Reason 1 – Incorrect Workbook Reference
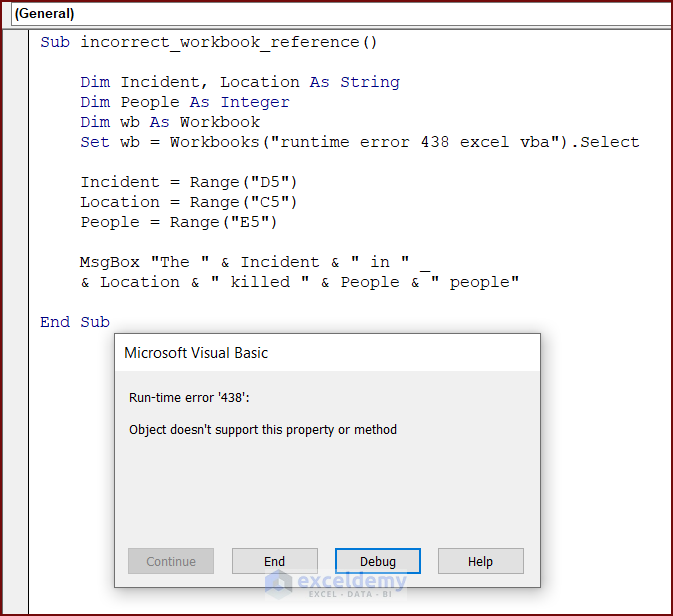
The following code has an incorrect workbook reference. Running this code will give runtime error 438.
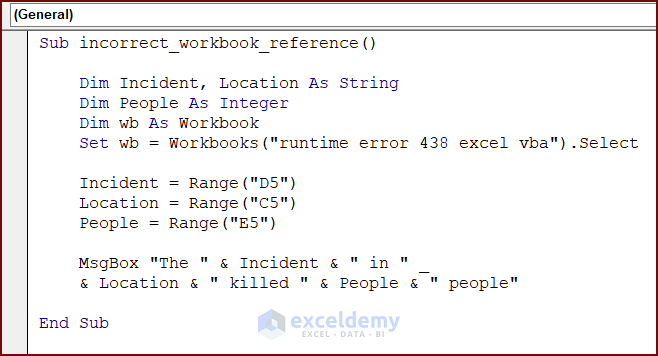 To understand the defective code, enter the following code in your VBA Editor and press the Run button or F5 key to run the code:
To understand the defective code, enter the following code in your VBA Editor and press the Run button or F5 key to run the code:
Sub incorrect_workbook_reference()
Dim Incident, Location As String
Dim People As Integer
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks("runtime error 438 excel vba").Select
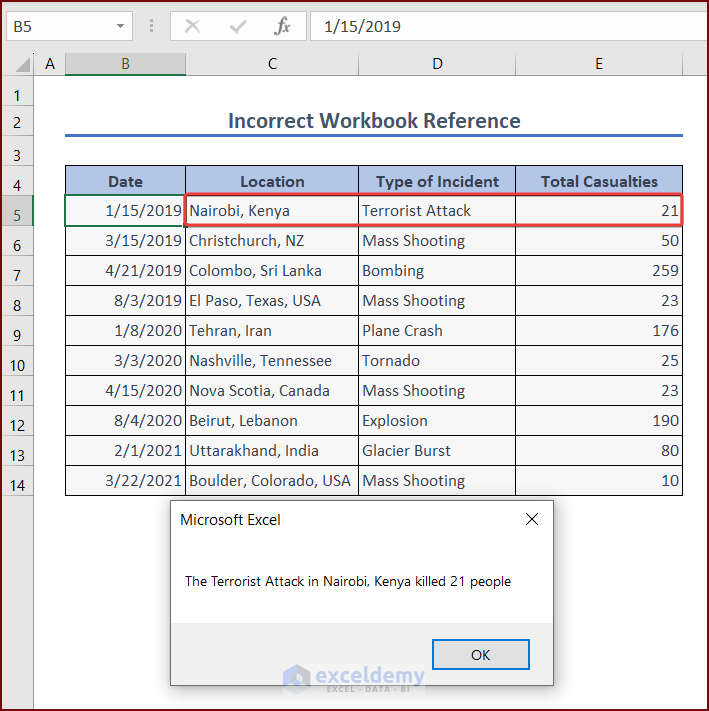
Incident = Range("D5")
Location = Range("C5")
People = Range("E5")
MsgBox "The " & Incident & " in " & Location & " killed " & People & " people"
End SubSolution: Correct Workbook Reference
Modify the previous code to eliminate runtime error 438. 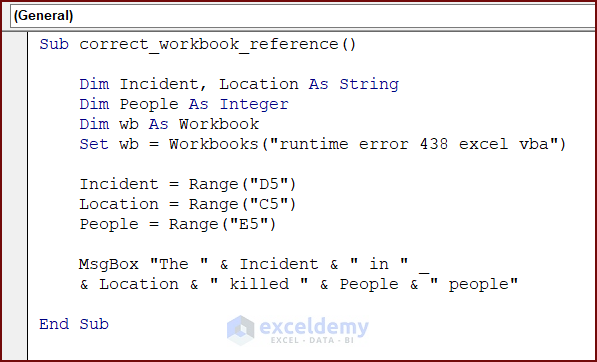
Sub correct_workbook_reference()
Dim Incident, Location As String
Dim People As Integer
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks("runtime error 438 excel vba")
Incident = Range("D5")
Location = Range("C5")
People = Range("E5")
