Some Excel files need frequent saving and closing for various reasons. Therefore, Excel VBA save and close workbook without prompt is necessary. Excel Prompts are confirmation windows that ensure file saving before closing Excel or making changes in workbooks.
This article discusses the reasons for Excel’s displaying prompts and demonstrates macro variants for Excel VBA save and close workbooks without prompts.
Excel Prompts for Saving and Closing Workbook
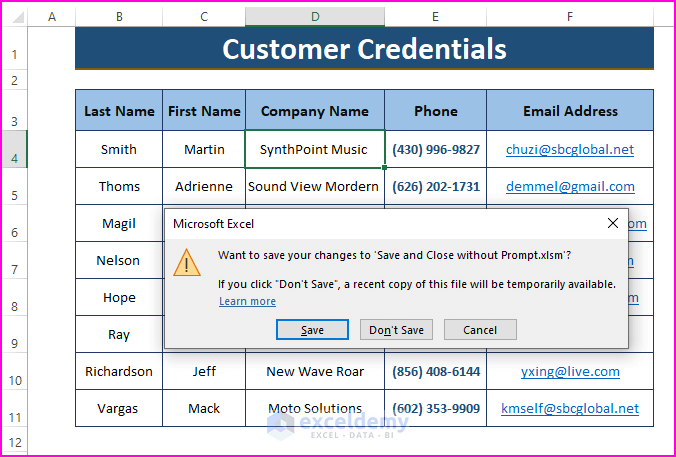
In Excel files, after making changes in data- whenever users attempt to close the workbook without saving it first, Excel displays a window saying, “Want to save your changes to…”. This window is referred to as Prompts.
Similar things happen when users want to save files in different formats, such as xlsx to xlsm.
3 Suitable Examples of Excel VBA to Save and Close Workbook Without Prompt
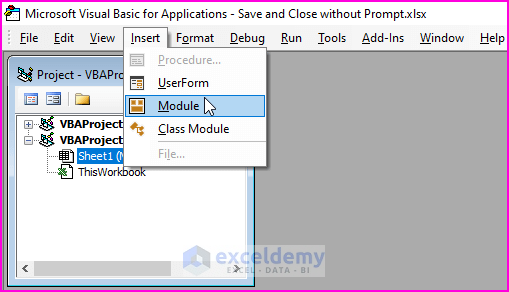
Excel VBA Macros are powerful tools to achieve outcome-oriented results. To apply a macro, users need to insert a Module in the Microsoft Visual Basic window. Also, they need to save the workbook format as xlsm to be able to run the macro. Follow the below steps to insert and to be able to run the macro.
➤ Press ALT+F11 or go to Developer tab > Visual Basic to open Microsoft Visual Basic. In the window, move to Insert > Module to insert a module.
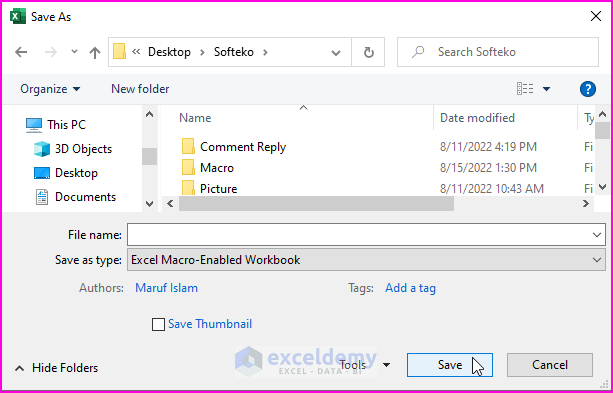
➤ Save the Excel workbook as an Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook.
Afterward, follow the below section to have multiple macros according to your needs.
Example 1: Save and Close Workbook Without Prompt in Assigned Location
For saving changes and closing worksheets, Excel files need confirmation by selecting options offered using Excel Prompts. However, a couple of lines of macro can save and close a workbook in the assigned location.
🔼 Paste the following macro into the module.
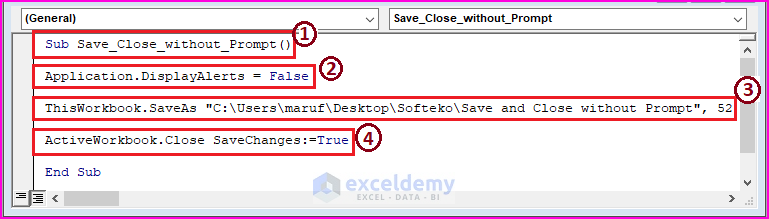
Sub Save_Close_without_Prompt()
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ThisWorkbook.SaveAs "C:\Users\maruf\Desktop\Softeko\Save and Close without Prompt", 52
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=True
End SubMacro Explanation
1 – start the macro procedure by declaring the Sub name. You can assign any name to the code.
2 – the Application.DisplayAlerts statement is set to False to prevent Save and Close Excel prompts.
3 – the ThisWorkbook.SaveAs takes a Path to save the changed file in a specific format (i.e., xlsm=52).
