The Dir function, FSO early binding, and FSO late binding will be used.
Key Concept of Function & Feature for Listing
i. Dir Function
The Dir function returns the first file name in the specified folder.
ii. File System Object (FSO)
A File System Object (FSO) allows the VBA code to create, read, modify, and delete files and folders, as well as perform other file system operations, such as copying, moving, and renaming files and folders.
Early Binding
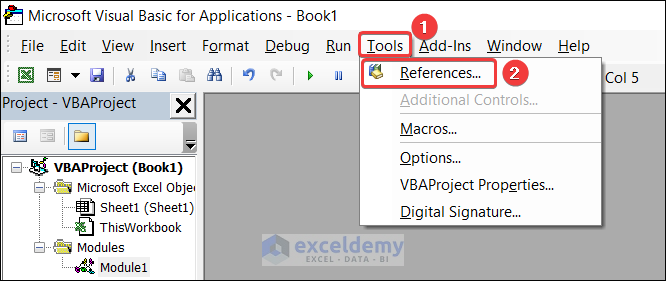
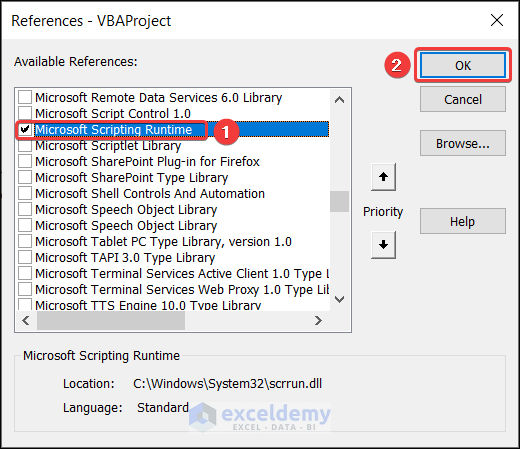
Early binding in VBA explicitly declares the type of an object at compile time, using the Dim statement with the As keyword. It is automatically opened when the workbook is launched. The Microsoft Scripting Runtime box must be checked.
Go to Tools and click References.
Search Microsoft Scripting Runtime and check the box.
Late Binding
Late binding in VBA declares an object without specifying its type until runtime. When using late binding with the File System Object (FSO), the CreateObject function is used to create an FSO object, rather than explicitly declaring it with the Dim statement.
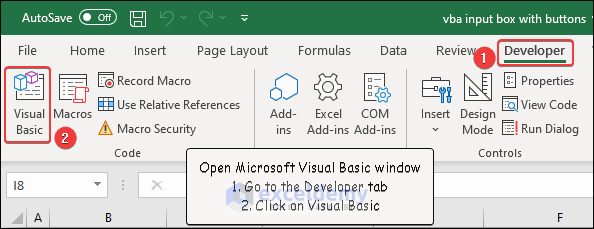
How to Launch the VBA Editor in Excel
Go to the Developer tab and click Visual Basic. You can also open it by pressing Alt+F11.
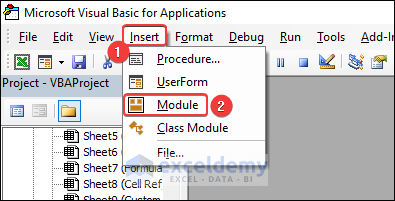
In the Insert tab, click on Module to open the code Module.
Using Excel VBA to List Files in the Folder and Subfolders – 3 Examples
Files will be listed from the folder “E:\Softeko\UDF\”.
Example 1 – Listing All Files in a Folder in Excel Worksheet
Use the Dir function and the File System Object.
1.1 Using the File System Object Early Binding
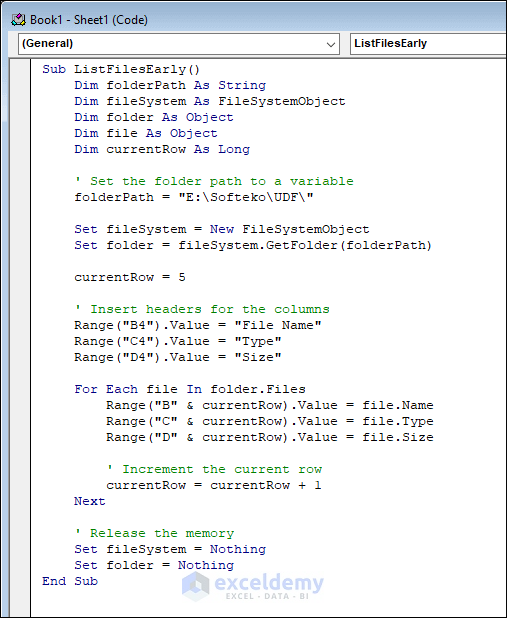
Use the FSO Early Binding to list all files in a folder. Enter the following VBA code.
