Method 1 – Embed VBA to Hide a Single Row in Excel
Steps:
- Press Alt + F11 on your keyboard or go to the tab Developer -> Visual Basic to open Visual Basic Editor.
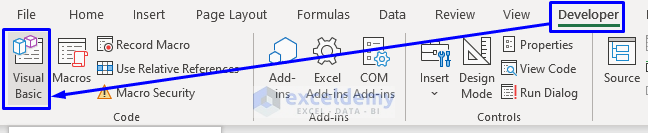
- In the pop-up code window, from the menu bar, click Insert -> Module.
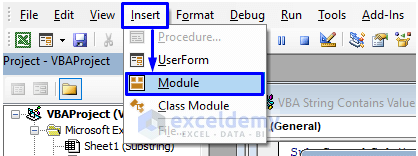
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
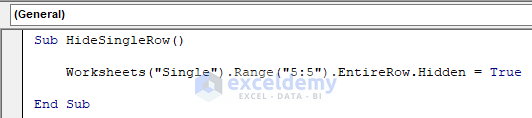
Sub HideSingleRow()
Worksheets("Single").Range("5:5").EntireRow.Hidden = True
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
Here,
- Worksheets(“Single”) = Set the worksheet name.
- Range(“5:5”) = Pass row number 5 inside the Range method.
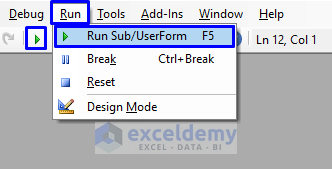
- Press F5 on your keyboard or from the menu bar select Run -> Run Sub/UserForm. Click on the small Run icon in the sub-menu bar to run the macro.
After the successful code execution, look at the image below for the result.
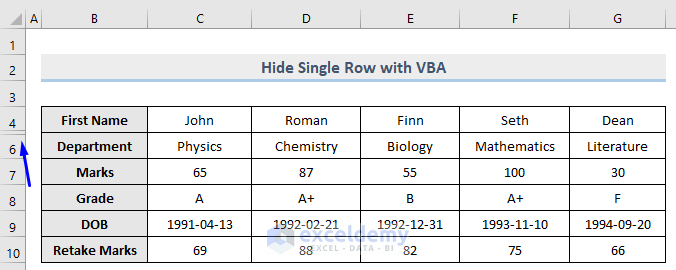
Row number 5 is hidden after successfully executing the VBA code.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideSingleRow()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
Worksheets("Single").Range("5:5").EntireRow.Hidden = TrueHide the entire 5th row from the worksheet named “Single“.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 2 – Insert VBA to Hide Contiguous Rows in Excel
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
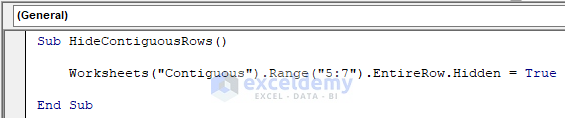
Sub HideContiguousRows()
Worksheets("Contiguous").Range("5:7").EntireRow.Hidden = True
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
Here,
- Worksheets(“Contiguous”) = Set the worksheet name.
- Range(“5:7”) = Pass row number 5 to 7 inside the Rangemethod.
- Run the macro as we showed you in the above section. The result is shown in the image below.
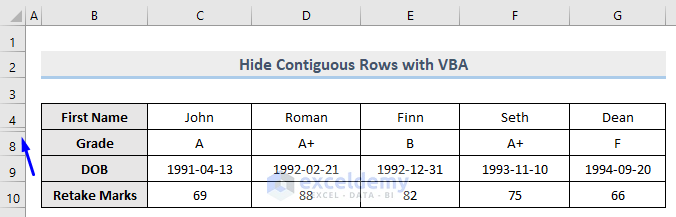
The above image shows that rows 5 to 7 are hidden now after successful code execution.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideContiguousRows()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
Worksheets("Contiguous").Range("5:7").EntireRow.Hidden = TrueHide entire rows from the 5th row to the 7th row from the worksheet named “Contiguous“.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 3 – Embed VBA to Hide Non-Contiguous Rows in Excel
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
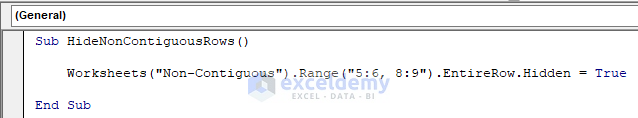
Sub HideNonContiguousRows()
Worksheets("Non-Contiguous").Range("5:6, 8:9").EntireRow.Hidden = True
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
Here,
- Worksheets(“Non-Contiguous”) = Set the worksheet name.