4 – the ActiveWorkbook and SaveChanges statements execute the Close and Save Changes commands respectively.
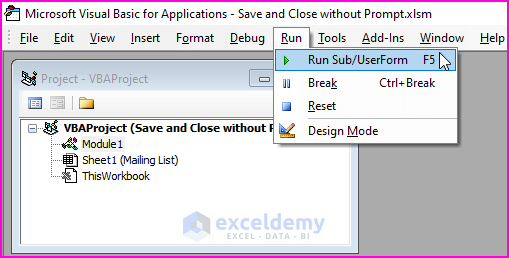
🔼 Now, go to Run > Click Run Sub/UserForm or press F5 to run the macro.
🔼 Excel takes a moment, then saves the changes and closes the active workbook. Only the Excel application with no open workbook remains. Click on Close to exit Excel.
Read More: Excel VBA: Save and Close Workbook
Example 2: Conditional Saving and Closing a Workbook Without Prompt After Making Changes
In this case, normal users happen to change the workbook repeatedly. Therefore, they can use the following macro to ensure the saving of Excel files.
🔼 Type the following lines in the module.
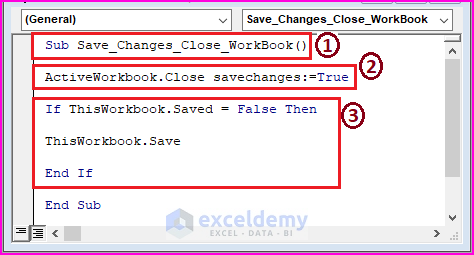
Sub Save_Changes_Close_WorkBook()
ActiveWorkbook.Close savechanges:=True
If ThisWorkbook.Saved = False Then
ThisWorkbook.Save
End If
End SubMacro Explanation
1 – declare the Sub name.
2 – the ActiveWorkbook.Close statement closes the workbook, and the SaveChanges statement saves the changes.
3 – perform a condition using the VBA IF function to ensure saving of the current workbook.\
🔼 Repeat Example 1’s steps to run the macro and exit from Excel.
Read More: Excel VBA: Close Workbook Without Saving
Example 3: Saving and Closing a Specific Workbook Without Prompt
Often, users need to save and close a specific workbook. In that case, this macro enables users to save and close the assigned Excel workbook without a prompt.
🔼 Use the below macro in the inserted module.
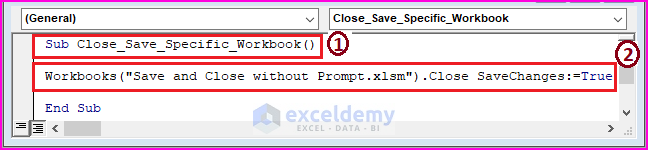
Sub Close_Save_Specific_Workbook()
Workbooks("Save and Close without Prompt.xlsm").Close SaveChanges:=True
End SubMacro Explanation
1 – begin the macro code by declaring the VBA Macro Code’s Sub name.
2 – the VBA Workbooks property takes the Close and Save Changes command of a specific Excel workbook.
🔼 Go through Example 1’s steps to close and save the workbook.
Checking Saved Files for Confirmation
Users open the desired Excel files and make changes, then execute the macro to save and close the workbook. However, sometimes users need to cross check the outcomes.
🔼 Open any Excel workbooks. Then make changes, such as adding an extra row (here it’s row number 12).
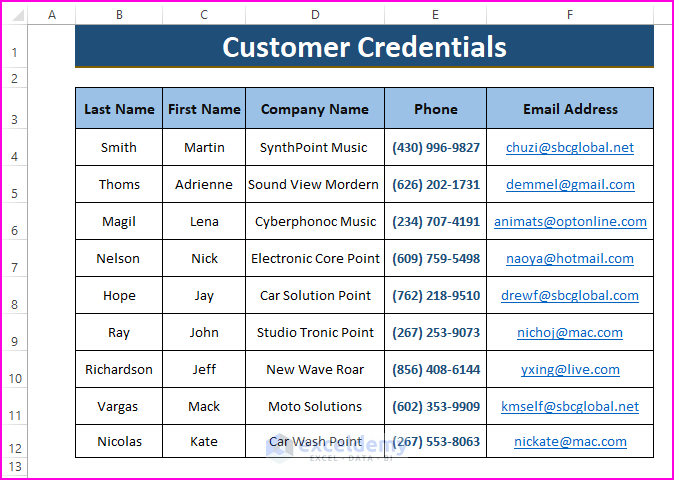
🔼 After making changes within the workbook, run the macro using the previous instructions. As the macro is subject to saving and closing the Excel workbook, again open the same workbook to see whether the assigned macro saved the changes or not.
🔼 You see from the below picture that the macro saves the changes as expected.
Read More: How to Close Workbook at Specific Time Using Excel VBA
Download Excel Workbook
Conclusion
In this article, we discuss Excel Prompts and demonstrate multiple examples of how Excel VBA saves and closes workbooks without prompts. We hope this article clarifies all the aspects regarding saving and closing workbooks without selecting any prompt options. Comment if you have further inquiries or have anything to add.