Example 1 – Create a Timer Loop with Intervals in Excel
- Go to the Developer tab and select Visual Basic from the Code section.
- Select ThisWorkbook in the Project – VBAProject window and insert this code.
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
'Call timer_loop
End Sub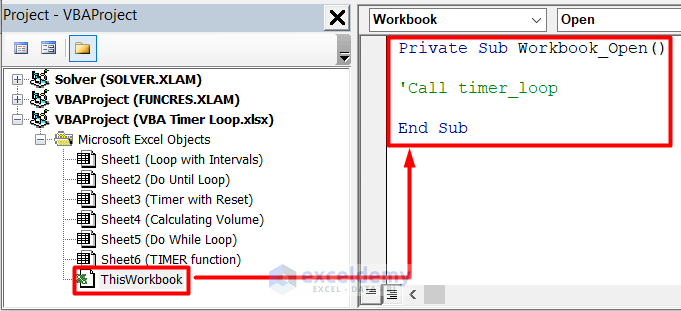
- Open a Module from the Insert tab.
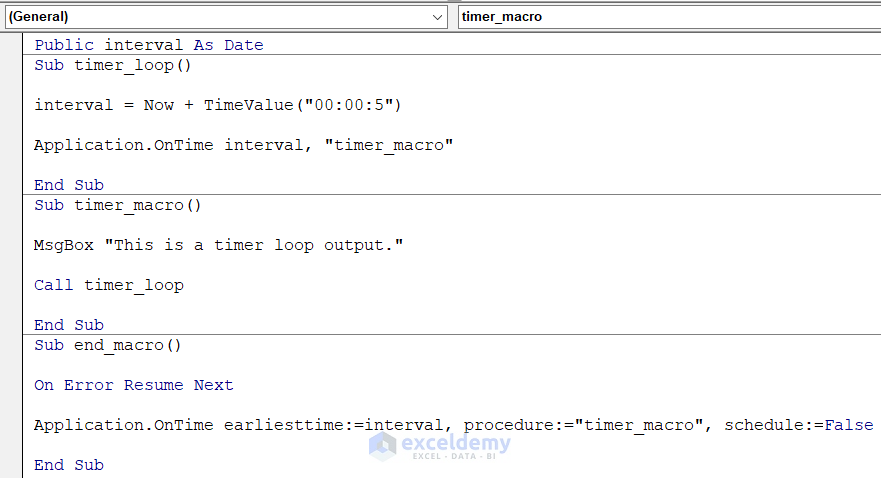
- Insert this code in the Code window and press Ctrl + S to save it.
Public interval As Date
Sub timer_loop()
interval = Now + TimeValue("00:00:5")
Application.OnTime interval,"timer_macro"
End Sub
Sub timer_macro()
MsgBox "This is a timer loop output."
Call timer_loop
End Sub
Sub end_macro()
On Error Resume Next
Application.OnTime earliesttime:=interval, procedure:="timer_macro", schedule:=False
End Sub
- Go to the Insert tab and select Rectangle:Rounded Corner from the Shapes group. You can choose any other shape.
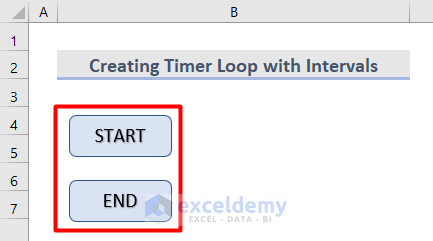
- Insert shapes as buttons in the worksheet like this.
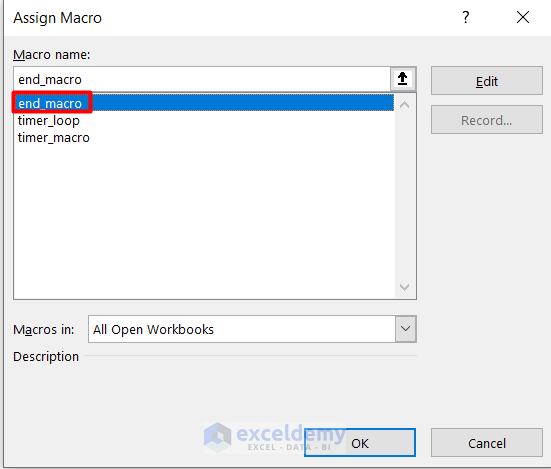
- Right–click on the START button and choose Assign Macro from the Context Menu.
