Method 1 – Excel VBA Code to Vlookup Values for Multiple Matches
1.1. Return Multiple Values for Matches in One cell with Separators in Between with VBA
We attached a demonstrative video here for your better understanding.
Steps:
- Go to the Developer tab and click Visual Basic to open the editor window.
- Press ALT+F11 from your keyboard to open Visual Basic.
- Click Insert and select the Module option to open a new module.
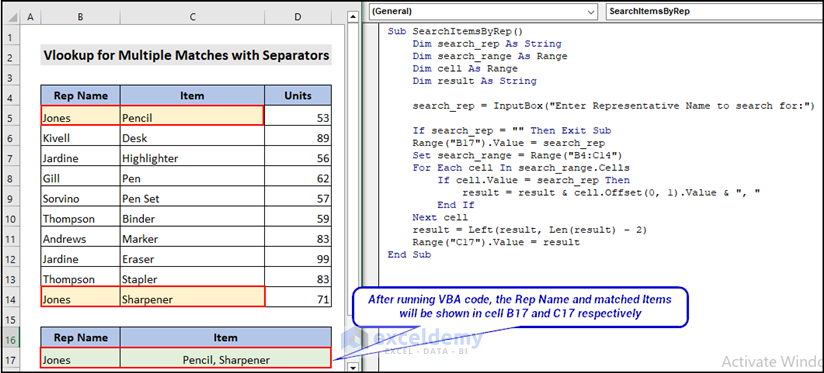
- Insert the following code in the code editor and press F5 to run the entire code.
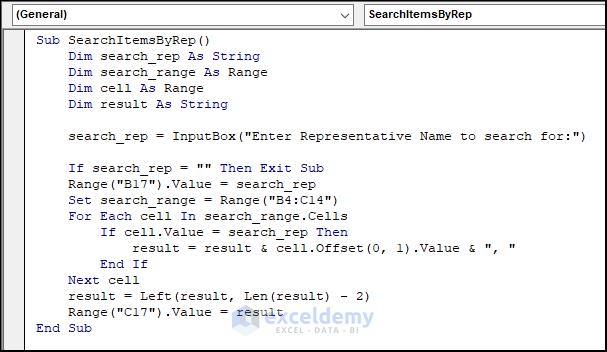
Sub SearchItemsByRep()
Dim search_rep As String
Dim search_range As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim result As String
'Prompt user to enter search rep name
search_rep = InputBox("Enter Representative Name to search for:")
If search_rep = "" Then Exit Sub 'Exit sub if user cancels or enters nothing
Range("B17").Value = search_rep
'Specify search range
Set search_range = Range("B4:C14") 'replace with your own range
'Loop through each cell in range and concatenate results
For Each cell In search_range.Cells
If cell.Value = search_rep Then
result = result & cell.Offset(0, 1).Value & ", "
End If
Next cell
'Remove trailing comma and space
result = Left(result, Len(result) - 2)
'Output results to cell C17
Range("C17").Value = result
End SubCode Breakdown
Sub SearchItemsByRep()- This line starts the subroutine named “SearchItemsByRep“.
Dim search_rep As String
Dim search_range As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim result As String- These lines declare four variables: search_rep as a string to hold the representative name being searched for, search_range as a range object to hold the range of cells to search, cell as a range object to represent the current cell in the search range and result as a string to hold the concatenated search result.
search_rep = InputBox("Enter Representative Name to search for:")- This line prompts the user to enter the search rep name to search for using the InputBox function and assigns the entered value to the search_rep variable.
If search_rep = "" Then Exit Sub - This line checks whether the user entered a representative name or canceled the input box. If you enter an empty value or cancel the input box, the subroutine is exited using the Exit Sub statement.
Set search_range = Range("B4:C14")- In this part of the code, you specify the search range, which is B4:C14. You can replace it with your range.
For Each cell In search_range.Cells
If cell.Value = search_rep Then
result = result & cell.Offset(0, 1).Value & ", "
End If
Next cell- Use a For Each loop to iterate through each cell in the search_range variable. If the current cell value matches the search_rep variable, the item value in the current cell is concatenated.
result = Left(result, Len(result) - 2) This removes trailing commas and spaces.
Range("C17").Value = result
This shows the output results to cell C17.