- Range(“5:6, 8:9”) = Pass row number 5 to 6 and 8 to 9 inside the Range method.
- Run this piece of code, and the result is shown in the following image.
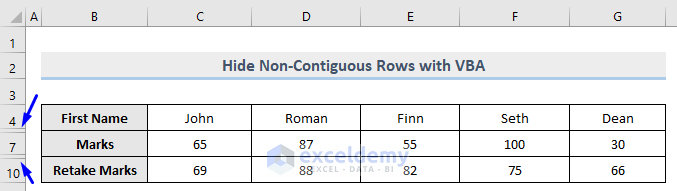
Rows 5 to 6 and 8 to 9 are now hidden after successful code execution.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideNonContiguousRows()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
Worksheets("Non-Contiguous").Range("5:6, 8:9").EntireRow.Hidden = TrueHide the entire 5th, 6th, 8th and 9th rows from the worksheet named “Non-Contiguous“.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 4 – Insert VBA to Hide All Rows Containing Texts in Excel
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
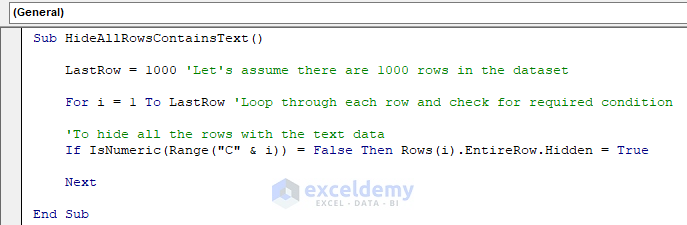
Sub HideAllRowsContainsText()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 1 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'To hide all the rows with the text data
If IsNumeric(Range("C" & i)) = False Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
Next
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
Here,
- IsNumeric(Range(“C” & i)) = The data in our dataset starts from column C, so we passed C inside the Range method.
- Run this code.
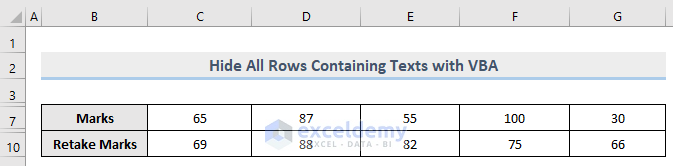
LYou will notice all the rows that contained text values are now hidden from the dataset.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideAllRowsContainsText()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
LastRow = 1000Let’s assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset.
For i = 1 To LastRowStart looping through each row from the first row to the last row and check for the required condition.
If IsNumeric(Range("C" & i)) = False Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = TrueIf there are non-numeric values in Column C then hide all the rows from that column that hold the numeric values. Our data starts from Column C, that’s why we pass Column C as the parameter. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
NextTo continue the FOR Loop till it reaches all the rows.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 5 – Embed Macro to Cloak All Rows Containing Numbers in Excel
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
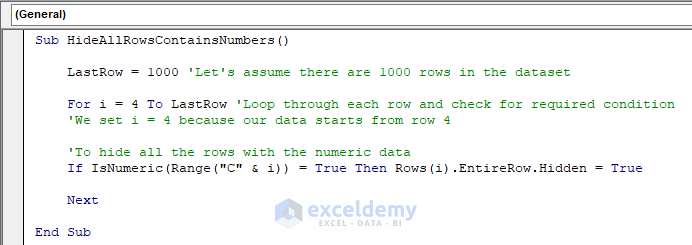
Sub HideAllRowsContainsNumbers()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide all the rows with the numeric data
If IsNumeric(Range("C" & i)) = True Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
Next
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
Here,
- IsNumeric(Range(“C” & i)) = The data in our dataset starts from column C, so we passed C inside the Range method.
- Run this code and notice the image below.
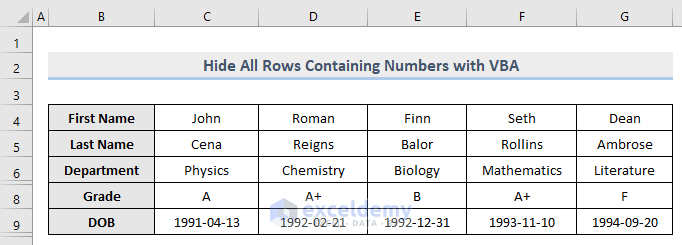
All the rows that contained numeric values before are now hidden.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideAllRowsContainsNumbers()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
LastRow = 1000Let’s assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset.
