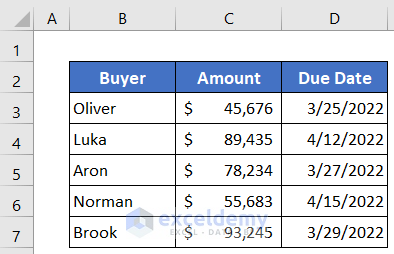
We’ll use the following dataset that represents some buyers’ invoice amounts and due dates.
Method 1 – Combine TODAY, AND, and IF Functions to Set a Due Date Reminder in Excel
We’ll check for the date 7 days ahead of the current date. The formula will return Yes if any date passes the due date. Otherwise, it will show No.
Steps:
- Select the cell E5.
- Insert the following formula in it:
=IF(AND(D5<>"",TODAY()+$D$11>=D5),"Yes","No")- Press the Enter button.
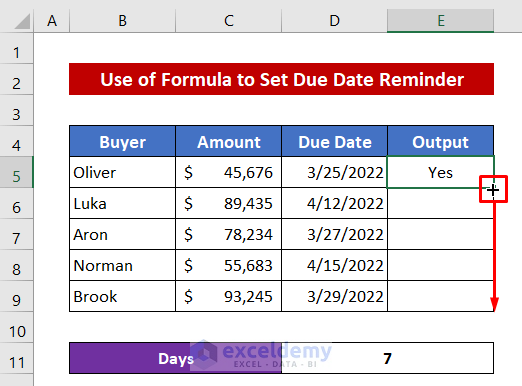
- Drag down the Fill Handle icon to copy the formula for the other cells.
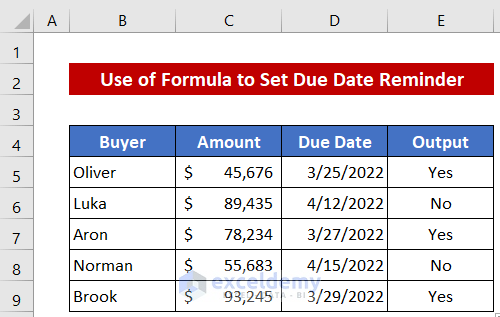
- You will get all the outputs like the image below.
⏬ Formula Breakdown:
➤ TODAY()+$D$11>=D5
Checks the date- 7 days ahead of the current date whether it is greater than or equal to the date of Cell D5 or not. It returns:
TRUE
➤ D5<>””
Checks if the Cell D5 is empty, in this case it returns:
TRUE
➤ AND(D5<>””,TODAY()+$D$11>=D5)
The AND function will combine both outputs. If any output is FALSE, it will return FALSE.
TRUE
➤ IF(AND(D5<>””,TODAY()+$D$11>=D5),”Yes”,”No”)
The IF function will return Yes for TRUE and No for FALSE.
Yes
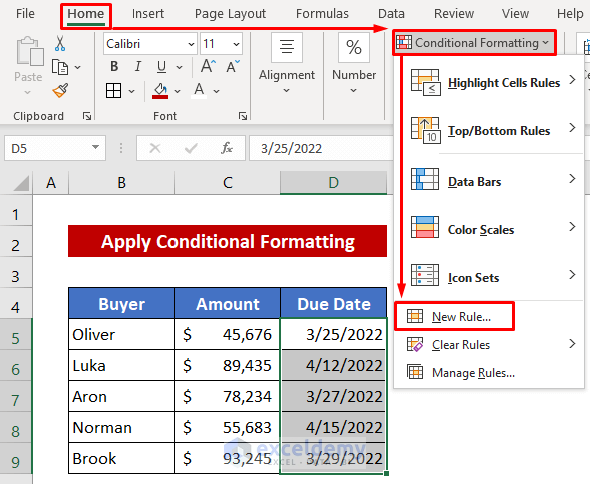
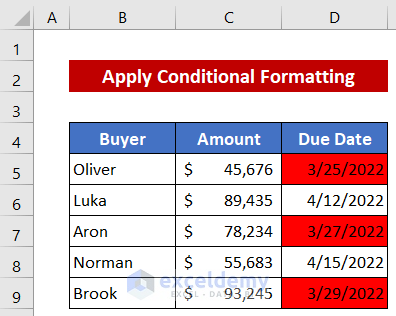
Method 2 – Apply Conditional Formatting to Set a Due Date Reminder in Excel
Steps:
- Select the dates.
- Go to Conditional Formatting and select New Rule.
- A dialog box will open up.
