In this Excel tutorial, you’ll learn
-What is a running total
-What are the uses of running total
-How to calculate running total in Excel
-And how to create a running total chart in Excel
We’ll use the Microsoft 365 for our article. You can also use other versions of Excel for these methods.
The running total can analyze cumulative data or track the progress of a value over time. You can use this when you deal with financial data, such as sales figures or expenses.
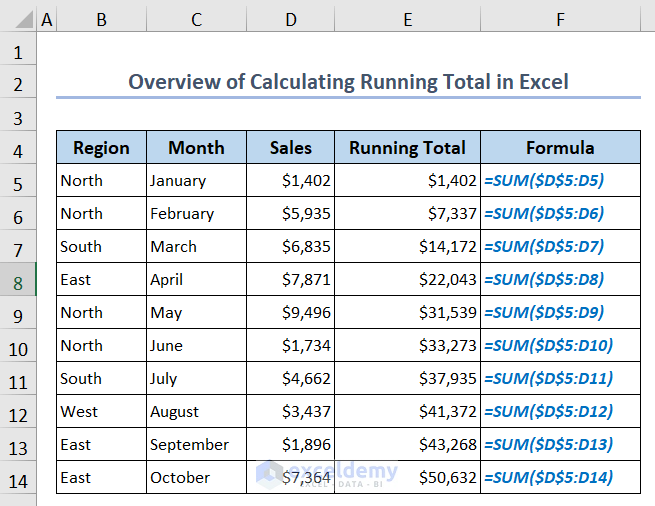
In the following overview image, we use the SUM function to calculate the running total of sales values.
Download Practice Workbook
What Is a Running Total?
A running total, or a cumulative sum, is a series of partial sums of any set of data. The running total shows the summary of data as it accumulates over time.
Suppose, we have the first value: X. If we get the second value: Y, the running total will be: X+Y. Similarly, if there’s a third value: Z, the updated running total will be: X+Y+Z.
What Are the Uses of Running Total?
You can use the running total in many areas. Some of them are:
- You can use it in the cash register operation of any store. Cash registers in particular show a running total of different products as they are scanned into the system. They usually keep track of all transactions that take place throughout the day in a running total as well.
- The running total is useful in sports. An excellent example of a running total is in the sport of cricket. Every time a player scores a run, the total run gets increased. As a result, the final score is only the aggregate of the runs or running total.
- You need to calculate the running total if you work in a sales position. If you have a quota, you can use a running total to monitor your progress. Managers use these running totals to assess the performance of workers on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis.
- You can use the running total in the year-to-date calculation. The running total tracks a specific task or activity from a specific date until the end of the year.
- Businesses frequently use the running totals to manage their inventories as they have to keep track of how many goods are sold. Then, they compare that number to how many items they have on hand.
- You can use the running total in the balance sheet. You can clearly see any assets and liabilities at any time with the use of balance sheets.
- You can also use the running total for calculating your bank balance.
- Ride-sharing companies and delivery services use the running total to track the mileage. As a result, drivers are compensated per mile.
- You may track your daily or weekly calorie intake using the running totals. You can track your calories in order to lose weight. For this purpose, use Excel to input the number of calories in each meal. Then, calculate how many calories you’ll consume over the course of a day or a week.
How Many Methods Are There to Calculate Running Total in Excel?
You can calculate the running total in Excel using the 10 methods described here. Follow along to learn about them.
1. Use a Custom Formula to Calculate Running Total
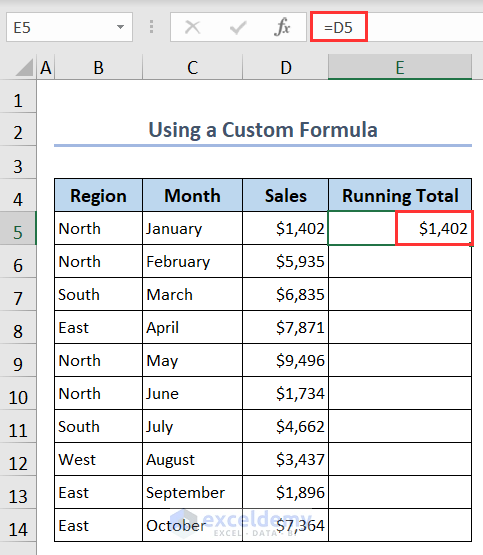
You can use a cell reference in a custom formula to calculate the running total.
- Type the following formula in cell E5 to get the exact same sales amount:
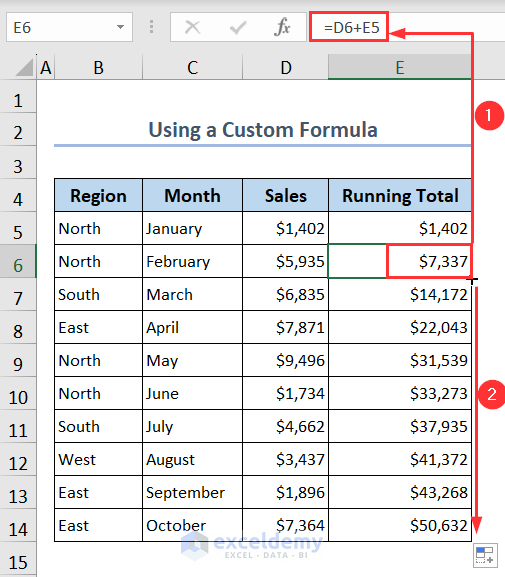
=D5- Again, type the following formula in cell E6:
=D6+E5- Apply the Fill Handle tool to copy the formula in the rest of the cells. You’ll get the running total.
2. Apply SUM Function to Get Running Total
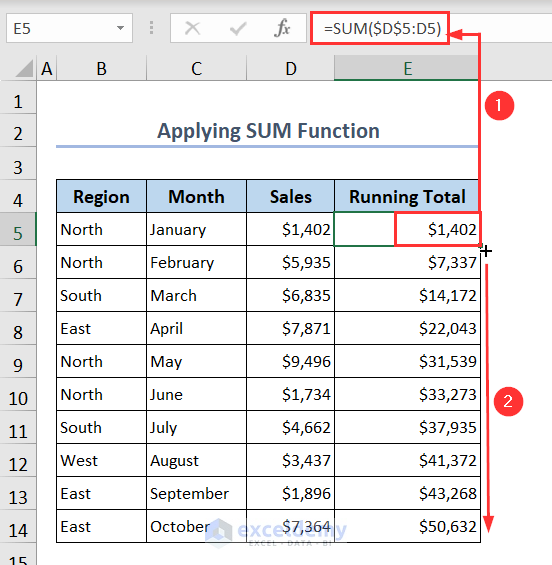
You can apply the SUM function with a partially locked cell reference to calculate the running total in Excel.
- Write the following formula in cell E5.