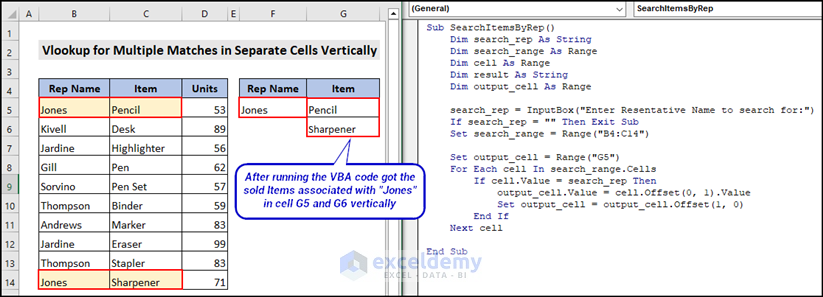
1.2. Return Multiple Values for Matches in Separate Cells Vertically with VBA
This is a demonstrative video of the whole approach for your better understanding:
Steps:
- Insert a new module by clicking Insert and then Module.
- A new module named Module 2 will be created.
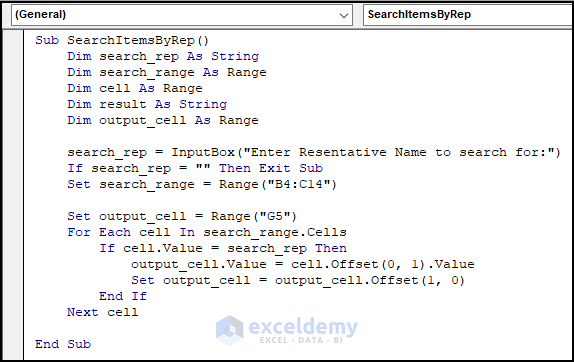
- Insert the following code in that new module and press F5 from your keyboard to run the entire code.
Sub SearchItemsByRep()
Dim search_rep As String
Dim search_range As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim result As String
Dim output_cell As Range
'Prompt user to enter search rep name
search_rep = InputBox("Enter Resentative Name to search for:")
If search_rep = "" Then Exit Sub 'Exit sub if user cancels or enters nothing
'Specify search range
Set search_range = Range("B4:C14") 'replace with your own range
'Initialize output cell to show output
Set output_cell = Range("G5")
'Loop through each cell in range and concatenate results
For Each cell In search_range.Cells
If cell.Value = search_rep Then
output_cell.Value = cell.Offset(0, 1).Value
Set output_cell = output_cell.Offset(1, 0)
End If
Next cell
End SubCode Breakdown
Sub SearchItemsByRep()- This line starts the subroutine named “SearchItemsByRep“.
Dim search_rep As String
Dim search_range As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim result As String
Dim output_cell As RangeThese lines declare five variables: search_rep, search_range, cell, result, output_cell
search_rep = InputBox("Enter Representative Name to search for:")- This line prompts the user to enter the search rep name to search for using the InputBox function and assigns the entered value to the search_rep variable.
If search_rep = "" Then Exit SubExit sub if the user cancels or enters nothing
Set search_range = Range("B4:C14")Specify the search range.
Set output_cell = Range("G5")Initialize the cell to show output.
For Each cell In search_range.Cells
If cell.Value = search_rep Then
output_cell.Value = cell.Offset(0, 1).Value
Set output_cell = output_cell.Offset(1, 0)
End If
Next cellUse a For Each loop to iterate through each cell in the search_range variable. If the current cell value matches the search_rep variable, the item value in the current cell is concatenated.
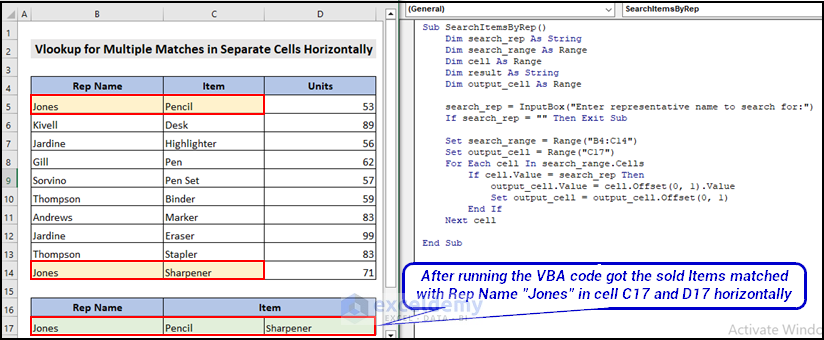
1.3. Return Multiple Values for Matches in Separate Cells Horizontally with VBA
This is a demonstrative video of the whole approach for your better understanding:
Steps:
- Insert another new module by clicking Insert and then Module.
