Introduction to VBA Array
Arrays are powerful tools for managing data, and they allow you to group related values under a single variable name. Here are the four types of string arrays you can work with in VBA:
Type 1 – Declare Static String Array
If you want an array that can store string values with a fixed size, you can declare a static string array. For example:
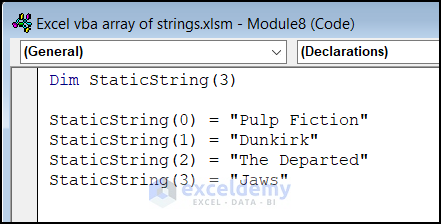
You can also define the start and end positions of an array by using “To”.
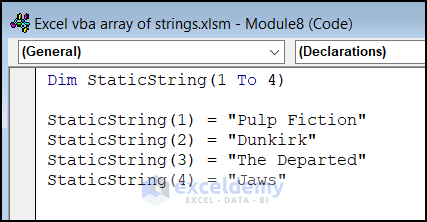
Type 2 – Declare Variant String Array
When you want to store string values without specifying the array size upfront, you can declare a variant-type array. Variants can hold any data type, including strings:
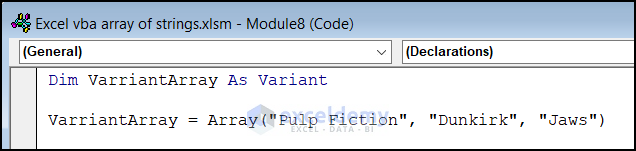
Type 3 – Declare String Array Using Split Function
You can create an array by splitting a string using a delimiter. For instance, if you have a comma-separated list of movie titles, you can split it into an array:
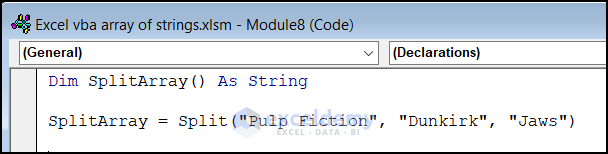
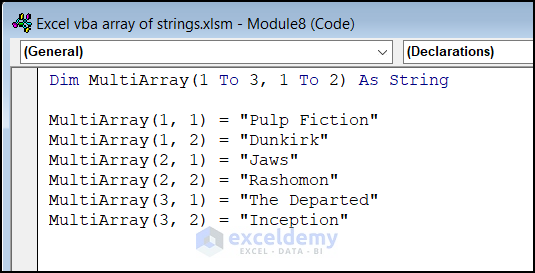
Type 4 – Declare Multidimensional Array
Multidimensional arrays allow you to organize data in more than one dimension. For example, a 3×2 array can hold values like this:
Read More: How to Declare Array in Excel VBA
How to Launch VBA Editor in Excel
- Go to the Developer tab and click on Visual Basic.
- You can also open it by pressing Alt+F11 on your keyboard.
- Go to the Insert tab and click on Module to launch the code Module.
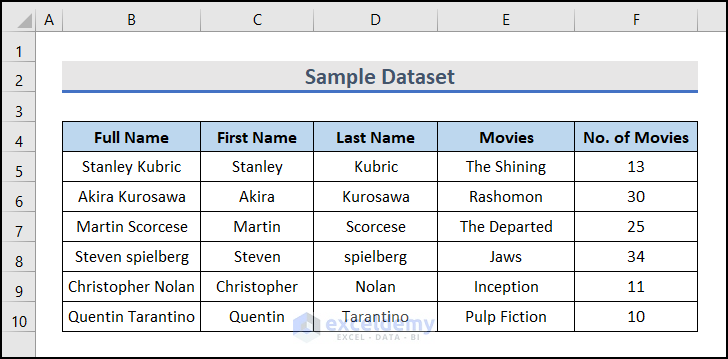
Dataset Overview
We’ll use the following dataset to demonstrate the 4 examples:
Example 1 – Use VBA Array Function with String
Suppose we want to store movie titles in an array and insert them into a column in Excel. Here’s the code:
Sub String_Array()
Dim Movies() As Variant
Dim numRows As Long
Dim i As Long
' Define the movies array
Movies = Array("The Shining", "Rashomon", "The Departed", _
"Jaws", "Inception", "Pulp Fiction")
numRows = UBound(Movies) + 1
' Insert the movies into column E starting from row 5
For i = 1 To numRows
Range("E" & i + 4).Value = Movies(i - 1)
Next i
End Sub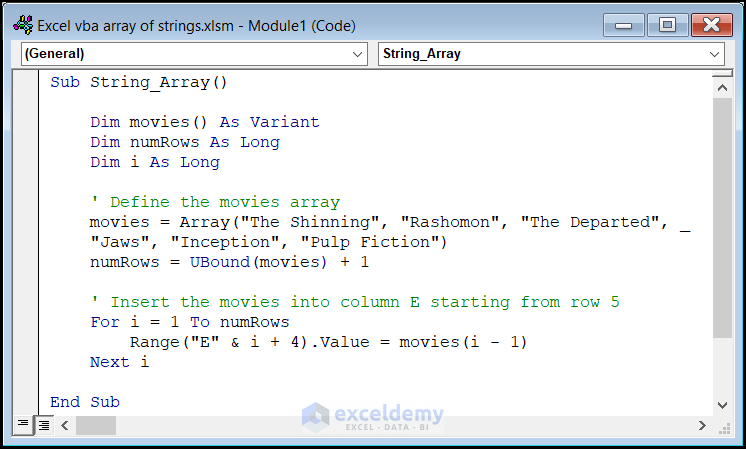
Code Breakdown
In this example:
-
- We create an array called Movies with six movie titles.