MsgBox "The " & Incident & " in " & Location & " killed " & People & " people"
End SubVBA Breakdown:
Sub correct_workbook_reference()
Dim Incident, Location As String
Dim People As Integer
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks("runtime error 438 excel vba")This VBA code defines three variables: Incident, Location, and People. It then sets a Workbook object variable wb to refer to a workbook named runtime error 438 excel vba, which is selected using the Workbooks method.
Incident = Range("D5")
Location = Range("C5")
People = Range("E5")The code then assigns the values of cells D5, C5, and E5 to the variables Incident, Location, and People, respectively.
MsgBox "The " & Incident & " in " & Location & " killed " & People & " people"
End SubFinally, a MsgBox is displayed showing the concatenation of the three variables in a sentence.
In this modified code, the Set statement has been used to correctly assign the reference to the workbook object named runtime error 438 excel vba.
Read More: How to Fix Excel Runtime Error 13 Type Mismatch in VBA
Reason 2 – Invalid Worksheet Reference
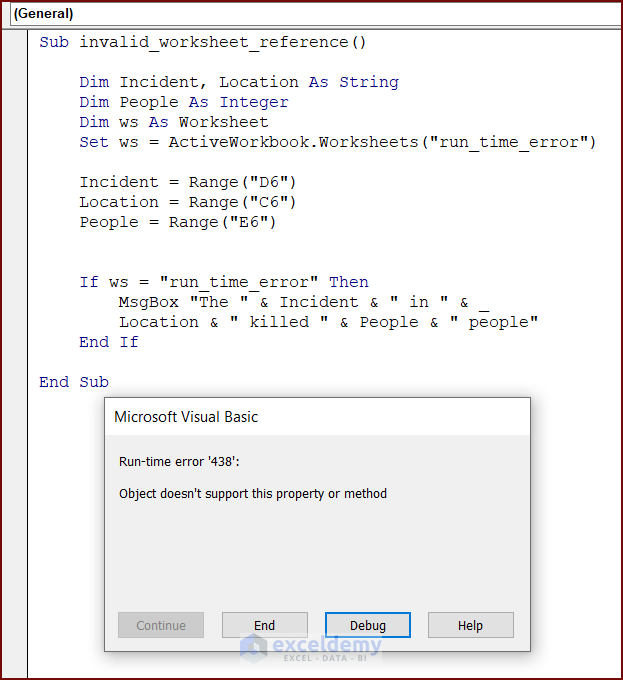
The following code has an invalid worksheet reference. Running this code will display runtime error 438.