For i = 4 To LastRowStart looping through each row from the first row to the last row and check for the required condition. We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
If IsNumeric(Range("C" & i)) = True Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = TrueIf there are numeric values in Column C then hide all the rows from that column that hold the numeric values. Our data starts from Column C, pass Column C as the parameter. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
NextTo continue the FOR Loop till it reaches all the rows.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 6 – Implement Macro to Hide Rows Containing Zero (0) in Excel
Suppose you want to hide only the rows from a specific column that are holding 0 (zero). Look at the following dataset where the E column holds 0 in row 7 and 82 in row 10. We will learn how to hide only the row that is holding 0 (row 7) with VBA in Excel.
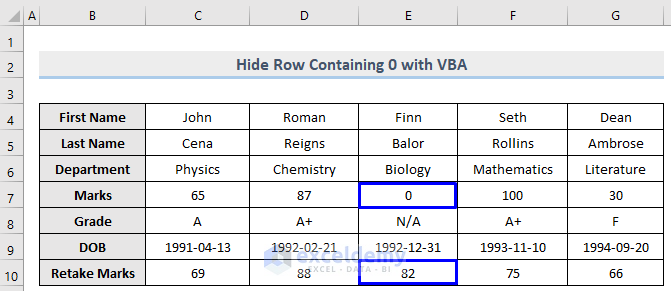
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
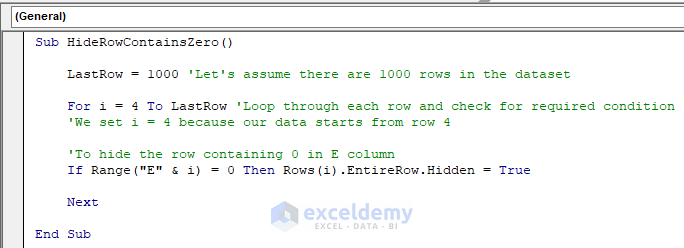
Sub HideRowContainsZero()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the row containing 0 in E column
If Range("E" & i) = 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
Next
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
- Run this code, and let’s see what happened as the result.
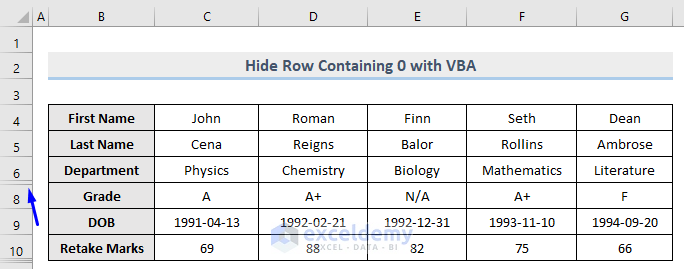
The row (row 7) that contains 0 in column E is now hidden whereas row 10 which carries 82 is unhidden.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideRowContainsZero()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
LastRow = 1000Assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset.
For i = 4 To LastRowStart looping through each row from the first row to the last row and check for the required condition. We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
If Range("E" & i) = 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = TrueIf Column E holds 0, then hide all the rows from that column that hold the value. You can modify this line by passing the column address according to your dataset.
NextTo continue the FOR Loop till it reaches all the rows.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 7 – Implement VBA Macro to Hide Rows Holding Negative Values
Just as you can hide rows that contain zero from the same column, you can hide rows that hold negative values. With the dataset shown below, where column E contains both negative and positive values, we will see the VBA code that hides only the negative ones.
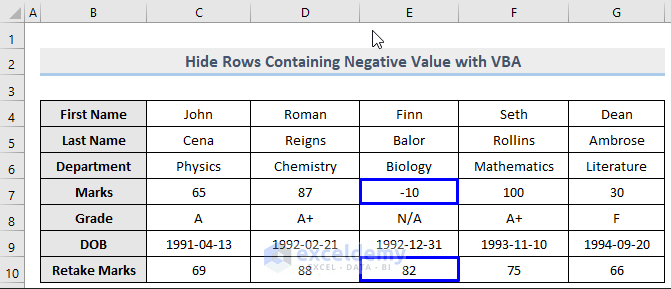
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
Sub HideRowContainsNegative()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the rows containing negative values in E column
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) < 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
- Run this piece of code.
