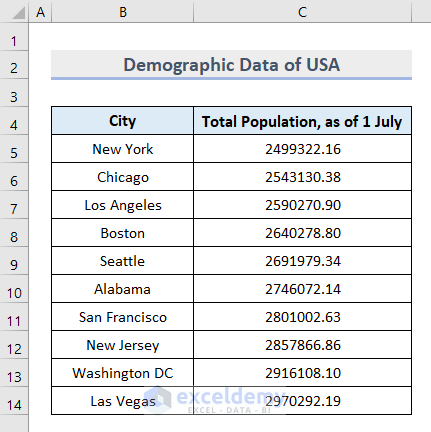
Step 1 – Creating an Excel Table from a Dataset
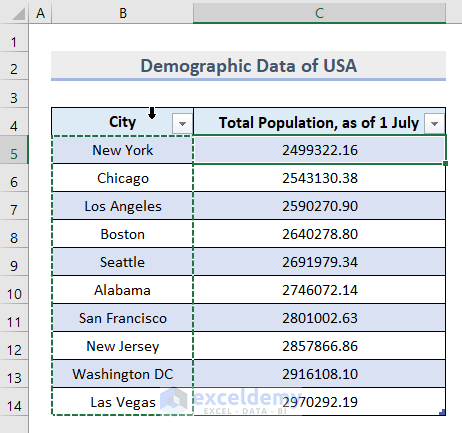
- Create a dataset with the information of 10 City Names and their Total Population on a given day in the cell range B5:C14.
- Click on any cell of the dataset and choose Table from the Insert tab.
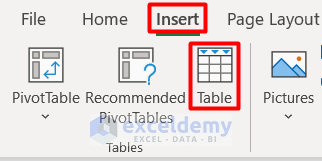
- You will see the Create Table window which automatically selects the cell range to create a table.
- Check the My table has headers box and press OK.
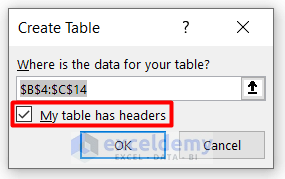
- You will see the dataset is converted to a table.
- You can find the table in the Table Name box under the Table Design tab
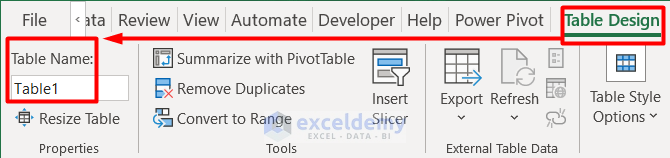
- You can change the table name.
Step 2 – Naming the Dataset List from the Name Manager
- Select any cell from Column B in the table.
- Go to the Formulas tab and select Define Name.

- You will see the New Name dialogue box.
- Provide any name in the Name box. We put CityNames.
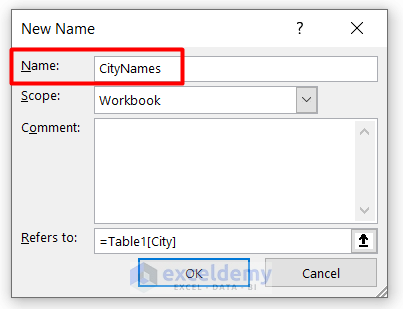
- Click on the Refers to box in the same window.
- Put the cursor over the header and it will show a black arrow.
- Left-click to select the cell range B5:B14.
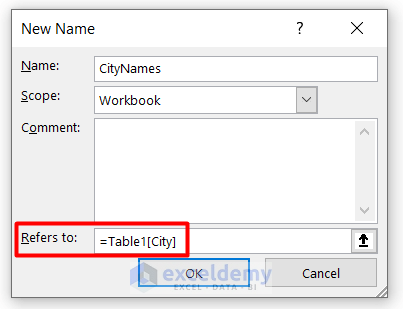
- You will see the list of names along with the table name in the Refers to box. Press OK.
- Follow the same procedure for the cell range C5:C14. Give it a different name.
- You will see the names in the Name Box in the upper left corner of the workbook.