To understand the defective code, enter the following code in your VBA Editor and press the Run button:
Sub invalid_worksheet_reference()
Dim Incident, Location As String
Dim People As Integer
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("run_time_error")
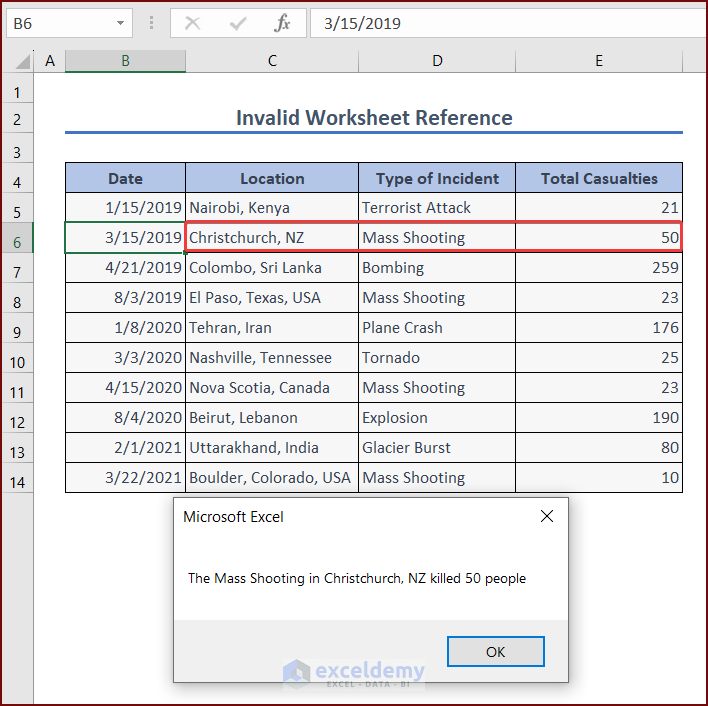
Incident = Range("D6")
Location = Range("C6")
People = Range("E6")
If ws = "run_time_error" Then
MsgBox "The " & Incident & " in " & Location & " killed " & People & " people"
End If
End SubSolution: Insert Valid Worksheet Reference
Modify the code to eliminate runtime error 438.

Sub valid_worksheet_reference()
Dim Incident, Location As String
Dim People As Integer
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("run_time_error")
Incident = Range("D6")
Location = Range("C6")
People = Range("E6")
If ws.Name = "run_time_error" Then
MsgBox "The " & Incident & " in " & Location & " killed " & People & " people"
End If
End SubVBA Breakdown:
Sub valid_worksheet_reference()
Dim Incident, Location As String
Dim People As Integer
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("run_time_error")This VBA code defines three variables: Incident, Location, and People. It then sets a Worksheet object variable, ws that refer to a worksheet named run_time_error within the active workbook, using the ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets method.
Incident = Range("D6")
Location = Range("C6")
People = Range("E6")The code then assigns the values of cells D6, C6, and E6 to the variables Incident, Location, and People, respectively.
If ws.Name = "run_time_error" Then
MsgBox "The " & Incident & " in " & Location & " killed " & People & " people"
End If
End SubThe code checks if the worksheet variable ws refers to a worksheet named “run_time_error” using an If statement. It then shows a MsgBox.
In this modified code to fix the error, ws.Name has been used to check the name of the worksheet object with a string, “run_time_error”. The Name property returns a string, so both sides of the If statement have the same data type. So, no error occurred this time.
