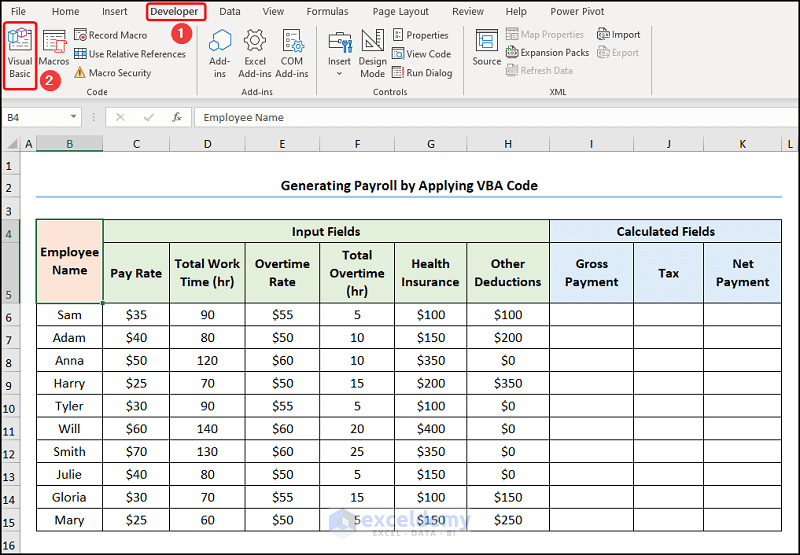
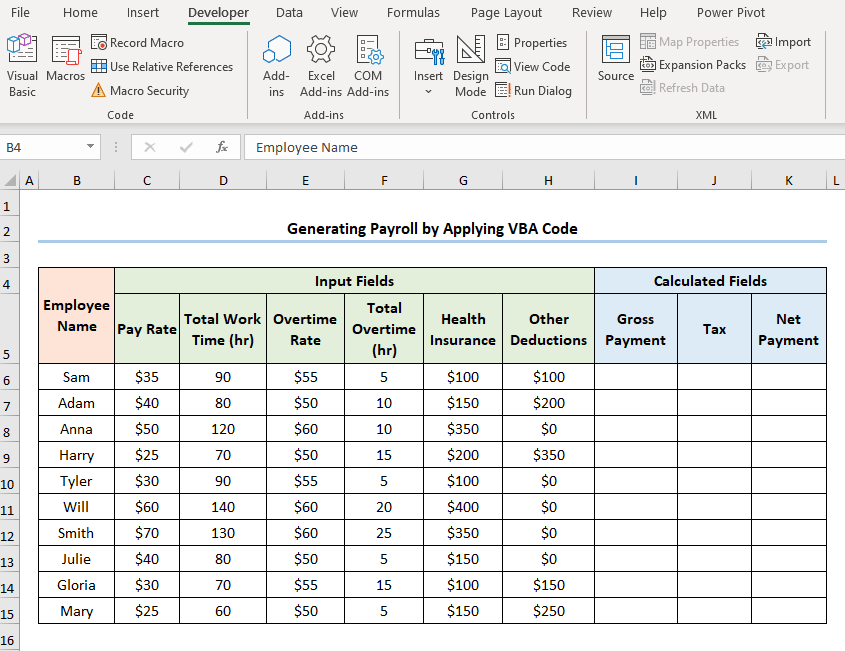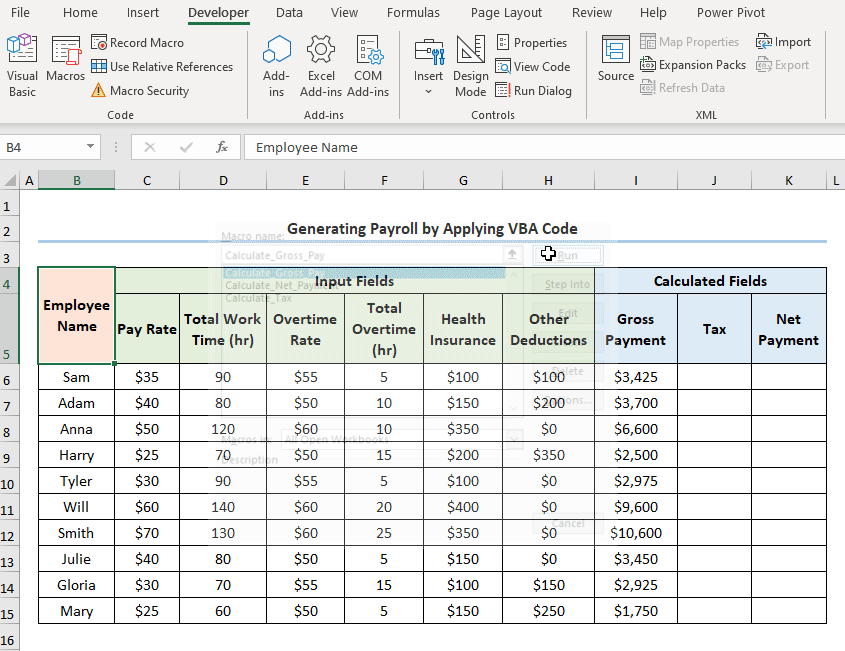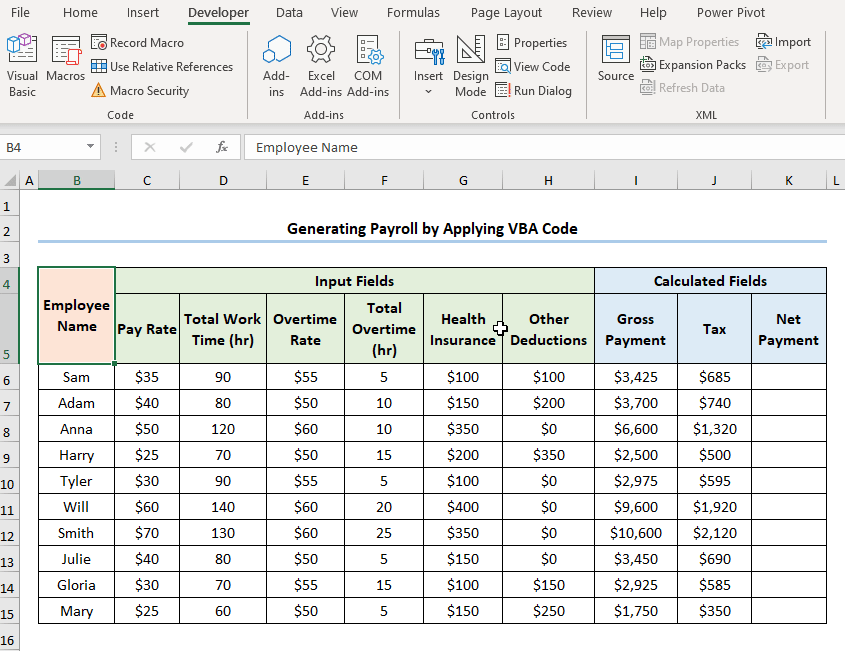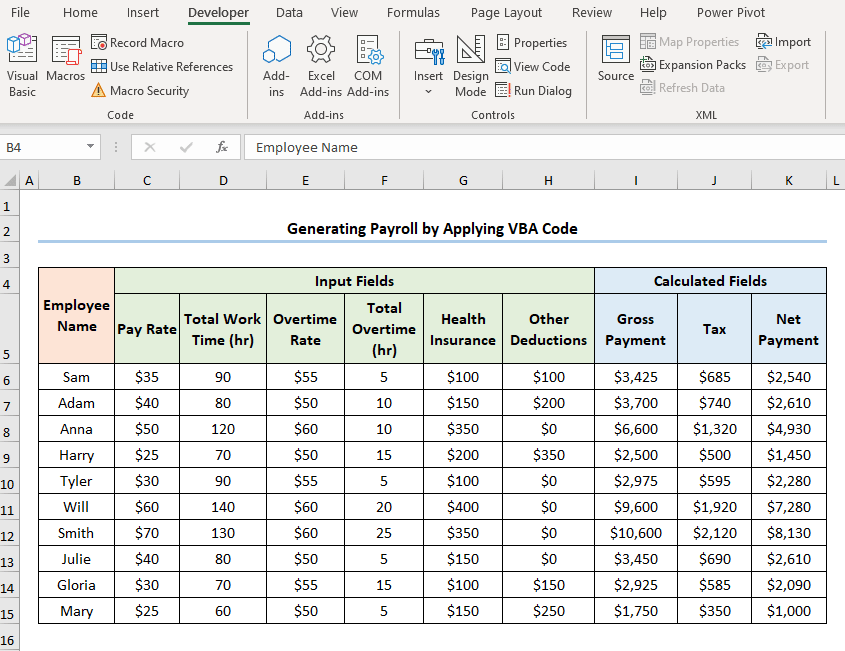
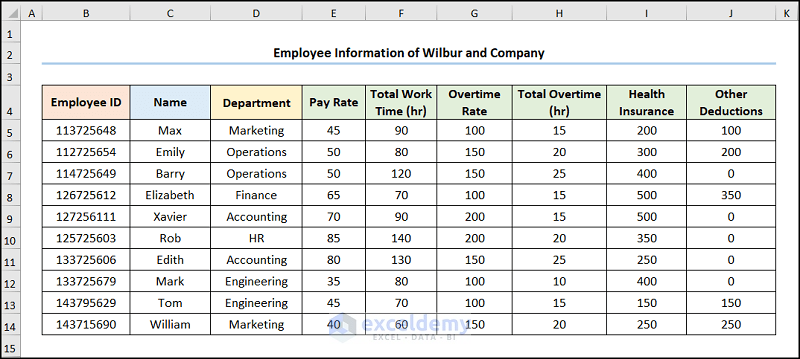
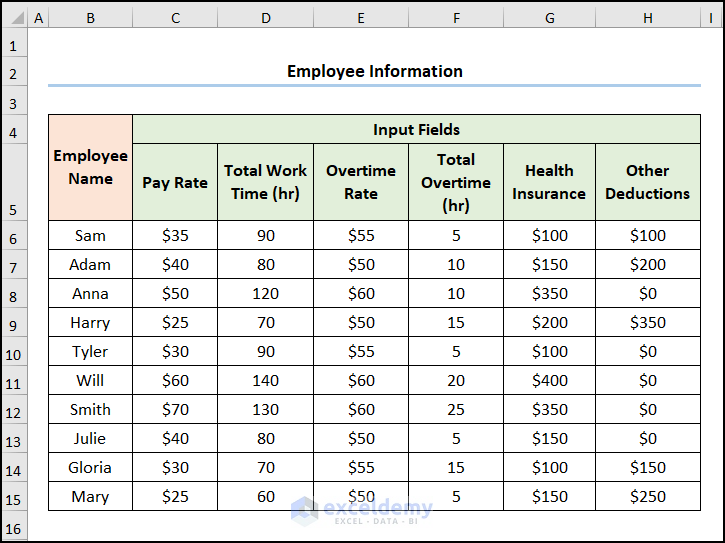
The following dataset shows Employee Information containing the “Employee Name,” “Pay Rate,” “Total Work Time,” “Overtime Rate,” “Total Overtime,” “Health Insurance,” and “Other Deductions.” Let’s explore how to generate payroll in Excel VBA with the necessary illustrations.