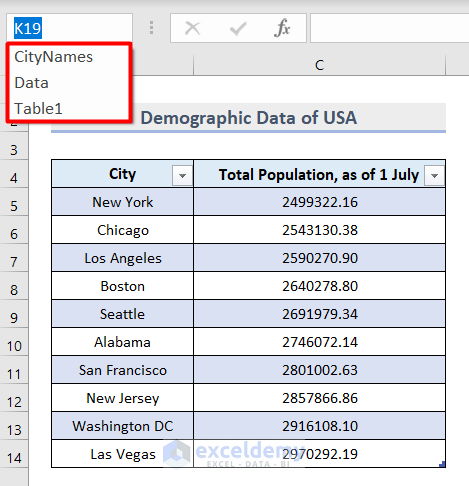
Step 3 – Creating a Drop Down List with Data Validation
- Select the cells where you want to apply Data Validation.
- Go to the Data tab and choose Data Validation in the Data Tools section.
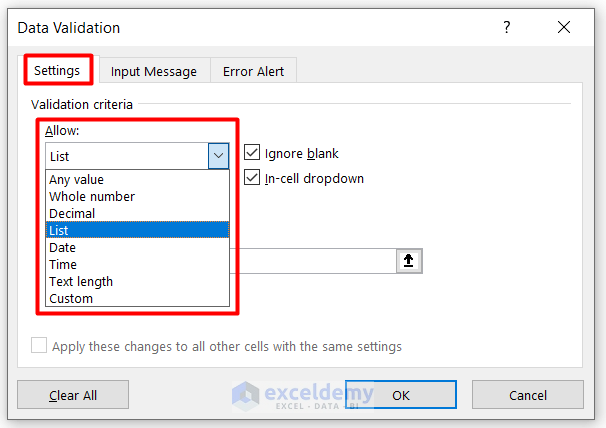
- In the Settings tab, choose List in the Allow box.
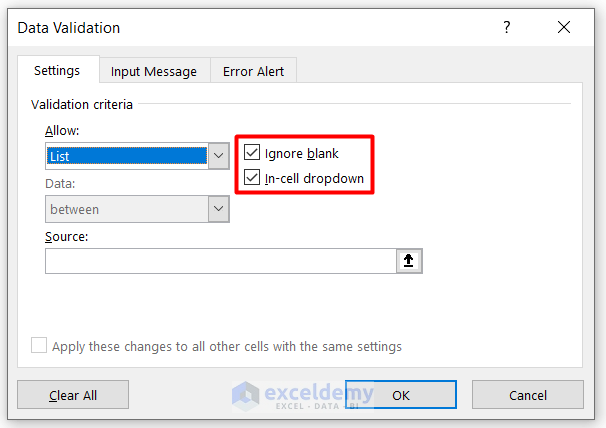
- Check the Ignore blank and In-cell dropdown boxes.
- Click on the Source box in this window and press F3 on your keyboard.
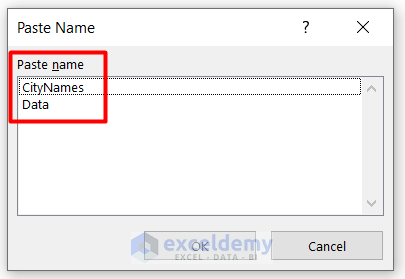
- You will see the Paste Name dialogue box with the name list.
- Choose CityNames from the list and press OK.
- You will see the first list’s name showing in the source box.
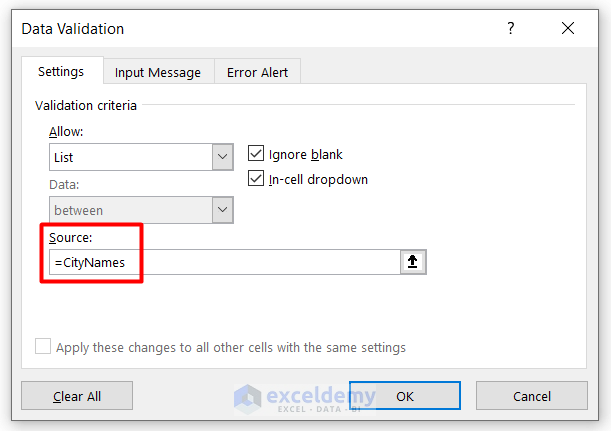
- Press OK and apply the same process for the second name list.
