So far, we have focused exclusively on pivot tables that are generated from a single table of data on this site. The Data Model feature has brought additional advantages to pivot charts. With the Data Model, we can use multiple tables of data in a single pivot table. We have to create one or more “table relationships” so the data can be tied together. The Data Model is a new feature introduced in Excel 2013. In this article, we will show you 6 steps to create a pivot table Data Model in Excel.
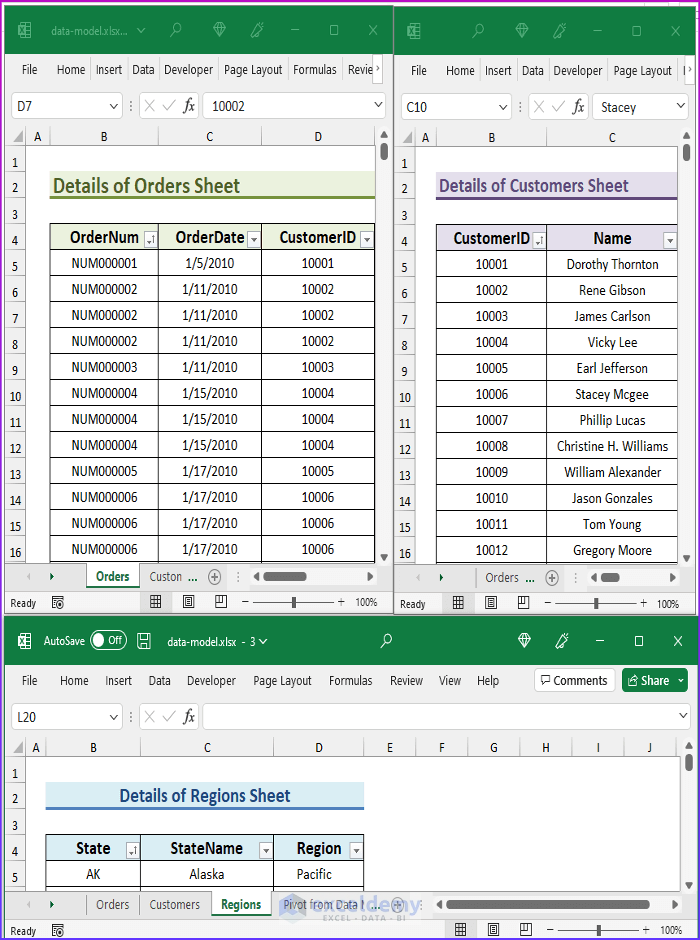
The following figure shows parts of three tables that are in a single workbook. Each worksheet is in the same workbook, just shown in a separate window. The worksheets are Orders, Customers, and Regions. Every worksheet has a table, and we have also named these 3 tables Orders, Customers, and Regions (to keep it organized). The Orders table contains information about product orders. The Customers table contains information about the company’s customers, and the Regions table contains regional information.
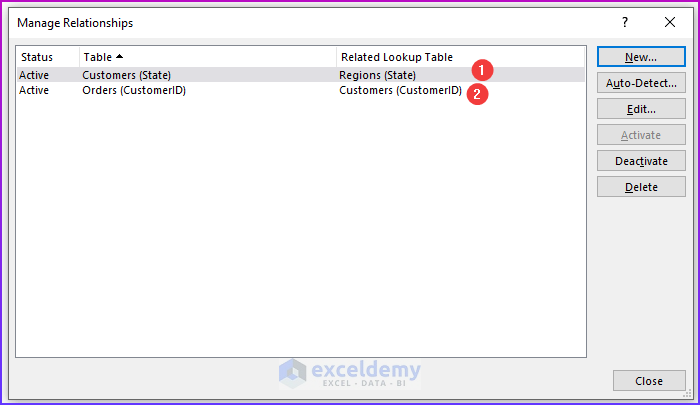
If you look at the tables closely, you will find that the Orders and Customers tables have the CustomerID column in common, and the Customers and Regions tables have the State column in common (download the workbook to see the common things). We shall use these common columns to form relationships among the tables.
One to Many Relationships
Notice that the relationships between the tables are “one-to-many”. For every row in the Orders table, there is exactly one corresponding row in the Customers table, and that row is determined by the CustomerID column. Similarly, for every row in the Customers table, there is exactly one corresponding row in the Regions table, and that row is determined by the State column.
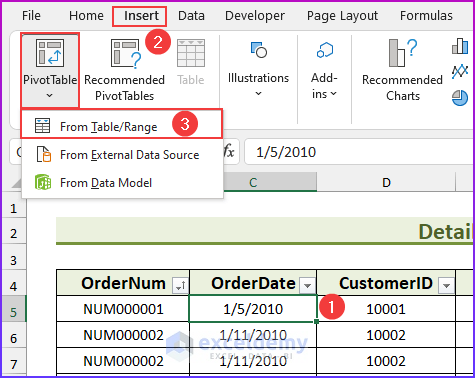
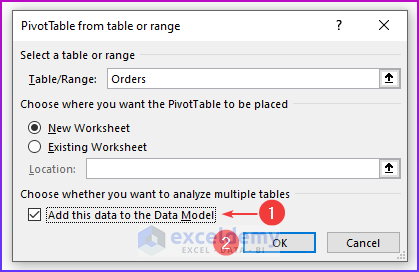
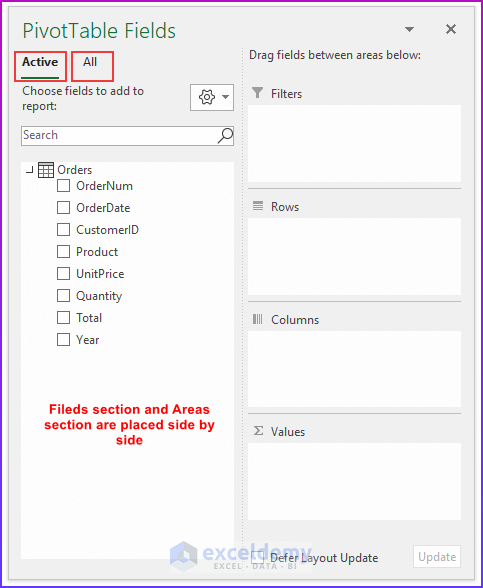
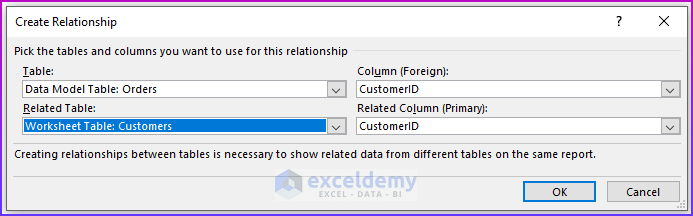
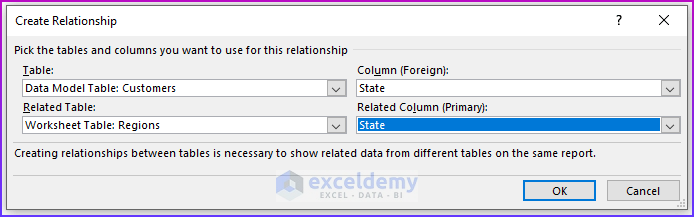
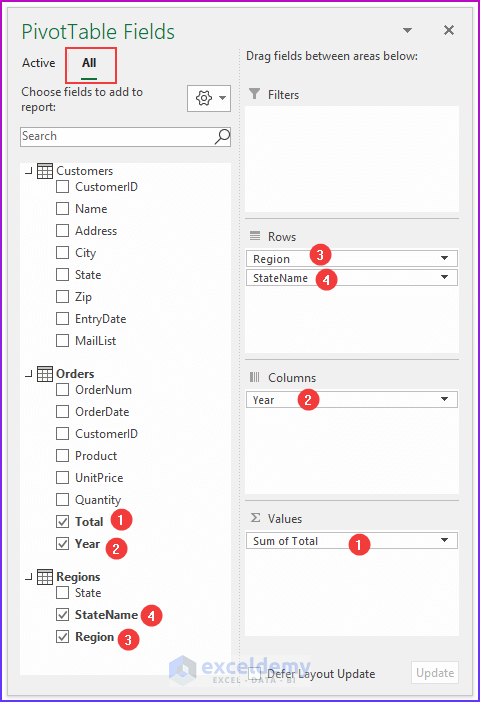
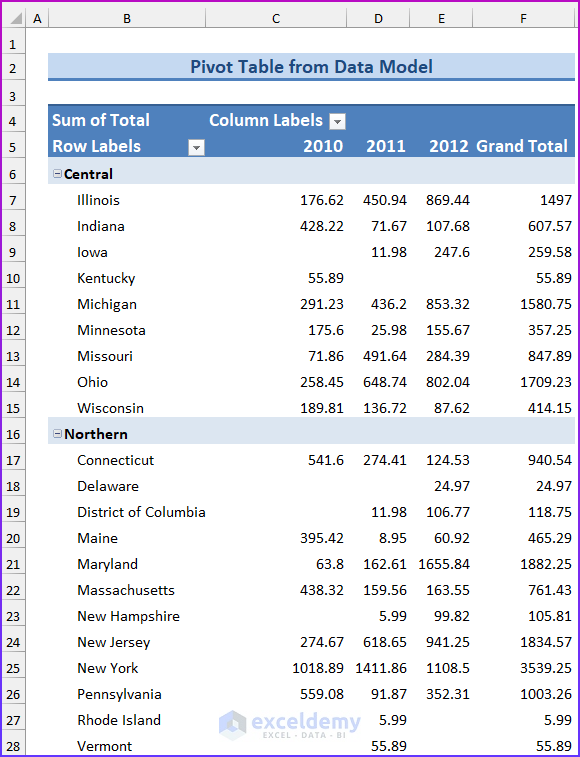
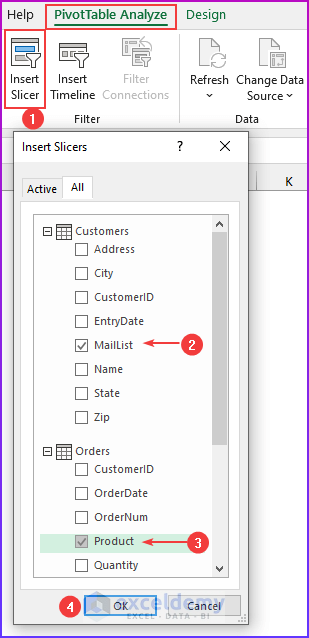
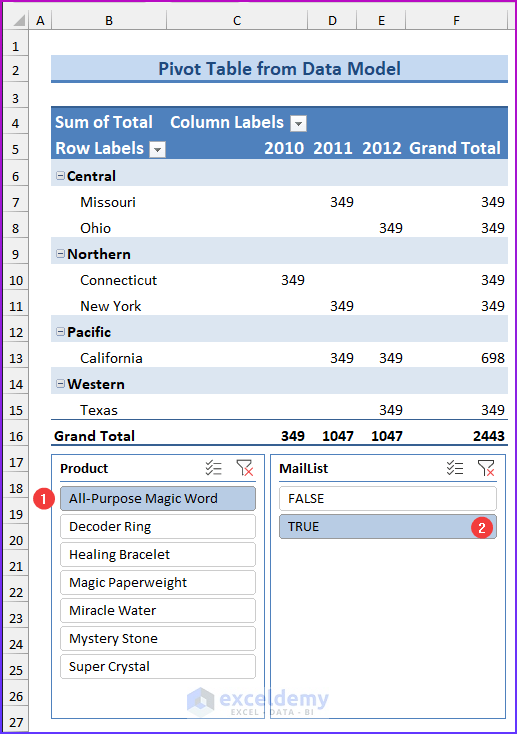
💡 Notes: A pivot table created using the Data Model has some restrictions when compared with a pivot table created from a single data table. The most notable one is: that you can’t create groups. In addition, you can’t create calculated fields or calculated items. Our goal in this example is to summarize sales by state, by region, and by year. Notice that the sales and date information is in the Order table, the state information is in the Customers table, and the region names are in the Regions table. Therefore, we shall use all these three tables to create our target pivot table. Here is the step-by-step process we have used to create the pivot table: For the first step, we will insert a pivot table from the dataset. Select any cell within the Orders table and choose Insert ➪ PivotTable ➪ From Table/Range. The Create PivotTable dialog box will appear. Choose the data that you want to analyze and choose where you want the PivotTable report to be placed – these two options will remain as it is. Select the Add This Data to the Data Model check box, and click OK. Now, we are going to set up the relationships among the tables. Choose PivotTable Tools ➪ Analyze ➪ Calculations ➪ Relationships. The Manage Relationships dialog box will appear. In the Table drop-down, select Orders, and in the Column (Foreign), select CustomerID; in the Related Table, select Customers, and in the Related Column (Primary), select CustomerID. 💡 Notes: If you forget to set up the table relationships in advance, Excel will prompt you to do so when you try to add a field to the pivot table from a different data table. We have established a table relationship. Now just drag the field names to the appropriate areas of the PivotTable Fields task pane: In this final step, we added two slicers (MailList and Product) to enable filtering of the pivot table by customers who are on the mailing list and by-products. 💡Tips: You can convert the pivot table to formulas. To do this, select any cell in the pivot table and choose PivotTable Tools ➪ Analyze ➪ OLAP Tools ➪ Convert to Formulas. The pivot table will be replaced by cells that use formulas. These formulas are generated with the CUBEMEMBER and CUBEVALUE functions. Although the new range of data will no longer be a pivot table, the formulas will update when the data changes. Download Practice Workbook We have shown you 6 easy steps to create a pivot table Data Model in Excel. If you have any questions, feel free to comment below. Happy Excelling :). << Go Back to Pivot Table in Excel | Learn Excel
Step 1: Inserting PivotTable
Step 2: Adding Data to Data Model
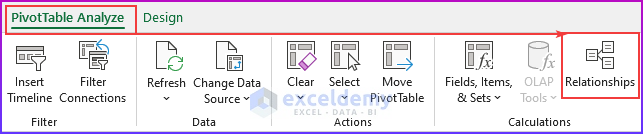
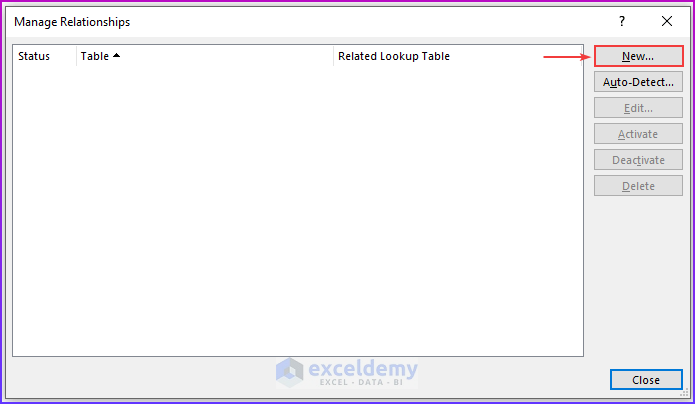
Step 3: Managing Relationships
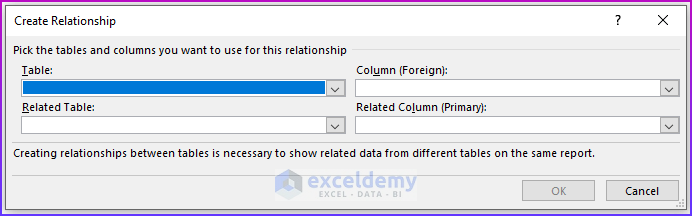
Step 4: Creating Relationship
Step 5: Inserting PivotTable Fields to Areas
Step 6: Adding Slicers
Conclusion
How to Create Pivot Table Data Model in Excel: Knowledge Hub