Step 1: Insert the VBA Code into a Module
- Go to the Developer tab >> click the Visual Basic button.
This opens the Visual Basic Editor in a new window.
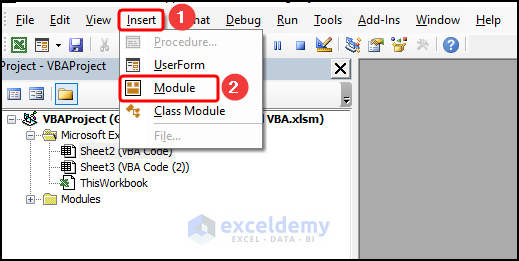
- Go to the Insert tab >> Select Module.
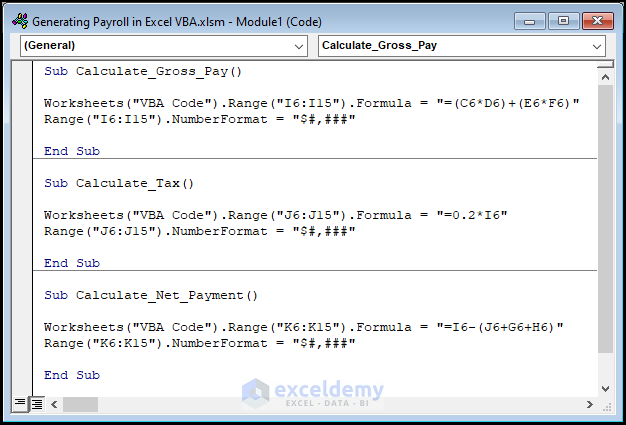
Copy the code from here and paste it into the window as shown below:
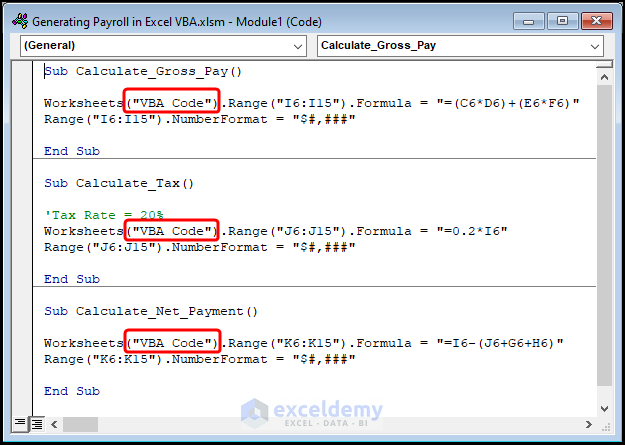
Sub Calculate_Gross_Pay()
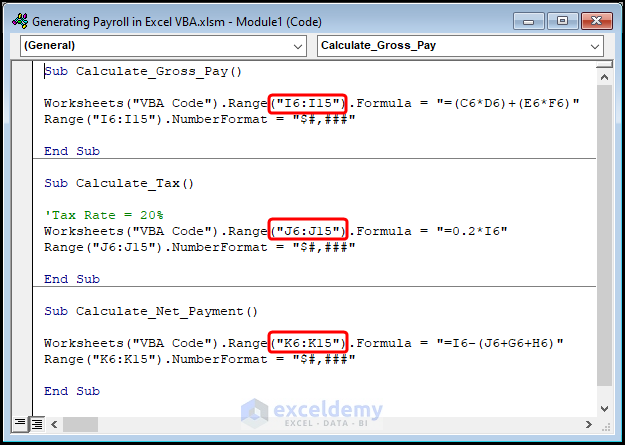
