Method 1 – Finding Average Marks of Each Exam
Steps
- We would like to find the average, excluding the absent text.
- Select cell C13.
- Write down the following formula.
=AVERAGEIFS(C5:C11, C5:C11, "<>Absent")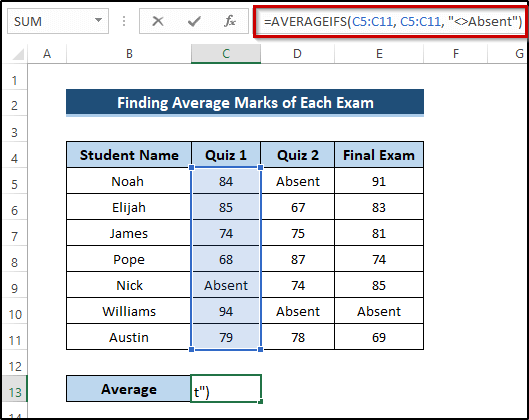
- Press Enter to apply the formula.
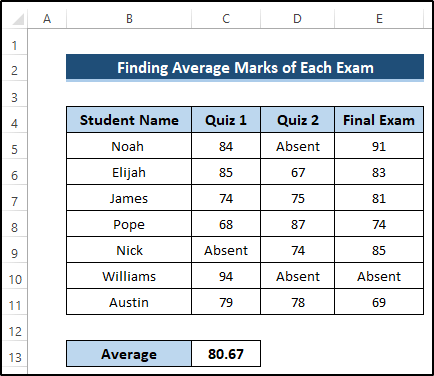
- Drag the Fill Handle icon up to cell E13.
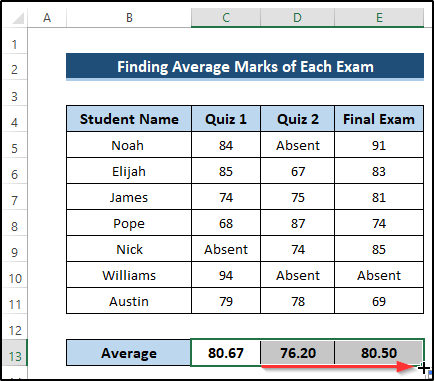
Breakdown of the Formula
AVERAGEIFS(C5:C11, C5:C11, “<>Absent”): The AVERAGEIFS function takes the average range and criteria range and returns the required average. The average range is C5 to C11, and our criteria range is C5 to C11 when it is not equal to Absent text. The AVERAGEIFS function takes this range and searches the given criteria. It returns the required average, excluding the Absent text.
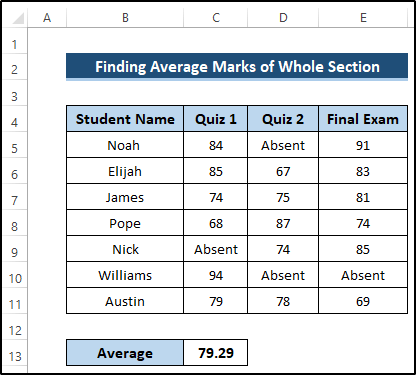
Method 2 – Finding Average Marks of Whole Section
Steps
- Find the average, excluding the absent text.
- Select cell C13.
- Write down the following formula.
=AVERAGEIFS(C5:E11, C5:E11, "<>Absent")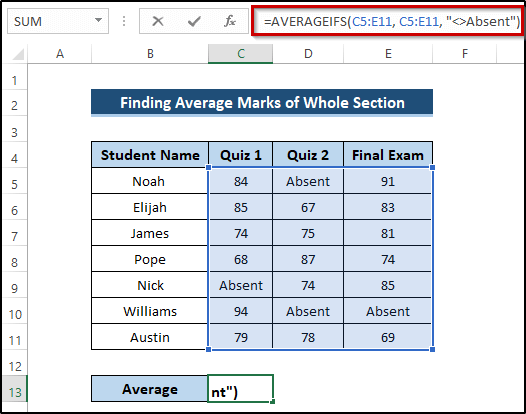
- Press Enter to apply the formula.