Reason 3 – Incorrect Range Object Reference
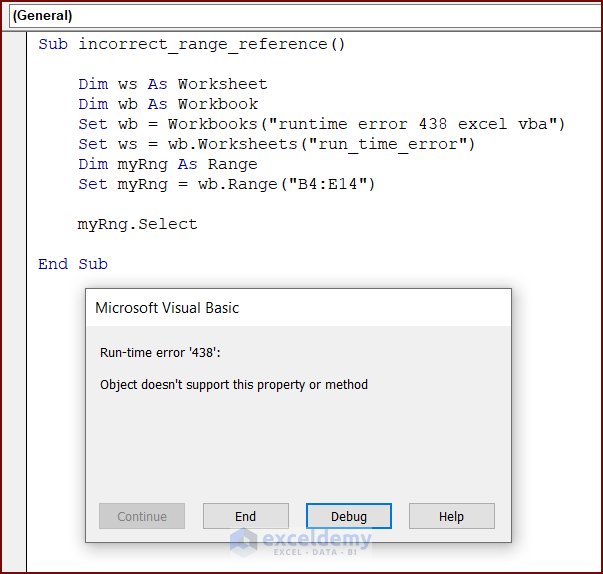
The following code has an incorrect range object reference. Running this code will display runtime error 438.
To understand the defective code, enter the following code in your VBA Editor and press the Run button or F5 key to run the code:
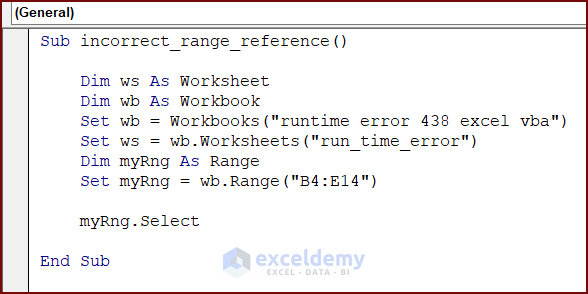
Sub incorrect_range_reference()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks("runtime error 438 excel vba")
Set ws = wb.Worksheets("run_time_error")
Dim myRng As Range
Set myRng = wb.Range("B4:E14")
myRng.Select
End SubSolution: Insert Correct Range Object Reference
Modify the code to eliminate runtime error 438.
Enter the modified code in your VBA Editor and press the Run button or F5 key to run the code:
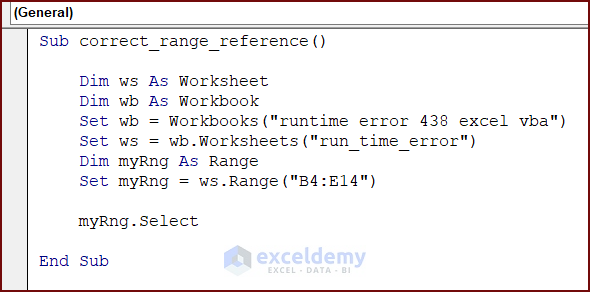
Sub correct_range_reference()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks("runtime error 438 excel vba")
Set ws = wb.Worksheets("run_time_error")
Dim myRng As Range
Set myRng = ws.Range("B4:E14")
myRng.Select
End SubVBA Breakdown:
Sub correct_range_reference()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks("runtime error 438 excel vba")
Set ws = wb.Worksheets("run_time_error")This VBA code sets a Workbook object variable wb to refer to a workbook named runtime error 438 excel vba, using the Workbooks method. It then sets a Worksheet object variable ws to refer to a worksheet named run_time_error within the workbook wb, using the Worksheets method.
Dim myRng As Range
Set myRng = ws.Range("B4:E14")
myRng.Select
End SubThe code defines a Range object variable myRng to refer to cells B4:E14 of the worksheet, ws, using the Range method.
To fix the error, the modified code uses the ws worksheet object instead of the wb workbook object to set the myRng range. It selects the myRng range using the Select method.