- Then, apply the Fill Handle tool to get the running total:
=SUM($D$5:D5)3. Use SUMIF Function to Compute Running Total with Criteria
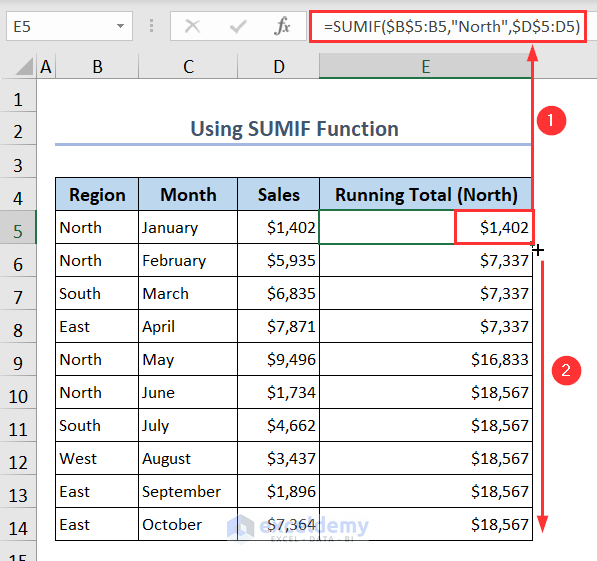
You can use the SUMIF function to calculate the running total in Excel with criteria. In this example, we use this function to calculate the running total of the North region.
- Insert the following formula in cell E5.
- Then, apply the Fill Handle tool to get the running total of the North region:
=SUMIF($B$5:B5,"North",$D$5:D5)4. Combine SCAN and LAMBDA Functions to Calculate Running Total at One Click
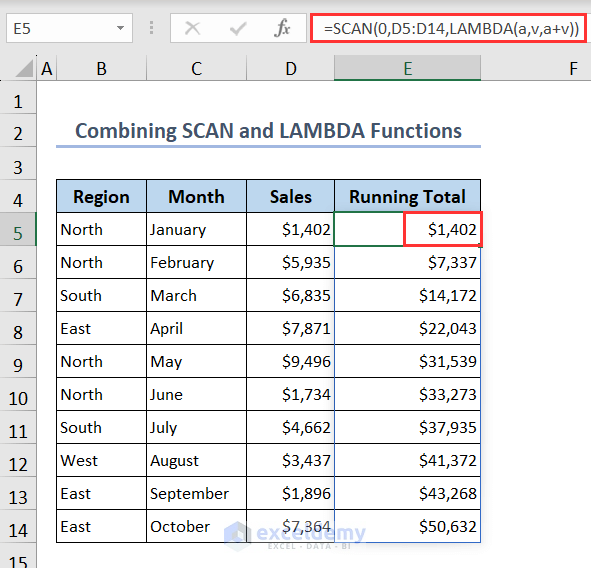
You can combine the SCAN and LAMBDA functions to calculate the running total in one click.
- Write the following formula in cell E5 to get the running total at one click:
=SCAN(0,D5:D14,LAMBDA(a,v,a+v))Formula Breakdown
- LAMBDA(a,v,a+v)– Here a represents the accumulated value and v represents the current value in the iteration. The expression a+v adds the current value to the accumulated value using the LAMBDA function.
- SCAN(0,D5:D14,LAMBDA(a,v,a+v))– Here the initial value is set to 0. Then, the second argument D5:D14 represents the range of values over which the SCAN function will iterate. Finally, the SCAN function performs the LAMBDA expression calculation for each value.
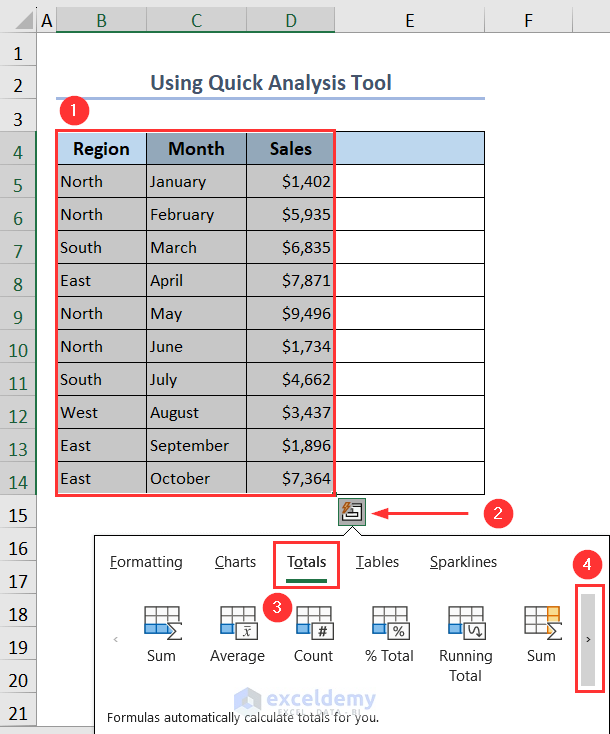
5. Use Quick Analysis Tool to Calculate Running Total Automatically
- Select the whole dataset and click on the Quick Analysis Tool button.
- Click on the Total tab and then press the slider button.
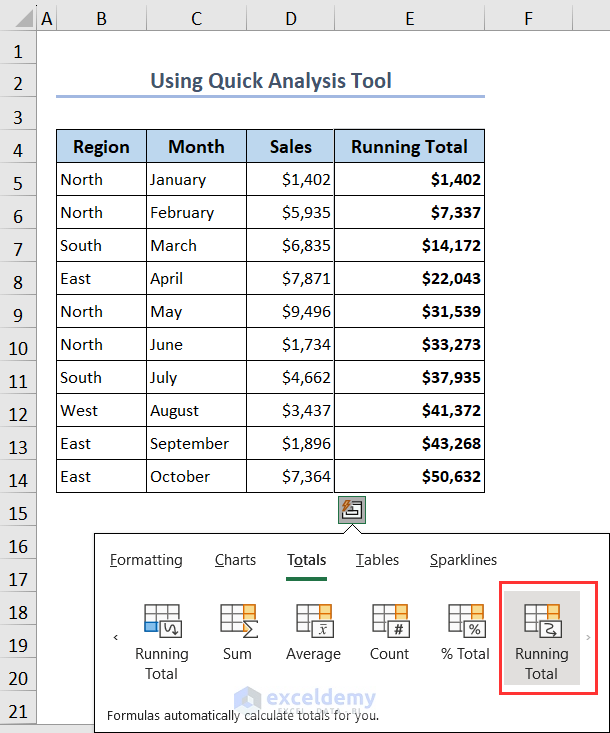
- Select Running Total (yellow color) from here. You’ll get the running total of your values placed automatically in column E.
6. Use Table Feature to Calculate Running Total at Once
We use the Table feature and a custom formula to calculate the running total at once.
- Select the whole dataset (B4:E14).
- Then, go to Insert > Table. Or press Ctrl + T from your keyboard.