Breakdown of the Formula
AVERAGEIFS(C5:E11, C5:E11, “<>Absent”): The AVERAGEIFS function takes the average range and criteria range and returns the required average. The average range is C5 to E11, and our criteria range is C5 to E11 when it is not equal to Absent text. The AVERAGEIFS function takes this range and searches the given criteria. Finally, it returns the required average for the whole section, excluding the Absent text.
Method 3 – Using AVERAGEIFS with Multiple Criteria
Steps
- Select cell C13.
- Write down the following formula.
=AVERAGEIFS(G5:G11,D5:D11,"<>North",D5:D11,"<>South")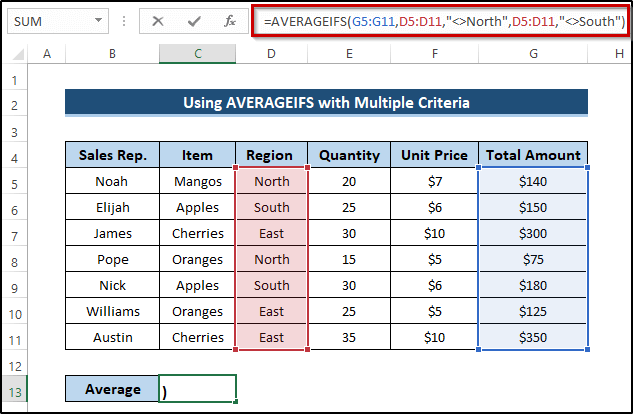
- Press Enter to apply the formula.
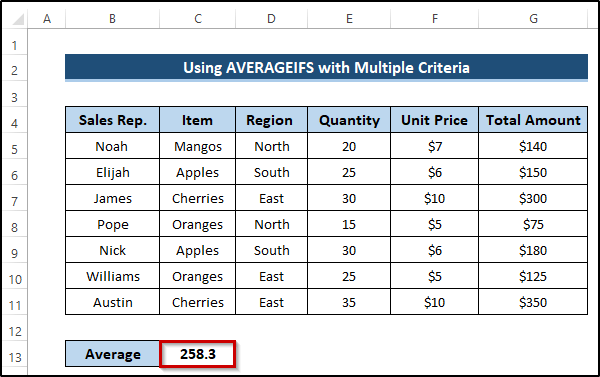
Breakdown of the Formula
AVERAGEIFS(G5:G11,D5:D11,”<>North”,D5:D11,”<>South”): The AVERAGEIFS function takes the average range and criteria range and returns the required average. The average range is G5 to G11, and our criteria range is D5 to D11. When the range of cells D5 to D11 is not equal to the north and not equal to the south, it will return the average of the given range of cells. That means they will return the average for the east region.
How to Use AVERAGEIFS If Value Is Not Equal to Blank in Excel
Method 1 – Using AVERAGEIFS for Single Column
Steps
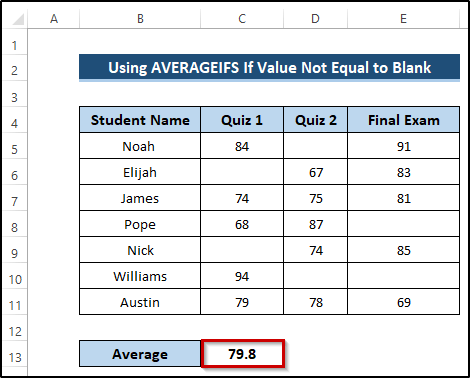
- Select cell C13.
- Write down the following formula.
=AVERAGEIFS(C5:C11, C5:C11, "<>")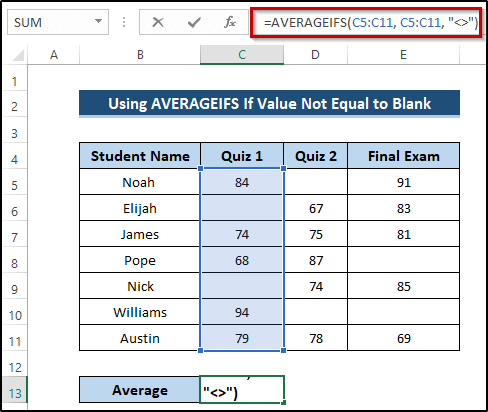
- Press Enter to apply the formula.