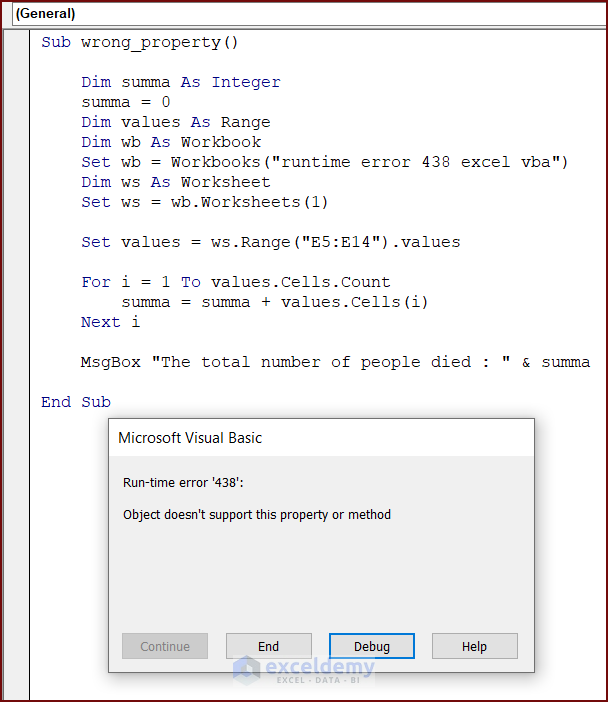
Reason 4 – Wrong Property of an Object
The following code includes the wrong property of an object. Running this code will display runtime error 438.
To understand the defective code, enter the following code in your VBA Editor and press the Run button or F5 key to run the code:
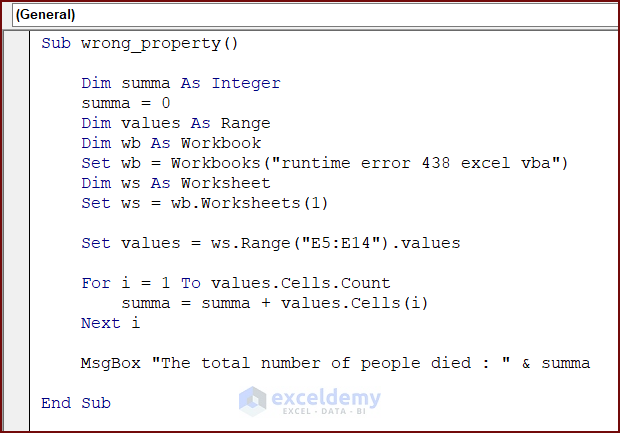
Sub wrong_property()
Dim summa As Integer
summa = 0
Dim values As Range
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks("runtime error 438 excel vba")
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = wb.Worksheets(1)
Set values = ws.Range("E5:E14").values
For i = 1 To values.Cells.Count
summa = summa + values.Cells(i)
Next i
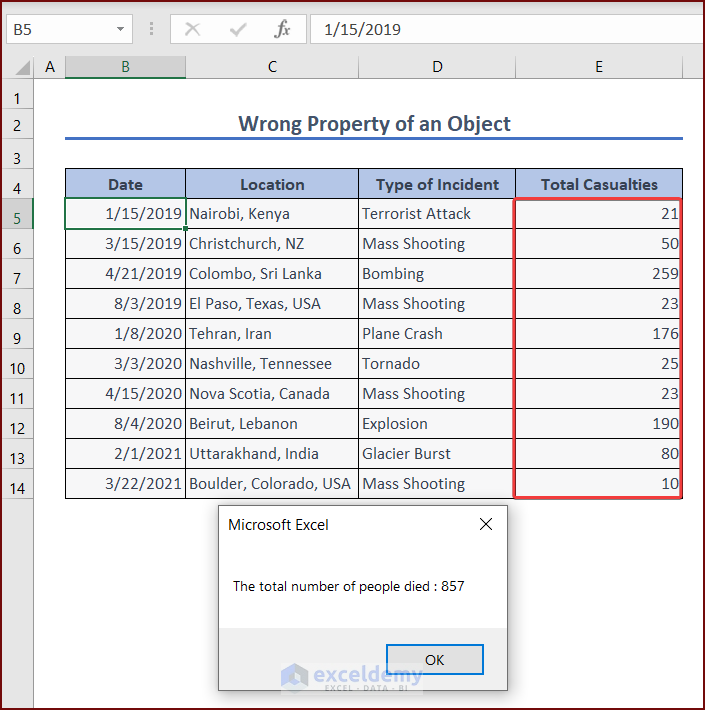
MsgBox "The total number of people died : " & summa
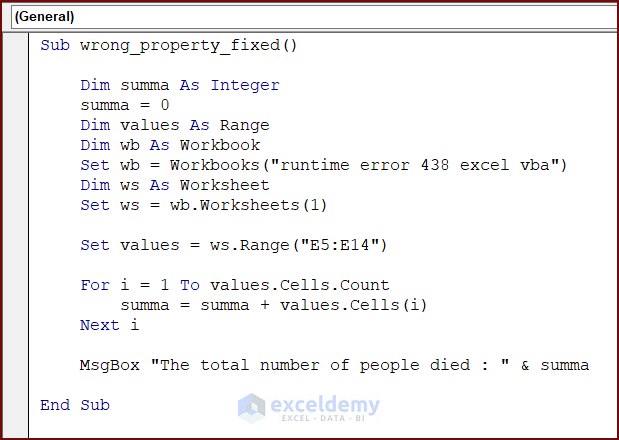
End SubSolution: Remove the Wrong Property of an Object
Modify the code to eliminate runtime error 438.
Enter the modified code in your VBA Editor and press the Run button or F5 key to run the code:
Sub wrong_property_fixed()
Dim summa As Integer
summa = 0
Dim values As Range
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks("runtime error 438 excel vba")
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = wb.Worksheets(1)
Set values = ws.Range("E5:E14")
For i = 1 To values.Cells.Count
summa = summa + values.Cells(i)