Sub ListFilesEarly()
Dim folderPath As String
Dim fileSystem As FileSystemObject
Dim folder As Object
Dim file As Object
Dim currentRow As Long
' Set the folder path to a variable
folderPath = "E:\Softeko\UDF\"
Set fileSystem = New FileSystemObject
Set folder = fileSystem.GetFolder(folderPath)
currentRow = 5
' Insert headers for the columns
Range("B4").Value = "File Name"
Range("C4").Value = "Type"
Range("D4").Value = "Size"
For Each file In folder.Files
Range("B" & currentRow).Value = file.Name
Range("C" & currentRow).Value = file.Type
Range("D" & currentRow).Value = file.Size
' Increment the current row
currentRow = currentRow + 1
Next
' Release the memory
Set fileSystem = Nothing
Set folder = Nothing
End SubCode Breakdown
folderPath = "E:\Softeko\UDF\"
Set fileSystem = New FileSystemObject
Set folder = fileSystem.GetFolder(folderPath)- folderPath = “E:\Softeko\UDF sets the value of the “folderPath” variable to the file path “E:\Softeko\UDF”.
- Set fileSystem = New FileSystemObject creates a new instance of the FileSystemObject and assigns it to the “fileSystem” variable.
For Each file In folder.Files
Range("B" & currentRow).Value = file.Name
Range("C" & currentRow).Value = file.Type
Range("D" & currentRow).Value = file.Size
' Increment the current row
currentRow = currentRow + 1
Next- starts a loop that will execute once for each file in the “Files” collection of the “fileSystem” object.
- stores the file names, types, and sizes in columns B, C, and D.
Set fileSystem = Nothing
Set folder = Nothing- releases memory used by FileSystemObject.
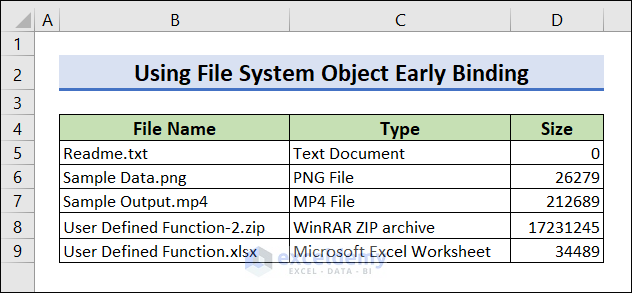
Press F5 or click Run button to see the output.

Read More: Excel VBA to Count Files in Folder and Subfolders
1.2 Using the Dir Function
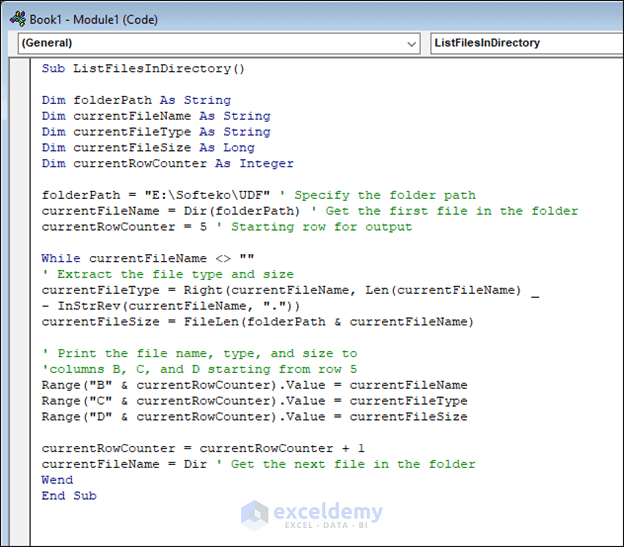
The Dir Function will be used to list file names. Use the VBA code below.
Sub ListFilesInDirectory()
Dim folderPath As String
Dim currentFileName As String
Dim currentFileType As String
Dim currentFileSize As Long
Dim currentRowCounter As Integer
folderPath = "E:\Softeko\UDF" ' Specify the folder path
currentFileName = Dir(folderPath) ' Get the first file in the folder
currentRowCounter = 5 ' Starting row for output
While currentFileName <> ""
' Extract the file type and size
currentFileType = Right(currentFileName, Len(currentFileName) _
- InStrRev(currentFileName, "."))
currentFileSize = FileLen(folderPath & currentFileName)
' Print the file name, type, and size to
'columns B, C, and D starting from row 5
Range("B" & currentRowCounter).Value = currentFileName
Range("C" & currentRowCounter).Value = currentFileType
Range("D" & currentRowCounter).Value = currentFileSize
currentRowCounter = currentRowCounter + 1
currentFileName = Dir ' Get the next file in the folder
Wend
End SubCode Breakdown
folderPath = "E:\Softeko\UDF\"
currentfileName = Dir(folderPath)- declares a variable called folderPath and assigns it to “E:\Softeko\UDF\”.
- creates a variable named currentfileName and assigns the value returned by the Dir() function.
currentfileType = Right(currentfileName, Len(fileName) - InStrRev(fileName, "."))
currentfileSize = FileLen(folderPath & currentfileName)- currentfileType = Right(fileName, Len(currentfileName) – InStrRev(currentfileName, “.”)) declares a variable named fileType. The Right function extracts the last portion of the currentfileName starting from the “.”.
- currentfileSize = FileLen(folderPath & currentfileName) calculates the file size by concatenating folderPath and currentfileName variables.
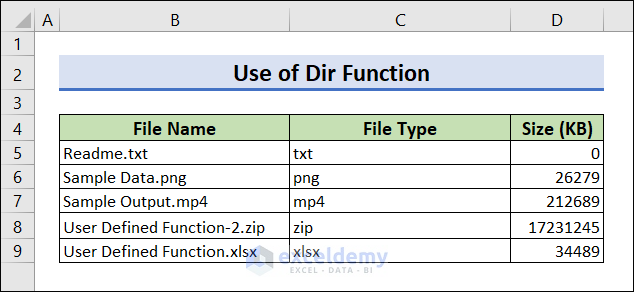
Run the code. All file names, types, and sizes are listed in your worksheet.