Worksheets("VBA Code").Range("I6:I15").Formula = "=(C6*D6)+(E6*F6)"
Range("I6:I15").NumberFormat = "$#,###"
End Sub
Sub Calculate_Tax()
Worksheets("VBA Code").Range("J6:J15").Formula = "=0.2*I6"
Range("J6:J15").NumberFormat = "$#,###"
End Sub
Sub Calculate_Net_Payment()
Worksheets("VBA Code").Range("K6:K15").Formula = "=I6-(J6+G6+H6)"
Range("K6:K15").NumberFormat = "$#,###"
End Sub⚡ Code Breakdown:
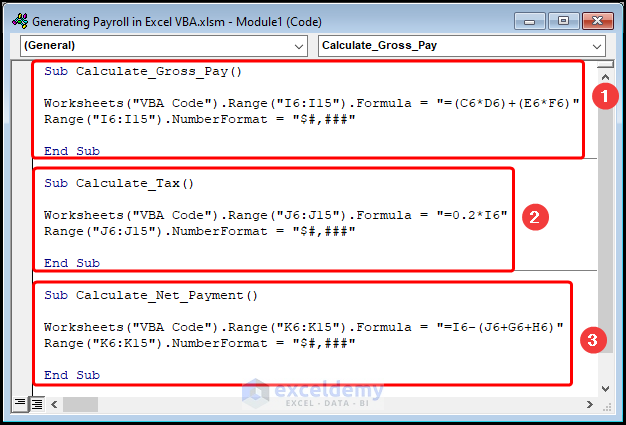
We’ll explain the 3 VBA Macros.