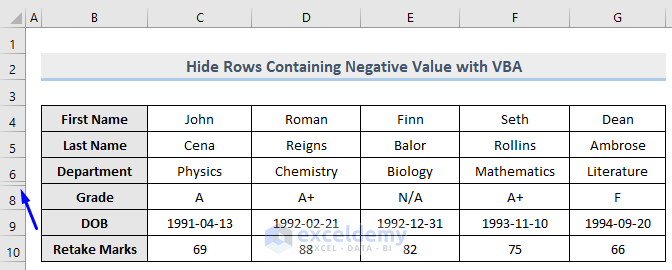
From the image above, row 7 which contains the negative value (-10) in column E is now hidden whereas row 10 which carries 82 is unhidden.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideRowContainsNegative()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
LastRow = 1000Assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset.
For i = 4 To LastRowStart looping through each row from the first row to the last row and check for the required condition. We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) < 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
If Column E holds numeric values that are less than 0, that means they are negative values, then hide the entire rows that carry negative values from that column.
NextContinue the FOR Loop till it reaches all the rows.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 8 – Embed VBA to Conceal Rows Containing Positive Values
This time with the dataset given below where column E contains both zero and positive values, we will see the VBA code that hides only the positive ones.
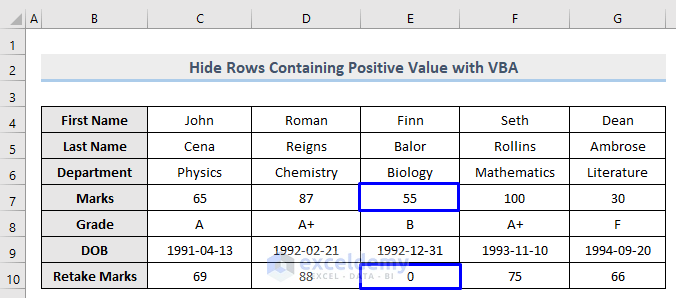
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
Sub HideRowContainsPositive()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the rows containing positive values in E column
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) > 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
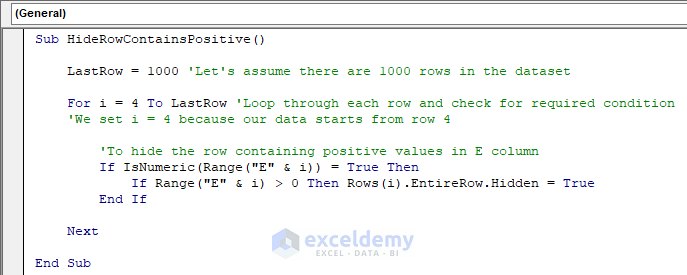
- Run this code, and the result is shown in the following image.
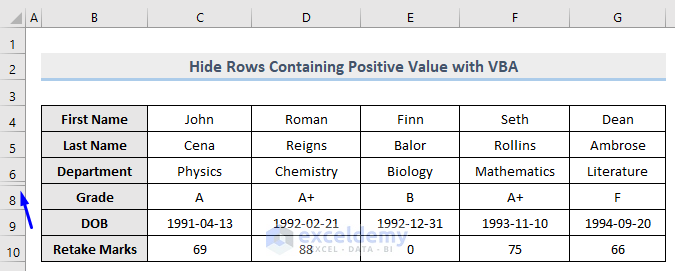
Row 7 which contains the positive value (55) in column E is now hidden whereas row 10 which carries 0 is unhidden.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideRowContainsPositive()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
LastRow = 1000Assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset.
For i = 4 To LastRowStart looping through each row from the first row to the last row and check for the required condition. We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) > 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
If Column E holds numeric values that are greater than 0, that means they are positive values, then hide the entire rows that carry positive values from that column.
NextContinue the FOR Loop till it reaches all the rows.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 9 – Macro to Hide Rows That Contain Odd Numbers in Excel
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
Sub HideRowContainsOdd()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the rows containing odd values in E column
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) Mod 2 = 1 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
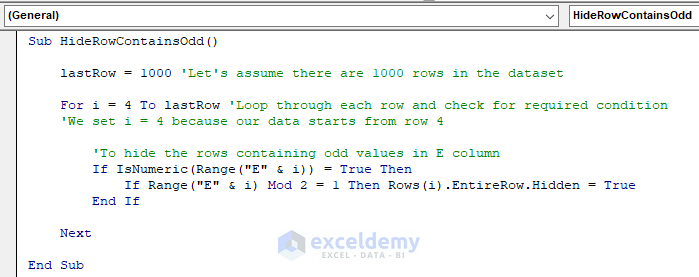
- Run this piece of code.