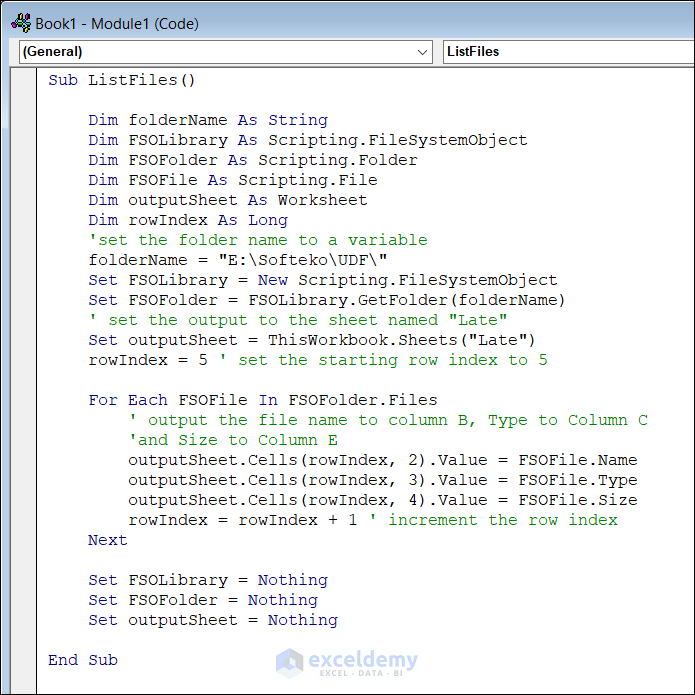
1.3 Using the File System Object Late Binding
Use the FSO Late Binding. Enter the following code.
Sub ListFiles()
Dim folderName As String
Dim FSOLibrary As Scripting.FileSystemObject
Dim FSOFolder As Scripting.folde
Dim FSOFile As Scripting.file
Dim outputSheet As Worksheet
Dim rowIndex As Long
'set the folder name to a variable
folderName = "E:\Softeko\UDF\"
Set FSOLibrary = New Scripting.FileSystemObject
Set FSOFolder = FSOLibrary.GetFolder(folderName)
' set the output to the sheet named "Late"
Set outputSheet = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Late")
rowIndex = 5 ' set the starting row index to 5
For Each FSOFile In FSOFolder.files
' output the file name to column B, Type to Column C
'and Size to Column E
outputSheet.Cells(rowIndex, 2).Value = FSOFile.Name
outputSheet.Cells(rowIndex, 3).Value = FSOFile.Type
outputSheet.Cells(rowIndex, 4).Value = FSOFile.Size
rowIndex = rowIndex + 1 ' increment the row index
Next
Set FSOLibrary = Nothing
Set FSOFolder = Nothing
Set outputSheet = Nothing
End SubCode Breakdown
Set FSOLibrary = New Scripting.FileSystemObject
Set FSOFolder = FSOLibrary.GetFolder(folderName)- Set FSOLibrary = New Scripting.FileSystemObject creates an instance of the FileSystemObject class from the Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library and assigns it to the FSOLibrary variable using the New
- The GetFolder() method of the FileSystemObject object obtains a reference to a specific folder in the file system, specified by folderName, which is a string variable containing the full path to the folder.
For Each FSOFile In FSOFolder.files
' output the file name to column B, Type to Column C
'and Size to Column E
outputSheet.Cells(rowIndex, 2).Value = FSOFile.Name
outputSheet.Cells(rowIndex, 3).Value = FSOFile.Type
outputSheet.Cells(rowIndex, 4).Value = FSOFile.Size
rowIndex = rowIndex + 1 ' increment the row index
Next- starts a loop that iterates over all the files in the folder referenced by FSOFile.
- stores file names, types, and sizes in columns B, C, and D.
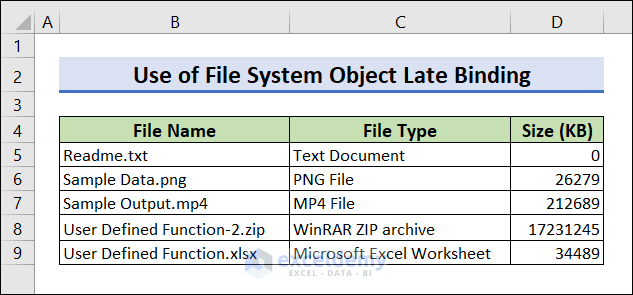
Run the code by pressing F5 to get the list of all files.
Read More: Excel VBA to List Files in Folder with Specific Extension
Example 2. Listing All Files in a Folder and Subfolder in the Worksheet
2.1 Using the File System Object Early Binding
Use the File System Object Early Binding to list files from all subfolders.
- Go to Microsoft Visual Basic window and insert a Module.
- Enter the code below.