- A new module named Module 3 will be created.
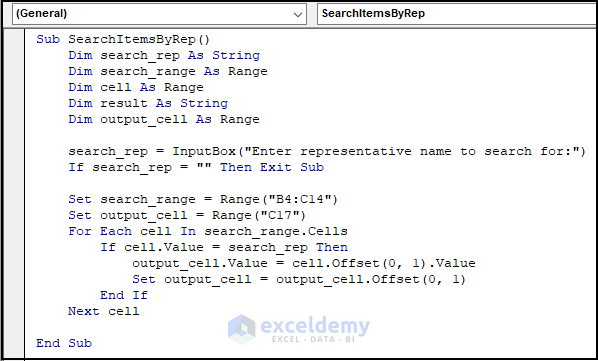
- Insert the following code in that new module and press F5 to run the entire code.
Sub SearchItemsByRep()
Dim search_rep As String
Dim search_range As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim result As String
Dim output_cell As Range
'Prompt user to enter search rep name
search_rep = InputBox("Enter representative name to search for:")
If search_rep = "" Then Exit Sub 'Exit sub if user cancels or enters nothing
'Specify search range
Set search_range = Range("B4:C14") 'replace with your own range
'Initialize output cell to show output
Set output_cell = Range("C17")
'Loop through each cell in range and concatenate results
For Each cell In search_range.Cells
If cell.Value = search_rep Then
output_cell.Value = cell.Offset(0, 1).Value
Set output_cell = output_cell.Offset(0, 1)
End If
Next cell
End SubMethod 2 – Excel VBA to Create a User-Defined Function to Vlookup for Multiple Matches
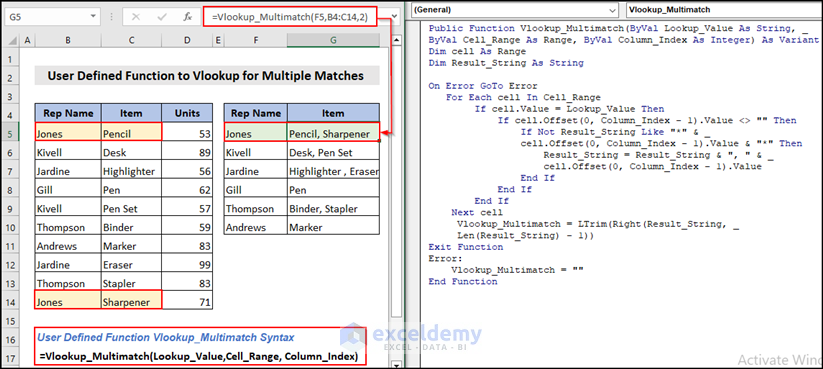
2.1. User-Defined Function to Vlookup for Multiple Values From Dataset
This is a demonstrative video of this approach for your better understanding:
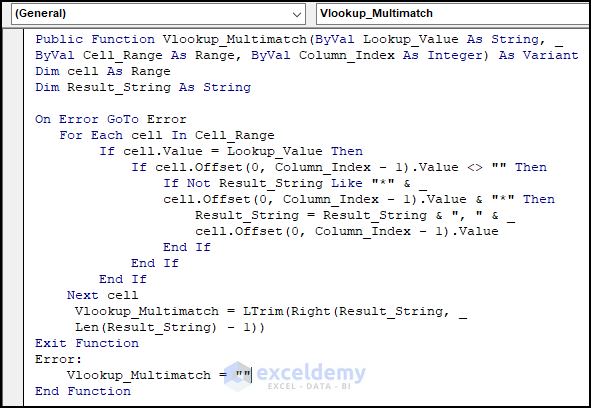
Create a VBA function (similar to the VLOOKUP function) that checks each cell in a column and adds the lookup value if found. We attached the VBA code below.
