VBA Now Function Overview
Function Objective
The Now function returns the current date and time based on the user’s computer’s default settings.
Syntax
=Now()
Returns
The function provides the date and time from the computer’s system clock.
VBA Format Function Overview
Function Objective
This Format function generates a formatted string based on the specified format code.
Syntax
=Format(Expression, [ Format ], [ FirstDayOfWeek ], [ FirstWeekOfYear ])
Argument
| ARGUMENT | REQUIRED/OPTIONAL | EXPLANATION |
|---|---|---|
| Expression | REQUIRED | A valid expression. |
| Format | OPTIONAL | User-defined format for the output. |
| FirstDayOfWeek | OPTIONAL | Specifies the first day of the week. |
| FirstWeekOfYear | OPTIONAL | Specifies the first week of the year. |
Settings
The firstdayofweek has the following settings:
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseSystem | 0 | Use NLS API setting |
| vbSunday | 1 | Sunday |
| vbMonay | 2 | Monday |
| vbTuesday | 3 | Tuesday |
| vbWednesday | 4 | Wednesday |
| vbThursday | 5 | Thursday |
| vbFriday | 6 | Friday |
| vbSaturday | 7 | Saturday |
The setting of the firstweekofyear argument is below:
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseSystem | 0 | Use the NLS API setting. |
| vbFirstJan1 | 1 | Consider the week containing January 1 as the starting week. |
| vbFirstFourDays | 2 | Start with the week containing at least four days in the year. |
| vbFirstFullWeek | 3 | Start with the first full week of the year. |
Returns
The function produces an output value according to the specified format.
Format Symbols
We have two types of format symbols used in the function:
- Date
- Time
Date Symbol
| Symbol | Range |
|---|---|
| d | 1-31 (Day of the month without leading zero) |
| dd | 01-31 (Day of the month with leading zero) |
| w | 1-7 (Day of Week starts with Sunday as 1) |
| ww | 1-53 (Week of the year without leading zero. January 1 considered as week 1) |
| m | 1-12 (Month of the year without leading zero, like January=1) |
| mm | 01-12 (Month of the year with leading zero, like January=01) |
| mmm | Presents abbreviated month names. |
| mmmm | Presents full month name. |
| y | 1-366 (Days of the year) |
| yy | 00-99 ( Last two digits of the year) |
| yyyy | 100-9999 (Three or four digits of the year) |
Time Symbol Read More: Excel VBA: Insert Timestamp When a Macro Is Run Remember that the date value will be shown according to the computer’s system default calendar (e.g., Gregorian, Hijri, etc.). Users can modify the examples to suit their specific needs. You can download the practice workbook from here:
Symbol
Range
h
0-23 (Hour of the day without leading zero. 1-12 restricted when AM or PM are mentioned)
hh
00-23 (Hour of the day with leading zero. 01-12 restricted when AM or PM are mentioned)
n
0-59 (Minutes of the hour without leading zero)
nn
00-59 (Minutes of the hour with leading zero)
m
0-59 (Minutes of the hour without leading zero). Only when h or hh ar mentioned.
mm
00-59 (Minutes of the hour with leading zero). Only when h or hh ar mentioned.