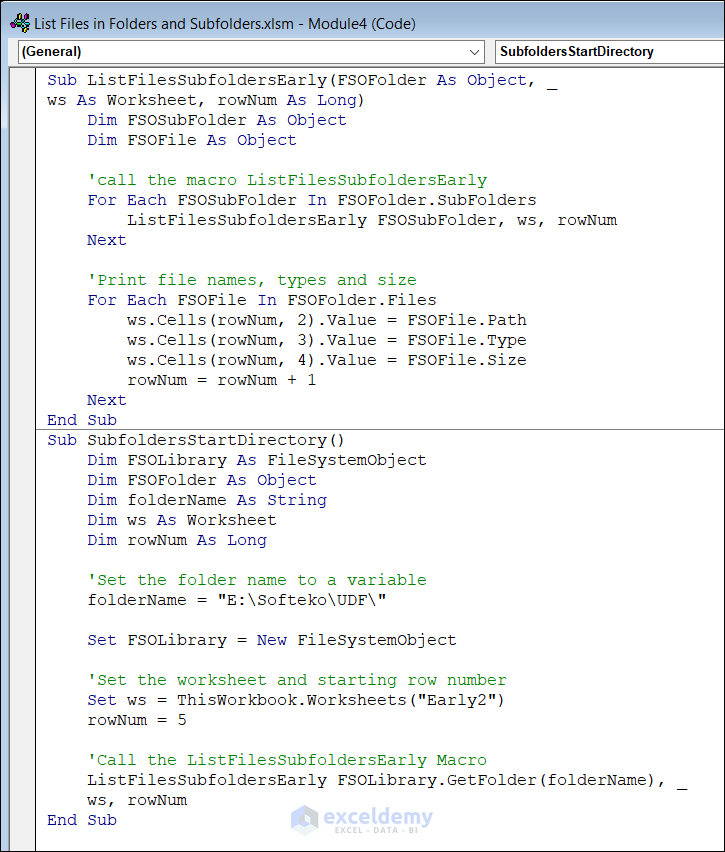
Sub ListFilesSubfoldersEarly(FSOFolder As Object, _
ws As Worksheet, rowNum As Long)
Dim FSOSubFolder As Object
Dim FSOFile As Object
'call the macro ListFilesSubfoldersEarly
For Each FSOSubFolder In FSOFolder.subFolders
ListFilesSubfoldersEarly FSOSubFolder, ws, rowNum
Next
'Print file names, types and size
For Each FSOFile In FSOFolder.files
ws.Cells(rowNum, 2).Value = FSOFile.path
ws.Cells(rowNum, 3).Value = FSOFile.Type
ws.Cells(rowNum, 4).Value = FSOFile.Size
rowNum = rowNum + 1
Next
End Sub
Sub SubfoldersStartDirectory()
Dim FSOLibrary As FileSystemObject
Dim FSOFolder As Object
Dim folderName As String
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim rowNum As Long
'Set the folder name to a variable
folderName = "E:\Softeko\UDF\"
Set FSOLibrary = New FileSystemObject
'Set the worksheet and starting row number
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Early2")
rowNum = 5
'Call the ListFilesSubfoldersEarly Macro
ListFilesSubfoldersEarly FSOLibrary.GetFolder(folderName), _
ws, rowNum
End SubCode Breakdown
For Each FSOSubFolder In FSOFolder.subFolders
ListFilesSubfoldersEarly FSOSubFolder, ws, rowNum
Next- calls the macro named ListFilesSubfoldersEarly.
For Each FSOFile In FSOFolder.files
ws.Cells(rowNum, 2).Value = FSOFile.path
ws.Cells(rowNum, 3).Value = FSOFile.Type
ws.Cells(rowNum, 4).Value = FSOFile.Size
rowNum = rowNum + 1
Next- lists the file names, types, and sizes in columns B, C, and D.
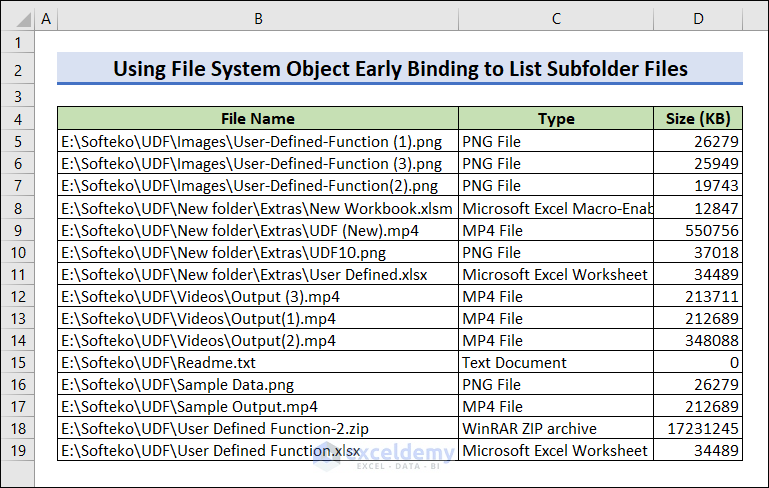
- Run the code to see the output.