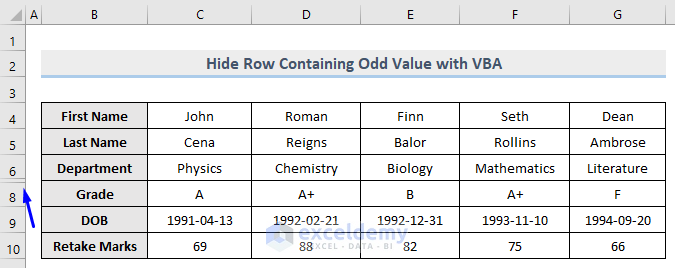
Only row 7 which contains the odd number (55) in column E is now hidden whereas row 10 which carries the even number (82) is unhidden.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideRowContainsOdd()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
LastRow = 1000Assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset.
For i = 4 To LastRowStart looping through each row from the first row to the last row and check for the required condition. We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) Mod 2 = 1 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
If Column E holds numeric values that produce 1 as the remainder when divided by 2, that means which are odd values, then hide the rows that carry odd numbers from that column.
NextContinue the FOR Loop till it reaches all the rows.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 10 – VBA to Hide Rows Containing Even Numbers in Excel
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
Sub HideRowContainsEven()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the rows containing even values in F column
If IsNumeric(Range("F" & i)) = True Then
If Range("F" & i) Mod 2 = 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
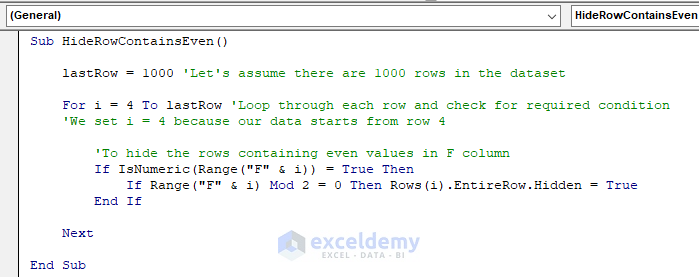
- Run this code and see the result in the following image.
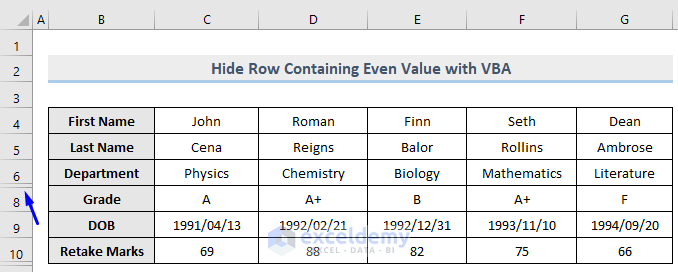
Only row 10 which contains the even number (75) in column F is now hidden whereas row 7 which carries the even number (100) is unhidden.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideRowContainsEven()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
LastRow = 1000Assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset.
For i = 4 To LastRowStart looping through each row from the first row to the last row and check for the required condition. We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
If IsNumeric(Range("F" & i)) = True Then
If Range("F" & i) Mod 2 = 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
If Column F holds numeric values which produce 0 as the remainder when divided by 2, that means which are even values, then hide the entire rows that carry even numbers from that column.
NextContinue the FOR Loop till it reaches all the rows.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 11 – Insert VBA to Hide Rows That Are Greater Than a Specific Condition in Excel
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
Sub HideRowContainsGreater()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the rows containing values greater than 80 in E column
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) > 80 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
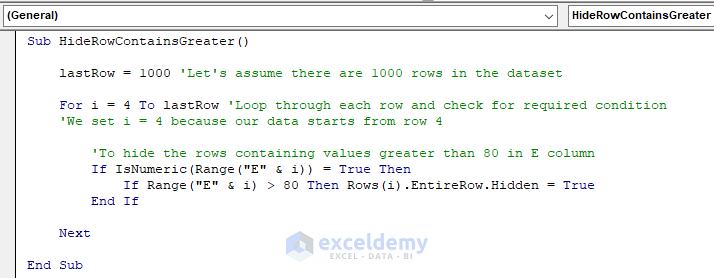
- Run this code.