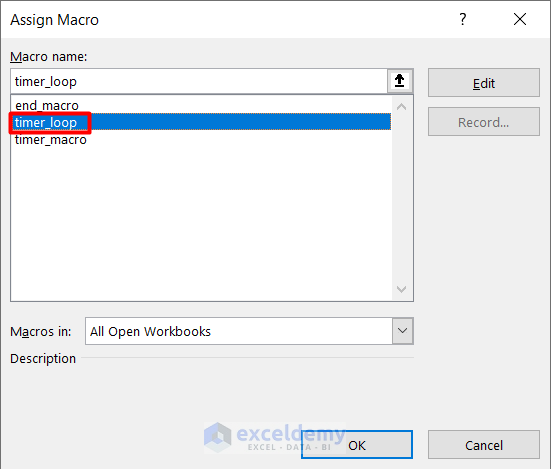
- Select the timer_loop macro from the Assing Macro window and press OK.
- Assign the end_macro code to the END button.
- Press the START button and, after every 5 seconds, this message box will appear in your workbook.
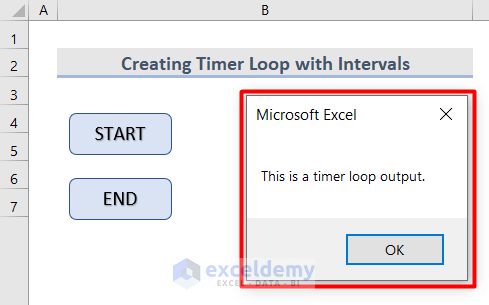
- Press the END button to stop the process.
Read More: How to Create a Timer with Milliseconds in Excel VBA
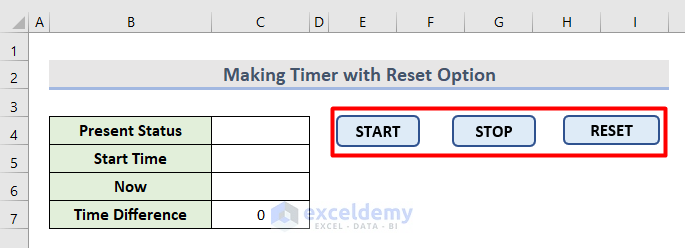
Example 2 – Make a Timer with a Reset Option in Excel
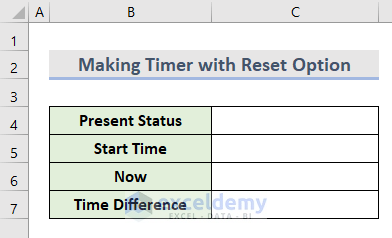
- Make a dataset with the following cells.
- Insert this formula in C7 that will define the Time Difference between the Start Time and Now time.
=C6-C5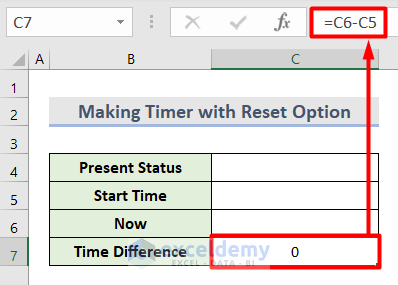
- Open the VBA Editor by pressing Alt + F11 on your keyboard.
- Open Insert and choose Module, then insert this code in the Code page.
Sub Timer_Start()
Dim wksh As Worksheet
Set wksh = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Timer with Reset")
wksh.Range("C4").Value = "Start"
If wksh.Range("C5").Value = "" Then
wksh.Range("C5").Value = Now
End If
x:
VBA.DoEvents
If wksh.Range("C4").Value = "Stop" Then Exit Sub
wksh.Range("C6").Value = Now
GoTo x
End Sub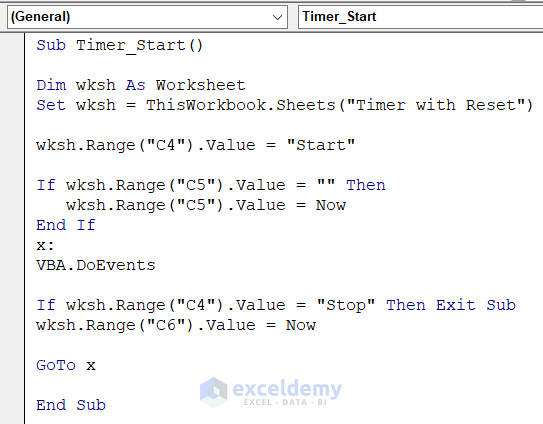
- Open a new Module window and insert this code that will stop the time.