Insert the following code in a new module and press F5 to run the entire code.
Public Function Vlookup_Multimatch(ByVal Lookup_Value As String, ByVal Cell_Range As Range, ByVal Column_Index As Integer) As Variant
'Declare a variable to hold the current cell in the loop
Dim cell As Range
'Declare a string variable to hold the matching values
Dim Result_String As String
'Define the error handling routine
On Error GoTo Error
'Loop through each cell in the specified range
For Each cell In Cell_Range
'Check if the current cell matches the lookup value
If cell.Value = Lookup_Value Then
'Check if the value in the specified column is not empty
If cell.Offset(0, Column_Index - 1).Value <> "" Then
'Check if the value is not already in the result string
If Not Result_String Like "*" & cell.Offset(0, Column_Index - 1).Value & "*" Then
'Add the value to the result string
Result_String = Result_String & ", " & cell.Offset(0, Column_Index - 1).Value
End If
End If
End If
Next cell
'Trim leading spaces and return the result string
Vlookup_Multimatch = LTrim(Right(Result_String, Len(Result_String) - 1))
'Exit the function
Exit Function
'Define the error handling routine
Error:
'Return an empty string if an error occurs
Vlookup_Multimatch = ""
End Function
Code Breakdown
Public Function Vlookup_Multimatch(ByVal Lookup_Value As String, ByVal Cell_Range As Range, ByVal Column_Index As Integer) As VariantThis function takes a lookup value, a range of cells, and a column index and returns a concatenated string of all matching values in the specified column.
Dim cell As Range Declare a variable to hold the current cell in the loop.
Dim Result_String As String Declare a string variable to hold the matching values.
On Error GoTo Error Define the error handling routine.
We used a nested For Each loop here. The function uses a loop to iterate through each cell in the specified range. If the cell’s value matches the lookup value, it checks if the corresponding cell in the selected column is not empty. If it is not empty and the cell’s value is not already included in the result string, it adds its value to the result string.
The function returns the result string as a variant data type. If there are no matches, the function returns an empty string.
Note:
Remember that this function can only handle exact matches between the lookup and cell values in the specified range. If you need to perform a partial or fuzzy game, you must modify the function or use a different method.
This function takes 3 arguments like the VLOOKUP function: Lookup value, LookupRange, and ColumnNumber.
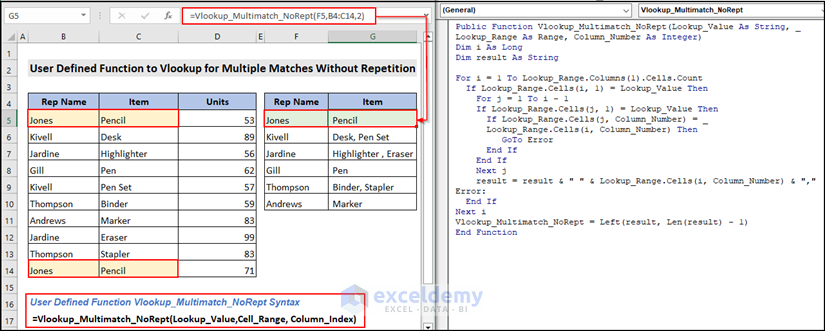
Here is the final output image.
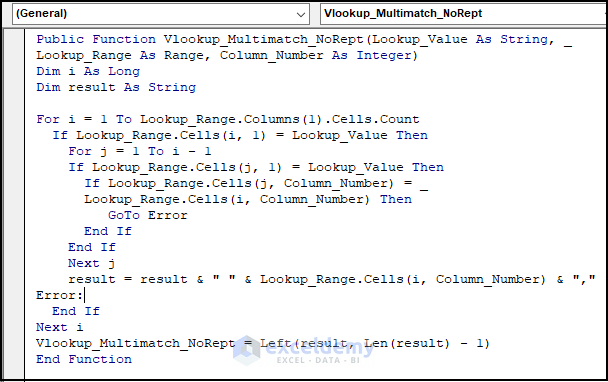
2.2. Creating VBA User-Defined Function to Get Multiple Lookup Values in a Single Cell (Without Repetition)
Note:
In cell C14, we have inserted the Item “Pencil” instead of “Sharpener” so you can understand the scenario clearly.