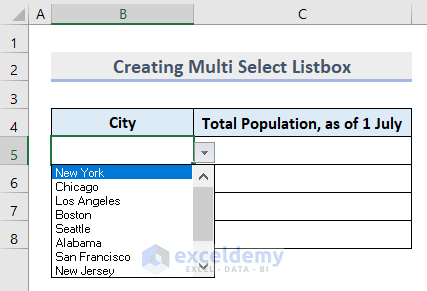
- You will see that Data Validation is activated on the selected cells.
Step 4 – Inserting VBA Code to the Worksheet
- Right-click on the worksheet and select View Code from the Context Menu.
- Insert this code on the page.
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
Dim rngDV As Range
Dim oldVal As String
Dim newVal As String
Dim strList As String
On Error Resume Next
Application.EnableEvents = False
Set rngDV = Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeAllValidation)
On Error GoTo exitHandler
If rngDV Is Nothing Then GoTo exitHandler
If Not Intersect(Target, rngDV) Is Nothing Then
If Target.Validation.Type = 3 Then
strList = Target.Validation.Formula1
strList = Right(strList, Len(strList) - 1)
strDVList = strList
frmDVList.Show
End If
End If
exitHandler:
Application.EnableEvents = True
End Sub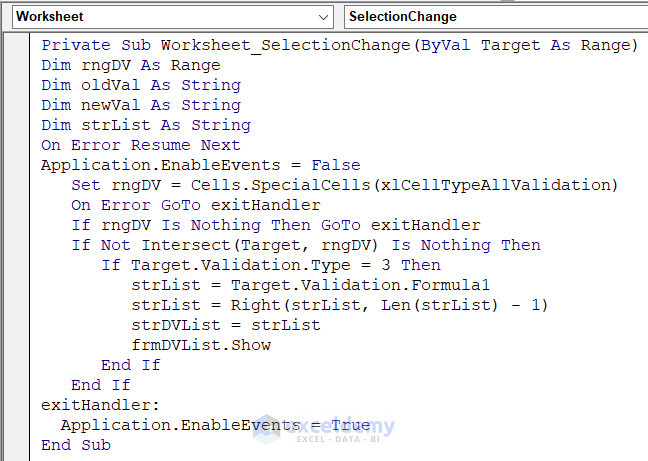
- Go to the Insert tab and select Module.
- The workbook name must be selected in the Project Object window.
- Rename the module as modSettings and insert this code.
Option Explicit
Global strDVList As String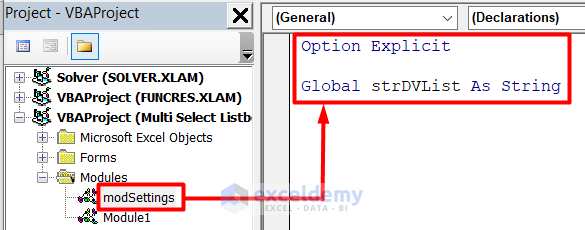
Step 5 – Creating a UserForm with a Listbox and Buttons
- Select the workbook in the Project-VBAProject window in the Visual Basic editor.
- Go to the Insert tab and select UserForm.
- You will get the UserForm interface like this.
- You will also get the Toolbox window.
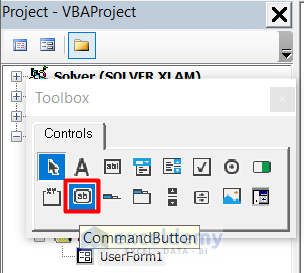
- Drag a ListBox to the UserForm.
- The ListBox will look like this. Adjust the size by dragging the edges of the box.
- Drag a CommandButton twice to UserForm as well to create two buttons.
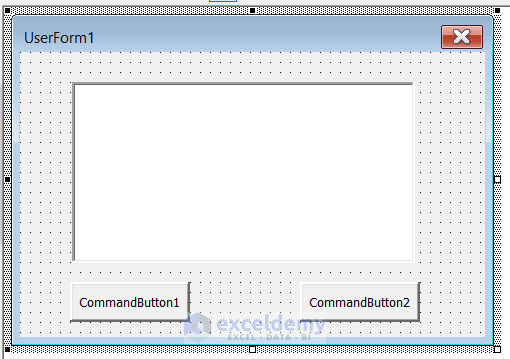
- The final output looks like this.