Next i
MsgBox "The total number of people died : " & summa
End SubVBA Breakdown:
Sub wrong_property_fixed()
Dim summa As Integer
summa = 0
Dim values As Range
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks("runtime error 438 excel vba")
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = wb.Worksheets(1)This VBA code defines a variable summa as an integer and initializes it to zero. It then defines a Range object variable values and a Worksheet object variable ws. The code sets ws to refer to the first worksheet in the workbook runtime error 438 excel vba using the Worksheets method.
Set values = ws.Range("E5:E14")
For i = 1 To values.Cells.Count
summa = summa + values.Cells(i)
Next i
MsgBox "The total number of people died : " & summa
End SubThese lines set values to refer to the values of cells E5:E14 in the worksheet, ws. The code used a For Loop to sum up the values in the values range and finally got the summation of the numbers in an output MsgBox.
To fix the error, we removed the .values property and set the range of values to the desired range.
Read More: [Fixed!] Excel VBA Run Time Error 1004
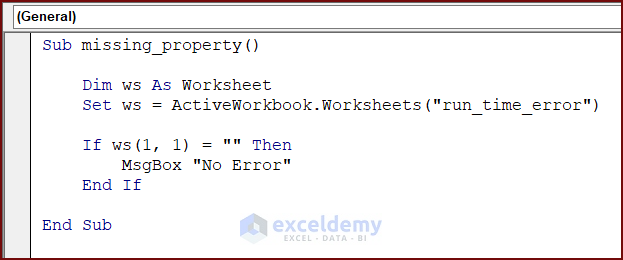
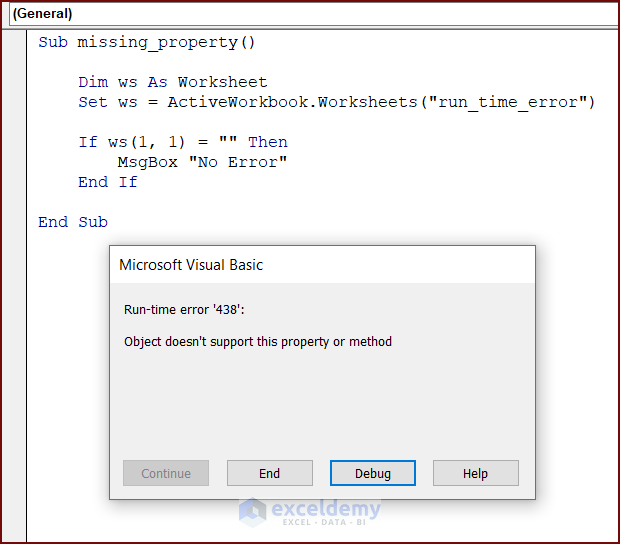
Reason 5 – Missing Property of an Object
The following code has an object whose property is missing. Running the code, will display runtime error 438.