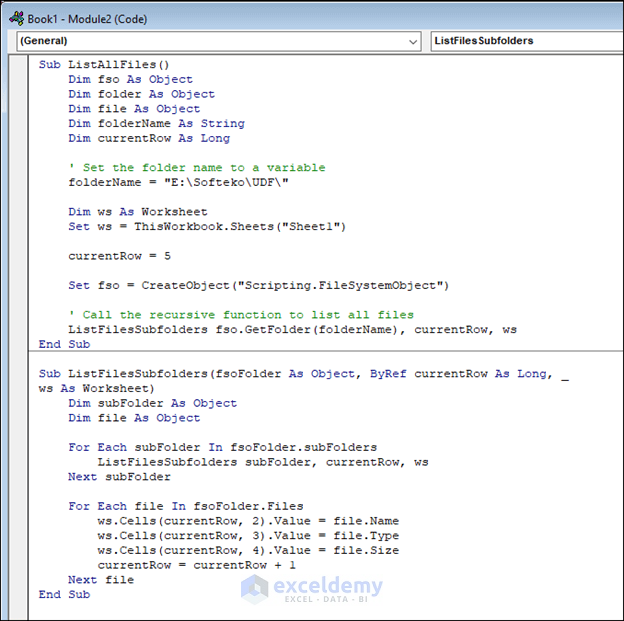
2.2 Using the File System Object Late Binding
List all files in subfolders, using the File System Late Binding. Enter the following code.
Sub ListAllFiles()
Dim fso As Object
Dim folder As Object
Dim file As Object
Dim folderName As String
Dim currentRow As Long
' Set the folder name to a variable
folderName = "E:\Softeko\UDF\"
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1")
currentRow = 5
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
' Call the recursive function to list all files
ListFilesSubfolders fso.GetFolder(folderName), currentRow, ws
End Sub
Sub ListFilesSubfolders(fsoFolder As Object, ByRef currentRow As Long, _
ws As Worksheet)
Dim subFolder As Object
Dim file As Object
For Each subFolder In fsoFolder.subFolders
ListFilesSubfolders subFolder, currentRow, ws
Next subFolder
For Each file In fsoFolder.Files
ws.Cells(currentRow, 2).Value = file.Name
ws.Cells(currentRow, 3).Value = file.Type
ws.Cells(currentRow, 4).Value = file.Size
currentRow = currentRow + 1
Next file
End SubCode Breakdown
Sub ListFilesSubfolders(fsoFolder As Object, ByRef currentRow As Long, _
ws As Worksheet)
Dim subFolder As Object
Dim file As Object
For Each subFolder In fsoFolder.subFolders
ListFilesSubfolders subFolder, currentRow, ws
Next subFolder
For Each file In fsoFolder.Files
ws.Cells(currentRow, 2).Value = file.Name
ws.Cells(currentRow, 3).Value = file.Type
ws.Cells(currentRow, 4).Value = file.Size
currentRow = currentRow + 1
Next file
End Sub- declares two variables named FSOSubFolder and FSOFile as object.
- loops through the subfolders in the FSOFolder parameter.
- ListFilesSubfoldersLate FSOSubFolder, currentRow calls the ListFilesSubfoldersLate subroutine recursively, passing in the FSOSubFolder parameter as the new FSOFolder parameter and the currentRow parameter unchanged. The code stores outputs in the specified cells.
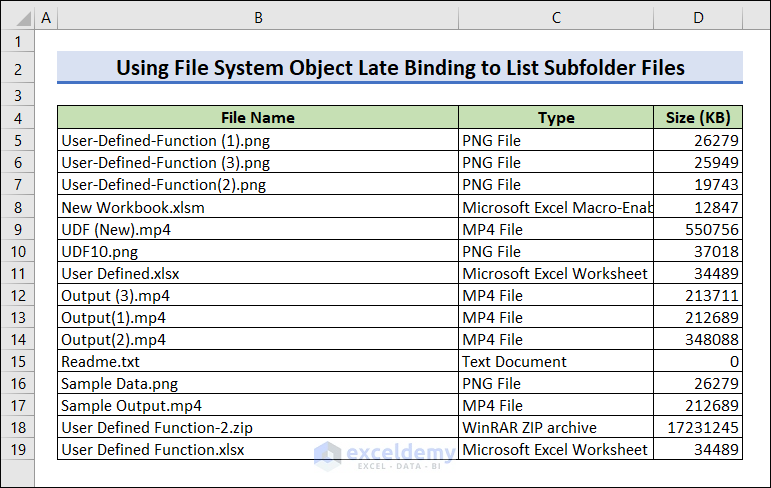
Run the code to see the list of all files in the folder and subfolders.
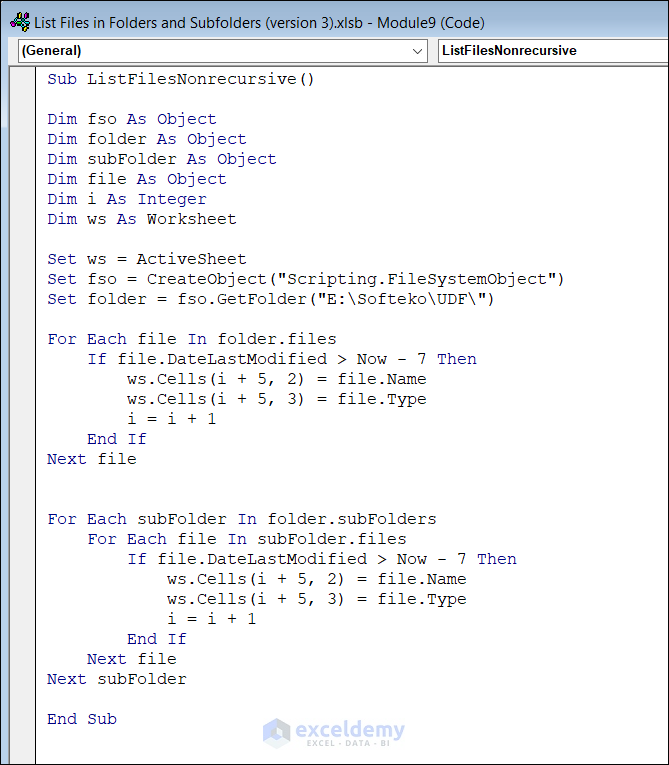
Example 3 – Listing Files in Folders and Subfolders Using a Non-Recursive VBA Method
Enter this code.