Here is a demonstrative video of this approach for your better understanding:
We attached the VBA code below. Follow this to get the result.
Insert the following code in a new module and press F5 from your keyboard to run the entire code.
Public Function Vlookup_Multimatch_NoRept(Lookup_Value As String, Lookup_Range As Range, Column_Number As Integer)
'Declare variable i as a long data type
Dim i As Long
'Declare variable result as a string data type
Dim result As String
'Loop through each cell in column 1 of Lookup_Range
For i = 1 To Lookup_Range.Columns(1).Cells.Count
'If the current cell in column 1 of Lookup_Range matches Lookup_Value
If Lookup_Range.Cells(i, 1) = Lookup_Value Then
'Loop through each cell in column 1 of Lookup_Range before the current cell
For j = 1 To i - 1
'If a previous cell in column 1 of Lookup_Range matches Lookup_Value
If Lookup_Range.Cells(j, 1) = Lookup_Value Then
'If the value in column Column_Number for the previous cell matches the value in column Column_Number for the current cell
If Lookup_Range.Cells(j, Column_Number) = Lookup_Range.Cells(i, Column_Number) Then
GoTo Error 'Go to the Error label and skip the next line of code
End If
End If
Next j
'Add the value in column Column_Number for the current cell to the result string with a comma separator
result = result & " " & Lookup_Range.Cells(i, Column_Number) & ","
Error:
End If
Next i
'Return the result string with the last comma removed
Vlookup_Multimatch_NoRept = Left(result, Len(result) - 1)
End FunctionCode Breakdown
Public Function Vlookup_Multimatch_NoRept(Lookup_Value As String, Lookup_Range As Range, Column_Number As Integer)This function takes three arguments: Lookup_Value, Lookup_Range, and Column_Number. Lookup_Value is the value you want to search for, Lookup_Range, Lookup_Range is the range of cells you want to search, Lookup_Value, and Column_Number is the column number within Lookup_Range to return a value.
Dim i As Long Declare variable i as a long data type.
Dim result As String Declare variable result as a string data type.
For i = 1 To Lookup_Range.Columns(1).Cells.Count Loop through each cell in column 1 of Lookup_Range.
If Lookup_Range.Cells(i, 1) = Lookup_Value Then If the current cell in column 1 of Lookup_Range matches Lookup_Value
For j = 1 To i - 1 Loop through each cell in column 1 of Lookup_Range before the current cell.
If Lookup_Range.Cells(j, 1) = Lookup_Value Then If a previous cell in column 1 of Lookup_Range matches Lookup_Value.
If Lookup_Range.Cells(j, Column_Number) = Lookup_Range.Cells(i, Column_Number) ThenIf the value in column Column_Number for the previous cell matches the value in column Column_Number for the current cell.
GoTo Error It goes to the Error label and skips the following line of code.
Next jMoves to the next cell in column 1 of Lookup_Range.
result = result & " " & Lookup_Range.Cells(i, Column_Number) & "," Adds the value in column Column_Number for the current cell to the result string with a comma separator
Error: This is defined Error label.
Next iMoves to the next cell in column 1 of Lookup_Range
Vlookup_Multimatch_NoRept = Left(result, Len(result) - 1) Returns the result string with the last comma removed.
This is the final output image of the whole approach.
How to Vlookup for Multiple Matches with Formula in Excel
Find matched values from the dataset without VBA by applying the Excel built-in VLOOKUP function. The VLOOKUP function is one of the most commonly used functions in Microsoft Excel.
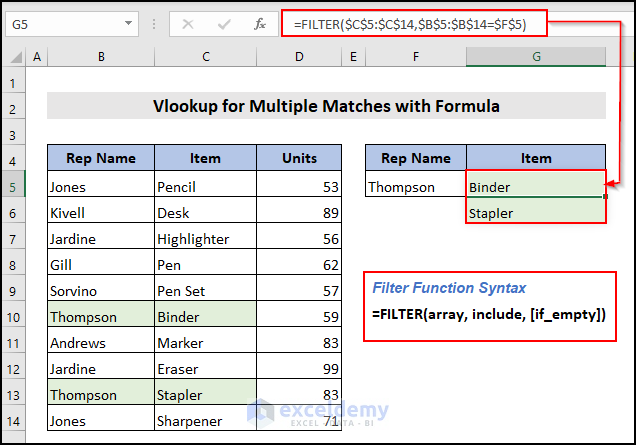
Use only be using the FILTER function. Find the Items associated with the representative name Thompson.