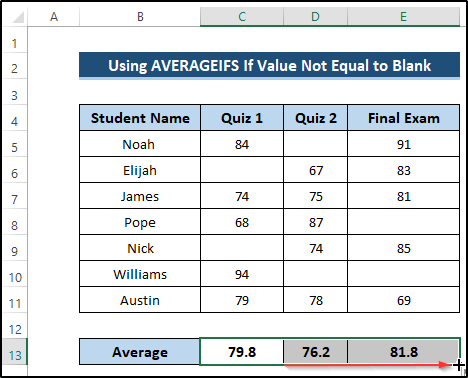
- Drag the Fill Handle icon up to cell E13.
Breakdown of the Formula
AVERAGEIFS(C5:C11, C5:C11, “<>”): The AVERAGEIFS function takes the average range and criteria range and returns the required average. The average range is C5 to C11, and our criteria range is C5 to C11 when it is not equal to blank. The AVERAGEIFS function takes this range and searches the given criteria. It returns the required average excluding the blanks.
Method 2 – Using AVERAGEIFS for Multiple Columns
Steps
- Select cell C13.
- Write down the following formula.
=AVERAGEIFS(D5:D11,B5:B11,"<>",C5:C11,"<>")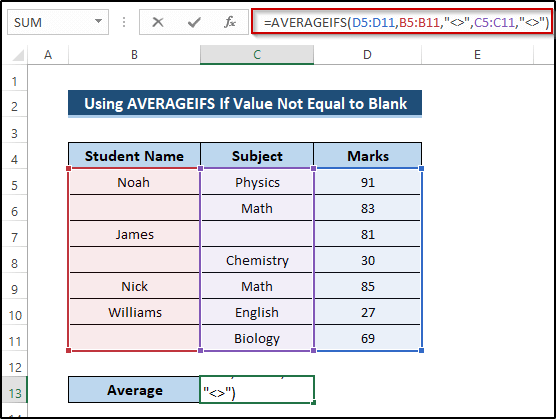
- Press Enter to apply the formula.
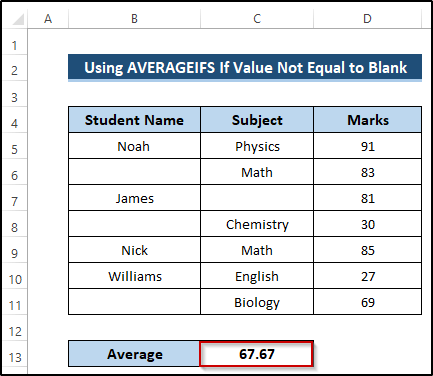
Breakdown of the Formula
AVERAGEIFS(D5:D11,B5:B11,”<>”,C5:C11,”<>”): The AVERAGEIFS function takes the average range and criteria range and returns the required average. We take two criteria. When the range of cells B5 to B11 is not equal to blank, and also the range of cells C5 to C11 is not equal to blank, then the function ignores those blanks and finds out the required average from the range cells D5 to D11. When it finds a blank, it will ignore the whole row.
Things to Remember
- If a cell in the given criteria range is blank, the AVERAGEIFS function will count as zero.
- If the cells don’t meet the criteria, the AVERAGEIFS function shows the #DIV/0! error value.
- If the range of finding average is a blank or text value, the AVERAGEIFS function shows the #DIV0! error value.
Download Practice Workbook
Download the practice workbook below.
Related Articles
- How to Apply AVERAGEIFS Function Between Two Dates in Excel
- How to Use AVERAGEIFS Function for Multiple Columns
<< Go Back to Excel AVERAGEIFS Function | Excel Functions | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