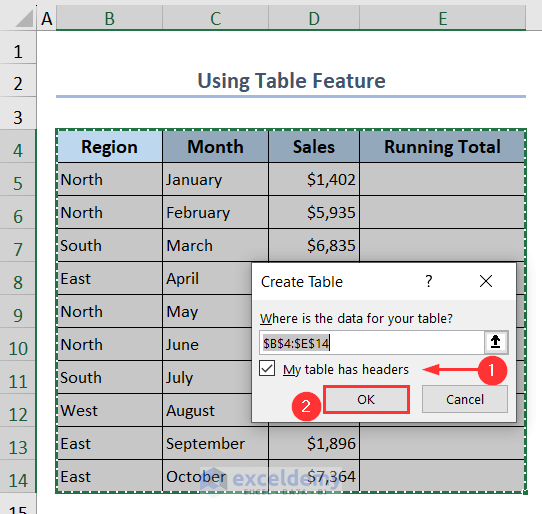
- Tick the option My table has headers under the Create Table window.
- Press OK.
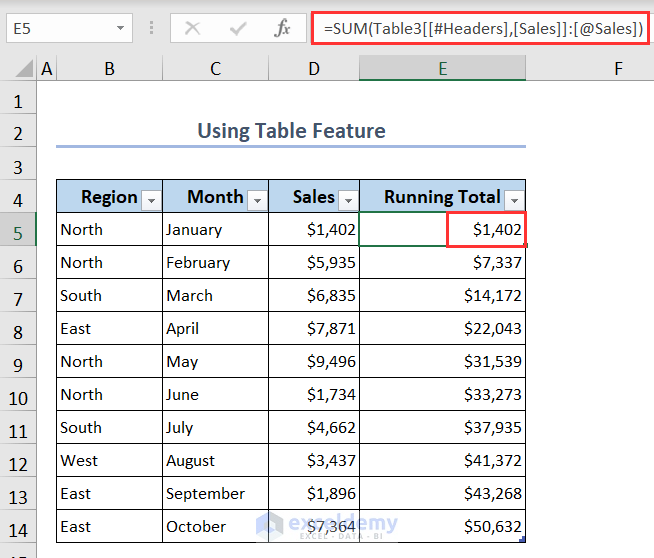
- The Table is ready to use. Put the following formula in cell E5 and get the running total at once:
=SUM(Table3[[#Headers],[Sales]]:[@Sales])- Here, we use Table3 as our table’s name and we summed the Sales column of our table.
7. Apply Power Query to Calculate Running Total
You can use the Power Query tool to calculate the running total by adding a column in the Power Query editor.
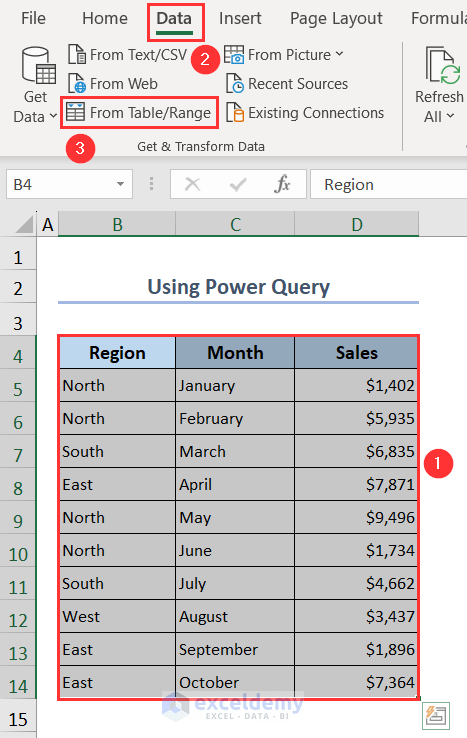
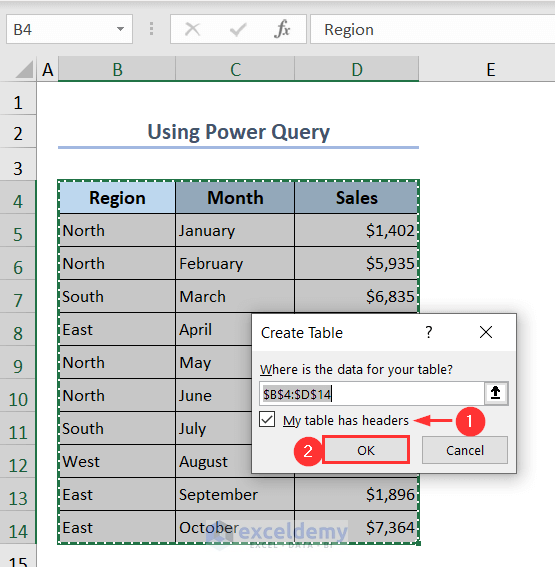
- Select the whole dataset.
- Go to Data > From Table/Range.
- In the Create Table window, tick the option: My table has headers.
- Press OK.
Power Query Editor will open.
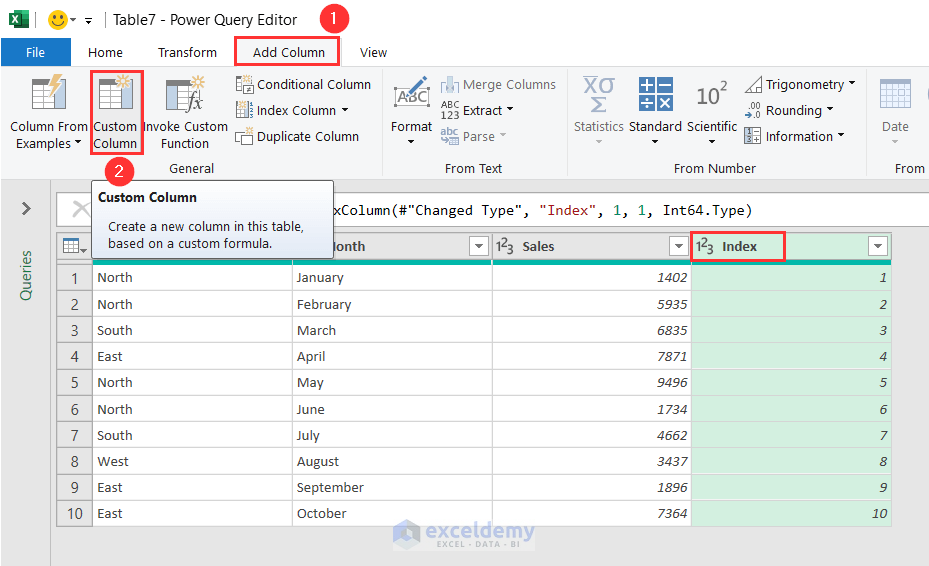
- Go to the Add Column tab and select From 1 from the Index Column drop-down menu.
- A new column titled Index will be added beside the Sales column.
- Now, select Custom Column under the Add Column tab.