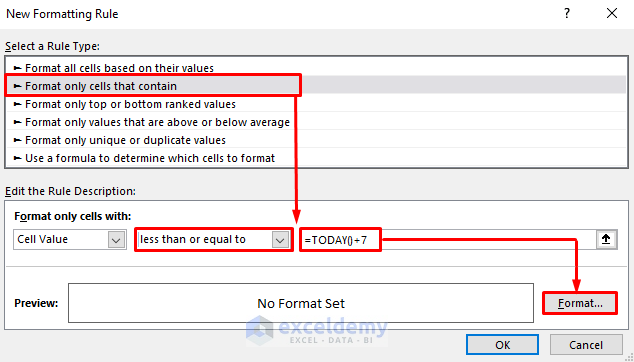
- Click Format only cells that contain from the Select a Rule Type box.
- From the Format only cells with section, select less than or equal to in the second box.
- Use the following formula in the third box:
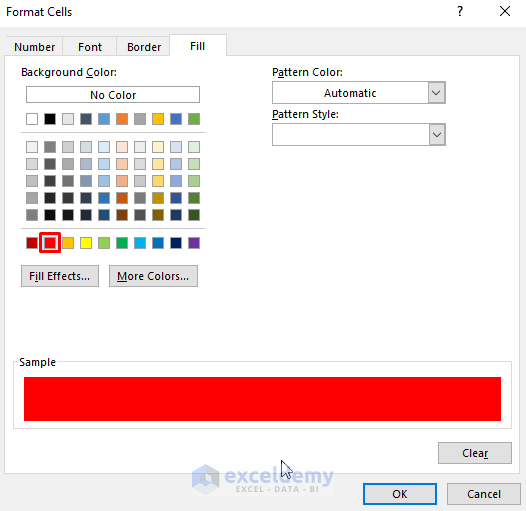
=TODAY()+7- Click Format. The Format Cells dialog box will appear.
- In the Fill section, pick your desired color. We picked a red hue.
- Press OK, and you’ll go back to the previous dialog box.
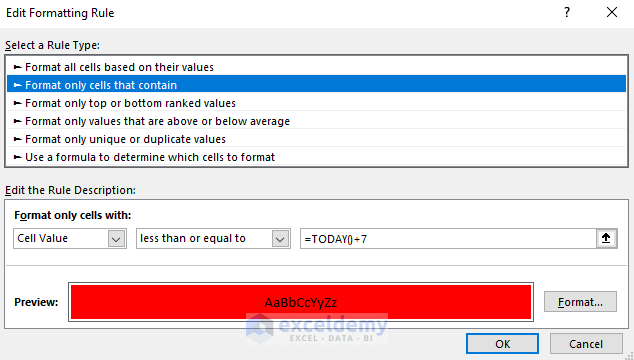
- Press OK.
- Here’s the result for the sample.
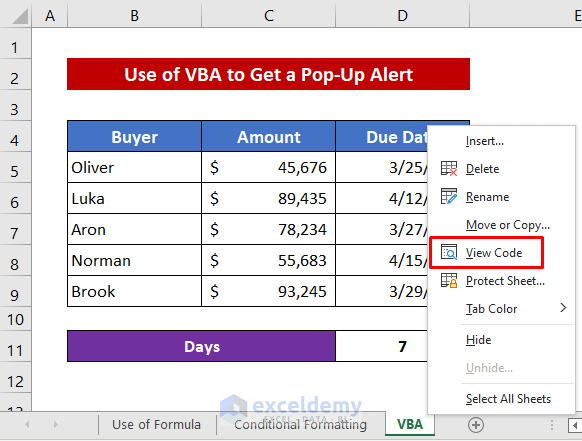
Method 3 – Embed VBA Macro to Get a Pop-Up Alert for a Due Date
Steps:
- Right-click on the sheet title.
- Select View Code from the Context menu.
- A VBA window will open up.