- In the first macro, “Calculate_Gross_Pay”, use the Worksheet and Range objects to apply the formula to the I6:I15 range of cells located in the “VBA Code” worksheet.
- Next, utilize the Number Format property to format the results as Currency.
- Similarly, compute the “Tax” and “Net Payment” by executing the second and third macros.
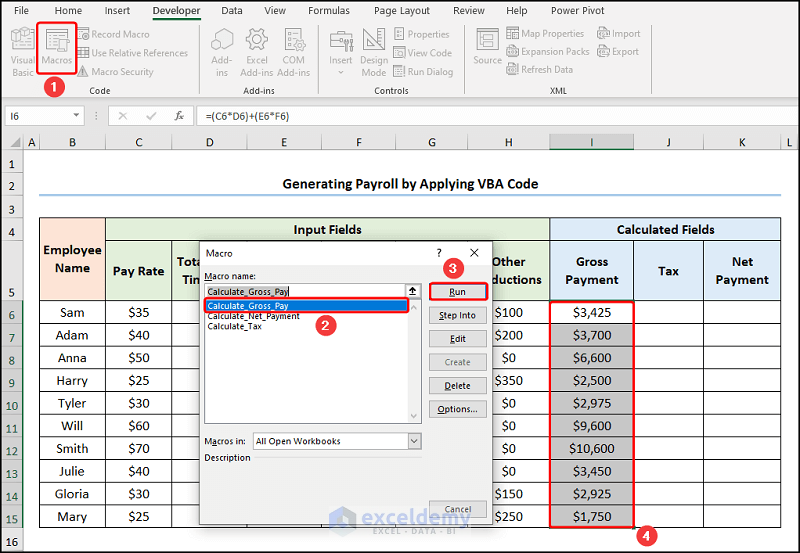
Step 2: Run the VBA Macros
- Close the VBA window >> click the Macros button.
This opens the Macros dialog box.
- Select the “Calculate_Gross_Pay” macro >> Press Run.