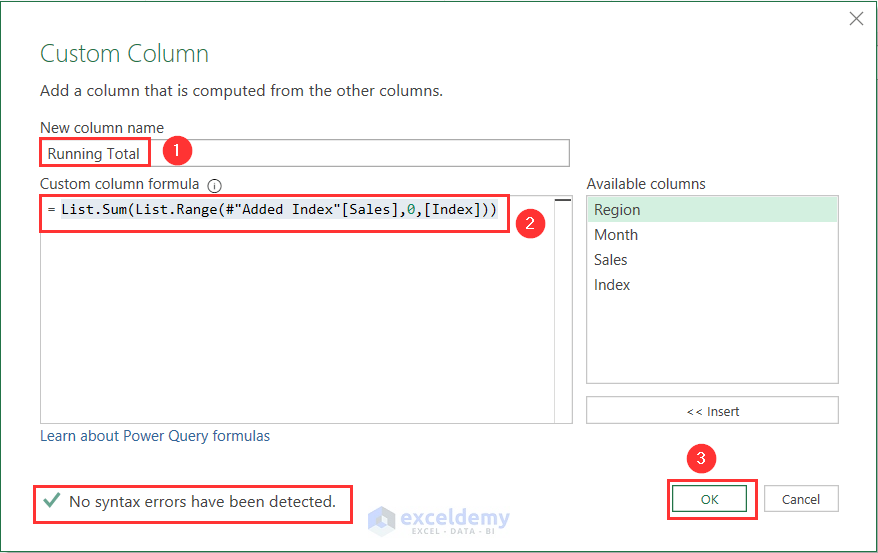
- In the Custom Column window, type a new column name. Here we put Running Total as the name.
- Then, put the following formula in the formula box:
=List.Sum(List.Range(#"Added Index"[Sales],0,[Index]))- Here, Sum gives the sum of the range within the dataset. List.Range gives the range of Sales and it will change depending on the Index value.
- Check whether No syntax errors have been detected appear or not. If it appears, press the OK button.
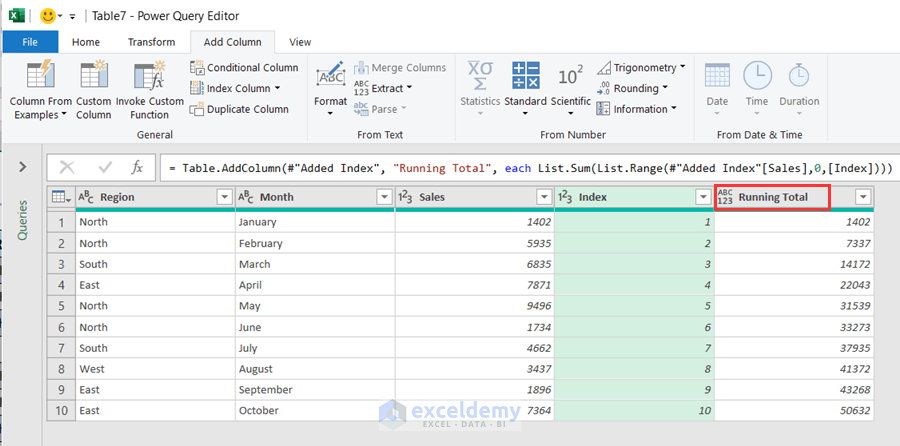
- A new column titled Running Total will be added beside the Index column.
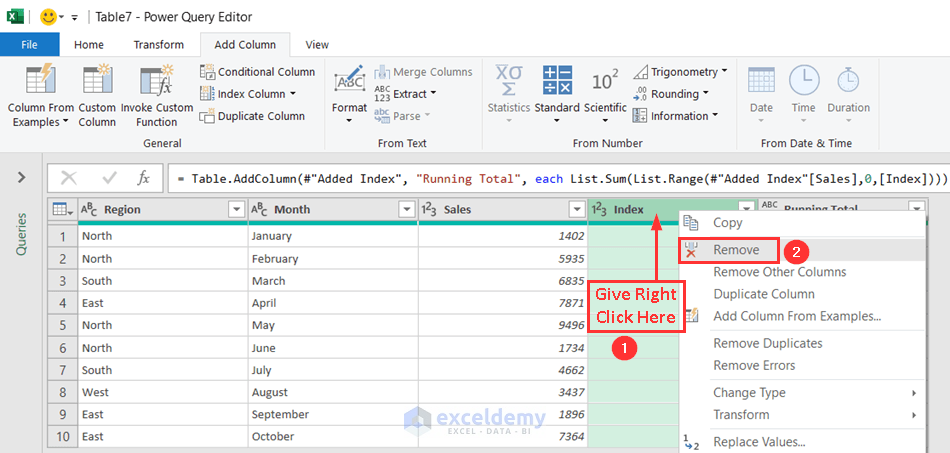
- Right-click on the empty space of the Index column.
- Select the Remove option.
- The Index column is removed. Now, go to the Home tab and select Close & Load.
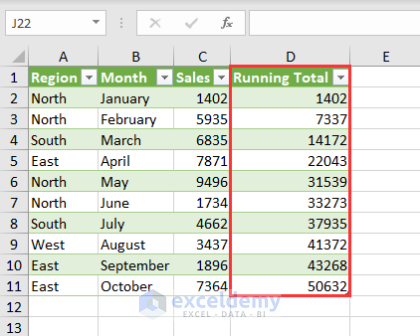
Finally, you’ll get the running total of your sales values along with the dataset in a new worksheet.
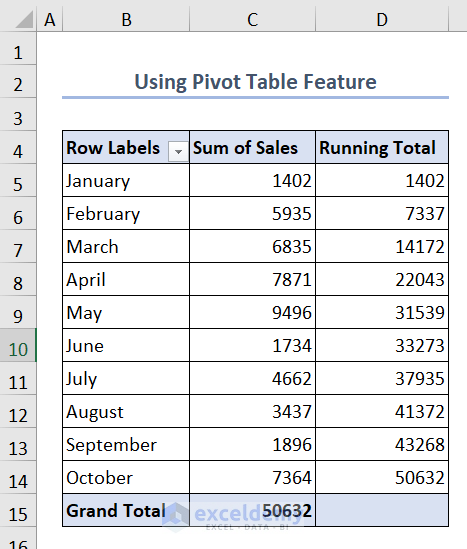
8. Use Pivot Table Feature to Calculate Running Total
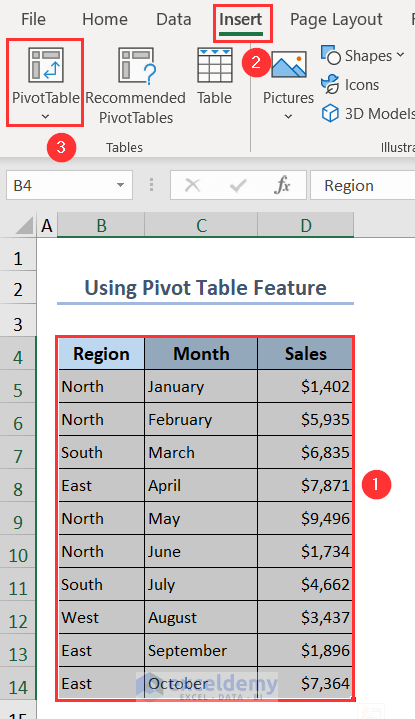
- Select B4:D14 and go to Insert > PivotTable.