- The numRows variable calculates the number of rows needed.
- The loop inserts each movie title into column E, starting from row 5.
- Press F5 or click on the Run button to run the code.
Example 2 – Split Strings and Store Them in VBA Array
In this scenario, we’ll take a column of full names (from cells B5 to B10), split them into first and last names, and store these components in two different columns.
Here’s the code for achieving this:
Sub SplitNames()
Dim Names() As Variant
Dim firstNames() As Variant
Dim lastNames() As Variant
Dim numRows As Long
Dim i As Long
' Get the names from column B
Names = Range("B5:B10").Value
numRows = UBound(Names, 1)
' Split the names into first and last names
ReDim firstNames(1 To numRows)
ReDim lastNames(1 To numRows)
For i = 1 To numRows
nameParts = Split(Names(i, 1), " ")
firstNames(i) = nameParts(0)
lastNames(i) = nameParts(UBound(nameParts))
Next i
' Write the first and last names into columns C and D
Range("C5:C10").Value = WorksheetFunction.Transpose(firstNames)
Range("D5:D10").Value = WorksheetFunction.Transpose(lastNames)
End Sub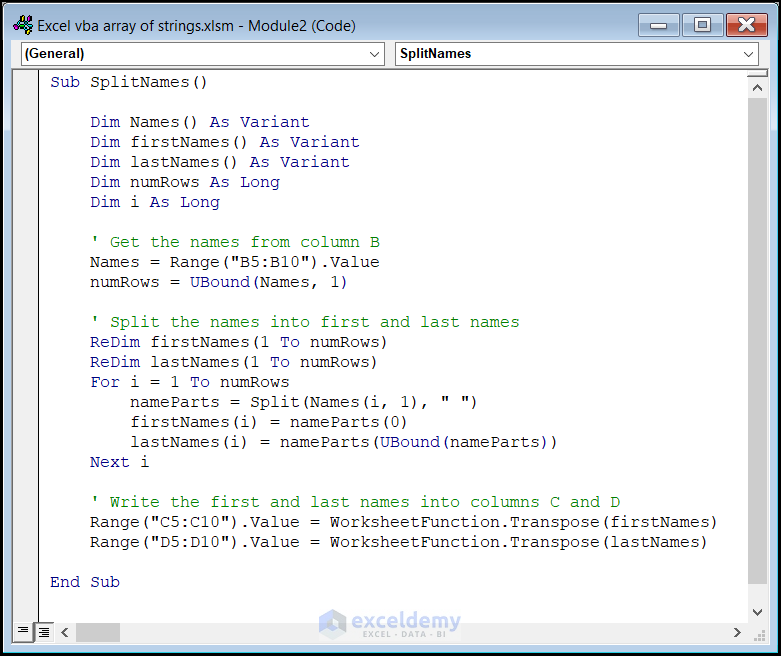
Code Breakdown
-
- We retrieve the full names from cells B5 to B10 and store them in an array called Names.
- The variable numRows calculates the number of rows in the Names array.
- We split each full name into first and last names using the Split function.
- Two arrays, firstNames and lastNames, hold the corresponding components.
- We write the first names to column C and last names to column D.
- Run the code to get your desired results.
Example 3 – Create a Dynamic String Array
Sometimes, when working with arrays, we don’t know the exact number of elements in advance. In such cases, we need a dynamic array—one that can grow as we encounter new elements to store. To resize an array dynamically, we’ll use the ReDim Preserve function.