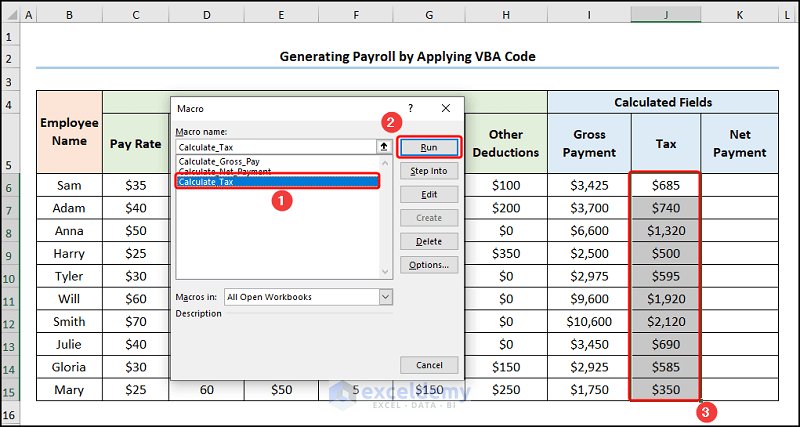
- Choose the “Calculate_Tax” macro >> press Run.
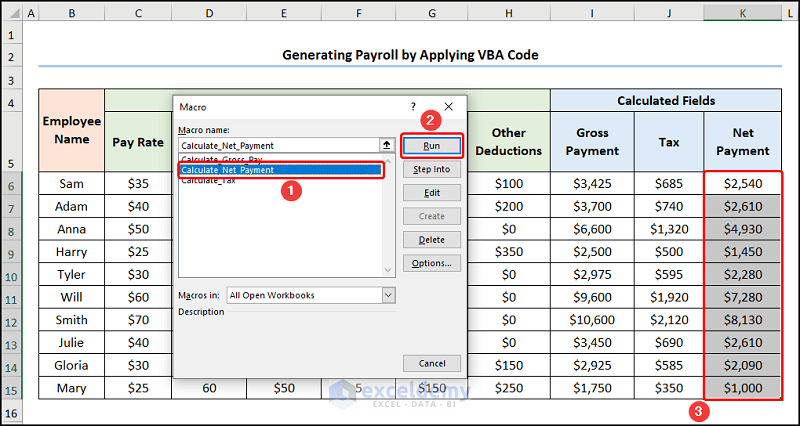
- Execute the “Calculate_Net_Payment” macro.
The results should appear in the animated GIF given below.
How to Automate Payroll in Excel
Alternatively, we can automate payroll in Excel using the VLOOKUP function to pull data from a source worksheet to calculate the employee payroll. The Employee Information of the Wilbur and