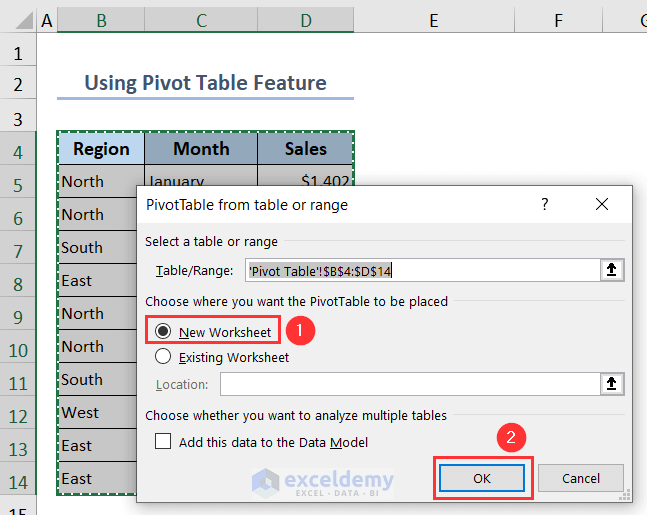
- Choose the option New Worksheet under the PivotTable from table or range window.
- Press OK.
- The PivotTable Fields window will open.
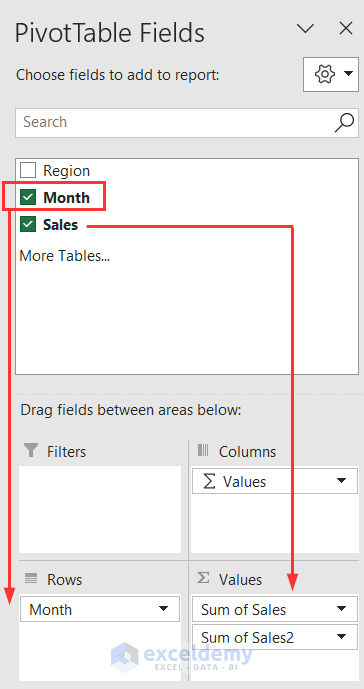
- Drag the Month under the Rows field once and the Sales under the Values field twice.
- You’ll get a dataset like below.
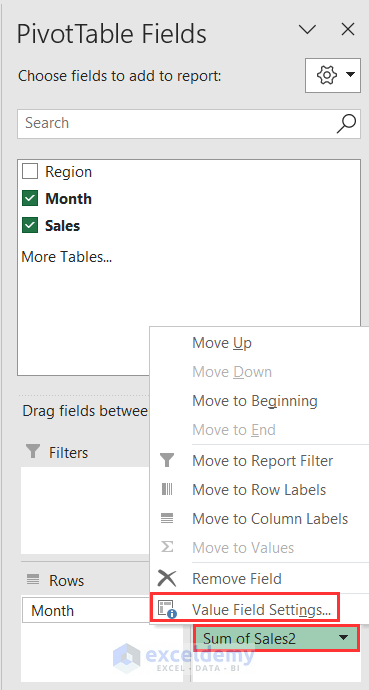
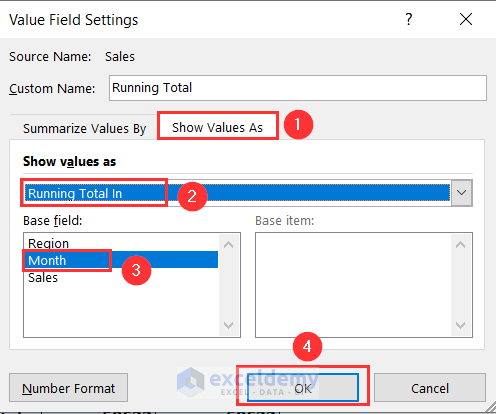
- In the PivotTable Fields window, go to the Value Field Settings by clicking on the Sum of Sales2 drop-down.
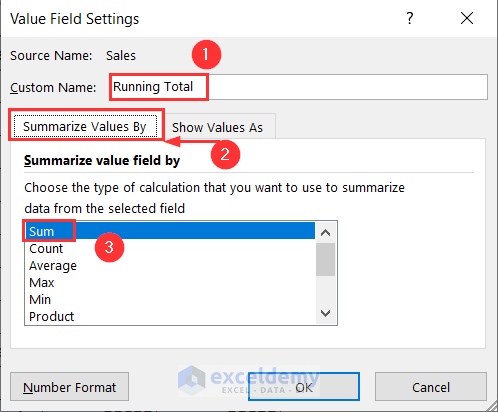
- In the Value Field Settings wizard, put the name as Running Total.
- Go to Summarize Values By tab and choose Sum from the drop-down.
- Go to the Show Values As tab and choose Running Total In under this option.
- Select Month as the Base field and press OK.
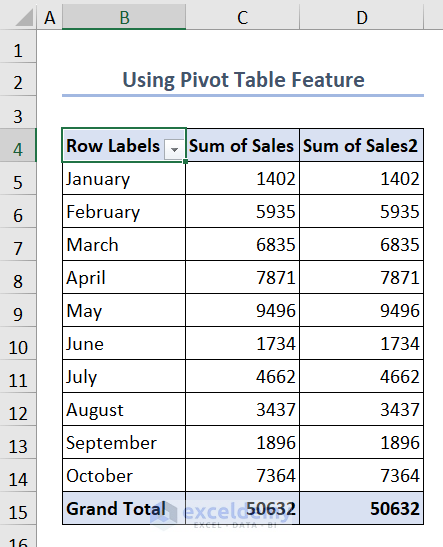
- You’ll see the running total in column D.
9. Apply Power Pivot and DAX Measures Together
If you want to calculate the running total using a DAX formula, you can combine the Power Pivot and DAX measures.
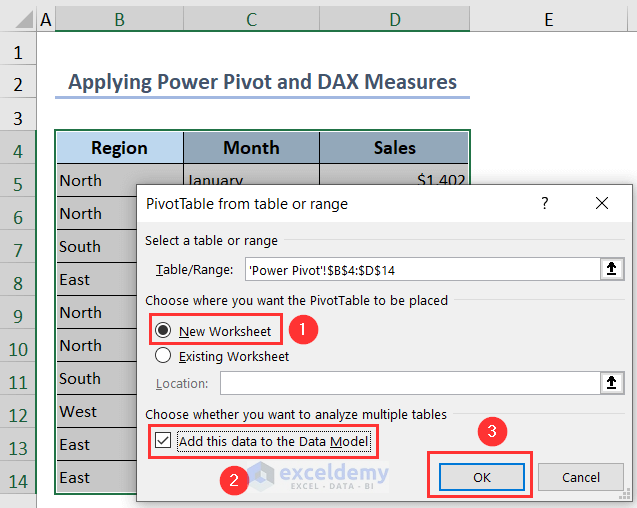
- Select B4:D14 >> go to Insert >> PivotTable.