Here’s the code for creating a dynamic string array:
Sub Dynamic_Array()
Dim Names() As String
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
Dim allNames As String
'Store the names with more than 20 movies in an array
j = 0
For i = 5 To 10
If Range("E" & i).Value > 20 Then
' Resize the Names array to include the current name
ReDim Preserve Names(j)
Names(j) = Range("B" & i).Value
j = j + 1
End If
Next i
'Concatenate all the names into a single string
allNames = Join(Names, ", ")
'Display all the names in a message box
MsgBox "Director names with more than 20 movies are: " & allNames
End Sub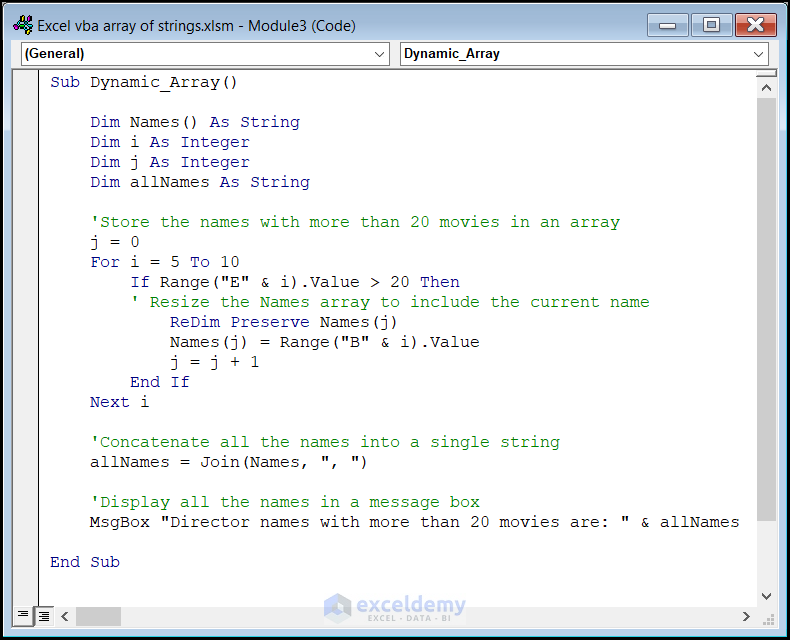
Code Breakdown
-
- We initialize an empty string array called Names.
- The loop checks if the value in column E (for rows 5 to 10) exceeds 20.
- If it does, we resize the Names array and add the corresponding director’s name.
- We concatenate all the names into a single string and display them in a message box.
- Run the code to get your desired results.
Example 4 – Use LBound and UBound Functions with VBA String Array
The LBound and UBound functions help us determine the lower and upper bounds of an array. In this case, we’ll find the bounds of the movieNames array and store its elements in a worksheet.
Here’s the code:
Sub Array_LBOUND_UBOUND()
Dim movieNames() As String
Dim i As Integer
Dim lowerBound As Integer
Dim upperBound As Integer
Dim allMovies As String
'Store the movie names in an array
For i = 5 To 10
ReDim Preserve movieNames(i - 5)
movieNames(i - 5) = Range("E" & i).Value
Next i
'Determine the lower and upper bounds of the array
lowerBound = LBound(movieNames)
upperBound = UBound(movieNames)
'Concatenate all the movie names into a single string
allMovies = Join(movieNames, ", ")
'Display the movie names in a message box
MsgBox "The movie names are: " & allMovies
End Sub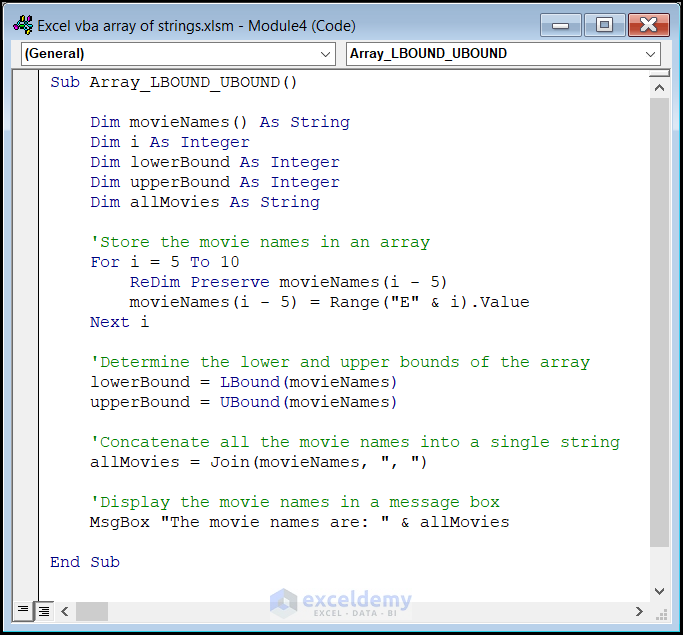
Code Breakdown
-
- We initialize an empty string array called movieNames.