Sub ListFilesNonrecursive()
Dim fso As Objec
Dim folder As Object
Dim subFolder As Object
Dim file As Object
Dim i As Integer
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set folder = fso.GetFolder("E:\Softeko\UDF\")
For Each file In folder.files
If file.DateLastModified > Now - 7 Then
ws.Cells(i + 5, 2) = file.Name
ws.Cells(i + 5, 3) = file.Type
i = i + 1
End If
Next file
For Each subFolder In folder.subFolders
For Each file In subFolder.files
If file.DateLastModified > Now - 7 Then
ws.Cells(i + 5, 2) = file.Name
ws.Cells(i + 5, 3) = file.Type
i = i + 1
End If
Next file
Next subFolder
End SubCode Breakdown
For Each file In folder.files
If file.DateLastModified > Now - 7 Then
ws.Cells(i + 5, 2) = file.Name
ws.Cells(i + 5, 3) = file.Type
i = i + 1
End If
Next file- The code checks if the file was modified within the last week. If it was, the code stores file names and types in columns B and C.
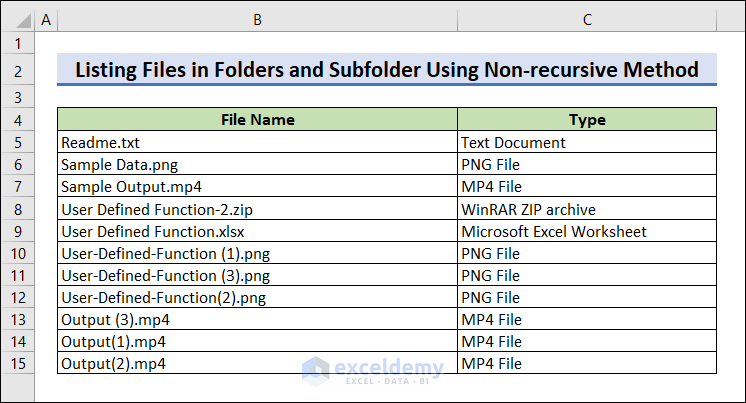
Run the code.
This is the output.
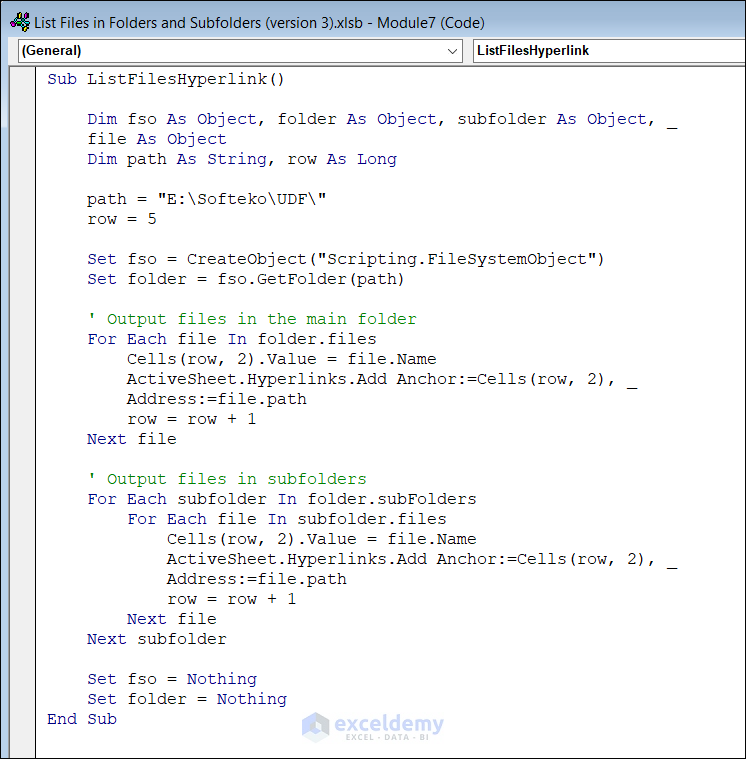
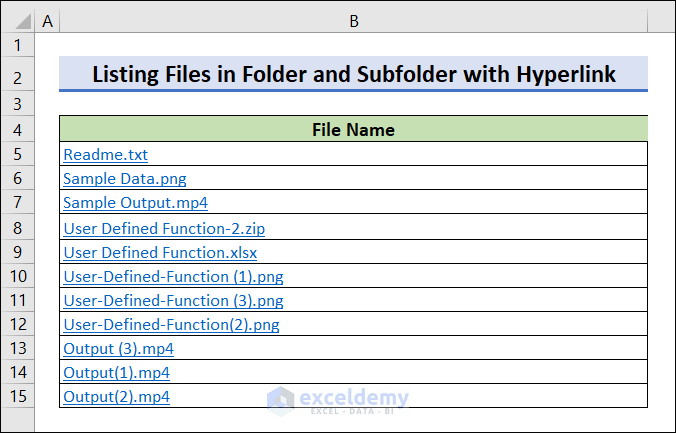
How to List Files in Folders and Subfolders with Hyperlinks with Excel VBA
The path is “E:\Softeko\UDF\”. Use the following code to list files and add hyperlinks.