Step 6 – Changing Properties
- Press F4 on the Visual Basic editor to open the Properties Window.
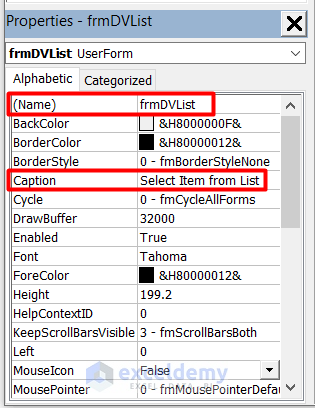
- Select the UserForm and change its Name and Caption.
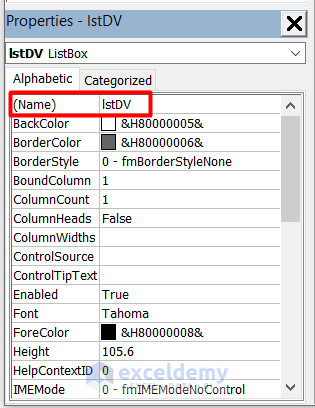
- Select the ListBox and change the Name.
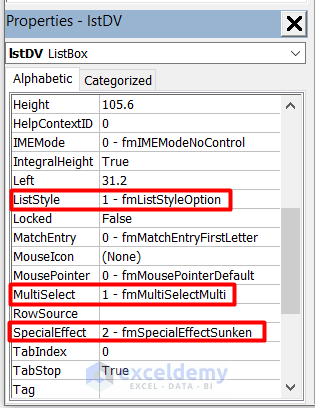
- Change the type of ListStyle, MultiSelect, and SpecialEffect as per the image below.
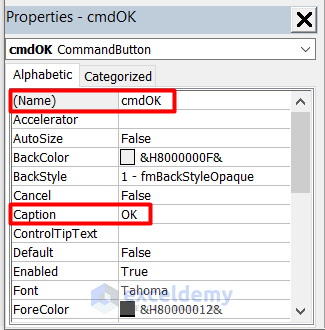
- Choose the first command button and make the following changes in the properties.
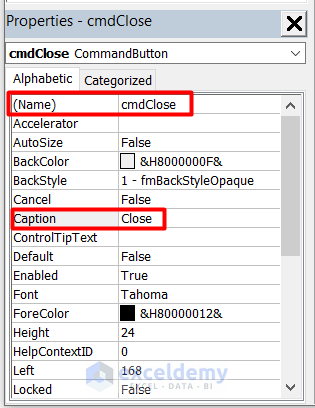
- Edit the properties of the second command button as well.
Step 7 – Applying VBA Code to the UserForm
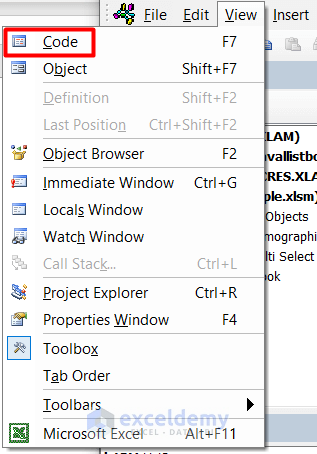
- Select the UserForm and go to the View tab, then select Code.
- Insert this code on the blank page. It will automatically run when the UserForm is opened.
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
Me.lstDV.RowSource = strDVList
End Sub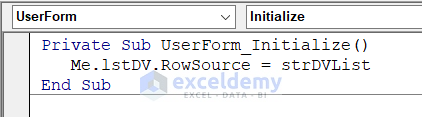
- Go back to the UserForm interface by clicking on Object on the View tab.
- Insert this code for the OK button in a similar way.