- The loop stores movie names from cells E5 to E10 in the array.
- The LBound and UBound functions determine the lower and upper bounds of the array.
- We concatenate all the movie names into a single string.
- We display the concatenated names in a message box.
- Run the code and you will find your desired output.
Handling Variant Type Array in Excel VBA
A variant-type array can hold different types of data, and we declare it using the keyword Variant. In the following example, we’ll store numbers in a variant-type array and sum all the elements within that array. Here’s the code:
Sub Variant_Array()
Dim Movies() As Variant
Dim TotalMovies As Long
Dim i As Long
' Assign values from cells E5 to E10 to the Movies array
Movies = Range("E5:E10").Value
' Loop through the elements of the array
For i = LBound(Movies) To UBound(Movies)
'sum up the values
TotalMovies = TotalMovies + Movies(i, 1)
Next i
' Display the total number of movies in a message box
MsgBox "Total number of movies: " & TotalMovies
End Sub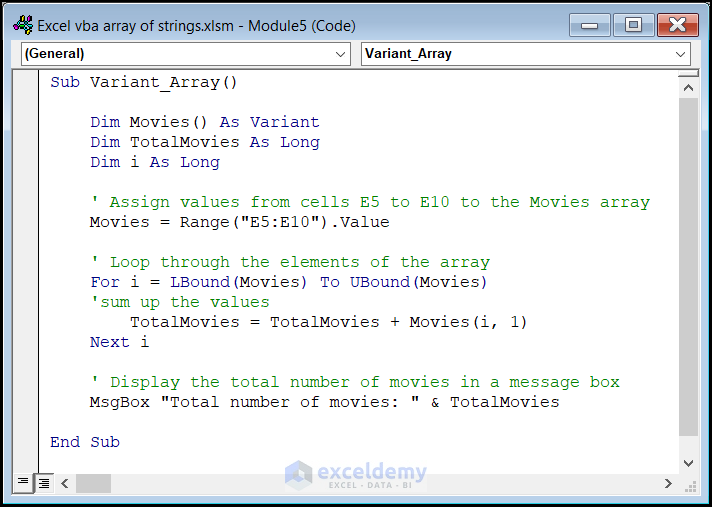
Code Breakdown
-
- We retrieve the values from cells E5 to E10 and store them in the Movies array.
- The loop calculates the sum of all elements in the array.
- We display the total number of movies in a message box.
Converting a Range to an Array of Strings in Excel VBA
You can easily assign elements from a range to an array in VBA. In this example, we’ll demonstrate how to create an array of strings from a specified range. Here’s the VBA code with explanations:
Sub Array_Range()
Dim movieArray() As Variant
Dim rowCount As Integer
movieArray = Range("E5:E10")
Dim concatenatedMovies As String
' Loop through the rows
For rowCount = 1 To UBound(movieArray)
concatenatedMovies = concatenatedMovies & _
movieArray(rowCount, 1) & vbNewLine
' Concatenate the element and a line break
Next rowCount
MsgBox "Movies in the array: " & vbNewLine & _
concatenatedMovies
End Sub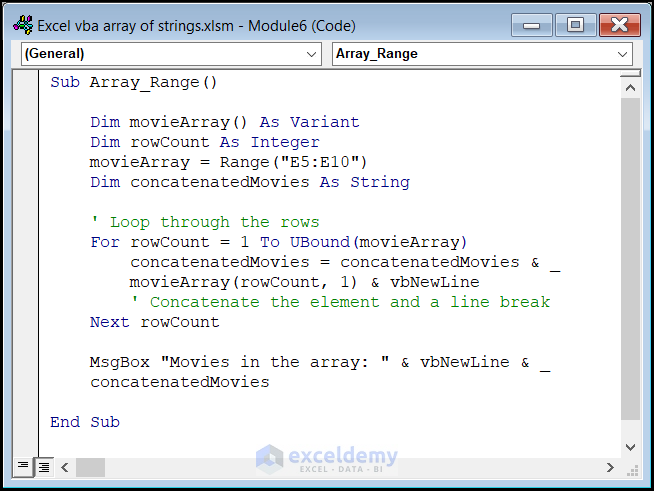
Code Breakdown
- movieArray retrieves data from the range E5:E10 and stores it in an array.
- The loop concatenates the value of each element in the first column of the current row to concatenatedMovies, adding a line break after each element.