s
0-59 (Seconds of the minute without leading zero)
ss
00-59 (Seconds of the minute with leading zero)
Example 1 – Using the NOW Function in Excel VBA
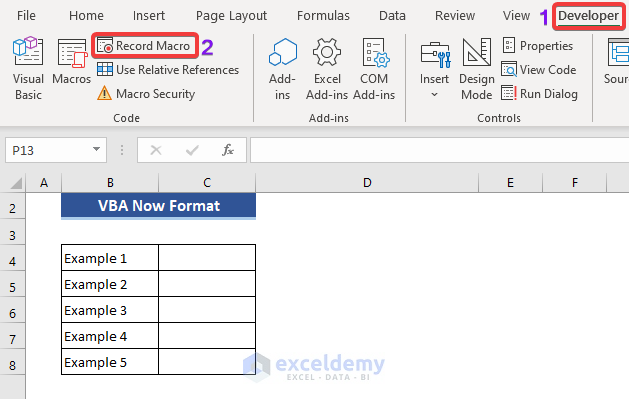
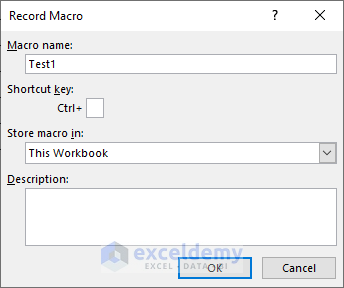
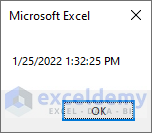
Sub Test1()
Dim Msg
Msg = Now()
MsgBox Msg
End Sub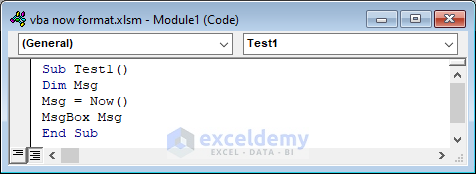
Example 2 – Using the FORMAT Function in VBA
Sub Test2()
Dim Msg
Dim date1 As Date
date1 = #1/27/1993#
Msg = Format(date1, "Long Date")
MsgBox Msg
End Sub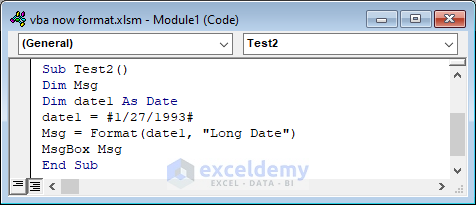

Example 3 – Combining NOW and FORMAT Function in VBA
Sub Test3()
Dim Msg
Dim date1 As Date
date1 = Now()
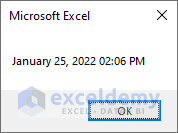
Msg = Format(date1, "mmmm dd, yyyy hh:mm AM/PM")
MsgBox Msg
End Sub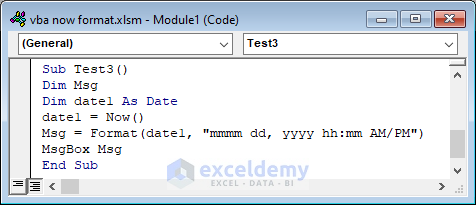
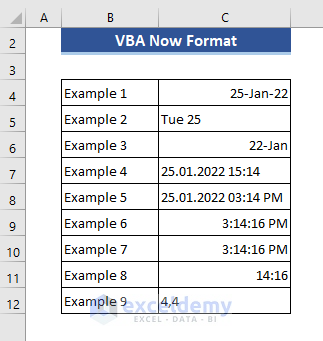
Example 4 – Formatting Current Time in Different Ways using NOW and FORMAT Function
Sub Test4()
Range("C4") = Format(Now(), "Long Time")
End Sub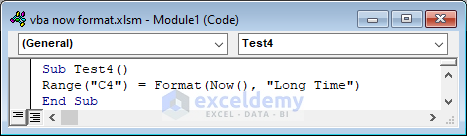
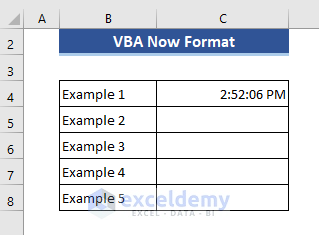
Sub Test4()
Range("C4") = Format(Now(), "dd mmmm yy")
Range("C5") = Format(Now(), "ddd dd")
Range("C6") = Format(Now(), "mmmm yy")
Range("C7") = Format(Now(), "dd.mm.yyyy hh:mm")
Range("C8") = Format(Now(), "dd.mm.yyyy hh:mm Am/PM")
Range("C9") = Format(Now(), "Long Time")
Range("C10") = Format(Now(), "hh:mm:ss AM/PM")
Range("C11") = Format(Now(), "n:ss")
Range("C12") = Format(Now(), "w,ww", 7, vbFirstJan1)
End Sub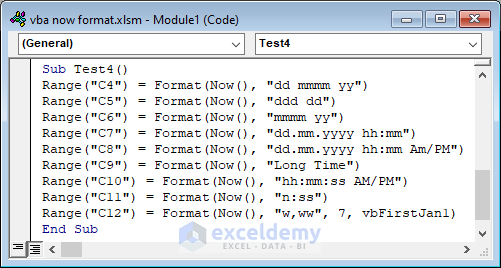
Things to Remember
Download Practice Workbook