Company dataset shows the “Employee ID,” “Name,” “Department,” “Pay Rate,” “Total Work Time,” “Overtime Rate,” “Total Overtime,” “Health Insurance,” and “Other Deductions.”
Steps:
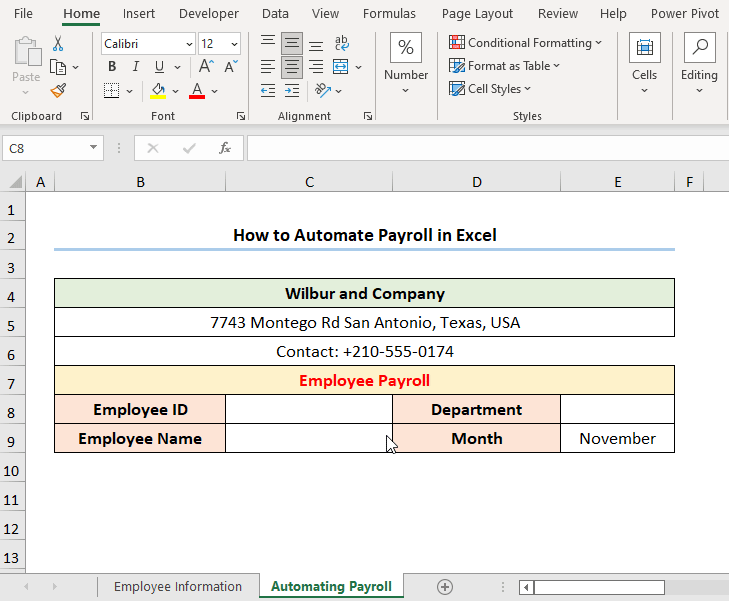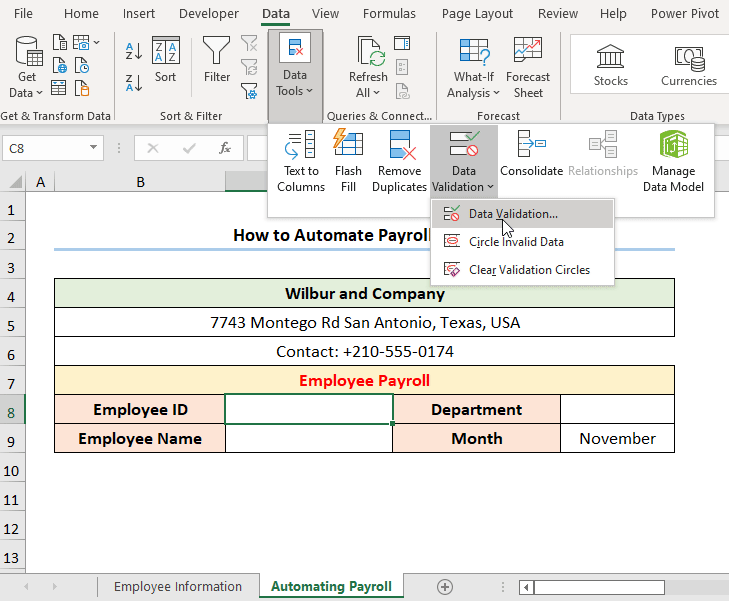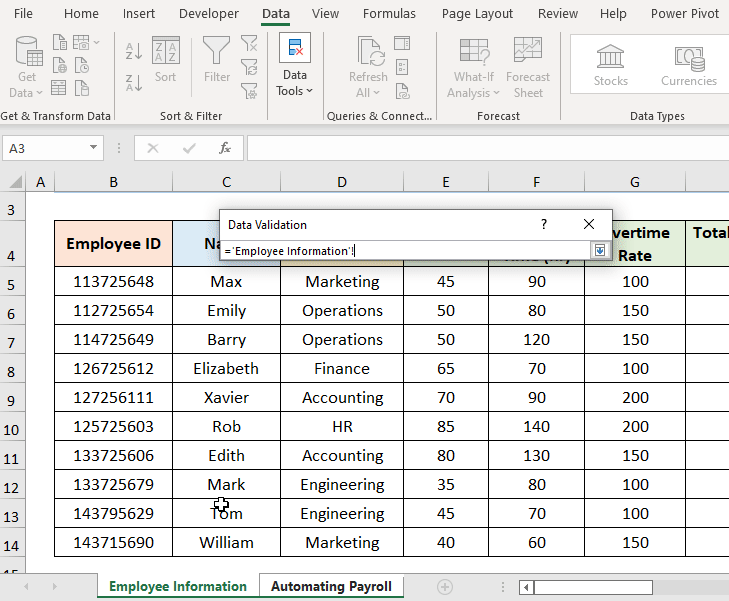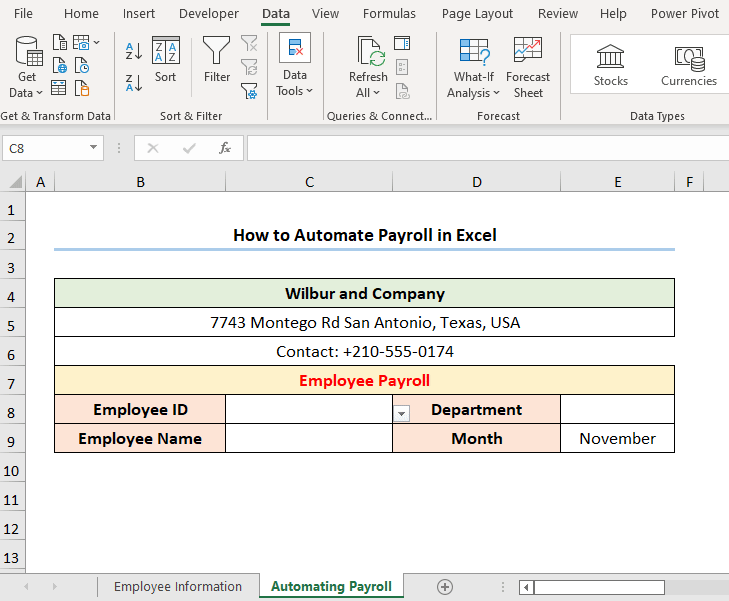
- Go to the C8 cell >> Move to the Data tab.
- Insert a Data Validation drop-down by following the steps shown in the GIF.