Sub ListFilesHyperlink()
Dim fso As Object, folder As Object, subFolder As Object, _
file As Object
Dim path As String, row As Long
path = "E:\Softeko\UDF\"
row = 5
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set folder = fso.GetFolder(path)
' Output files in the main folder
For Each file In folder.files
Cells(row, 2).Value = file.Name
ActiveSheet.Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Cells(row, 2), _
Address:=file.path
row = row + 1
Next file
' Output files in subfolders
For Each subFolder In folder.subFolders
For Each file In subFolder.files
Cells(row, 2).Value = file.Name
ActiveSheet.Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Cells(row, 2), _
Address:=file.path
row = row + 1
Next file
Next subFolder
Set fso = Nothing
Set folder = Nothing
End SubCode Breakdown
For Each file In folder.files
Cells(row, 2).Value = file.Name
ActiveSheet.Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Cells(row, 2), _
Address:=file.path
row = row + 1
Next file- Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Cells(row, 2), Address:=file.path adds a hyperlink to the path. .
Run the code to see the list of files with hyperlinks.
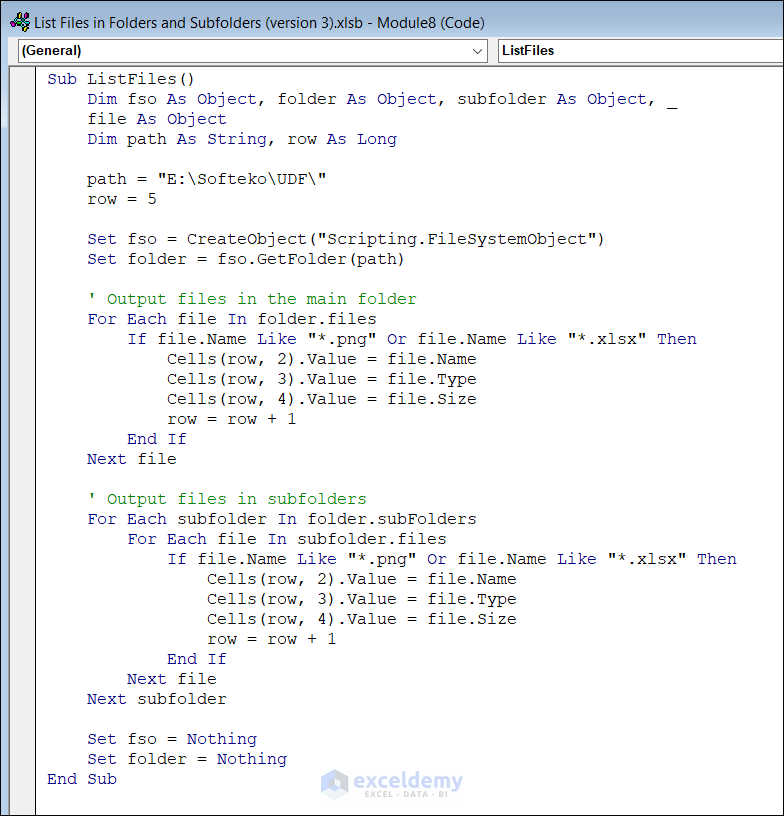
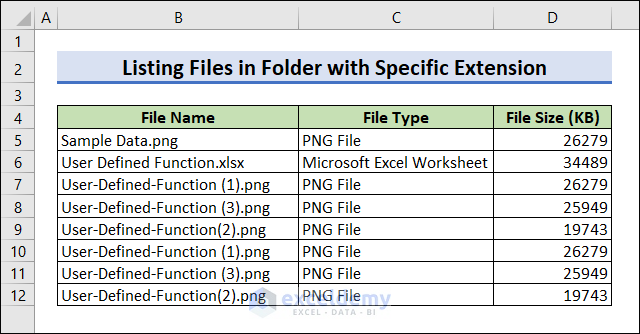
How to List Files in a Folder with Specific Extensions in Excel with VBA
This code lists all files with the .png and .xlsx extensions.
Sub ListFiles()
Dim fso As Object, folder As Object, subFolder As Object, _
file As Object
Dim path As String, row As Long
path = "E:\Softeko\UDF\"
row = 5
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set folder = fso.GetFolder(path)
' Output files in the main folder
For Each file In folder.files
If file.Name Like "*.png" Or file.Name Like "*.xlsx" Then
Cells(row, 2).Value = file.Name
Cells(row, 3).Value = file.Type
Cells(row, 4).Value = file.Size
row = row + 1
End If
Next file
' Output files in subfolders
For Each subFolder In folder.subFolders
For Each file In subFolder.files
If file.Name Like "*.png" Or file.Name Like "*.xlsx" Then
Cells(row, 2).Value = file.Name
Cells(row, 3).Value = file.Type
Cells(row, 4).Value = file.Size
row = row + 1
End If
Next file
Next subFolder
Set fso = Nothing
Set folder = Nothing
End SubCode Breakdown
For Each file In folder.files
If file.Name Like "*.png" Or file.Name Like "*.xlsx" Then
Cells(row, 2).Value = file.Name
Cells(row, 3).Value = file.Type
Cells(row, 4).Value = file.Size
row = row + 1
End If
Next file- checks if the file name matches either the pattern “*.png” or “*.xlsx” using Like
- finds a match, and stores the file names, types, and sizes in the specified columns.