Sub Timer_Stop()
Dim wksh As Worksheet
Set wksh = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Timer with Reset")
wksh.Range("C4").Value = "Stop"
End Sub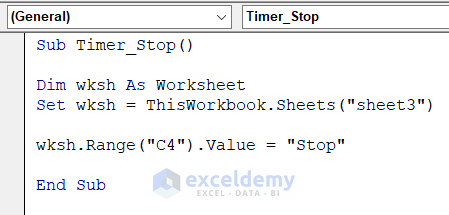
- Open another Module window and enter this code that will reset the timer to 0.
Sub Timer_Reset()
Dim wksh As Worksheet
Set wksh = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Timer with Reset")
wksh.Range("C4").Value = "Stop"
wksh.Range("C5:C6").ClearContents
End Sub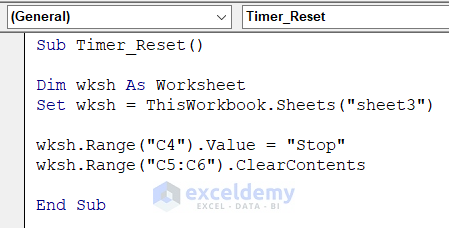
- Assign buttons with the Insert and Shapes command and choose any shape from the drop-down list.
- Insert 3 buttons, START, STOP, and RESET.
- Put 0 in Cell F6.
- Right–click on it and select Format Cells from the Context Menu.
- Choose any time format from the Time section in the Format Cells window.
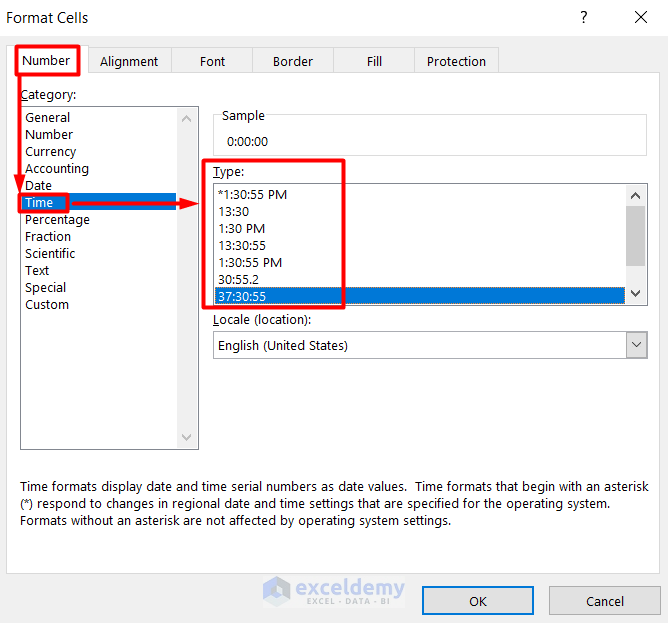
- Format the time format of Cell C7 as well.
- Right-click on the START button and choose Assign Macro.
- Select Timer_Start macro and press OK to assign it to the button.
- Assign the Timer_Stop and Timer_Reset macros to the STOP and RESET buttons, respectively.
- Insert this formula in F6.
=C7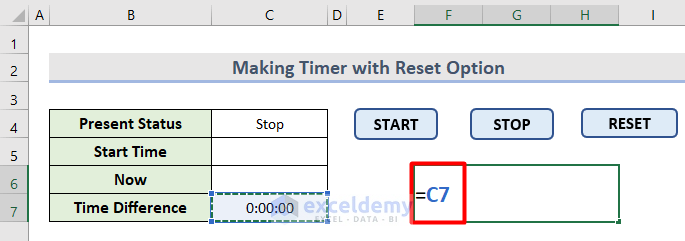
- Operate the timer with the buttons in a loop like this.