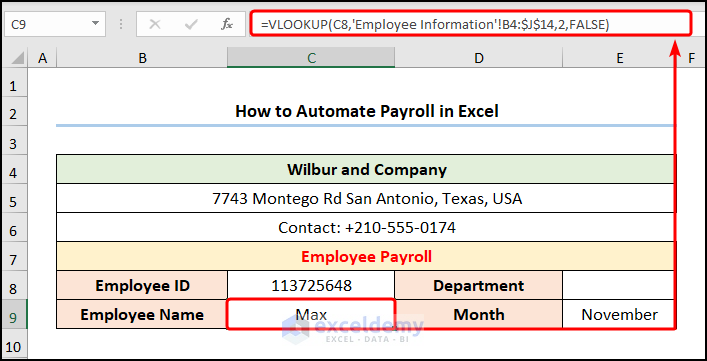
- Go to cell C9 and insert the following formula:
=VLOOKUP(C8,'Employee Information'!B4:$J$14,2,FALSE)
Cell C8 refers to the “Employee ID”.
Formula Breakdown:
- VLOOKUP(C8,’Employee Information’!B4:$J$14,2,FALSE) → looks for a value in the left-most column of a table and then returns a value in the same row from a column you specify. Here, C8 ( lookup_value argument) is mapped from the B4:J14 (table_array argument) array. Next, 2 (col_index_num argument) represents the column number of the lookup value. Lastly, FALSE (range_lookup argument) refers to the Exact match of the lookup value.
- Output → Max
Note: Please use Absolute Cell Reference by pressing the F4 key on your keyboard.
- Use the VLOOKUP function to retrieve information related to “Max” and, in each case, specify the correct column number. For instance, the column number for “Department” is “3”, for “Pay Rate” is “4”, and so on.
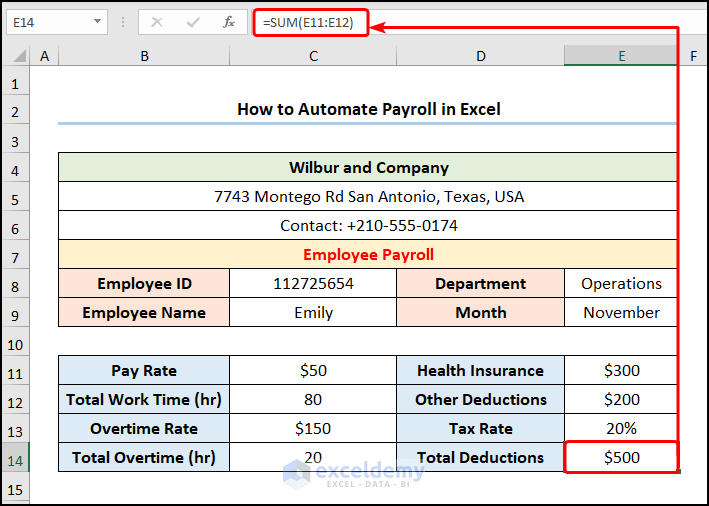
- Apply the SUM function to calculate the “Total Deductions”.
=SUM(E11:E12)
The E11 and E12 cells indicate the deductions for “Health Insurance” and “Other Deductions”.
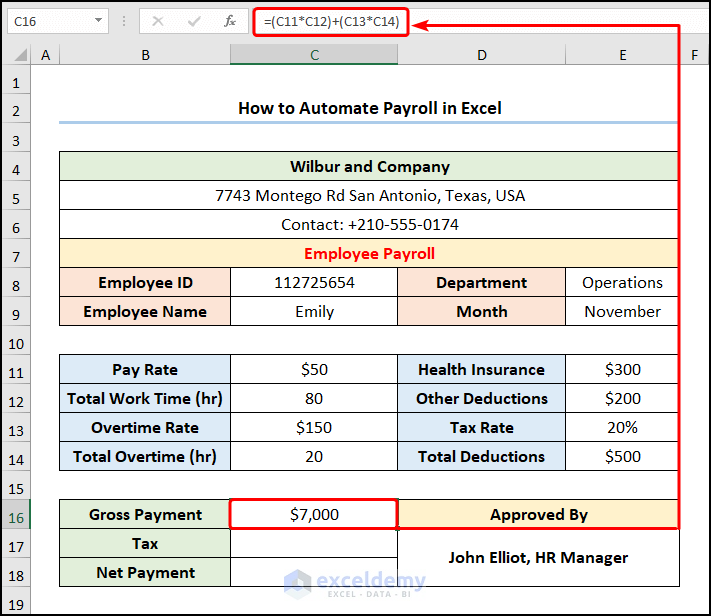
- Enter the following formula into the C16 to obtain the “Gross Pay”:
=(C11*C12)+(C13*C14)
The C11, C12, C13, and C14 cells represent the “Pay Rate,” “Total Work Time,” “Overtime Rate,” and “Total Overtime”.