- Choose New Worksheet and tick the option Add this data to the Data Model under the PivotTable from table or range window.
- Press OK.
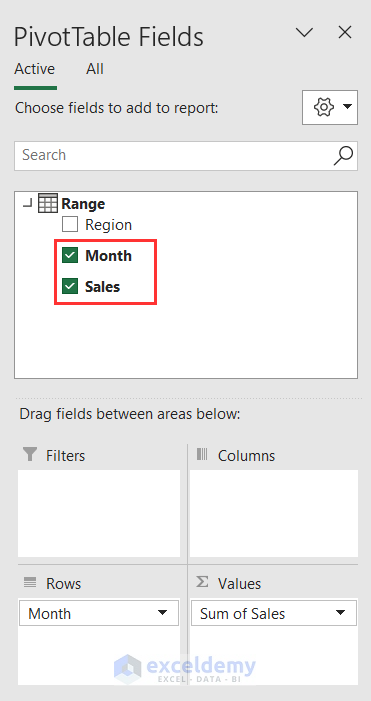
- Select Month and Sales. These 2 will automatically get added to the Rows and Values fields respectively under the PivotTable Fields pane.
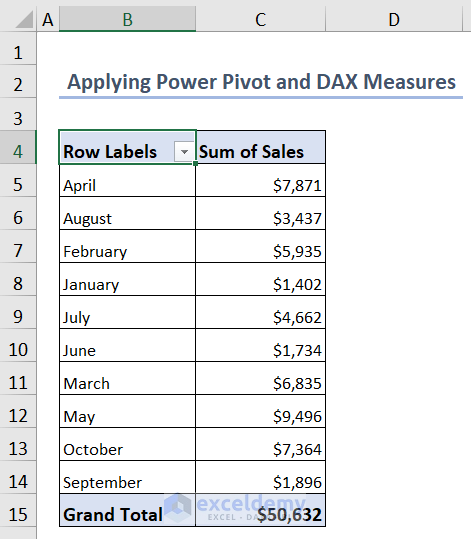
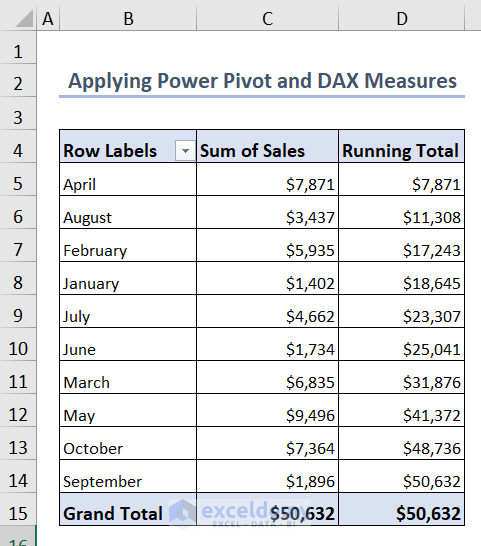
- And, you’ll see a dataset like this in your Excel sheet.
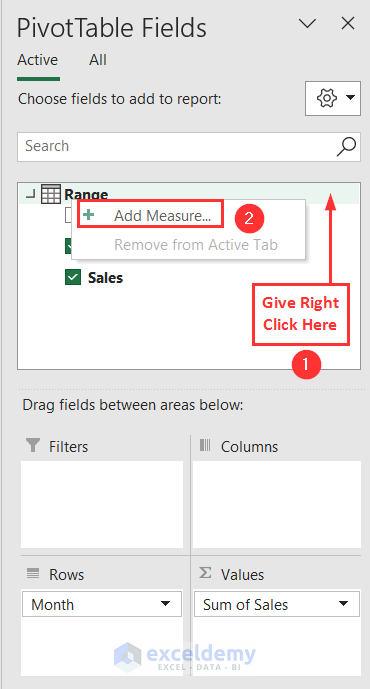
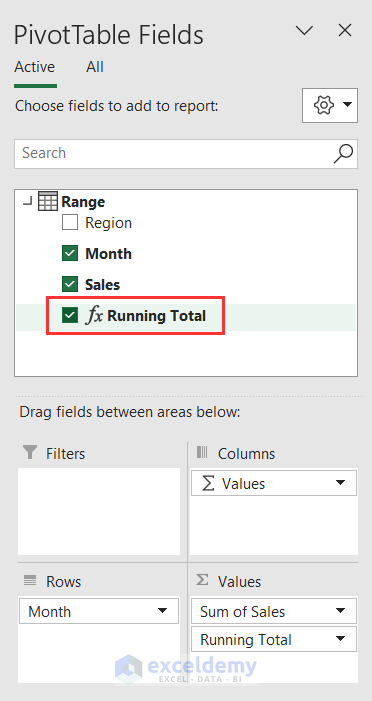
- In the PivotTable Fields pane, right-click on the empty space of Range. Then, click on the Add Measure option.
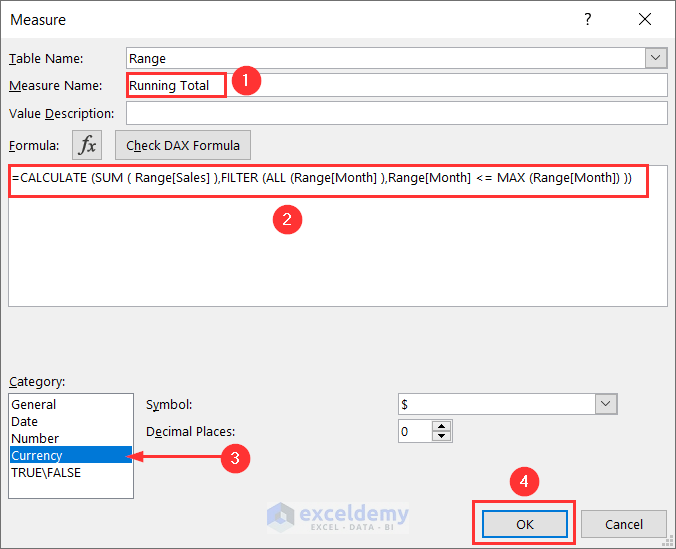
- You’ll find yourself in the Measure window. Give a name like Running Total. Put the DAX formula in the formula box:
=CALCULATE (SUM ( Range[Sales] ),FILTER (ALL (Range[Month] ),Range[Month] <= MAX (Range[Month]) ))- Here, Range[Sales] refers to the Sales column and Range[Month] indicates the Month column of the dataset.
- Select Currency as the Category and press OK.
- Running Total is added now in the PivotTable Fields window.
- Tick it to add this to your Excel sheet.
You’ll obtain the running total of the sales values.
10. Apply Relative Named Range and R1C1 Style with SUM Function
You can apply the Named Range feature with the SUM function to calculate the running total. But, for this, you have to change the reference style of your Excel file. Generally, your Excel file is in A1 style. We need to change it to R1C1 style.