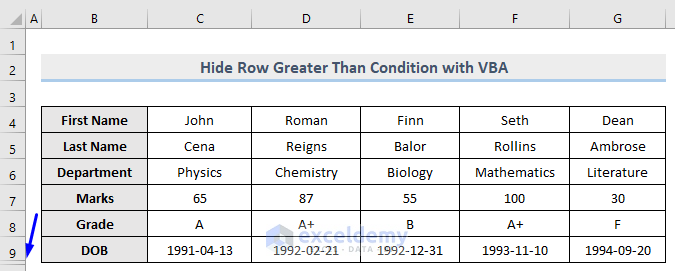
Only row 10 which contains 82 (greater than 80) in column E is now hidden whereas row 7 which carries 55 is unhidden.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideRowContainsGreater()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
LastRow = 1000Assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset.
For i = 4 To LastRowStart looping through each row from the first row to the last row and check for the required condition. We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) > 80 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
If Column E holds numeric values greater than 80, then hide the entire rows that carry those numbers from that column.
NextContinue the FOR Loop till it reaches all the rows.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Criteria 12: Embed VBA to Hide Rows That Are Less Than a Specific Condition in Excel
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
Sub HideRowContainsLess()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the rows containing values less than 80 in E column
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) < 80 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
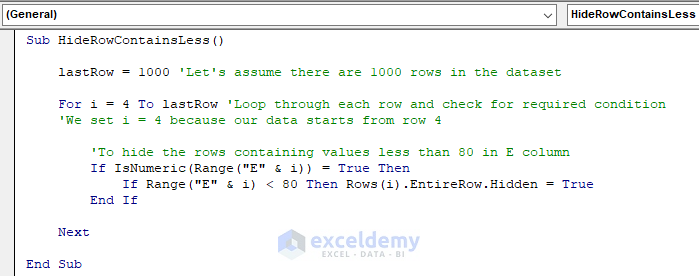
- Run this piece of code. The result is shown in the image below.
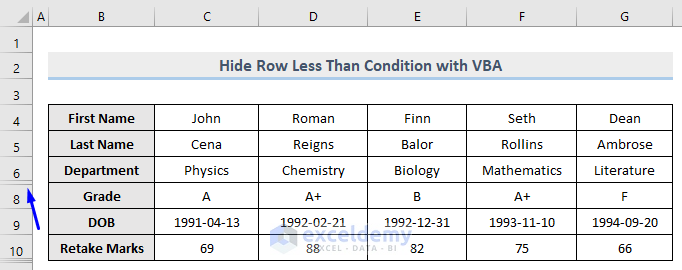
Only row 7 which contains 55 (which is less than 80) in column E is now hidden whereas row 10 which carries 82 is unhidden.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideRowContainsLess()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
LastRow = 1000Assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset.
For i = 4 To LastRowStart looping through each row from the first row to the last row and check for the required condition. We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) < 80 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End IfIf Column E holds numeric values less than 80, then hide the entire rows that carry those numbers from that column.
NextContinue the FOR Loop till it reaches all the rows.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Criteria 13: Macro to Hide Rows Based on Cell Text Value in Excel
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
Sub HideRowCellTextValue()
StartRow = 4
LastRow = 10
iCol = 4
For i = StartRow To LastRow
If Cells(i, iCol).Value <> "Chemistry" Then
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = False
Else
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next i
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
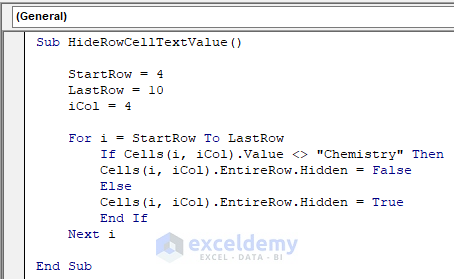
Here,
- StartRow = 4 -> First row of the dataset.
- LastRow = 10 -> Last row of the dataset.
- iCol = 4 -> The column address that holds the text value.
- Run this code, and the result is shown in the image below.
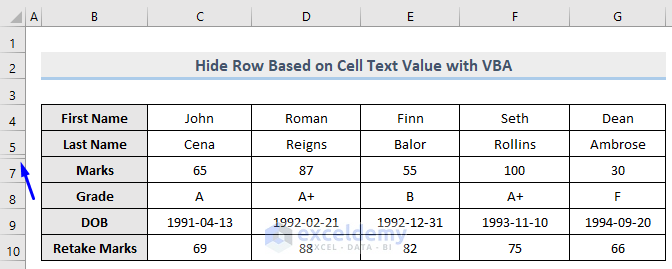
Row number 6 which consists of the word “Chemistry” is now hidden from our dataset.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideRowCellTextValue()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
StartRow = 4Declare the first row of the dataset. We set StartRow = 4 because our data starts from row 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
LastRow = 10Declare the last row of the dataset. We set LastRow = 10 because our data ends in row 10. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
iCol = 4Declare the column address that holds the text value. We will hide rows based on the value residing in Column D, so we set iCol = 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
For i = StartRow To LastRow
If Cells(i, iCol).Value <> "Chemistry" Then
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = False
Else
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next iStart looping from the declared first row (4) to the declared last row (10). If the iteration variable i finds the word “Chemistry” in any row of the declared column (D), then hides the entire rows. It continues iterating until it reaches all the rows from that column.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 14 – VBA Macro to Hide Rows Based on Cell Numeric Value in Excel
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
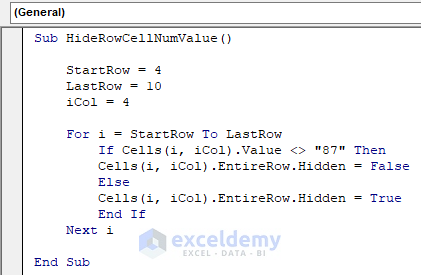
Sub HideRowCellNumValue()
StartRow = 4
LastRow = 10
iCol = 4
For i = StartRow To LastRow
If Cells(i, iCol).Value <> "87" Then
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = False
Else
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next i
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
Here,
- StartRow = 4 -> First row of the dataset.
- LastRow = 10 -> Last row of the dataset.
- iCol = 4 -> The column address that holds the text value.
- Run this piece of code.
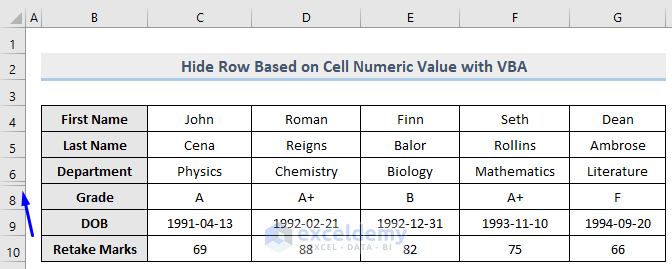
Row number 7 which consists of the numeric value “87” is now hidden.
VBA Code Explanation
Sub HideRowCellNumValue()Provide a name for the sub-procedure of the macro.
StartRow = 4Declare the first row of the dataset. We set StartRow = 4 because our data starts from row 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
LastRow = 10Declare the last row of the dataset. We set LastRow = 10 because our data ends in row 10. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
iCol = 4Declare the column address that holds the textvalue. We will hide rows based on the value residing in Column D, so we set iCol = 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
For i = StartRow To LastRow
If Cells(i, iCol).Value <> "87" Then
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = False
Else
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next iStart looping from the declared first row (4) to the declared last row (10). If the iteration variable i finds the number “87” in any row of the declared column (D), then it hides the entire rows. It continues iterating until it reaches all the rows from that column.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Method 15 – Implement Macro to Hide Rows Based on Inserted Condition in Worksheet
Steps:
- Right-click on the worksheet of interest. A list of options will appear.
- From the appeared option list, select View Code.
- You will be redirected to the code window of the specific worksheet. Copy the following code and paste it into the code window.
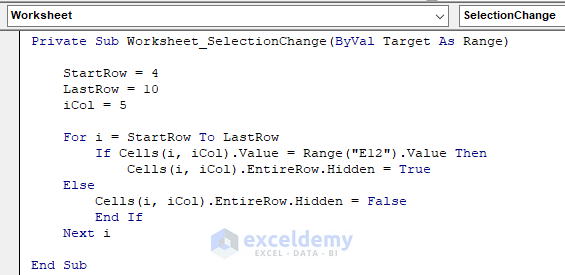
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
StartRow = 4
LastRow = 10
iCol = 5
For i = StartRow To lastRow
If Cells(i, iCol).Value = Range("E12").Value Then
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = True
Else
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = False
End If
Next i
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
Here,
- StartRow = 4 -> First row of the dataset.
- LastRow = 10 -> Last row of the dataset.
- iCol = 5 -> The column address that holds the value, based on which we will hide the row.
- Don’t run this code; save it.