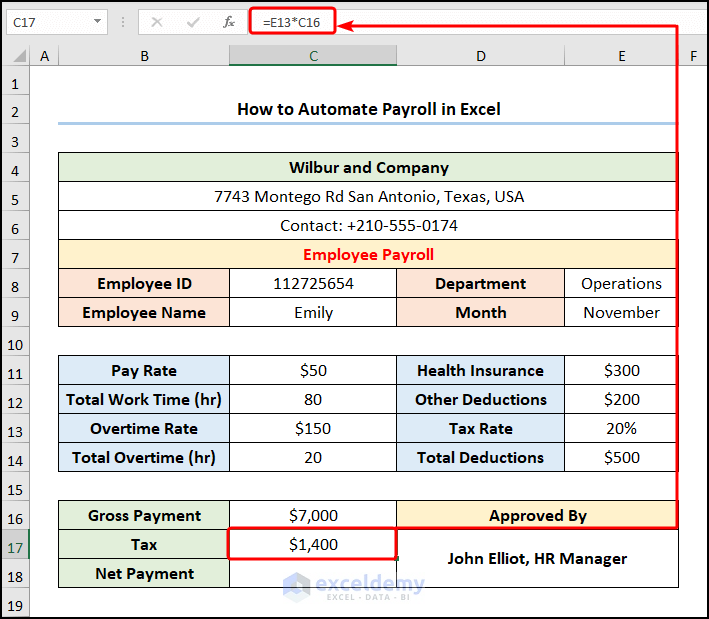
- Calculate the “Tax” using the following expression.
=E13*C16
The C16 and E13 cells indicate the “Gross Payment” and “Tax Rate”.
- Enter the formula into the Formula Bar to compute the Net Payment:
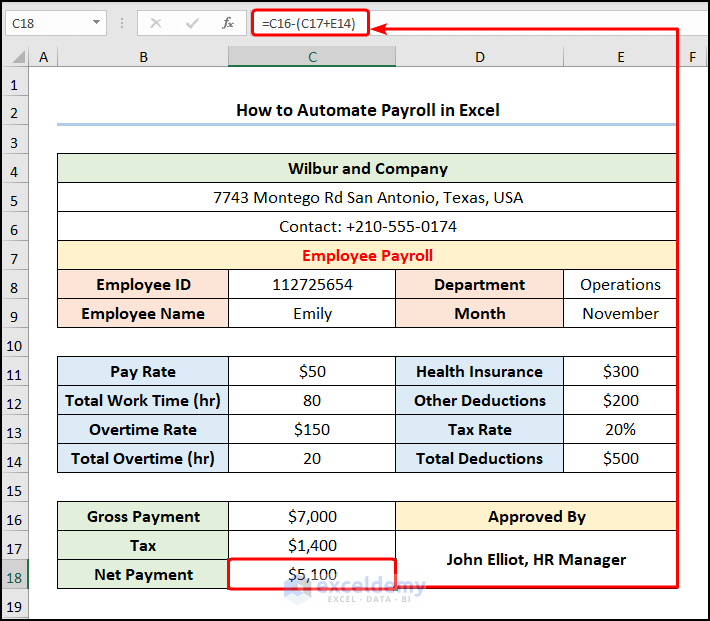
=C16-(C17+E14)
The C16 and C17 cells refer to the “Gross Payment” and “Tax Rate,” whereas the E14 cell represents the “Total Deductions”.
Read More: Payroll Exercises in Excel
Things to Remember
There are a few things to remember when running the VBA Code.
- Change the worksheet name to “VBA Code” or specify the correct worksheet name.
- Specify the appropriate range of cells where to return the calculated output.
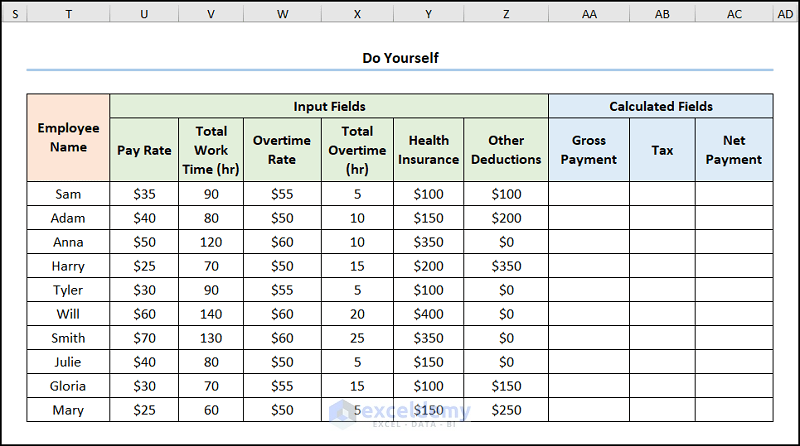
Practice Section
We have provided a practice section on the right side of each sheet so you can practice.
Download the Practice Workbook
<< Go Back to Formula List | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!