To understand the defective code, enter the following code in your VBA Editor and press the Run button or F5 key to run the code:
Sub missing_property()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("run_time_error")
If ws(1, 1) = "" Then
MsgBox "No Error"
End If
End SubSolution: Add Property of an Object
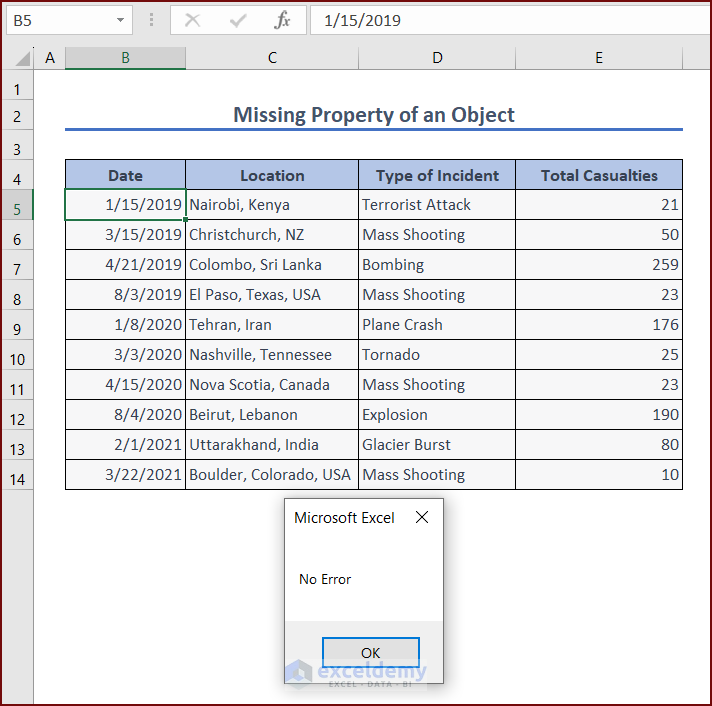
Modify the code to eliminate runtime error 438.
Enter the modified code in your VBA Editor and press the Run button or F5 key to run the code:
Sub missing_property_fixed()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("run_time_error")
If ws.Cells(1, 1) = "" Then
MsgBox "No Error"
End If
End SubVBA Breakdown:
Sub missing_property_fixed()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("run_time_error")This VBA code sets a Worksheet object variable, ws, to refer to a worksheet named run_time_error within the active workbook using the ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets method.
If ws.Cells(1, 1) = "" Then
MsgBox "No Error"
End If
End SubThe code checks if the value of the cell at the first row and first column of the ws worksheet is an empty string using an If statement. If the cell is empty, the code returns a MsgBox.
To fix the error, the code needs to use the Range or Cells method to refer to a specific cell or range of cells, like ws.Cells(1,1) or ws.Range(“A1”), instead of trying to access a cell without proper indexing.
Things to Remember
There are a few things to keep in mind to avoid runtime error 438 in Excel VBA:
- Check the spelling of the object or property
- Check for any missing reference
- Check if the object or property exists
Download Practice Workbook