Read More: How to Convert Range to Array in Excel VBA
Using Multidimensional Arrays in Excel VBA
Multidimensional arrays can have more than one dimension. You need to define the dimensions while declaring an array. In this example, we will create a two-dimensional array that will store the first and last names of the movie directors. The VBA code is explained in the following section.
Sub Multi_Array()
' Define the array to store the names
Dim nameArray(1 To 6, 1 To 2) As String
Dim numRows As Long
Dim numCols As Long
Dim concatenatedNames As String
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Range("C5:D10")
Dim cell As Range
Dim i As Long, j As Long
i = 1
j = 1
For Each cell In rng
nameArray(i, j) = CStr(cell.Value)
j = j + 1
If j > 2 Then
j = 1
i = i + 1
End If
Next cell
' Determine the number of rows and columns in the array
numRows = UBound(nameArray, 1)
numCols = UBound(nameArray, 2)
' Loop through the rows and columns to concatenate the names
For i = 1 To numRows
For j = 1 To numCols
concatenatedNames = concatenatedNames & nameArray(i, j)
If j < numCols Then
concatenatedNames = concatenatedNames & " "
End If
Next j
concatenatedNames = concatenatedNames & vbNewLine
Next i
MsgBox concatenatedNames
End Sub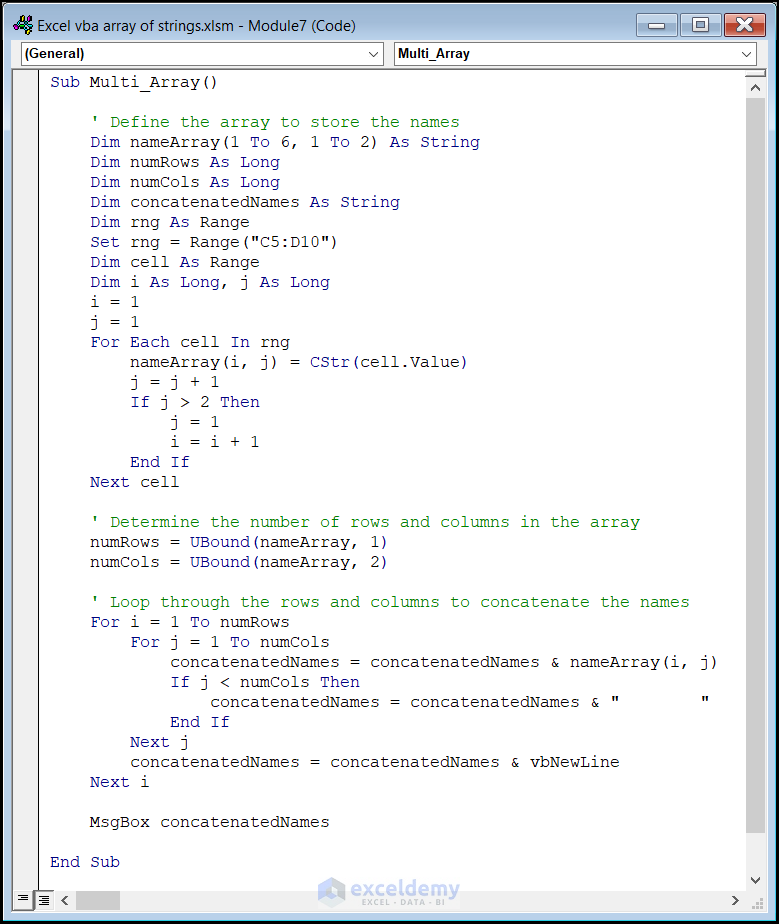
Code Breakdown
- nameArray is a 6×2 multidimensional array to store string values.
- The loop assigns values from the rng range object to the corresponding elements in the array.
- The concatenated names are displayed in a message box.
Read More: Excel VBA Multidimensional Arrays
Things to Remember
- The index of an array begins at zero. If we declare the array size to be 3, it can hold 4 elements.
- It is not recommended to fix the size of the array to avoid errors.
- The LBound and UBound functions are used to determine the size of the array.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How do I create an array of values in Excel VBA?
- You can create an array of values similar to the array of strings. Define the data type as needed, or use a variant to hold various data types.
- How do you create an array of variables in VBA?
- Arrays allow you to store multiple values in one variable. Use keywords like Dim, Static, Public, or Private. You can fix the array size in parentheses if desired.
- How do you create an array list in VBA?
- To create an array list, use the ArrayList class from the System.Collections namespace in the .NET Framework. Ensure that the box next to Microsoft.NET Framework is checked in the References dialogue box (found in the Tools menu in the Visual Basic Editor).
Download Practice Workbook
You can download the practice workbook from here:


