Excel is the most widely used tool for dealing with massive datasets. We can perform myriads of tasks of multiple dimensions in Excel. In this article, I will explain nominal vs effective interest rate in Excel. There are some differences between these two interest rates and I will explain them using an easy example.
Nominal vs Effective Interest Rate in Excel: 2 Practical Examples
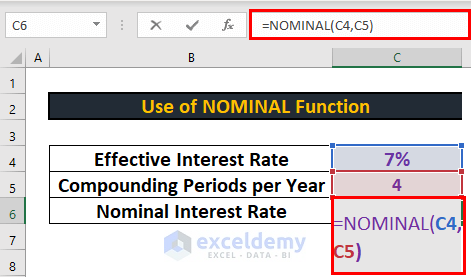
This is the dataset for converting effective interest rate to nominal interest rate.
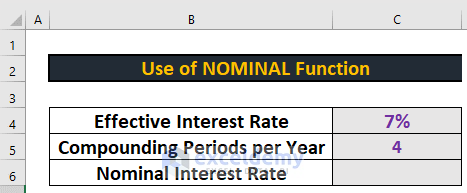
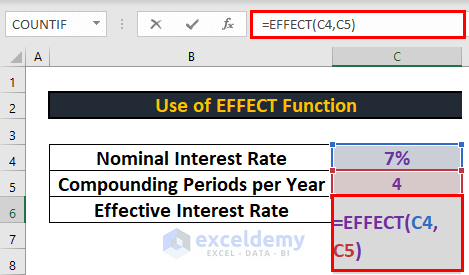
Similarly, there is another dataset for converting nominal interest rate to effective interest rate. I will use these datasets to calculate the interest rates.
1. Use of NOMINAL Function to Calculate Nominal Interest Rate in Excel
First of all, I will show you how to calculate the nominal interest rate. For this, I will use the NOMINAL function.
Steps:
- Go to C6 and write down the following formula
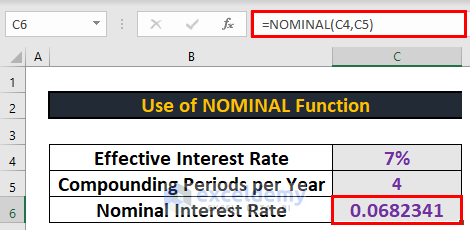
=NOMINAL(C4,C5)- Then, press ENTER to get the output.
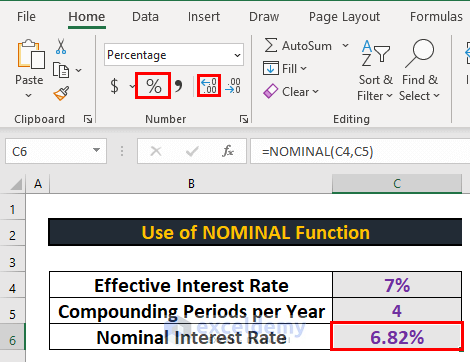
- Change the format to percentage.
- After that, increase the decimal place.
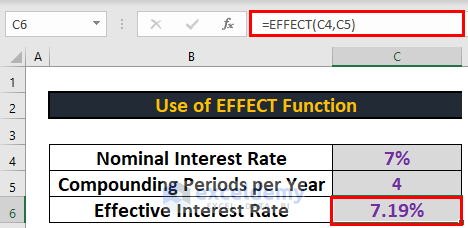
2. Use of EFFECT Function to Calculate Effective Interest Rate in Excel
Now, let’s see how to calculate the effective interest rate. I will use the EFFECT function to do so.
Steps:
- Go to C6 and write down the following formula
=EFFECT(C4,C5)
- After that, press ENTER to get the output.
Read More: How to Calculate Effective Interest Rate in Excel with Formula
Differences Between Nominal and Effective Interest
There are different types of interest rates and it is prudent for every investor or potential investor to know the differences between interest rates. The nominal interest rate is the simplest of the interest rates. In the case of the nominal interest rate, it is the given interest rate or stated interest rate of a bond or loan. The nominal interest rate is also referred to as the coupon rate for fixed-income investments.
On the other hand, The effective interest rate takes the effect of compounding into account. The difference between the nominal and effective rates widens as the compounding periods increase.
Let me illustrate this with a simple example.
If a bond pays 8% annually and compounds semiannually, an investor who invests $1,000 will receive $40 in interest payments after the first six months ($1,000 x.04), and $41.60 in interest payments after the next six months ($1,040 x.04). This investor receives $81.60 in total for the year. In this case, the nominal rate is 8%, but the effective rate is 8.16%.
The effective interest rate is generally higher than the nominal interest rate. Because effective interest rate considers compounding effect.
Things to Remember
- If the interest compounds semi-annually, the number of compounding periods per year is 2.
- If the interest compounds quarterly, the number of compounding periods per year is 4.
Download Practice Workbook
Conclusion
In this article, I have explained nominal vs effective interest rate in Excel. I hope it helps everyone. If you have any suggestions, ideas, or feedback, please feel free to comment below.
Related Articles
- How to Use Nominal Interest Rate Formula in Excel
- How to Calculate Weighted Average Interest Rate in Excel
- How to Calculate Periodic Interest Rate in Excel
<< Go Back to How to Calculate Interest Rate in Excel | Excel for Finance | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!