Private Sub cmdOK_Click()
Dim strSelItems As String
Dim lCountList As Long
Dim strSep As String
Dim strAdd As String
Dim bDup As Boolean
On Error Resume Next
strSep = ", "
With Me.lstDV
For lCountList = 0 To .ListCount - 1
If .Selected(lCountList) Then
strAdd = .List(lCountList)
Else
strAdd = ""
End If
If strSelItems = "" Then
strSelItems = strAdd
Else
If strAdd <> "" Then
strSelItems = strSelItems _
& strSep & strAdd
End If
End If
Next lCountList
End With
With ActiveCell
If .Value <> "" Then
.Value = ActiveCell.Value _
& strSep & strSelItems
Else
.Value = strSelItems
End If
End With
Unload Me
End Sub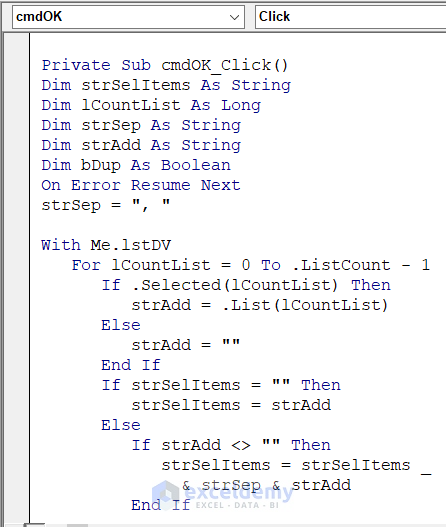
- Insert this code for the Close button using the same process.
Private Sub cmdClose_Click()
Unload Me
End Sub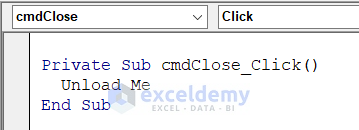
- Press Ctrl + S to save it and close the window.
Step 8 – Multi Select from ListBox
- Select cell B5 where we applied Data Validation.
- A ListBox will pop up asking you to Select Item from List.
- Choose more than one name from the list.
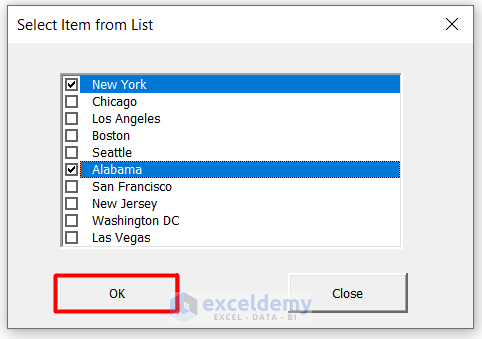
- Press OK.
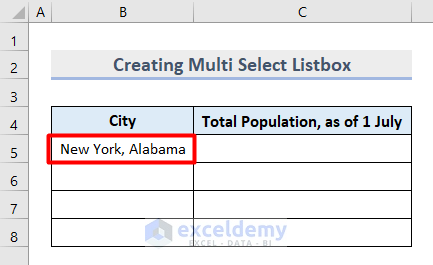
- You have successfully multi-selected from a ListBox and each name is separated by a comma (,).
Read More: Create ListBox for Multiple Columns in Excel VBA
Things to Remember
- Named ranges will not create a Data Validation rule if they are entered as a cell reference or with delimiters.
- The Global variable is applied for both UserForm and Worksheet VBA code. Any active cell name initially passes the code strDVList to a temporary range and then is used as a RowSource for the ListBox when a user opens the UserForm.
- You can combine multiple ranges in a single name.
Download the Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- How to Populate Excel VBA ListBox Using RowSource
- How to Sort ListBox with VBA in Excel
- Excel Button to Print Specific Sheets



I’m receiving a “Compile error: Variable not defined” and it’s highlighting “strDVList =”
Hello Julie,
You can try out the following code. I think it will work for you. Just make sure to change the number in Target.Column = 3 according to your column number of data validation.
Hello, I made a table with my data, but it doesn’t reference it. Is there anything I have to change about the code to reference my particular set of data?
Hello Sherry
Thanks for reaching out! Providing an ultimate solution without glancing at your Excel file is difficult. However, I suggest several things you may check to ensure the multi-selection drop-down works properly.
Ensure you have created named ranges for your dataset as described. Make sure that the strDVList variable correctly references your named range. To ensure that the named range CityNames is correctly referenced by strDVList, you can call the InitializeDVList subroutine in the Worksheet_SelectionChange event before it tries to use strDVList.
So, double-click on the user form and replace the existing code with the following:
Hopefully, these ideas will help you overcome your situation. Good luck.
Regards
Lutfor Rahman Shimanto
Excel & VBA Developer
ExcelDemy