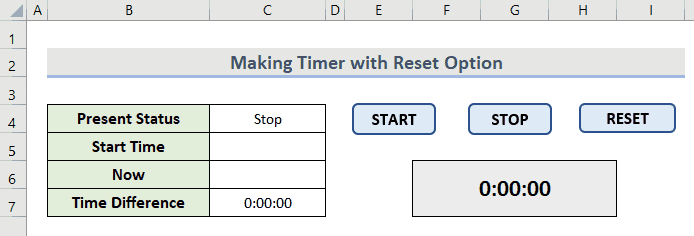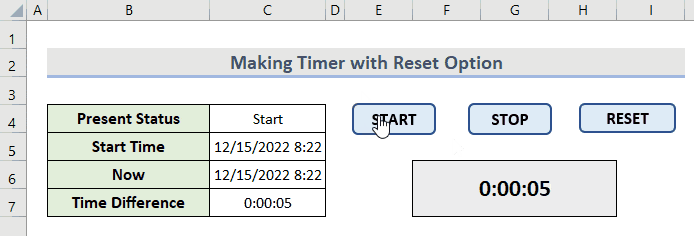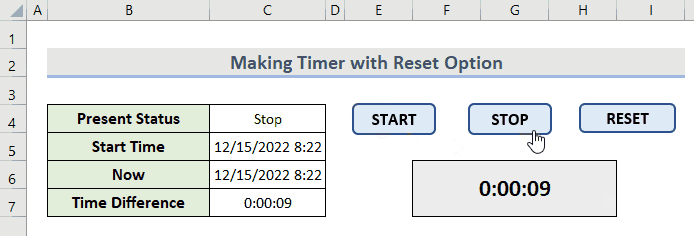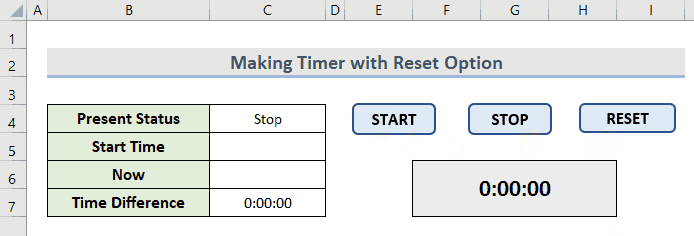
Read More: How to Create Timer Event with VBA in Excel
Example 3 – Calculate the Volume with a VBA TIMER Function in Excel
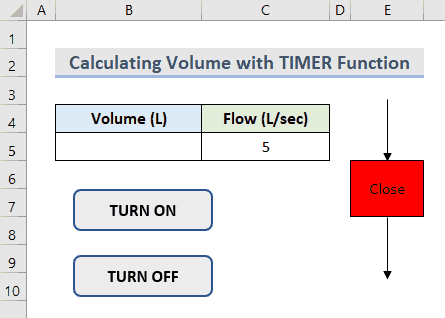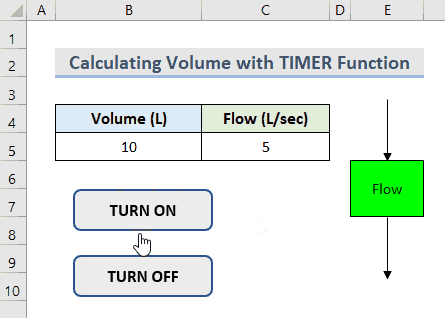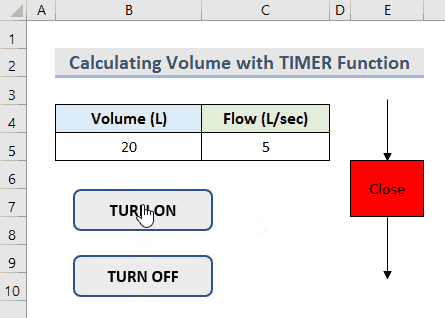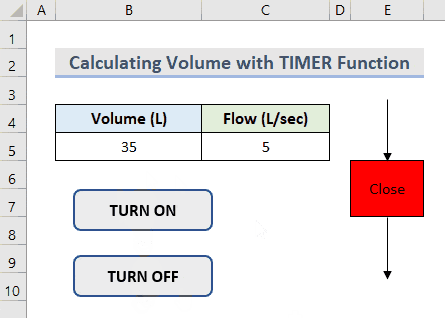
We need to calculate the amount of water to be filled in a tank with the pump machine. We will consider the Flow is 5 L/sec to fill up the tank.
- Insert this value in Cell C5.