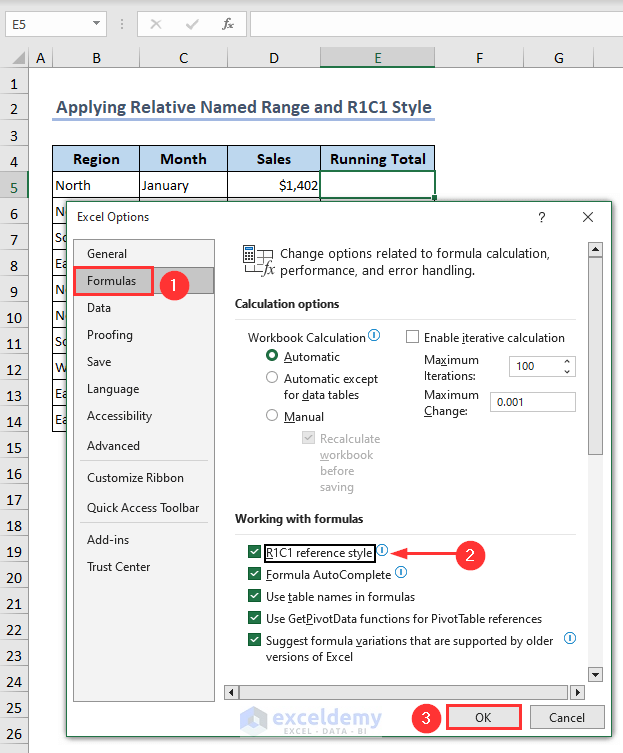
- Go to the File tab.
- Select Options under the Home tab.
- The Excel Options window will open up.
- Tick beside the R1C1 reference style option from the Formulas tab.
- Click OK.
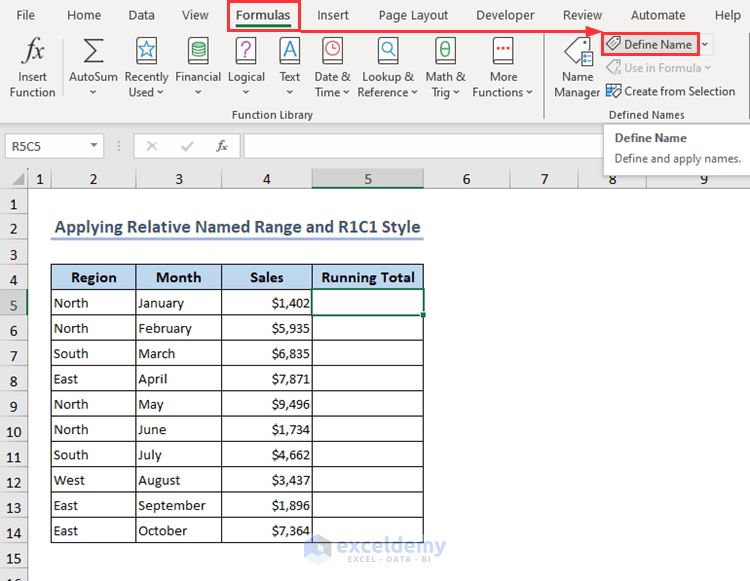
- The reference style will change to R1C1. Now, go to Formulas > Define Name.
- The New Name window will open up.
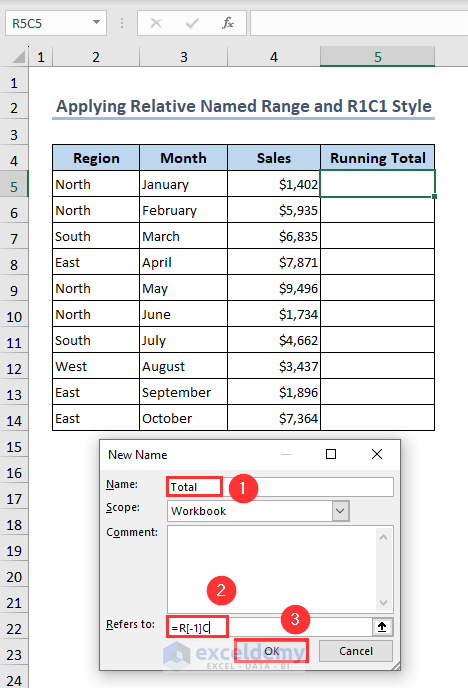
- Put a name, Total in the Name box.
- Insert the following formula in the Refers to box.
=R[-1]C- Click OK.
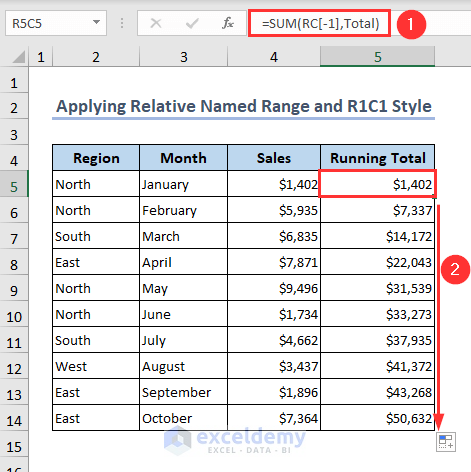
- Put the following formula in cell R5C5 and apply the Fill Handle tool:
=SUM(RC[-1],Total)You’ll obtain the running total of the sales values.
How to Create a Running Total Chart in Excel?
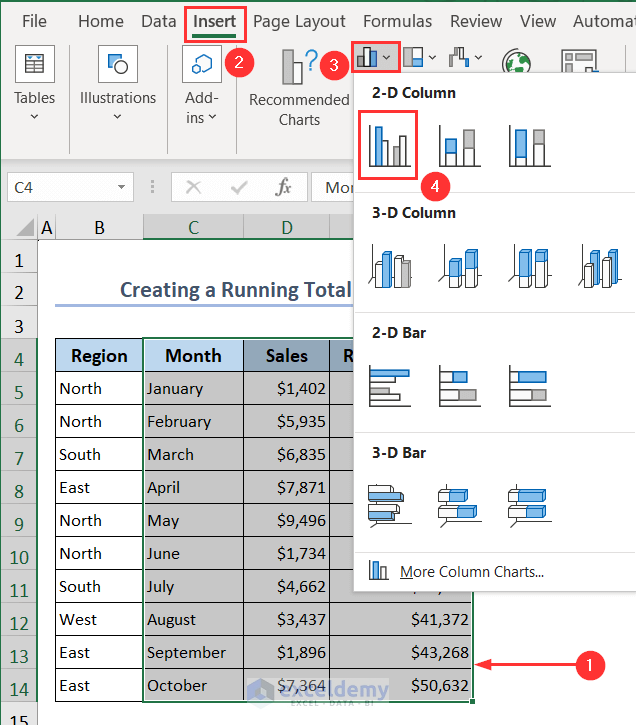
- Select the whole dataset excluding the Region column- C4:E14. Go to the Insert tab.
- Select 2D Clustered Column Chart from the Column Chart options.