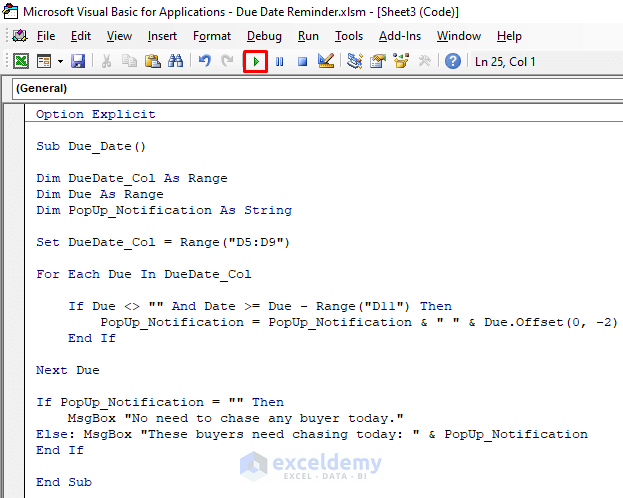
- Insert the following code in the module:
Option Explicit
Sub Due_Date()
Dim DueDate_Col As Range
Dim Due As Range
Dim PopUp_Notification As String
Set DueDate_Col = Range("D5:D9")
For Each Due In DueDate_Col
If Due <> "" And Date >= Due - Range("D11") Then
PopUp_Notification = PopUp_Notification & " " & Due.Offset(0, -2)
End If
Next Due
If PopUp_Notification = "" Then
MsgBox "No need to chase any buyer today."
Else: MsgBox "These buyers need chasing today: " & PopUp_Notification
End If
End Sub- Press the Run icon to run the code.
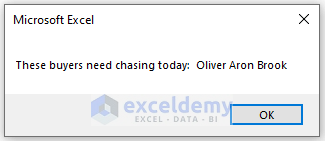
- A pop-up notification message box will send an alert with the buyer names.
Download the Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- How to Generate Automatic Email Alerts in Excel
- How to Create Notifications or Reminders in Excel
- How to Create Alerts in Excel
- How to Disable Alerts in Excel VBA
<< Go Back to Alerts in Excel | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!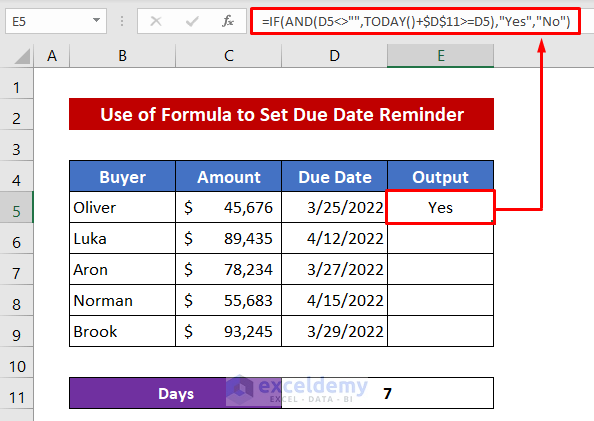



Thanks a lot for this protocol. I have managed to include all 3 methods in my excel file but now I would like to have the marco running when I’m opening the workbook. I have been trying this with Private Sub Workbook_open() but I’am not really sure how I can integrate this is in the codes.
Hello HOPE, thanks for your feedback. To do that, place Private Sub Workbook_open() in a new module and then call the previous Sub within it. I hope, it will work.
I have run the VBA but on another workbook sample but it is not showing the names of clients just the dates.
Good day, Daniel,
The issue you’re having might be because your workbook’s data range differs from the data range specified in our code.
Change the data range according to your worksheet.
This might be the solution to your issue. I’d appreciate it if you could send me the worksheet you’re working on so that I can better understand your issue and give you an exact solution.
Regards
Sakibul Hasan Nahid | ExcelDemy Team
Hello.
Once the code is embedded, will I get a daily pop-up notification for the specific day’s “buyers that need to be chased” as soon as i open the file? Also, once I have pressed “ok” on the pop-up notification, is there a way to bring it back up after it disappears?
Hello,
I’m having problems getting this to work for my spreadsheet. Any help will be grateful. example below.
Sub Due_Date()
Dim DueDate_Col As Range
Dim Due As Range
Dim PopUp_Notification As String
Set DueDate_Col = Range(“B4:I4”)
For Each Due In DueDate_Col
If Due “” And Date >= Due – Range(“J4″) Then
PopUp_Notification = PopUp_Notification & ” ” & Due.Offset(0, -2)
End If
Next Due
If PopUp_Notification = “” Then
MsgBox “PM Needed Soon.”
Else: MsgBox ” Schedule PM Maintenance Today: ” & PopUp_Notification
End If
End Sub
Hello Greg Smalls
Thanks for visiting our blog and sharing your problem so clearly. After reviewing your code, I assume you have a dataset like the following image.
The code you provided is OK; however, perhaps you have somehow messed up it when offsetting the names.
I have revised your code and made some changes that work perfectly for the mentioned dataset. Follow these steps:
I hope the idea and code will help you; good luck.
Regards
Lutfor Rahman Shimanto
Excel & VBA Developer
ExcelDemy