- Go back to the worksheet of interest. Insert any value from Column E in Cell E12. You will see that the whole row that contains the value will be hidden from that worksheet.
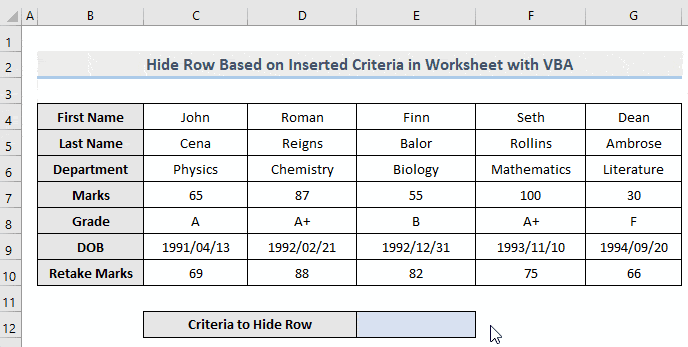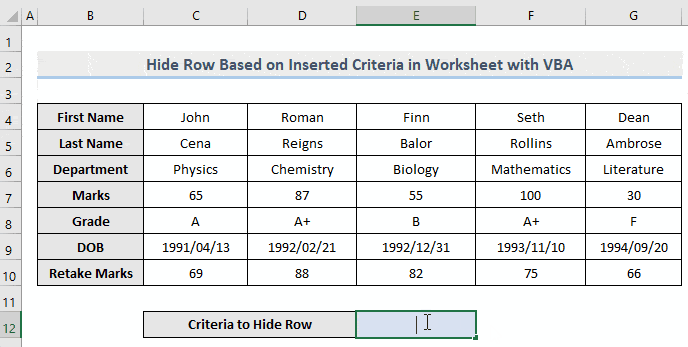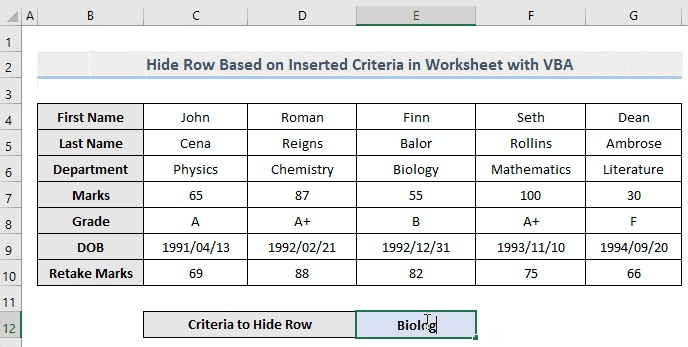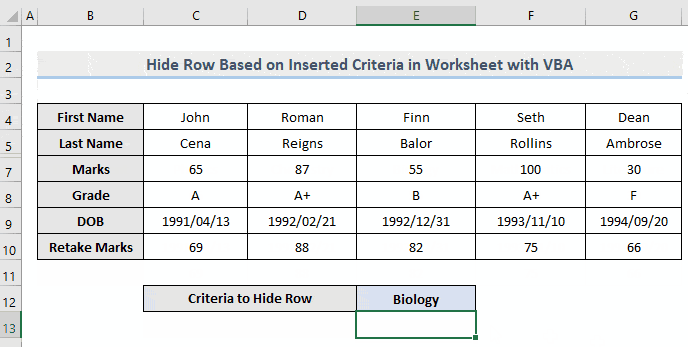
From the gif above, we inserted “Biology” in Cell E12 and as a result, the whole row 6 is now hidden.
VBA Code Explanation
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)Initiating an event under the specific worksheet where Target is passed as an argument with Range type. When the Range changes, the event occurs.
StartRow = 4Declare the first row of the dataset. We set StartRow = 4 because our data starts from row 4. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
LastRow = 10Declare the last row of the dataset. We set LastRow = 10 because our data ends in row 10. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
iCol = 5Declare the column address that holds the text value. We will hide rows based on the value residing in Column E, so we set iCol = 5. You must modify this line according to your dataset.
For i = StartRow To lastRow
If Cells(i, iCol).Value = Range("E12").Value Then
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = True
Else
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = False
End If
Next iStart looping from the declared first row (4) to the last row (10). If the iteration variable i finds any value in Cell E12 and if the value matches with any value in the declared column (E), then hides the entire rows. It continues iterating until it reaches all the rows from that column.
End SubEnd the sub-procedure of the macro.
Download Practice Workbook