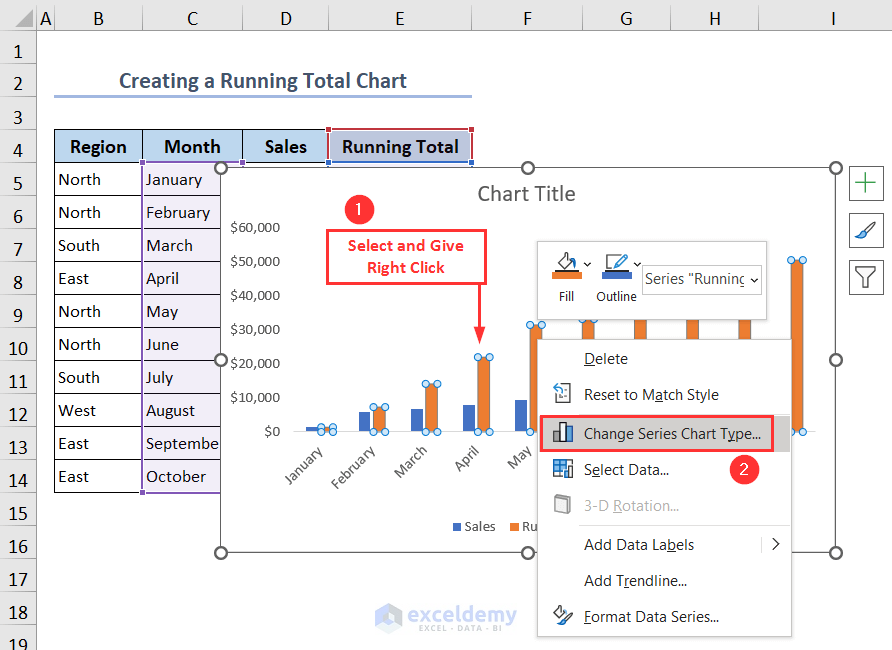
- Select the Running Total Columns (Orange Color) and right-click.
- Then, select Change Series Chart Type.
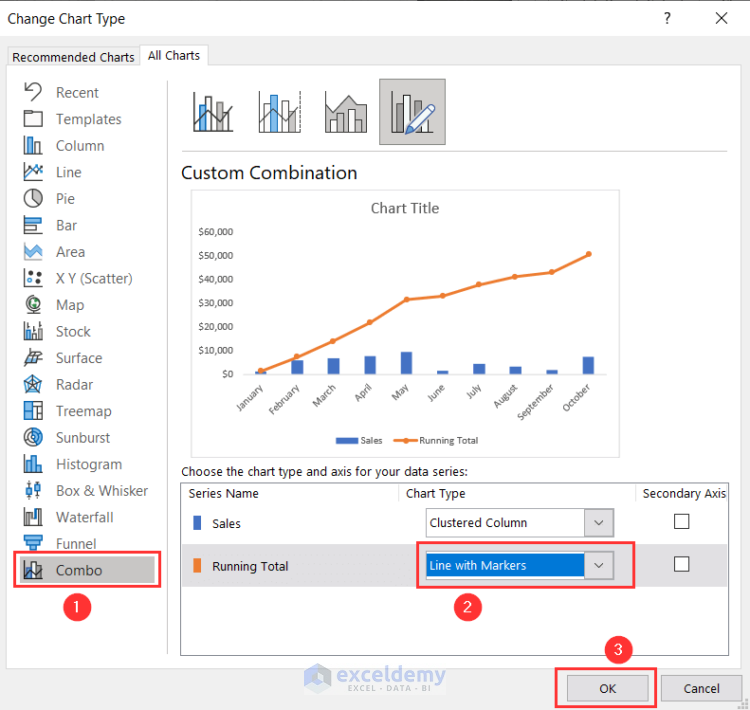
- Go to the Combo tab in the Change Chart Type window.
- Select Line with Markers for Running Total Chart and press OK.
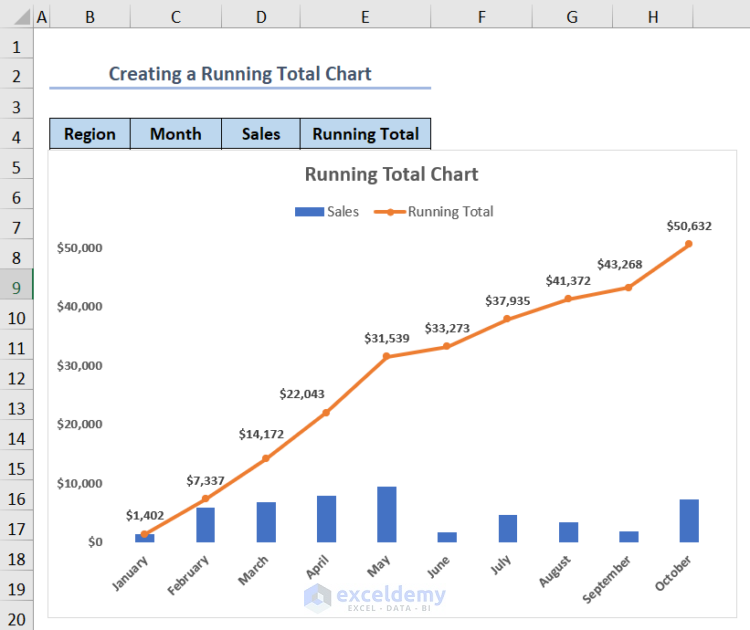
- The chart is now ready.
- We have done some formatting like giving the chart a title and adding legends to make the chart visually appealing.
Which Things You Have to Remember?
- A running total and the total sum are different. The running total sums the former value with the current value. But the total sum sums all the values.
- The running total is different from the running balance. In the running balance, when you add a new entry, the sum of values can grow or reduce. But in the running total, it’ll only grow.
- When we used the Named Range method, we changed the reference style to R1C1 from A1 style. This change is only applicable to this method.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is an example of a running total?
Answer: Suppose you work in a sales position and want to know the total number of items sold up to a particular date. In this case, you have to calculate the running total of the number of items sold instead of the sum.
2. What is the formula for a running balance in Excel?
Answer: There are a lot of formulas for a running balance in Excel. You can use a custom formula and SUM, SUMIF, SCAN, and LAMBDA functions to calculate the running balance. You’ll find all these methods in this article.
3. What is the purpose of running total in Excel?
Answer: The purpose of the running total in Excel is to add up the values of items as we enter new items and values over time.
4. Name the methods available to find the running total in Excel?
Answer: In this article, you’ll find all the methods available to find the running total in Excel. We can apply a custom formula and use SUM, SUMIF, SCAN, and LAMBDA functions to calculate the running total. Moreover, we use the Quick Analysis tool, Table, Pivot Table, Power Query, Power Pivot, and DAX measures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article provides 10 suitable methods to calculate the running total in Excel. The methods include built-in functions and tools or features from Excel. Use the SUMIF function to get the running total based on criteria. Combine SCAN and LAMBDA functions to get the total at once. You also learned the method of creating a running total chart and use cases of it. Drop comments for any queries.
Excel Running Total : Knowledge Hub
<< Go Back to How to Calculate in Excel | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!