Enter the Rep Name in cell F5 for whom you want to find the Items. Enter the following formula in cell G5 and press the ENTER key.
Formula Breakdown
- $C$5:$C$14 (Item) is the lookup_array. Look for the items. You can use your one as well.
- $B$5:$B$14 (Rep Name) is the matching_array. To determine the associated Items, you want to match the selected value(Thompson) with this Matching_array. You can use your one accordingly.
- $F$5(Rep Name) is the matching_value. Match the value with matching_array.
We have the Items Binder and Stapler, correlated to our selected Rep Name Thompson. You can also easily find matched values without using VBA code.
How to Use VLOOKUP Function with Multiple Criteria in Excel
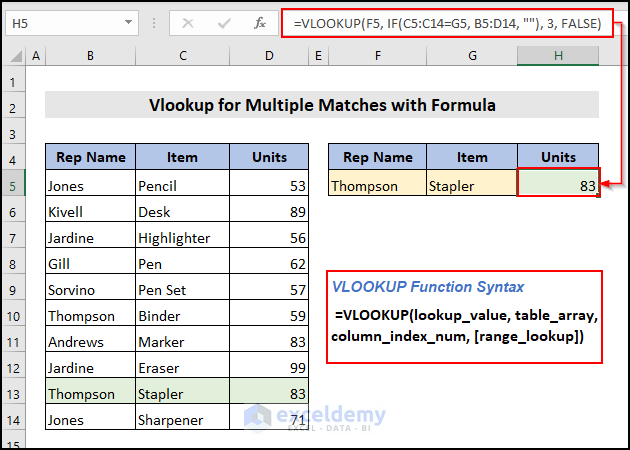
Use the VLOOKUP function to find values with multiple criteria in a table to extract their corresponding information. Demonstrate the steps to Vlookup values with various criteria using the VLOOKUP function.
Use the IF function here to define the lookup array for the VLOOKUP function. Follow these steps to complete the process.
Enter Rep Name and Item in cells F5 and G5. Find the Units based on these two criteria. Enter the following formula in cell H5 and press ENTER.
Unit “83” is based on the criteria Rep Name “Thompson” and Item “Stapler”. You can combine the IF function with the VLOOKUP function to find matched values based on multiple criteria.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. The Developer Tab Is Not Visible. What to Do?
If you can’t find the Developer tab in your Excel, follow the above note part of “How to Launch VBA Editor in Excel”.
2. Can I Use a Macro for VLOOKUP?
Make your work faster by using macros. Macros are great to increase your productivity or gain more time at work. Any process can be automated using the VBA coding language.
Here is an example of using a macro to perform a specific task.
Use macros in your work and enjoy using VBA macros. They will simplify your work and speed up the process.
3. What is a Substitute for VLOOKUP in Excel?
Use Excel INDEX and MATCH functions to Vlookup matched values as a substitute for VLOOKUP. You can read the article mentioned in ExcelDemy.
4. Can We Have Multiple Conditions in VLOOKUP?
Use the VLOOKUP function when applying multiple conditions to your dataset. The attached article will help you better and clearer understand how to use VLOOKUP in multiple conditions.
Key Takeaways from the Article
- We showed how to launch the VBA editor in Excel
- Chosen real-life dataset for better understanding.
- Focused on how to Vlookup multiple matched values with VBA code in Excel.
- Explained how to create a user-defined function for Vlookup values.
- Explained different approaches with VBA code.
- Provide solutions to readers’ frequently asked questions.
- Overall focused on using VBA code to Vlookup values from a dataset.
Download Practice Workbook
You can download the practice workbook from here:
Further Readings
- Use Excel VBA VLOOKUP to Find Values in Another Worksheet
- How to Use Excel VBA VLookup Within Loop
- Excel VBA to Vlookup in Another Workbook Without Opening