range("Book_List")Read More: How to Use Cell References in Excel Formula
Method 6 – Refer to Multiple Ranges in VBA in Excel
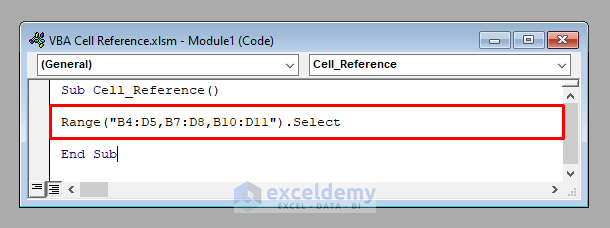
- To access the ranges B4:D5, B7:D8, and B10:D11, use:
Range("B4:D5,B7:D8,B10:D11")It’ll select the multiple ranges together.
- You can use the Union property of VBA to access multiple ranges together:
Union(Range("B4:D5"), Range("B7:D8"), Range("B10:D11"))- You can also access multiple Named Ranges together.
Range("Named_Range_1,Named_Range_2")- Put the worksheet name in front of inactive worksheets.
Worksheets("Sheet2").Range("B4:D5,B7:D8,B10:D11")Read More: Relative and Absolute Cell Address in the Spreadsheet
Method 7 – Refer to Rows and Columns in VBA in Excel
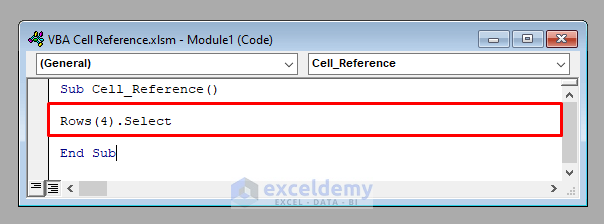
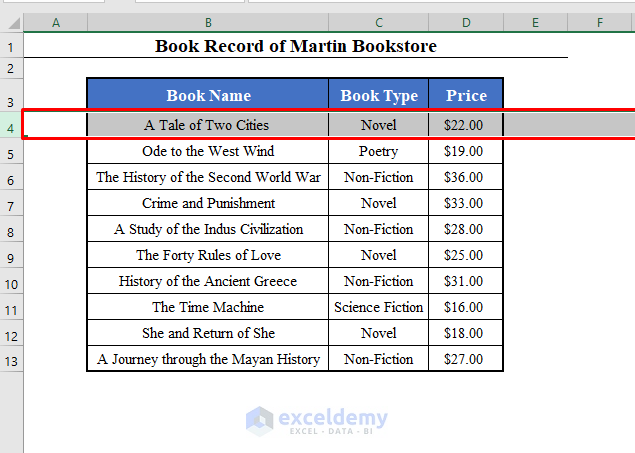
- To access the 4th row, use:
Rows (4)- It’ll select the entire 4th row.
- Columns(4) will access the entire 4th column.
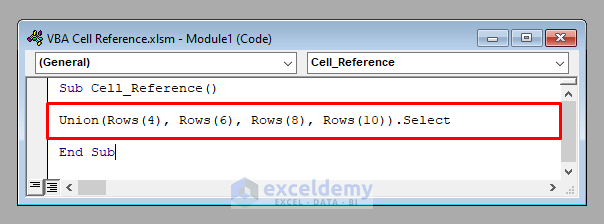
- To access multiple rows or columns together, use the Union property of VBA. To access the rows 4, 6, 8, and 10 together, use:
Union(Rows(4), Rows(6), Rows(8), Rows(10))It’ll select the entire rows 4, 6, 8, and 10.
Note: Add the name of the worksheet in front in case it’s an inactive one.
Worksheets("Sheet2").Rows (4)Read More: Difference Between Absolute and Relative Reference in Excel
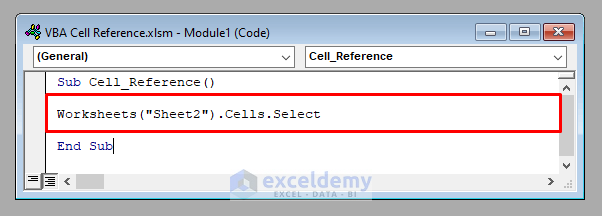
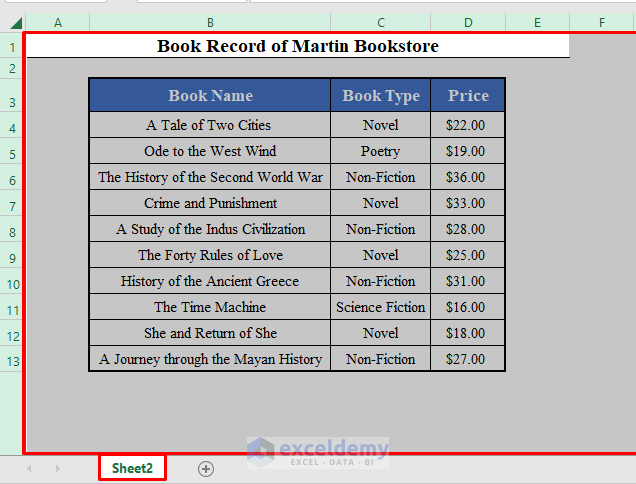
Method 8 – Refer to the Whole Worksheet in VBA in Excel
- To access the whole worksheet in VBA, use:
Cells- To refer to an inactive worksheet (For example, Sheet2), use:
Worksheet("Sheet2").CellsIt’ll select the whole worksheet Sheet2.
Read More: Excel VBA: R1C1 Formula with Variable
Download the Practice Workbook
Download this practice book to follow along while reading this article.
<< Go Back to Cell Reference in Excel | Excel Formulas | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!