Run the code to see the output. Only .png and .xlsx files will be listed.
How to List Files in Folders and Subfolders in a Text File Using VBA
Enter the code.
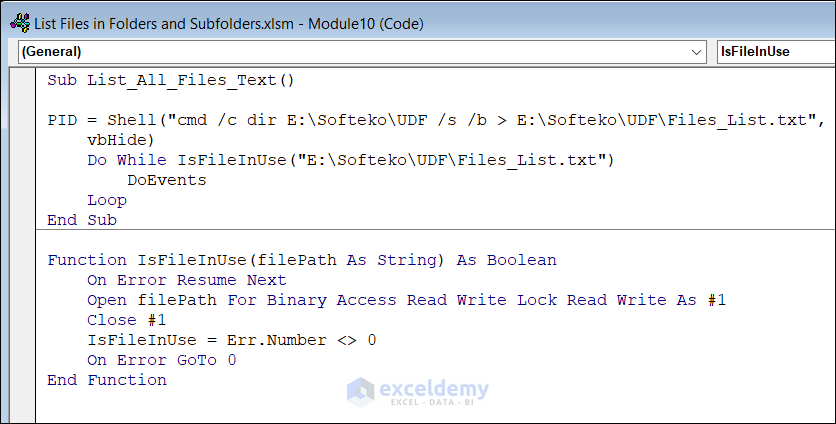
Sub List_All_Files_Text()
PID = Shell("cmd /c dir E:\Softeko\UDF /s /b > E:\Softeko\UDF\Files_List.txt", _
vbHide)
Do While IsFileInUse("E:\Softeko\UDF\Files_List.txt")
DoEvents
Loop
End Sub
Function IsFileInUse(filePath As String) As Boolean
On Error Resume Next
Open filePath For Binary Access Read Write Lock Read Write As #1
Close #1
IsFileInUse = Err.Number <> 0
On Error GoTo 0
End FunctionCode Breakdown
PID = Shell("cmd /c dir E:\Softeko\UDF /s /b > E:\Softeko\UDF\Files_List.txt", _
vbHide)
Do While IsFileInUse("E:\Softeko\UDF\Files_List.txt")
DoEvents
Loop- PID = Shell(“cmd /c dir E:\Softeko\UDF /s /b > E:\Softeko\UDF\Files_List.txt”, vbHide) executes the command dir E:\Softeko\UDF /s /b > E:\Softeko\UDF\Files_List.txt in the command prompt. The /s specifies that the command should be executed recursively on all subdirectories, while the /b specifies that only the file names should be displayed, without any additional information. The output of the command is redirected to a text file named txt in the E:\Softeko\UDF directory. The vbHide parameter specifies that the command prompt window should be hidden.
- Do While IsFileInUse(“E:\Softeko\UDF\Files_List.txt”) DoEvents Loop loops continuously until the txt file is no longer in use.
Run the code.
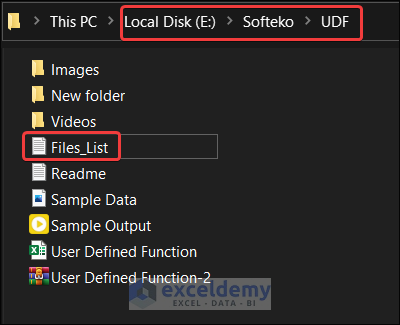
Go to the location of your text file.
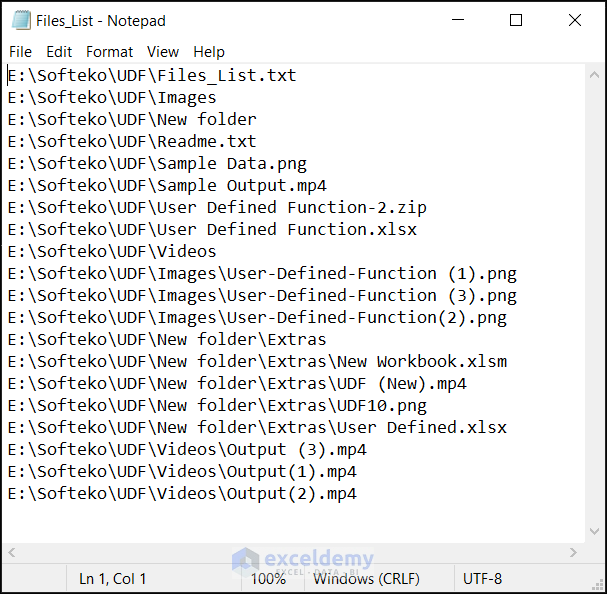
Open the text file and you will see the list of all files in the folder and subfolders.
Download Practice Workbook
Download the practice book.
Related Articles
- Excel VBA to Loop Through Files in Folder and Rename
- How to Use Excel VBA to Move Files
- Excel VBA: Delete Files with Wildcards