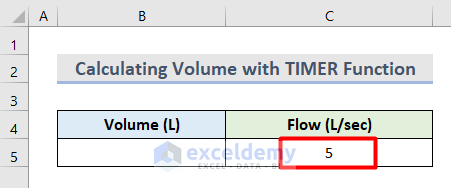
- Make a box in Cell E6.
- Isert two Arrows from the Insert Shapes command.
- Along with this, insert the TURN ON and TURN OFF buttons in the worksheet.
- Open the VBA Editor, then go to Insert and choose Module.
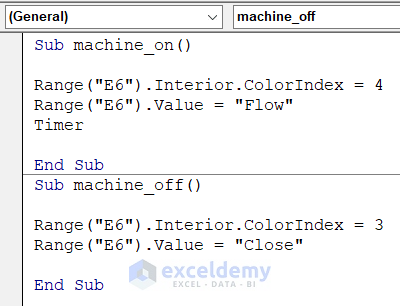
- Insert this code that will work on the TURN ON and TURN OFF buttons.
Sub machine_on()
Range("E6").Interior.ColorIndex = 4
Range("E6").Value = "Flow"
Timer
End Sub
Sub machine_off()
Range("E6").Interior.ColorIndex = 3
Range("E6").Value = "Close"
End Sub
- Open another Module and insert this code.
Sub Timer()
If Range("E6").Value = "Flow" Then
Application.OnTime Now() + TimeValue("00:00:01"), "Volume"
End If
End Sub
Sub Volume()
Range("B5").Value = Range("B5").Value + Range("C5").Value
Timer
End Sub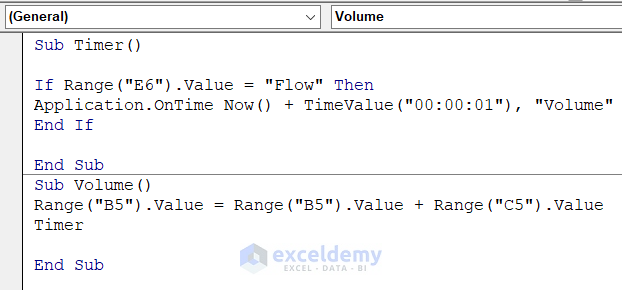
- Right–click the TURN ON button, select Assign Macro.
- Choose the machine_on macro and press OK.
- Assign the machine_off macro to the TURN OFF button.
- You can find the Volume of the water in the tank by clicking the buttons.
- To start the loop from 0, delete the value in Cell C5 and start the process again.
How to Use VBA Loops in Excel
Repeat a Text with Do Until Loop
We have a sample dataset that shows the information of 5 Employee Names in the cell range B5:B9. We want to define the Department in which each employee is working.

- Open the Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications window by pressing Alt + F11.
- Open Insert and choose Module, then insert this code.
Sub DoUntilTimerLoop()
Dim x As Integer
x = 5
Do Until x > 9
Cells(x, 3).Value = "Sells & Marketing"
x = x + 1
Loop
End Sub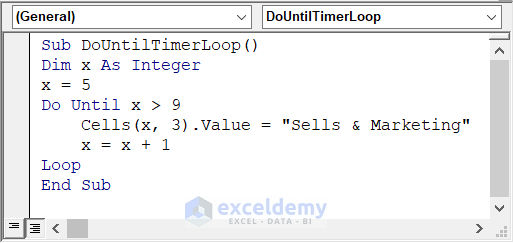
- Press F5 on your keyboard to run the code.
- We have all the Department names.

Insert the Month and Dates with a Do While Loop in Excel
- Insert this code inside a new Module in the VBA Editor window.
Sub CurrentMonthDates()
Dim CMDt As Date
Dim x As Integer
x = 0
CMDt = DateSerial(Year(Date), Month(Date), 1)
Do While Month(CMDt) = Month(Date)
Range("B5").Offset(x, 0) = CMDt
x = x + 1
CMDt = CMDt + 1
Loop
End Sub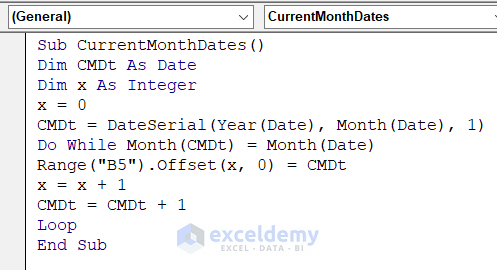
- Press F5 to Run the code. The code enters a list of dates in the current month.
Download the Practice Workbook


